Med-Surg Nursing: HIV and AIDS (Ch. 37)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Transmitted by body fluids containing HIV or infected CD4 lymphocytes
-blood, semen, vaginal secretions, amniotic fluid, breast milk
-most prenatal infections occur during delivery
casual contact does not cause transmission
breaks in skin or mucosa increase risk
Transmission of HIV
sharing needles
having sex with infected person
infants born/breast fed by HIV infected mothers
people who receive organ transplants, HIV infected blood, or blood products (especially between 1978 and 1985)
Risks Associated with HIV Infection
standard precautions
safer sex practices and safer behaviors
-abstain from sharing sexual fluids
-reduce # of sexual partners to one
-always use condoms
do not share needles
blood screening and treatment of blood products
Prevention
hand hygiene
PPE
soiled pt care equip handling
environmental control
textiles and laundry
needles and other sharps
pt resuscitation
Prevention for Healthcare Providers
postexposure prophylaxis
vaccination
Healthcare Provider Treatment
1- Primary infection (high viral load)
2- CD4 200- 499
3- AIDS diagnosis <200 CD4
3 Stages of HIV
Primary infection
HIV asymptomatic (most dangerous time)
HIV symptomatic
AIDS
Stages of HIV
Acute HIV infection/symdrome
Part of CDC category A
Symptoms: none to flu like syndrome
Window period: lack of HIV antibodies
Period of rapid viral replication and dissemination through the body (copy machine through the lymph system)
Viral set point: balance between amount of HIV and the immune response
Primary Infection
CDC category A
> 500 CD4+ T lymphocytes/mm3
Upon reaching viral set point, chronic asymptomatic state begins
Body has sufficient immune response to defend against infection
HIV Asymptomatic
CDC category B
200-499 CD4+ lymphocytes/mm3
CD4 T cells gradually fall
Pt. develops symptoms or conditions related to the HIV infection, which are not classified as category C conditions
HIV Symptomatic
CDC category C
>200 CD4+ lymphocytes/mm3
As levels drop below 100 cell/mm3 the immune system is significantly impaired
AIDS
The first opportunistic infections that you are likely to get if you have HIV are minor fungal infections caused by an overgrowth of Candida, the fungus that causes diaper rash in babies. Candida infections commonly occur in the mouth and throat (oral candidiasis or thrush), airways and lungs, or vagina (vaginal candidiasis). This fungus typically forms white patches on your gums, tongue and lining of your mouth, and can make it so painful to swallow that you lose your appetite. An infection in your vagina will cause itching or burning, and soreness and redness accompanied by a thick white discharge.
Treatment: TMP-SMZ or pentamidine, prophylactic TMP-SMZ
(CD4 cells: around 500)
Fungal infections (Candida)
Octreotide acetate for severe chronic diarrhea
Diarrhea Related to HIV/enteric pathogens
10% weight loss and chronic diarrhea or chronic weakness and fever with absence of other cause
protein energy malnutrition
anorexia, diarrhea, GI malabsorption, and lack of nutrition may contribute
Wasting Syndrome
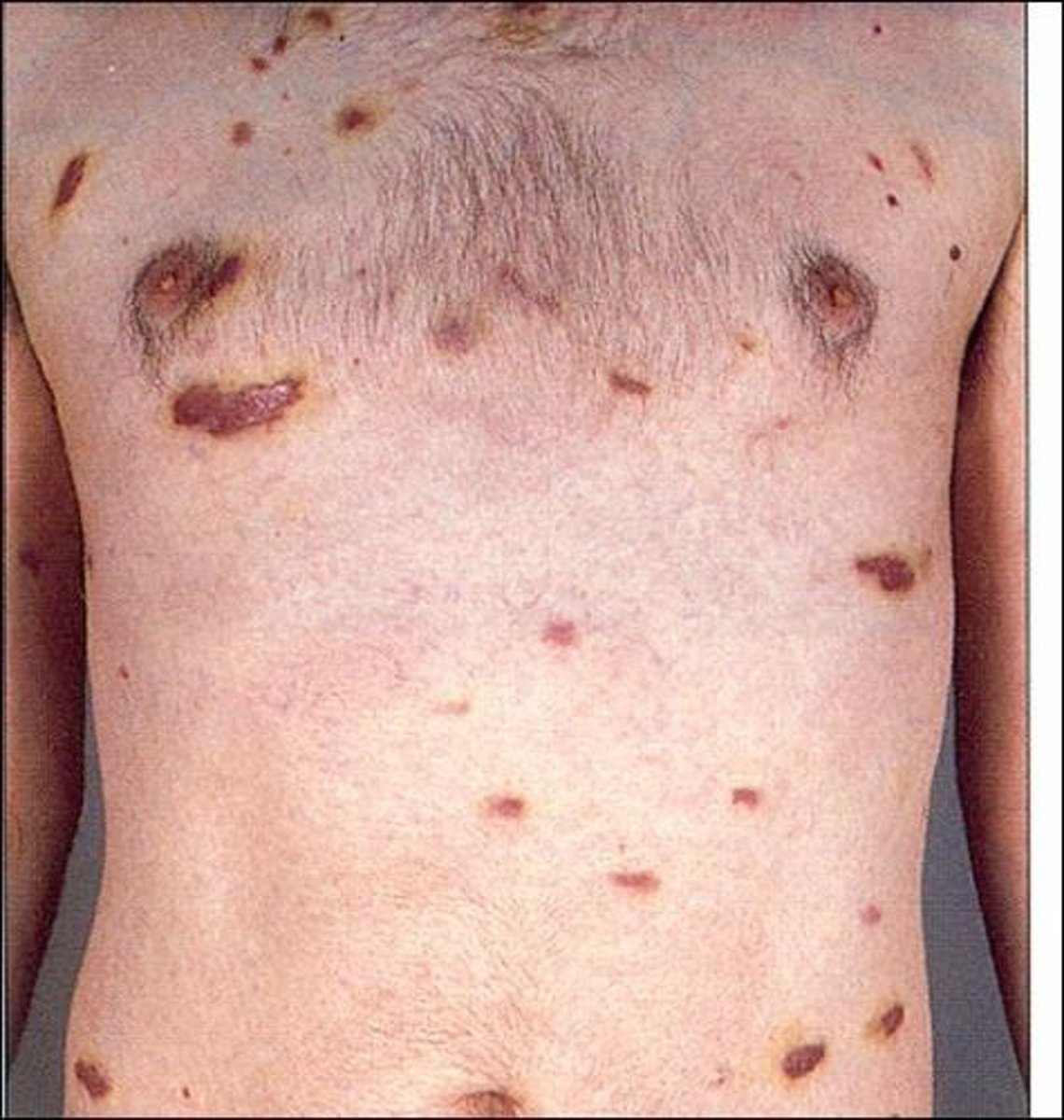
A tumour caused by a human herpes virus. The tumour usually appears as purplish lesions on the skin of your legs or face, or inside your mouth, and can spread to other parts of your body without you knowing it. If the cancer spreads to your guts or lungs, it can cause bleeding or difficulty with breathing that can be life threatening.
(CD4 count: 500 to 200)
Kaposi's sarcoma
A type of pneumonia that severely affects the lungs and is the most common opportunistic infection in people with AIDS. Signs and symptoms of pneumocystis can include shortness of breath, fever, dry cough and chest pain. It usually takes weeks or months to develop, but can be life threatening if not treated.
(CD4 count: 200 to 100)
Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia
Is everywhere and it is thought that most people throughout the world have been exposed to it, but mostly didn't notice. Nevertheless; like HIV, once you have the virus you have it for life. If you are HIV infected and have low CD4 cell counts, you should not be surprised if you get a cytomegalovirus infection in your gut, or your eyes (cytomegalovirus retinitis), where it may lead to blindness if you don't get treatment.
(CD4 count: 100-50)
Cytomegalovirus
Exists everywhere in the environment and can infect the lungs and intestines of people with severe immunodeficiency. It can be deadly if it spreads to other parts of your body.
(CD4 count: less than 50)
Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC)
Second most common malignancy occurring in people with AIDS. AIDS- related lymphomas tend to develop outside the lymph nodes, most commonly in the brain, bone marrow, and GI tract.
Aggressive growth and resistance to treatment
B-Cell lymphomas
Peripheral neuropathy
HIV encephalopathy
Cryptococcus neoformans
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
Other neurologic disorders
Depression
Neurologic Manifestations of HIV/AIDS
The amount of HIV in the pts bloodstream
When the viral load is tested, HCPs are looking for a certain number of particles in a milliliter of blood—what they call the particles copies. When a pt is being treated for HIV, the goal is to take a viral load down to the point that it is undetectable.
Anywhere between 40 to 75 copies in the sample of blood will be declared to have an "undetectable" viral load.
https://www.khanacademy.org/science/health-and-medicine/infectious-diseases/hiv-and-aids/v/what-is-hiv-and-aids
Viral Load
1. When CD4 count is 350-500
2. Viral load is >100,000 copies
3. Pregnancy, young child, progressed to AIDS, opportunistic infection (regardless of CD4 count)
When to start HAART Treatment
1/4 of all infected people with HIV are > 50 years old
blood transfusion before 1985 increases the risk
unprotected intercourse
reduction in immune system function
Gerontology Considerations
EIA- antibodies detected
Western blot test- antibodies detected, used to confirm EIA
Viral load- measure HIV RNA in plasma
CD4/CD8- markers found on lymphocytes, HIV kills CD4 which reduces the numbers
OraQuick- In-home HIV test
Lab Tests for Dx and tracking HIV
Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs)
Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs)
Protease inhibitors (PIs)
Integrate inhibitors
Use of combination therapy
Antiretroviral Agents
Assess physical and psychosocial status
Identify potential risk factors: IV drug abuse, risky sexual practices
Immune system function
Nutritional status
Skin integrity
Respiratory status and neurologic status (pg 1012)
Fluid and electrolyte balance
Knowledge level of HIV/AIDS
(pg 1016)
Nursing Process- Assessment
Impaired skin integrity
Diarrhea
Risk for infection
Activity Intolerance
Disturbed thought process
Ineffective airway clearance
Pain
Imbalanced Nutrition
Social Isolation
Anticipatory Grieving
Deficient Knowledge
Nursing Process- Diagnosis
Achievement and maint. of skin integrity
Resumption of usual bowel patterns
Absence of infection
Improved activity tolerance
Improved thought process
Improved airway clearance
Increased comfort, improved nutritional status
Increased socialization
Expression of grief
Increased knowledge regarding disease prevention and self-care
Absence of complications
Nursing Process- Planning
Frequent assessment of skin and mucosa
Encourage pt to maintain balance between rest and activity
Reposition at least every 2 hours and as needed
Pressure reduction devices
Instruct pt to avoid scratching
Use gentle, nondrying soaps and cleansers
Avoid adhesive tape
Perianal skin care
Nursing Process: Intervention- Skin
Assess bowel pattern and factors that may exacerbate diarrhea
Avoid foods that act as bowel irritants: raw fruits and veggies, carbonated beverages, spicy foods, foods of extreme temperatures
Small frequent meals
Administer meds as prescribed
Asses and promote self-care strategies to control diarrhea
Nursing Process: Intervention- Bowels
Maintain balance between activity and rest
Instruction regarding energy conservation technique
Relaxation measures
Collaboration with other members of the health care team
Nursing Process: Intervention- Activity
Assess mental and neurologic status
Use clear, simple language if mental status is altered
Establish and maintain a daily routine
Orientation techniques
Ensure pt safety and protect from injury
Strategies to maintain and improve functional ability
Instruct and involve family in communication and care
Nursing Process: Intervention- Thoughts
Monitor weight, I&O, and factors that interfere with nutrition
Dietary consult
Control of nausea with antiemetics (zofran)
Oral hygiene
Treatment of oral discomfort
Dietary supplements
May require enteral feeding or parenteral nutrition
Nursing Process: Intervention- Nutrition
Promote an atmosphere of acceptance and understanding
Assess social interactions and monitor behaviors
Allow pt to express feelings
Address psychosocial issues
Provide information related to the spread of infection
Educate ancillary personnel, family, and partners
Nursing Process: Intervention- Isolation
Improving airway clearance- position in semi-Fowler's or high Fowler's position, pulmonary therapy (coughing and deep breathing, postural drainage, percussion, and vibration)
ensure adequate rest
Pain- medication as prescribed, skin and perianal care
Nursing Process: Intervention- Other
https://www.khanacademy.org/science/health-and-medicine/infectious-diseases/hiv-and-aids/a/what-is-hivaids
Brunner and Suddarth's Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing 13th Edition Volume 1
References