MGMT100
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
What is the definition of leading in a management context?
the process of influencing others to achieve group or organisational goals.
What are the four functions of management?
Planning, Organising, Leading, Controlling.
What makes an effective leader?
Someone who is organised, communicates well with others, leads from within, and gains respect from the team.
What is the difference between power and influence?
Power is the potential ability to influence others; influence is the actual effect of one's actions on others' attitudes or behaviour.
What are the types of hard (position) power managers use?
Reward, Coercive, Legitimate.
What are the types of soft (personal) power managers use?
Expert, Referent.
Which sources of power result in resistance, compliance, and commitment?
Coercion → Resistance; Legitimate/Reward → Compliance; Expert/Referent → Commitment.
What is the "great person theory" of leadership?
The belief that leaders are born, not made, and possess certain innate traits.
Why don't traits alone make someone an effective leader?
Effective leadership involves applying strengths in context; traits help, but alone don't ensure success.
What is servant leadership?
focused on serving others, giving credit, and acting for the benefit of employees and society.
Which leadership style shows high concern for people and low concern for production?
Country Club Management (1,9).
What are the two dimensions of the Blake and Mouton Leadership Grid?
Concern for production and concern for people.
What is the key principle of Adams' Equity Theory?
People compare their input/output ratio to others' and are motivated to restore equity when they perceive imbalance.
What is motivation, according to Lecture 2?
the set of forces that initiates, directs, and makes people persist in efforts to accomplish a goal.
What is authentic leadership?
when leaders act according to their values, create trust, and inspire through openness.
What does organising help translate within an organisation?
Organising translates broader organisational objectives into actionable steps and coordination strategies.
What is the main purpose of organising?
To deploy organisational resources efficiently in order to achieve strategic goals.
What is the definition of organising in management?
Organising is the deliberate effort to align people, resources, and activities toward achieving shared objectives.
What is the difference between formal and informal structure?
Formal structure is officially created and documented; informal structure arises naturally through staff interactions.
What is the goal of a formal organisational structure?
To improve the effectiveness of an organisation in achieving its goals.
What is an informal organisational structure?
A 'shadow' structure made of unofficial and personal relationships not formally assigned.
What is work specialisation?
The degree to which tasks are broken down into individual jobs to achieve goals.
What are the four basic elements of organisational structure?
Work Specialisation, Departmentalisation, Differentiation, and Integration.
What is an organisational chart?
A diagram showing formal reporting relationships and arrangements of work positions.
What is job design?
The specification of task activities associated with a particular job.
What are some key methods of job design?
Job Simplification, Job Rotation, Job Enlargement, and Job Enrichment.
What is job enrichment?
Increasing a job's depth to make it more meaningful and encourage responsibility and growth.
What psychological states are influenced by enriched jobs?
Experienced meaningfulness of work, responsibility for outcomes, and knowledge of results.
What are the core characteristics in the Job Characteristics Model?
Skill variety, Task identity, Task significance, Autonomy, and Feedback.
What are the three types of organisational design related to job scope and depth?
Job Simplification (narrow, low depth), Rotation & Enlargement (wider, moderate depth), Job Enrichment (wide scope, high depth).
What is the purpose of department structure within an organisation?
To cluster individuals into units and departments to help achieve organisational goals efficiently.
In a functional departmental structure, how are jobs grouped?
Jobs are grouped according to what staff specialise in (e.g., HR, Marketing, Accounting).
What is one major advantage of a functional departmental structure?
It develops in-depth expertise and provides clear career paths within functions.
What is one advantage and one disadvantage of divisional structure?
Advantage: Focus on specific clients/products. Disadvantage: Duplication of resources.
In a functional departmental structure, how are jobs grouped?
Product/service, geography, and customer type.
What is a key disadvantage of functional departmentalisation?
It can lead to conflict between departments and managers being trained too narrowly.
What is a cross-functional team in a team-based structure?
A team made up of members from different functional areas who report both to their team and their functional department.
What are two disadvantages of team-based structures?
Dual loyalty/conflict and excessive time spent in meetings.
What is horizontal differentiation in an organisation?
Horizontal differentiation refers to the grouping of specialised jobs into departments within an organisation.
How does span of control relate to the shape of the organisation?
A narrow span of control results in a taller organisation, while a wide span creates a flatter one.
What is the "span of control" in vertical differentiation?
It's the number of subordinates a supervisor can effectively manage.
What is the typical loss of understanding in downward communication from CEO to production line workers?
Up to 80% of understanding can be lost as messages move down the hierarchy.
What is spatial dispersion in an organisational context?
It refers to how geographically spread out an organisation's offices, plants, and personnel are.
What does "integration" refer to in an organisational structure?
the level of coordination achieved among an organisation's internal units.
What is formalisation in the context of job roles and procedures?
Formalisation is the degree to which jobs and procedures are standardised within an organisation.
What are the characteristics of a highly formalised organisation?
Minimum discretion in tasks, many rules, and clearly defined job descriptions.
What are common techniques used to increase formalisation?
Employee selection, clearly defined role requirements, and formal rules, procedures, and policies.
What is centralisation in decision-making?
decision-making authority is concentrated at the top levels of management.
What is the opposite of centralisation, and what does it involve?
Decentralisation, where decision-making is distributed across various levels of the organisation.
What are key features of a bureaucratic (mechanistic) organisational design?
Clear division of labour, strict hierarchy, many formal rules, and promotions based on competence.
What are key traits of an adaptive (organic) organisational design?
Flexibility, informal communication, empowerment, and emphasis on performance and adaptability.
What is the external environment in business?
The external environment includes everything outside the organisation that can potentially affect it.
What causes uncertainty in an organisation's external environment?
Uncertainty is caused when managers lack sufficient information to predict environmental changes or organisational needs.
What are the two main factors that increase environmental uncertainty?
Rapid changes and a high number of external factors both increase uncertainty.
What are the two major components of the external environment?
The two major components are the general environment and the task environment.
What sectors are included in the task environment?
Customers, competitors, suppliers, and the labour market.
What is the task environment?
external sectors that directly affect the organisation's operations and success.
What is the general environment?
The general environment includes broader factors that indirectly affect the organisation, like social, economic, legal, and technological elements.
How does technology impact the general environment of a business?
It can create new business opportunities or make existing products/services obsolete.
Why should organisations be concerned with the natural environment?
Because natural resources are finite, and environmental impact affects long-term sustainability and public perception.
What is included in the legal/political environment?
Demographic characteristics, values, norms, work preferences, and education levels.
What are some key aspects of the socio-cultural environment?
It includes laws, regulations, political stability, and pressure from advocacy groups that influence organisational behaviour.
How does the economic environment affect organisations?
inflation, recession, and growth affect consumer spending and organisational strategies.
What role do suppliers and the labour market play in the task environment?
Suppliers influence production and costs; the labour market affects the organisation's ability to hire skilled workers.
Why are customers considered a crucial part of the task environment?
Because customers determine the demand for goods and services, directly impacting business success.
What is the significance of the international environment to organisations?
It brings both opportunities (like market expansion) and threats (like international competition or instability).
What is the partnership and consultation principles of the Treaty of Waitangi?
Working together, in good faith, providing for Māori autonomy, two people to live in one cokuntry
When was the treaty signed?
6th February 1840
The principles of active protection in the treaty are
Of Māori by the crown, of Māori interests, of possessions so that tikanga (culture and protocols) and taonga (treasures, e.g language) are valued.
The principles of exchange in the treaty are
The right of the crown to govern for the right of Māori to retain their full tribal authority and control over lands and possessions
What is diversity?
all the ways in which people differ
What is workplace diversity?
A workforce made up of people which different human qualities or who belong to various cultural groups
What is the definition of primary dimensions?
Core elements through which people shape their self image and world view
What are some primary dimensions?
Age, gender, physical ability, race, sexual orientation, Ethnicity
What is the definition of secondary dimensions?
Can be changed or acquired through one's lifetime and can impact how a person is viewed by others
What are some secondary dimensions?
Education, marital status, parental status, work background, income, geographic location, military experience, religious beliefs,
What has more impact on people, primary or secondary?
Primary
What does prejudice mean?
The tendency to view people who are different as being deficient
What does discrimination mean?
When people act on their prejudice
What is stereotyping?
Making assumptions about a group and you attach that to a particular person who belong to that group.
What is an entrepreneur?
Someone who identifies opportunities, creates valuable ideas, organises resources, takes risks, and drives innovation to build and achieve their visions
The term Aotearoa comes from which discoverers
Kuramarotini and Kupe
From 'chiefs of industry',the power of chiefs to allocate specific rights of land use to particular groups?
Mana rangatira
What was NZ's declaration of independence signed in 1835 called?
He Whakaputanga
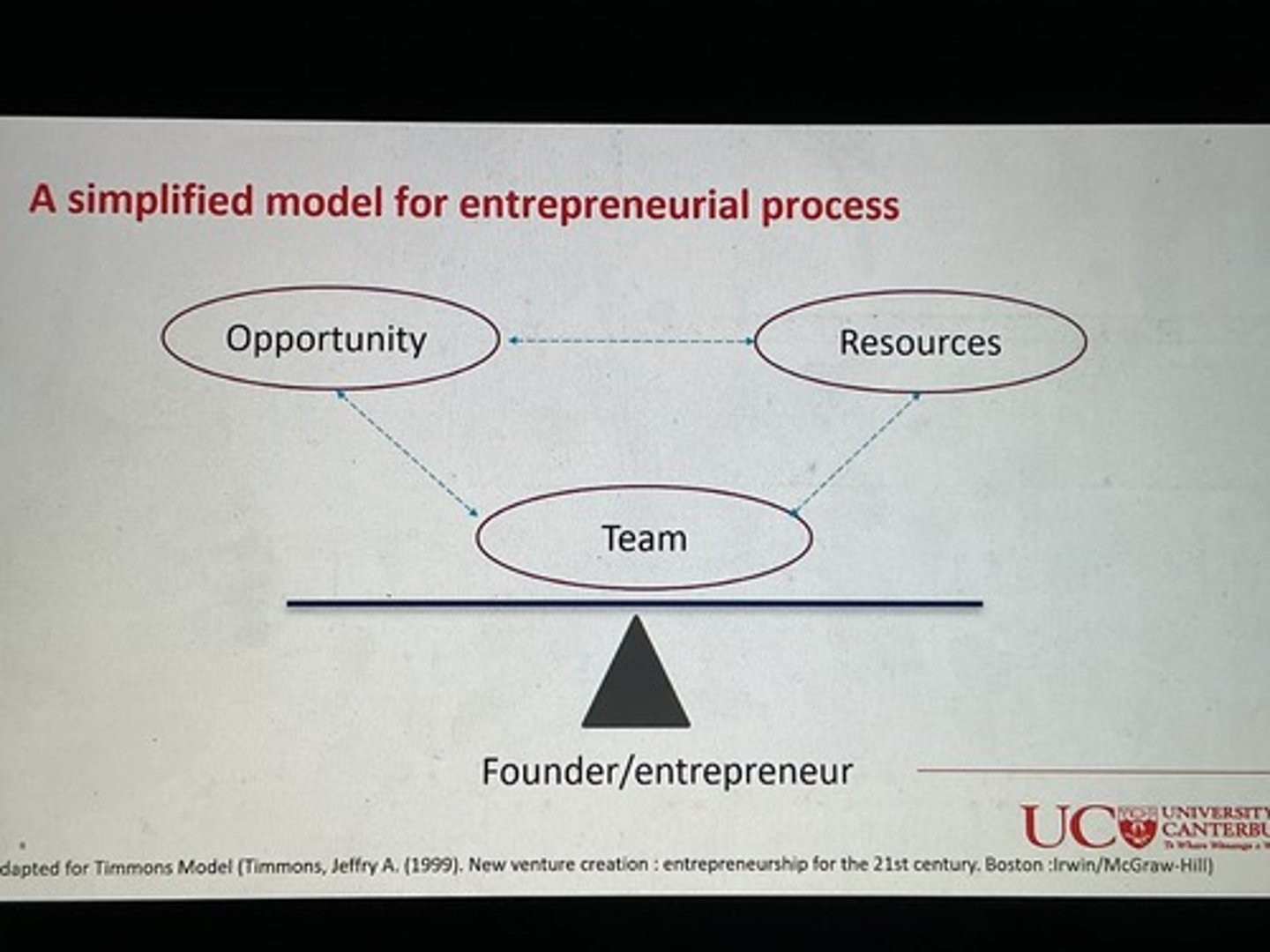
What factors do founder/entrepreneur balance?
Opportunity, resources, team
What are the characteristics of Māori entrepreneurship
Making positive different in community, having a positive reputation by increasing mana, making and using profits for values and principles
What are the core principles of Māori entrepreneurship
Communalism, reciprocity, and social gain over profits.
What is the NZ definition of a small business?
Enterprises with fewer than 20 employees, no formal management structure, independent entity, and relatively small market share
What are the unique contributions of small businesses?
A vehicle for entrepreneurship, encourages innovation and flexibility, closer relationships with customers, keeps larger firms competitive, generate new employment
What are the stages of growth for a small business?
Inception, survival, growth, expansion, maturity
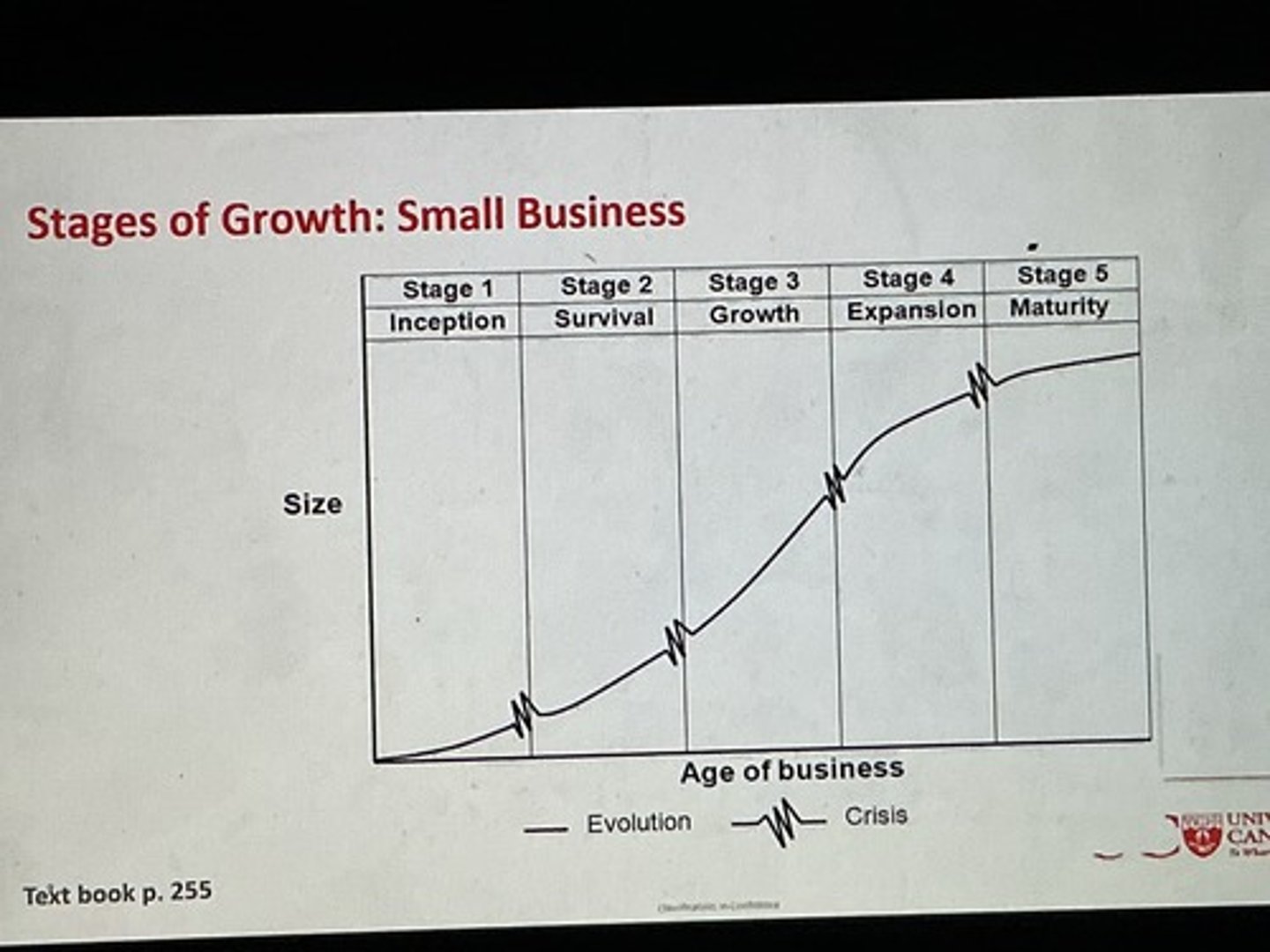
What is inception?
Focus is on creating products, attracting customers, and relying on the owners leadership and management skills.
What is survival?
The business is in workable entity and is producing product with enough customers, but cashflow is a concern.
What is growth?
Economically strong, sufficient size and market penetration, requires managers and systems, and is a threat to larger competitors
What is expansion?
Owner needs to delegate responsibility and develop management teams to manage growth.
What is maturity?
Business will become more formal in accounting, management, etc, will either succeed and develop or not.
What are the reasons for small business failures?
Lack of experience, expertise, strategy, poor financial control, growing to fast, lack of commitment, or ethical failure.
What are the three R's of entrepreneurial recovery and wellbeing
Respite, reappraisal, regimen
What is respite?
Involves interrupting work for both tangible relief and mental health.
What is reappraisal?
Involves cognitive exercises to reappraise stress and behaviours.
What is Regimen?
Enabling psychological and physical detachment through structure.