intro to business organizations
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is a fixed cost?
A cost that does not change no matter how many units of a good are produced
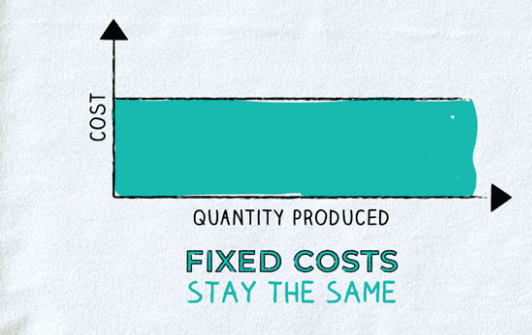
Example of a fixed cost?
Rent, insurance, manager salaries, or property taxes.
What is a variable cost?
A cost that changes with the number of units of a good produced.

Example of a variable cost?
Raw materials, hourly wages, shipping, utilities.
What does “marginal” mean in economics?
additional
What is marginal cost?
The cost of producing one additional unit of a good.
What is marginal revenue?
The revenue from selling one additional unit of a good.
What does every firm want to maximize?
Profit
Formula for Total Cost (TC)?
Fixed Cost (FC) + Variable Cost (VC
Formula for Average Total Cost (ATC)?
Total Cost ÷ Quantity.
Formula for Marginal Cost (MC)?
Change in Total Cost ÷ Change in Quantity
Formula for Total Revenue (TR)?
Price × Quantity
Formula for Marginal Revenue (MR)?
Change in Total Revenue ÷ Change in Quantity.
Formula for Profit (or Loss)?
Total Revenue – Total Cost.

What is a sole proprietorship?
A business owned by one individual who makes all decisions, keeps all profits, and has unlimited liability for debts.
Advantages of sole proprietorship?
Easy to form and dissolve, one owner makes decisions, profits taxed once, owner keeps all profits.
Disadvantages of sole proprietorship?
Unlimited liability (owner is personally responsible for debts).

What is a partnership?
A business owned by two or more co-owners (partners) who share profits and debts
What legal document do partnerships usually have?
Articles of Partnership.
Types of partnerships?
General partnership (equal share)
Limited partnership (silent partners)
Limited liability partnership (LLP).
Advantages of partnerships?
Specialization (partners divide work), profits taxed once, shared responsibilities.
Disadvantages of partnerships?
Unlimited liability (except in limited partnerships), complicated decision making, disagreements between partners.

What is a corporation?
A legal entity that can conduct business in its own name, separate from its owners.
Who owns corporations?
Stockholders (people who buy shares of stock).
What is a share of stock?
A claim on the assets of a corporation.
What is a dividend?
A payment of profits to shareholders.
Two types of stock?
Common and Preferred stock.
Advantages of corporations?
Limited liability (stockholders lose only what they invest).
Perpetual existence (continues even if owners leave/die).
Can raise large sums of money by selling stock.
Disadvantages of corporations?
Double taxation (corporation pays taxes on earnings, shareholders pay taxes on dividends).
Complicated and expensive to set up.
What is the role of a board of directors?
Decide corporate policies and goals.
How can corporations raise money besides stock?
By selling bonds (debt statements) or borrowing from banks.