Introduction to GIS Fundamentals and WVDOT Applications
1/454
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
455 Terms
What is GIS?
A geographic information system (GIS) is a system that creates, manages, analyzes, and maps all types of data, connecting data to a map and integrating location data with descriptive information.
What are the main functions of GIS?
GIS helps users understand patterns, relationships, and geographic context, improving communication, efficiency, and management decision-making.
What does GIS combine to aid in decision making?
GIS combines the 'Where' (geographical location) and the 'What' (information about a feature or item at that location).
What are the three main components of GIS?
The three main components of GIS are: 1) Geographical component (the 'where'), 2) Information component (the 'what'), and 3) System component.
What is the geographical component of GIS?
The geographical component includes datums and coordinates, representing the actual physical location of features.
What does the information component of GIS include?
The information component includes descriptive information about a feature, including facts and figures associated with it.
What is the system component of GIS?
The system component includes WVDOT geospatial data, infrastructure (software, hardware, GIS network), workforce, and finished products such as web maps and applications.
How does WVDOT use GIS?
WVDOT uses GIS for editing and maintaining the state road network, providing maps and applications, sharing geospatial information, analyzing transportation infrastructure, and highlighting projects.
What types of geospatial data can be included in GIS?
Geospatial data can include addresses, route numbers, street names, and parcel numbers.
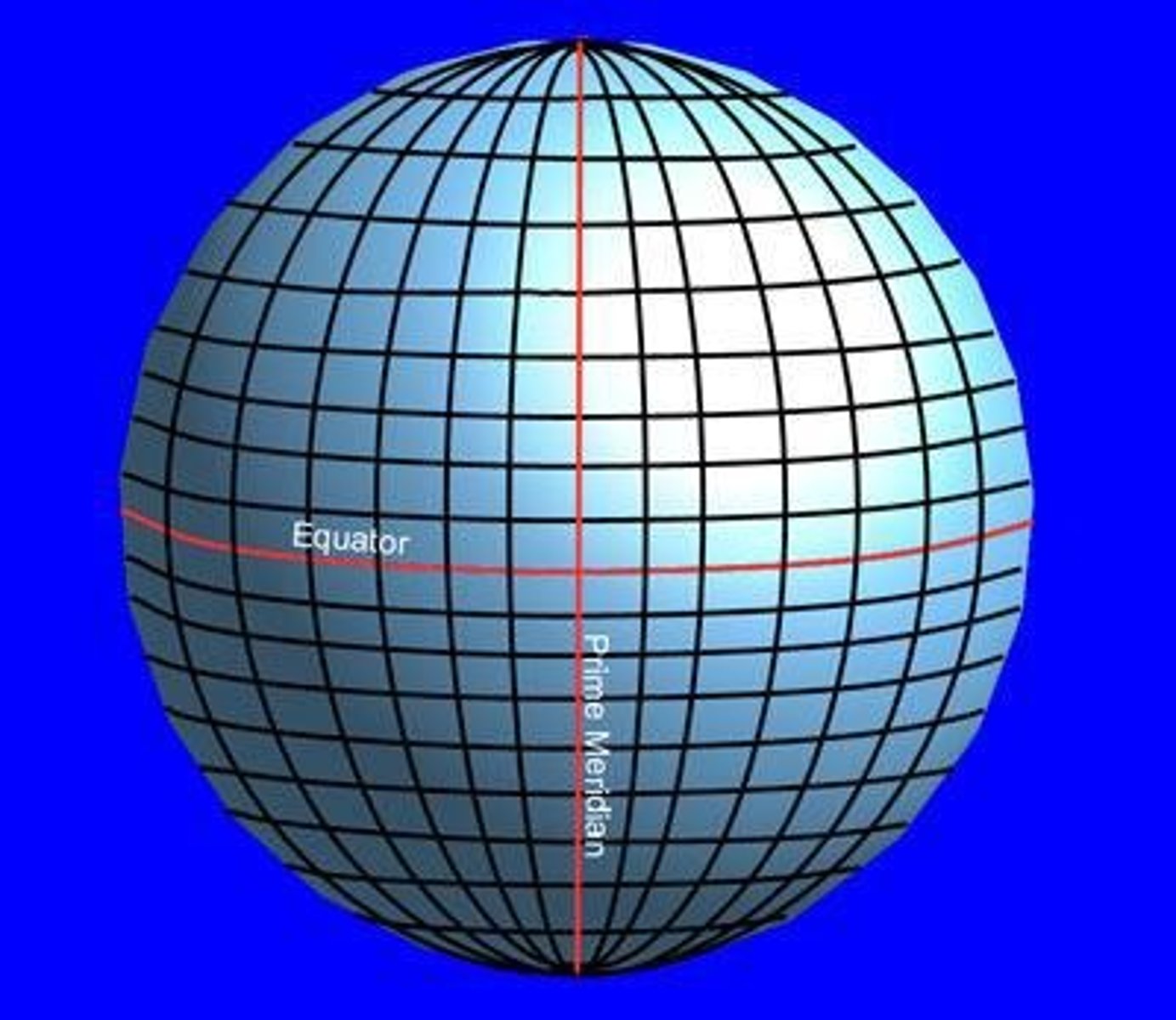
What is a coordinate system in GIS?
A coordinate system is a set of two measurements defined by north-south distance (Latitude) and east-west distance (Longitude) from a standard origin.
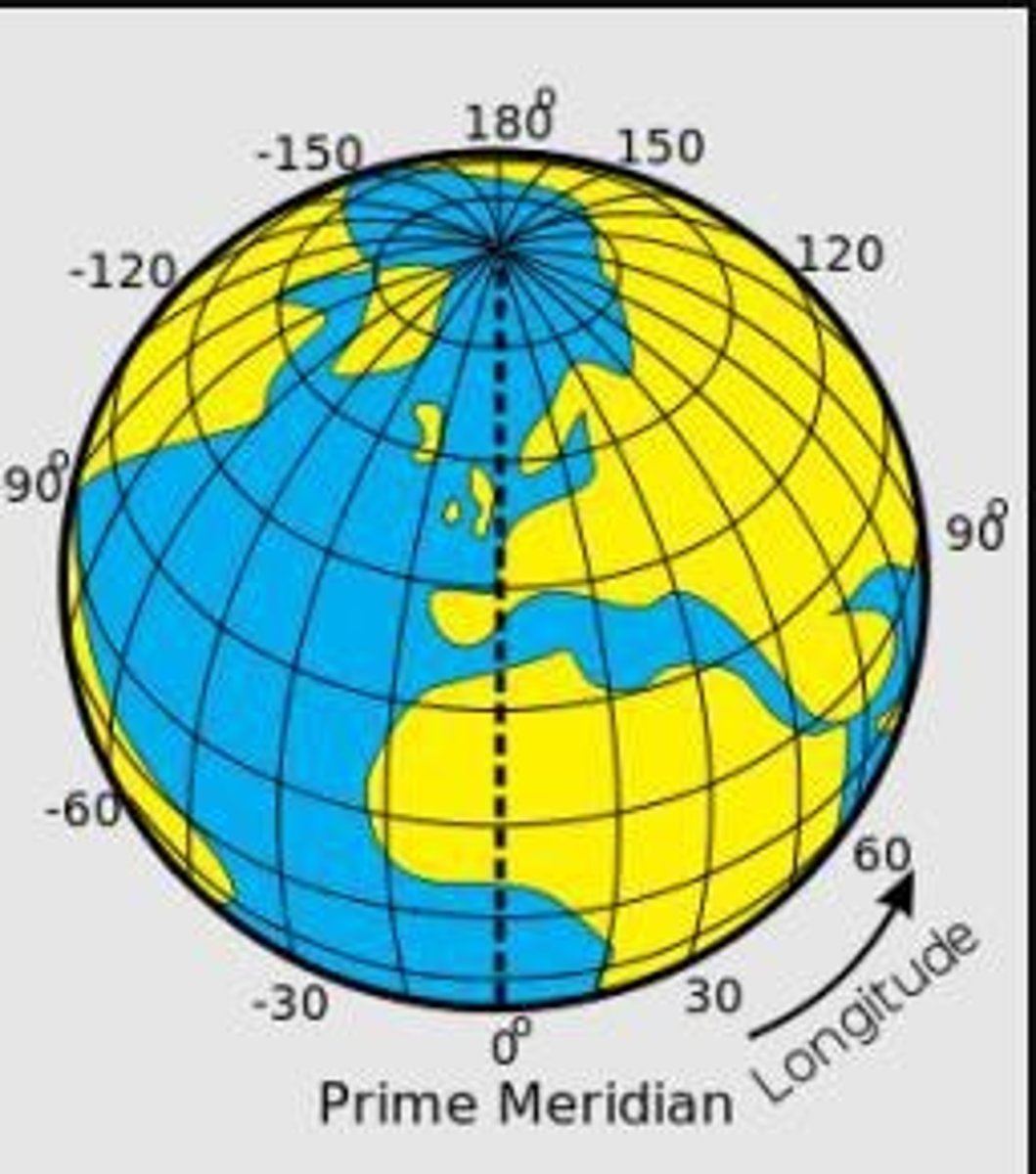
How is the Earth described in relation to GIS?
The Earth is described as an ellipsoid, similar to a soccer ball, which can be evenly sliced both horizontally and vertically.
What are meridians and parallels in GIS?
Meridians and parallels are the slices of the Earth that help define the coordinate system.
What does GIS provide for users?
GIS provides an at-a-glance reference, highlights and analyzes phenomena, and tells a story.
What is the significance of GIS in various industries?
GIS provides a foundation for mapping and analysis used in almost every industry and government agency.
What is the role of GIS in decision making?
GIS aids in decision making by integrating location data with descriptive information.
What types of products can GIS generate?
GIS can generate finished products including maps and applications.
What is the purpose of the WVDOT GIS ecosphere?
The WVDOT GIS ecosphere includes data locations, frequently used datasets, and the software, hardware, and network used to convert data into finished products.
How does GIS improve communication?
GIS improves communication by providing visual representations of data that are easier to understand.
What are some examples of features in GIS?
Features in GIS can be man-made (like buildings) or natural (like mountains).
What is the importance of understanding the Earth in GIS?
Understanding the Earth as an ellipsoid is crucial for accurately defining locations using coordinate systems.
How does GIS help in analyzing transportation infrastructure?
GIS helps in researching and analyzing the impact of transportation infrastructure on parcels, the environment, and historical places.
What is the relationship between GIS and mapping?
GIS connects data to maps, allowing for the visualization and analysis of spatial relationships.
What are meridians?
Imaginary lines that run north and south, also called longitude lines, intersecting at the poles and circling the globe 360 degrees.
What is the Prime Meridian?
The Prime Meridian is the origin of longitude at 0 degrees, sometimes referred to as the Greenwich Meridian.
What is the Antemeridian?
The Antemeridian, or International Date Line, is located at 180 degrees longitude.
What are parallels?
Imaginary lines that run east and west, also called latitude lines, that do not intersect each other and circle the globe 180 degrees.
What is the Equator?
The Equator is the origin of latitude at 0 degrees.
What are the four hemispheres created by the Prime Meridian and the Equator?
Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere, Eastern Hemisphere, and Western Hemisphere.
In which hemispheres is the United States located?
The United States is located in the Northern and Western Hemispheres.
What is the significance of latitude and longitude in GIS?
Latitude and longitude are used to determine the position on Earth where an object is located.
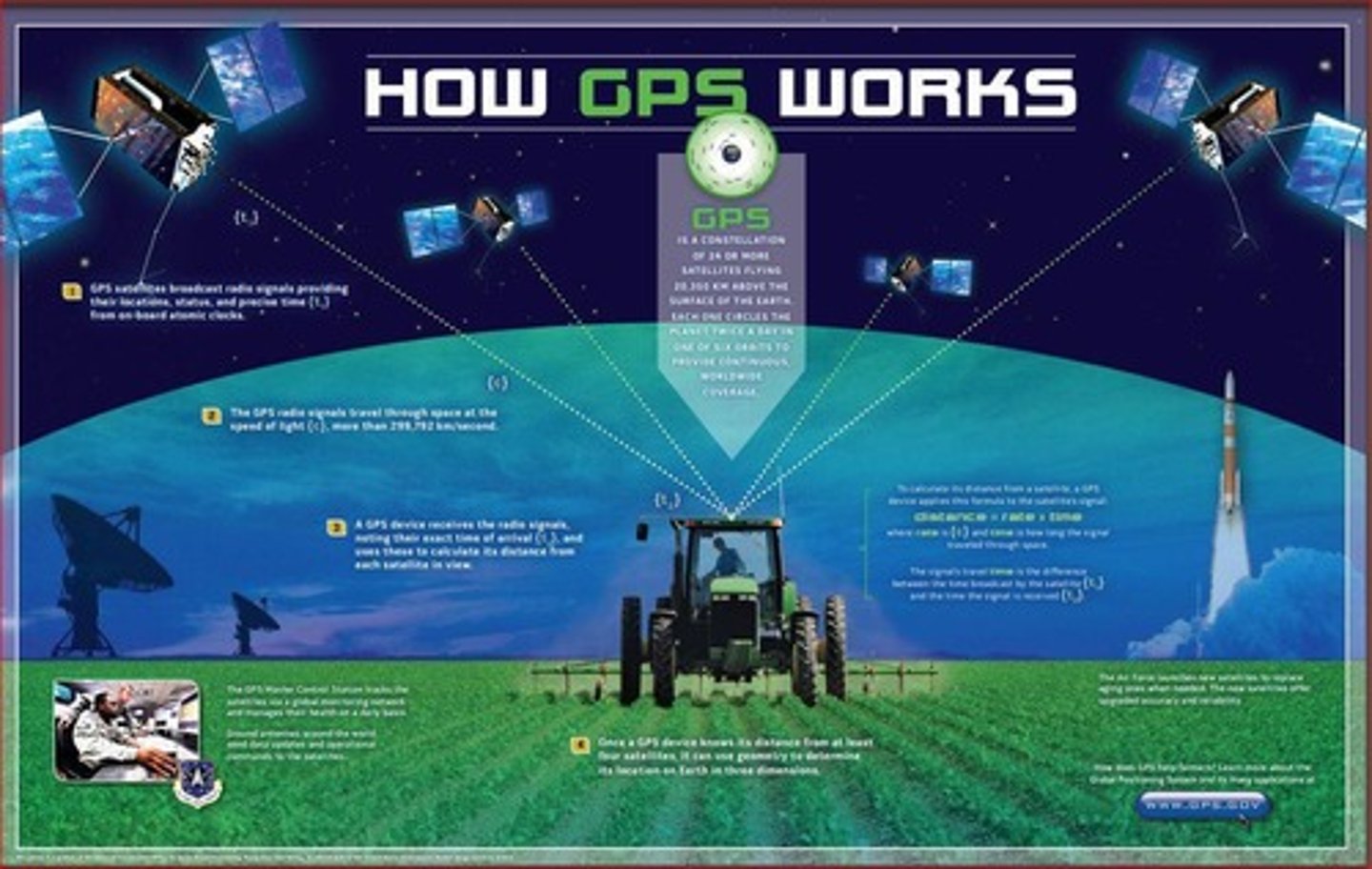
How does GPS work?
GPS uses a constellation of 24 or more satellites that broadcast signals to a receiver, which calculates its location based on the time of signal arrival from at least four satellites.
What does GPS stand for?
Global Positioning System.
What is GNSS?
Global Navigation Satellite System, which includes GPS and other satellite systems.
What is a Continuously Operating Reference Station (CORS)?
A strategically placed, highly accurate receiver that continuously transmits and records latitude, longitude, and elevation data.
What is the maximum latitude value?
90 degrees North or South.
What is the maximum longitude value?
180 degrees East or West.
How do coordinates determine distance on Earth?
The measurement between two or more coordinate points gives the distance between them.
What happens when you tap on a map in a mapping application?
It adds a point to your location and displays the coordinates of that point.
What is the role of satellites in GPS?
Satellites broadcast radio signals that allow GPS receivers to calculate their distance and location.
What is the distance above Earth where GPS satellites orbit?
About 20,350 kilometers (approximately 12,644 miles) above the Earth.
What is the function of a GPS receiver?
To receive signals from satellites and calculate the user's exact location based on those signals.
What is the relationship between GPS and GIS?
GPS provides precise location data that can be used in Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for mapping and analysis.
What do latitude and longitude coordinates represent?
The specific geographic location of a point on the Earth's surface.
What is the format of GPS coordinates?
Typically expressed in degrees, such as 38.33596N, 81.61046W.
What is the significance of the coordinates 0 degrees latitude and longitude?
They represent the intersection of the Equator and the Prime Meridian, known as the origin point for geographic coordinates.
What is the purpose of WV's CORS network?
To create a spatial reference system using geodetic markers and GPS receivers.
What elements does the spatial reference system define?
Gravity, Height, Latitude, Longitude, and Scale.
How does the spatial reference system aid in geographic information systems (GIS)?
It allows for accurate location of features such as roads and bridges.
What is the shape of the Earth as described in the notes?
The Earth is a spheroid shape.
What are the two types of imaginary lines used to define coordinates on Earth?
Latitude (east-west) and Longitude (north-south).
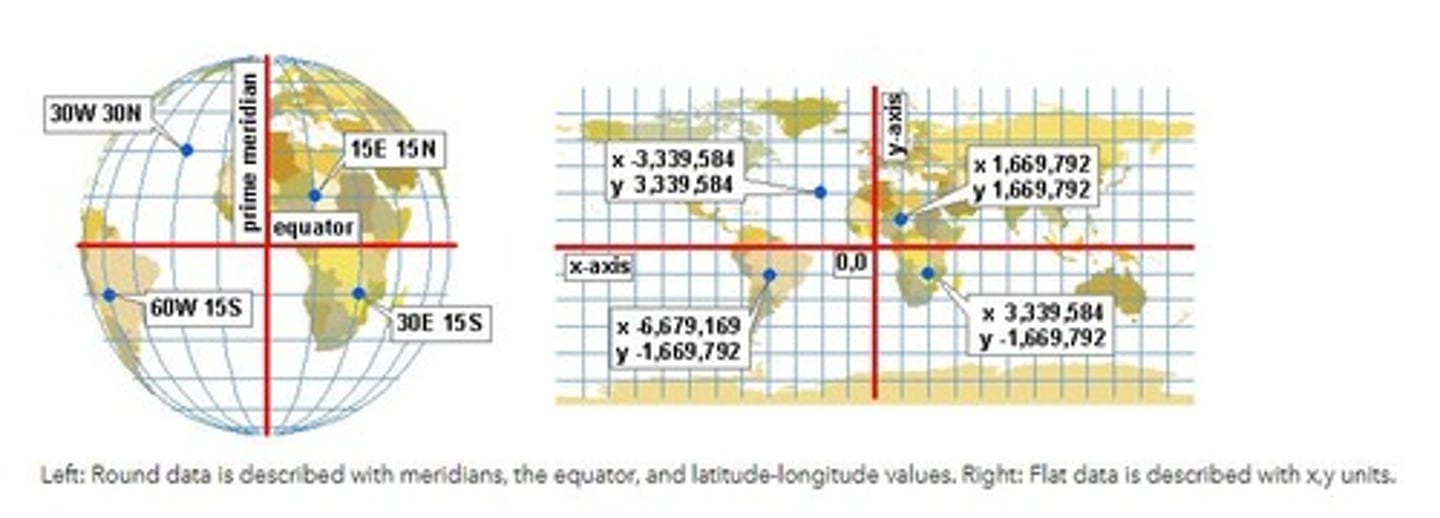
What is a Geodetic Marker?
A known point with latitude and longitude coordinates used in the spatial reference system.
What are the three key components used to build a GIS model?
Geodetics/Datums, Projections and Geographical Coordinate System, and Scale.
What is a Datum in the context of mapping?
A set of known points on the Earth's surface used as a reference for measuring locations.
What are the two types of Datums?
Geocentric (related to the center of the Earth) and Local (related to a defined area on the Earth's surface).
What is a Horizontal Datum?
It specifies the location of the origin, orientation, and dimensions of the reference ellipsoid.
Name two commonly used Horizontal Datums.
NAD1983 and WGS1984.
What is a Vertical Datum?
A set of fundamental elevations used as a reference for other elevations.
What is the basis for Geodetic Datums?
A combination of horizontal and vertical datums measured from satellites.
What is the significance of the Prime Meridian in defining coordinates?
It serves as the origin for measuring longitude.
What does the term 'scale' refer to in the context of GIS?
The relationship between distance on the map and actual distance on the ground.
What is the purpose of using GPS in the exercise mentioned?
To locate specific places and determine their latitude and longitude coordinates.
What is the relationship between latitude and the Equator?
Latitude lines run parallel to the Equator.
What is the relationship between longitude and the Prime Meridian?
Longitude lines run from the Prime Meridian to the poles.
What does 'NAD' stand for in NAD1983 and NAD1927?
North American Datum.
What is the role of the CORS network in mapping?
It provides accurate positioning data through GPS receivers.
How does a vertical datum relate to Mean Sea Level?
It is often based on Mean Sea Level at one or more points.
What are tidal datums based on?
Observations of tidal variations over a period of time.
What defines a geographical position on Earth?
A Geographical Coordinate System defines any geographical position using latitude (Y Coordinate) and longitude (X Coordinate), and optionally a vertical height (Z Coordinate).
What are latitude and longitude used for in a geographical coordinate system?
Latitude indicates degrees North and South of the equator, while longitude indicates degrees East and West from the prime meridian.
Why can't a geographical coordinate system measure distance, area, or volume?
Because it uses Lat/Long coordinates which are not suitable for measuring these dimensions.
What is the purpose of a projected coordinate system?
A projected coordinate system converts a three-dimensional model of the Earth's surface into a two-dimensional surface for use on screens or maps.
What does the conversion from a geographical to a projected coordinate system require?
It requires systematic conversions of latitude and longitude into a planar coordinate system.
What is a consequence of using a projected coordinate system?
It introduces distortion, where features farther from the origin of the projection appear more exaggerated.
What are the six classes of common projections in a projected coordinate system?
Conic, Cylindrical, Azimuthal, Conformal, Equal Area, and Equidistant.
What is a conic projection?
A conic projection maps the Earth onto a cone shape, with meridians mapped equally out from a central apex point, usually a pole.
Give an example of a conic projection.
Examples include Lambert Conformal Conic, Albers Conic, and Equidistant Conic.
What characterizes a cylindrical projection?
It projects the Earth onto a cylinder, with meridians as equally spaced vertical lines and circles of latitude as equally spaced horizontal lines.
Name an example of a cylindrical projection.
Examples include Mercator, Lambert Cylindrical Equal Area, and Gall Peters.
What is an azimuthal projection?
An azimuthal projection maps the Earth onto a flat plane, preserving equal distance and direction from a center point.
Provide an example of an azimuthal projection.
Examples include Azimuthal Equidistance, Gnomonic, and Stereographic.
What is a conformal projection?
A conformal projection preserves correct shapes and scale of small areas in all directions.
Name an example of a conformal projection.
Examples include Lambert Conformal, Transverse Mercator, and Stereographic.
What does an equal area projection preserve?
An equal area projection preserves area measures but usually distorts shape, angle, or scale.
Give an example of an equal area projection.
Examples include Albers Conic, Bonne, and Mollweide.
What does an equidistant projection preserve?
An equidistant projection preserves distance along one or two lines or between special points.
Name an example of an equidistant projection.
Examples include Plate Carree and Azimuthal Equidistant.
What is scale in the context of maps?
Scale represents the ratio or size of the model compared to the actual object, such as 1:87 meaning the model is 1/87th the size of the actual object.
How does scale affect the area shown on a map?
The larger the scale, the bigger the area shown; the smaller the scale, the smaller the area shown.
What are some common types of projections used in ESRI?
Common types include UTM (Universal Transverse Mercator), State Plane Coordinate, and WGS_1984_Web_Mercator_Auxiliary_Sphere.
Which projections are commonly used in WVDOT?
NAD1983 UTM Zone 17N and West Virginia State Plane Coordinates North and South.
What are the three categories of map scales based on their ranges?
Small Scale Maps: 0 - 250,000; Medium Scale Maps: 250,001 - 1,000,000; Large Scale Maps: Over 1,000,000.
What is the scale range for City maps in WVDOT?
1:5,000 to 20,000, classified as Small Scale Maps.
What is the scale range for County maps in WVDOT?
1:50,000 to 250,000, classified as Small Scale Maps.
What is the scale range for District maps in WVDOT?
1:500,000 to 1,000,000, classified as Medium Scale Maps.
What is the scale range for Statewide maps in WVDOT?
1:2,200,000 to 2,900,000, classified as Large Scale Maps.
What is GIS and what does it stand for?
GIS stands for Geographic Information System, which is a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, and present spatial or geographic data.
What are Meridians and Parallels in the context of geography?
Meridians are lines of longitude, while Parallels are lines of latitude.
What is a spatial reference in GIS?
A spatial reference defines how the two-dimensional, projected map in your GIS relates to real places on the earth.
What is the difference between a Geographical Coordinate System and a Projected Coordinate System?
A Geographical Coordinate System uses a three-dimensional spherical surface to define locations on the earth, while a Projected Coordinate System translates the earth's surface to a flat map.
What are the components of GIS information?
GIS information consists of processed and analyzed data that provides meaningful context about objects on a map.