Social Studies - Ancient Greece
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
9th Grade
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Topography - Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece had a very mountainous environment. This environment lead to hundreds of city-states like Athens and Sparta.
________ was isolated from the world due to being in the mountains
_______ had a lot of cultural diffusion and migrants due to being near the mediterranean sea
Athens
_______ was a democratic poli/city-state that’s economy was based off trade and had an artistic and philosophical culture.

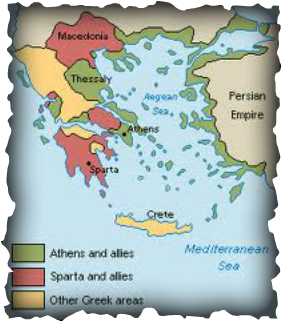
Geography of Athens
Located by both the Aegean Sea and the Mediterranean Sea which led to cultural diffusion and trade.
Politics of Athens
Democratic Republic
Free men over 18 could vote
Aristocracy
Women and slaves could not vote

Aristocracy
Ruled by rich, seen in city state of A ____

Economy of Athens
Based on trade
Used silver coins to trade

Social Aspect of Athens
Education: tried to make well rounded citizens of all males to participate in direct democracy
Women/slaves had no rights

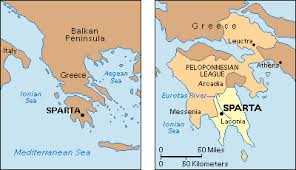
Geography of Sparta
Inland-farming
Isolated by mountains
Politics of Sparta
Oligarchy Government
Ruled by a few council of elders
Monarchy - 2 kings

2 Kings - Sparta
Two kings were needed in _____ due to:
One could go to war and die but,
There would still be another one at home who could appoint the next king

Economy of Sparta
Based on farming and conquest
Used iron bars which discouraged trade

Sparta
______ was an oligarchy city-state/poli whose economy was based on conquest and farming and culture was war/military.

Social Aspect of Sparta
Education: training for men and women to serve in the military
Women and slaves (helots) had some rights

Helots
The people who Spartans captured during war (slaves)
Spartans were very harsh
Could earn rights overtime

Persian Wars - Causes
Persia wanted to expand West to conquer Greek Poli/Aegean Sea for trade
Greeks wanted political, social, and economic freedom
Athens and Sparta united

Persian Wars - Effects
Persians had larger force but the Greeks defeated them with military strategy
Athens victory/control of trade/rebuilding led to Golden Age
Delian League (collective security), formed by Greek city states for protection. Led by Athens, resented by Sparta… Greece moves on. This leads to a GREEK GOLDEN AGE

Pericles
Main leader of Athenian government
Kept the direct democracy organized and prosperous

Socrates
Focused on moral and psychological questions
Used a series of question in debates to show the flaws in others’ ideas - a style called the “Socratic Method”

Plato
Student of Socrates
Discussed ethics, politics and the nature of ideas

Aristole
Student of Plato and tutor for Alexander the Great
Advances in science and logic influenced scholars for thousands of years

Pythagoras
Developed a method for explaining the relationship between angles and legs of right triangles now called the - Pythagorean Theorem

Euclid
Establishing the foundational principles of geometry and laying out a logical framework for mathematical reasoning using axioms and proofs

Homer
Created two poems that are still relevant today
The stories are used as templates for modern story tellers

Herodotus
Created the field of study of ‘history’
Wrote the truth and had no bias

Order of Important Events
Paleolithic Age, Neolithic Age, Persian Wars, Golden Age of Athens, Peloponnesian War, Hellenism

Peloponnesian Wars - Causes
Athens created the Delian League of Greek city-states after the Persian War for protection
Athens became rich from taxing other city-states and built the Parthenon
Sparta resented this and allied with other city-states against Athens
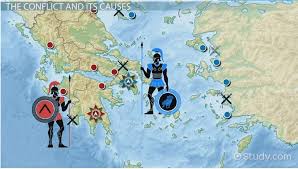
Peloponnesian Wars - Effects
Brutal 27 year civil war
Athens was defeated engine golden age
Sparta and all other Greek poli were greatly weakened leading to the rise of Alexander the Great (Macedonia)
