Tectonic Plates Chapter 10
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
review core concepts such as continental drift, seafloor spreading, and plate movement mechanisms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Plate Tectonic
The rigid plates of the earth’s crust drift and interact on the asthenosphere, leading to earthquakes, volcanoes and mountain building.
Crust
The Earth’s most outer layer, continental crust and oceanic crust.
Continental crust
thicker and less dense than oceanic crust
Oceanic crust
thinner and denser than continental crust
Lithosphere
The Earth’s rigid outer layer, made of crust and uppermost mantle, which is involved in tectonic activity.
Asthenosphere
The semi-molten upper mantle beneath the lithosphere, providing lubrication for plate movement and convective flow.
Divergent Boundary
Dividing plates that move away from each other resulting in new oceanic crust through volcanoes and widening ocean ridges.
Convergent Boundary
Where the plates move towards each other and can cause subduction, mountain building, or earthquakes.
Transform Fault
two plates slide against each other and cause earthquakes, without creating or breaking anything massive.
Mid-Ocean Ridge
An underwater mountain range formed by plate tectonics, where tectonic plates diverge and new oceanic crust is created.
Trench
A long, narrow, deep ocean trench marking the location of a plate subduction zone
Hot-Spot Volcano
A volcanic chain formed by a fixed mantle plume rising beneath a tectonic plate
Continental Drift
the hypothesis that continents were once connected as a single landmass and then gradually drifted apart
Pangaea
The supercontinent that existed approximately 200 million years ago
Alfred Wegener
A German scientist who, in 1915, proposed the theory of continental drift, supported by jigsaw-fit coastlines and fossil evidence.
Fossil evidence
Where the distribution of identical organism fossils are found across now-separate continents support the idea that there landmasses were once connected as one.
Marie Tharp
Was the first female scientist to map the Great Global Rift System
Great Global Rift System
The deep-sea mountain ranges and rift valley system was clearly illustrated by Thrap’s map that held crucial structures for understanding seafloor spreading.
Harry Hess
An american geologist who proposed the seafloor spreading hypothosis explaining the mechanism of the continental drift.
Seafloor Spreading
At mid ocean ridges magma builds up to create new oceanic crust, pushing the older oceanic crust to move outwards on both sides and eventually disappearing at the ocean trenches.
Seafloor age
Rocks found nearer to the mid ocean ridges are young while the rocks near the ocean trenches are old supporting seafloor spreading.
Sediment thickness evidence
Sediments are thin near mid ocean ridges and thick near ocean trenches.
Magnetic Striping
Magnetic stripping is the symmetrical pattern of magnetic reversals recorded in oceanic crust, providing key evidence that new seafloor continuously forms and spreads from mid-ocean ridges.
Convection Currents
Mantle thermal convection drives tectonic plates, where hot magma rises and cold rock sinks, forming a circulatory flow.
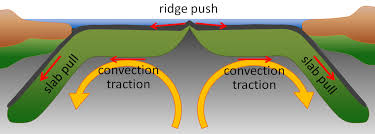
Ridge Push
The force of movement that pushes the plates away from each other from the mid ocean trench
Slab Pull
the result of ridge push when the plates go under the other plates and preform subduction.
The pacific plate
The worlds largest oceanic plate and it almost entirely made of oceanic crust
African Plate
Has the African continent and the respected oceanic crust, is a mixed type plate
The Eurasian Plate
Covers most of europe and asia, and a slight bit of oceanic crust.
The north American plate
North America, Greenland, and the adjacent Atlantic oceanic crust.
Antarctic Plate
Antarctica and the surrounding Southern Ocean oceanic crust.
Transform boundary Earthquakes
Causes earthquakes when the plates slide past each other- no destruction nor creation is completed
Subduction Zone volcanic arcs
"The subducting plate melts to produce magma, forming a series of volcanoes on the overriding plate."
Low-Velocity Layer
"The low-velocity zone in the asthenosphere, which is weak due to partial melting."