
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
What is the difference between income and wealth?
The 2 ways to measure richness is income and wealth.
Income - The flow of money a person or economy receives each year
Wealth - The sum of all of a person or economies assets.
What is the circular flow of income and what does it mean?
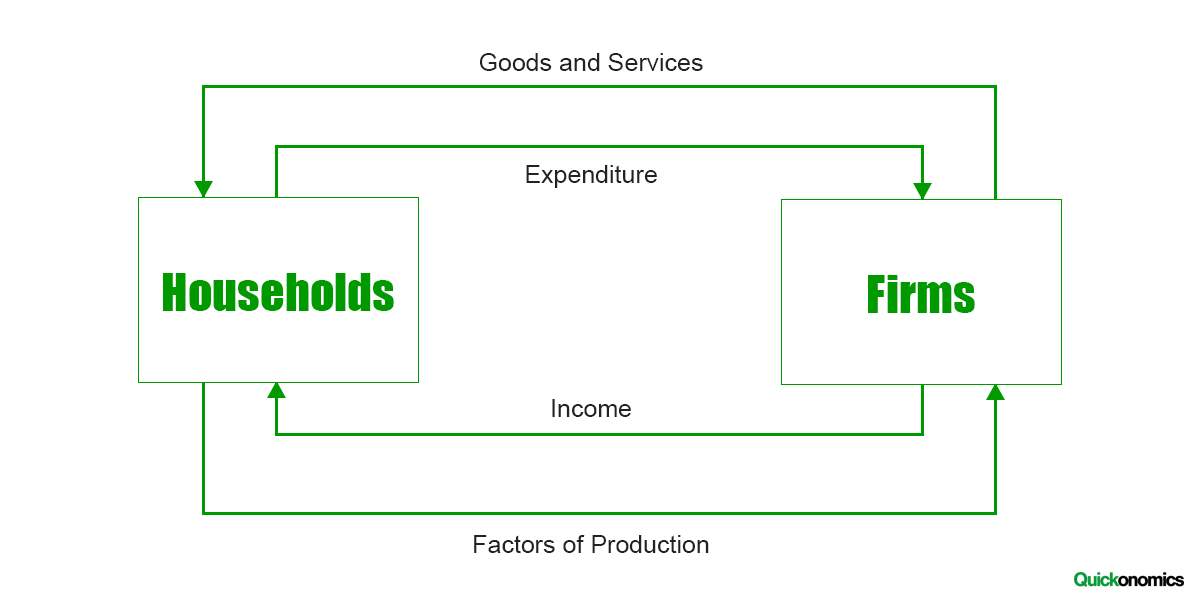
The model is used to show the movement of income in an economy between households and firms. Households earn money from giving factors of production, and in return earn factor incomes (Wages, rent).
What does the circular flow model show?
That National income=National expenditure=National output.
This is because the total spending from households must come from their total incomes. They then spend on the total output of goods and services produced by firms.
What do we use to measure national income?
We measure national output as it is equal to national income and easier to measure.
National output is measured by real GDP, which is the total value of goods and services produced by an economy, adjusted to inflation.
What are leakages and injections in an economy and what are the 3 types?
A leakage is when there is a withdrawal of money from the economy. The 3 types are Savings, Imports and Taxation (SIT).
An injection is when money is added to the economy. The 3 types of Government spending, investment and exports (GIX).
What is AD and what is the graph?
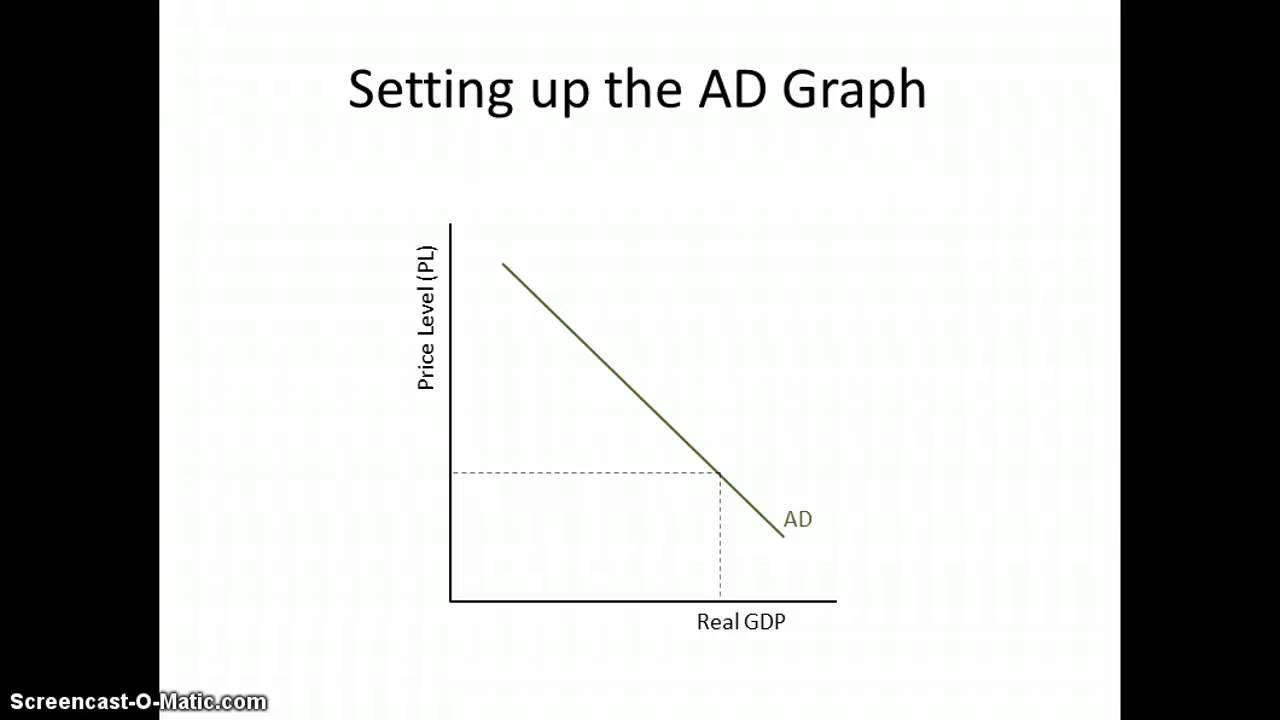
Aggregate demand is the total demand for goods and services in an economy.
What makes up AD and what are the percentages?
AD = C + I + G + (X-M)
Consumption - Consumer spending on goods and services, roughly 60% of AD
Investment - Spending by businesses on capital, makes up about 15-20% of AD. Of this, about 75% is by private sector investment.
Government spending - Money spent by the government on goods, services and public projects for the public to support the economy. Makes up roughly 20% of AD
Net exports - Measures the country’s exports-imports. Roughly 5% of AD.
What is Gross investment and Net investment?
Gross investment - The original value of a capital good
Net investment - Gross investment - depreciation
What are contractions and extensions in demand?
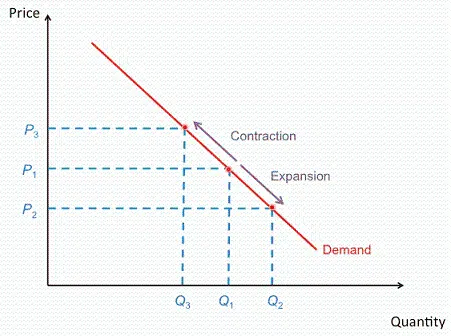
When the price level increases, there is a contraction in aggregate demand, meaning that real GDP decreases.
When the price level decreases, there is an extensions in aggregate demand, meaning that real GDP increases.
What is disposable income?
Disposable income is the money left over after taxes are payed.
What is the multiplier effect?
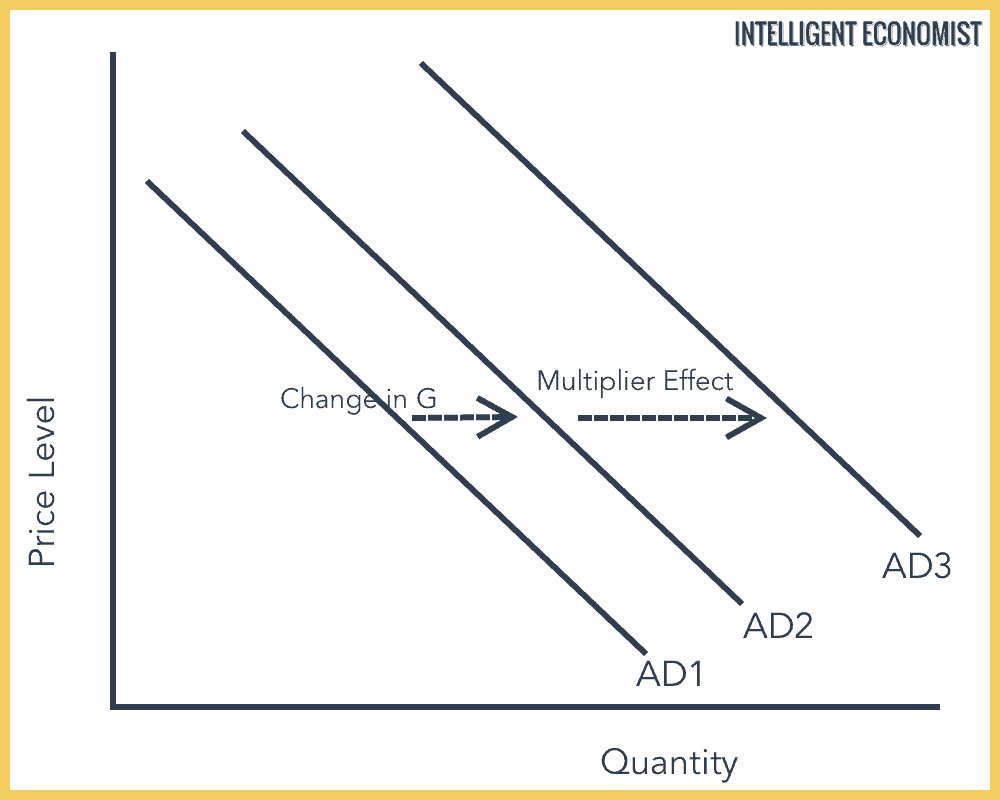
The multiplier effect is when an initial increase in an injection leads to a bigger overall effect on the economy.
What is an example of the multiplier effect?
Increased government spending on infrastructure (G) leads to an increased employment of workers, who spent their incomes (C) on firms, who can then hire more workers to consume (C).
This also leads to an increase in income tax, VAT and corporation tax to be reinvested (G). Firms may also increase investment (I).
What is the MPW and MPC?
Marginal propensity to withdraw - The fraction of additional income that is spent on withdrawals in the economy. Calculated by MPS+MPM+MPT.
Marginal propensity to consume - The fraction of additional income that is spent on goods and services. Calculated by △C/△Y(income)
MPC+MPW=1
What is the multiplier rate and how is it calculated?
The multiplier ratio is the amount that GDP increases following and initial injection.
It can be calculated by
1/1-MPC
1/MPW
1/MPS+MPM+MPT
What is the negative multiplier effect?
When an initial withdrawal from the economy leads to a larger decrease in real GDP.
How do benefits/pensions affect AD?
When the government increases benefits, there is an increase in consumption from households, increasing firms profits and potentially increasing investment from firms. This increases AD.
However, government spending will usually decrease as a result as, by paying out benefits, the government suffers the opportunity cost of being unable to spend on goods, services and projects.
What are interest rates?
How much interest you'll get from the bank - return on savings
How do interest rates affect AD?
An increase in interest rates leads to in increase in the return on savings, meaning that consumer are more incentivised to save and MPS increases. Therefore, AD decreases.
An increase in interest rates leads to higher mortgage payments, meaning less disposable income to spending on goods. Therefore, AD decreases. Furthermore, a decrease in demand for housing decreases house prices, leading to the negative wealth effect.
An increase in interest rates would increase the cost of borrowing, potentially decreasing investment from firms. Therefore, AD decreases.
What is the positive and negative wealth effect?
Positive wealth effect - When an increase in wealth makes consumers feel more confident and they therefore increase their consumption.
Negative wealth effect - When a decrease in wealth makes consumers less confident and they therefore decrease consumption
How does consumer and investor confidence (animal spirits) effect AD?
When consumers are more confident, they are less worried about the future, so they save less and spend more, increasing AD.
When investor confidence/animal spirits are high, investment will increase causing an increase in AD.
What factors can influence government spending (G)?
- Economic conditions - In a recession, the government might increase spending to stimulate the economy, whereas in other times they may decrease spending to keep the inflation rate stable
- Age distribution of the population - A population full of older people may mean more spending, such as on social care. A younger population may mean more spending on education. In either case, govt spending is likely to increase.
What factors can effect net trade (X-M)?
- Real incomes - When real incomes are higher, there tends to be increased demand for foreign goods and services. This leads to a decrease in AD.
- Exchange rates - A stronger pound will make imports cheaper and exports more expensive, meaning that net trade may decrease, decreasing AD.