Chapter 27 - Control
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
endorcrine system
The system of glands that produce hormones responsible for the control and coordination of the body.
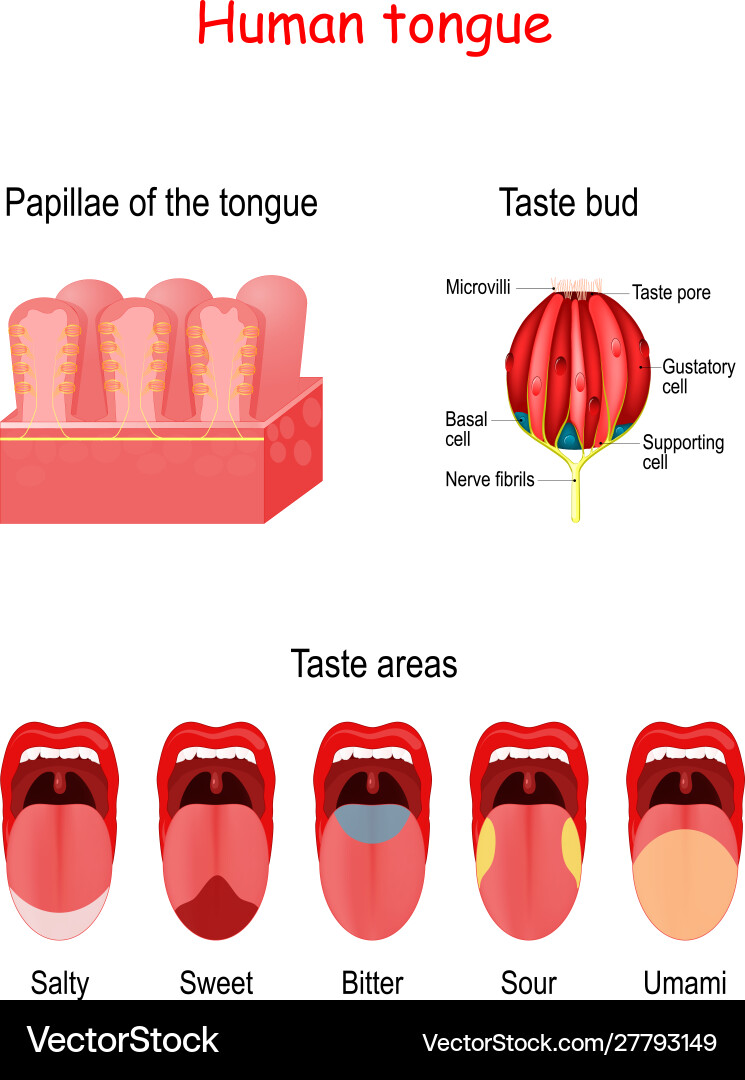
taste buds
Part of the peripheral nervous system
Can sense at least 4 basic tastes
Send nerve impulses to the parietal lobes
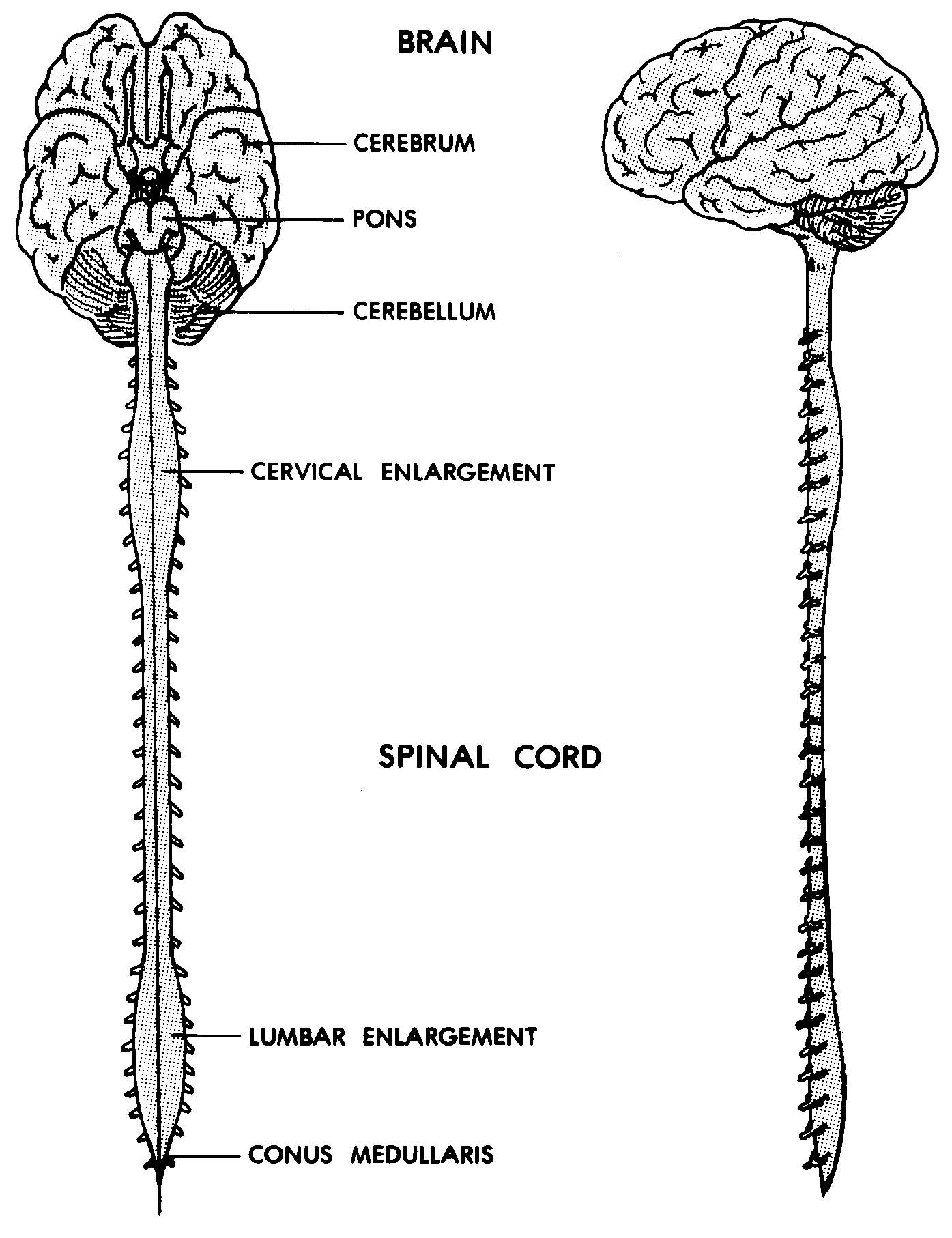
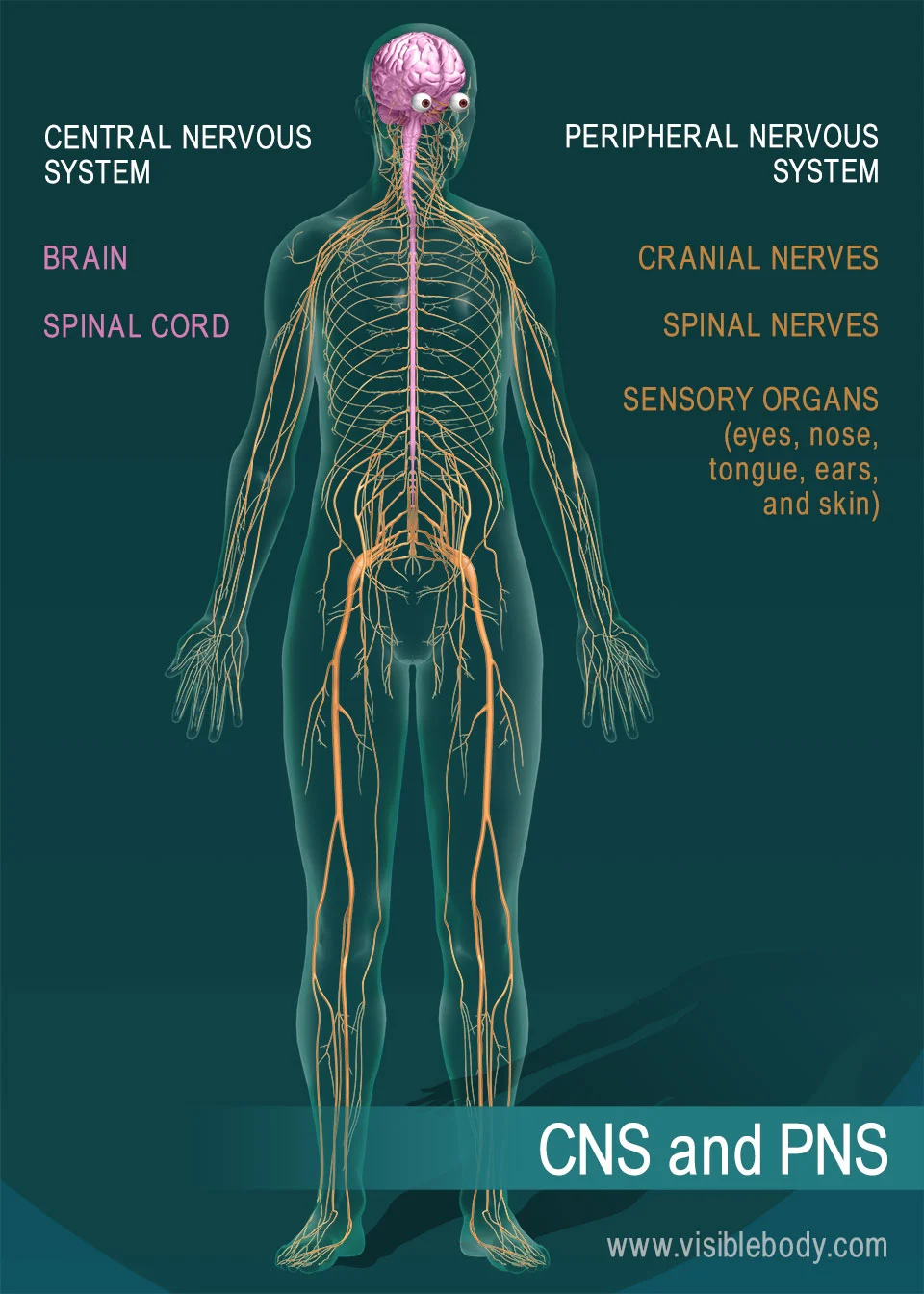
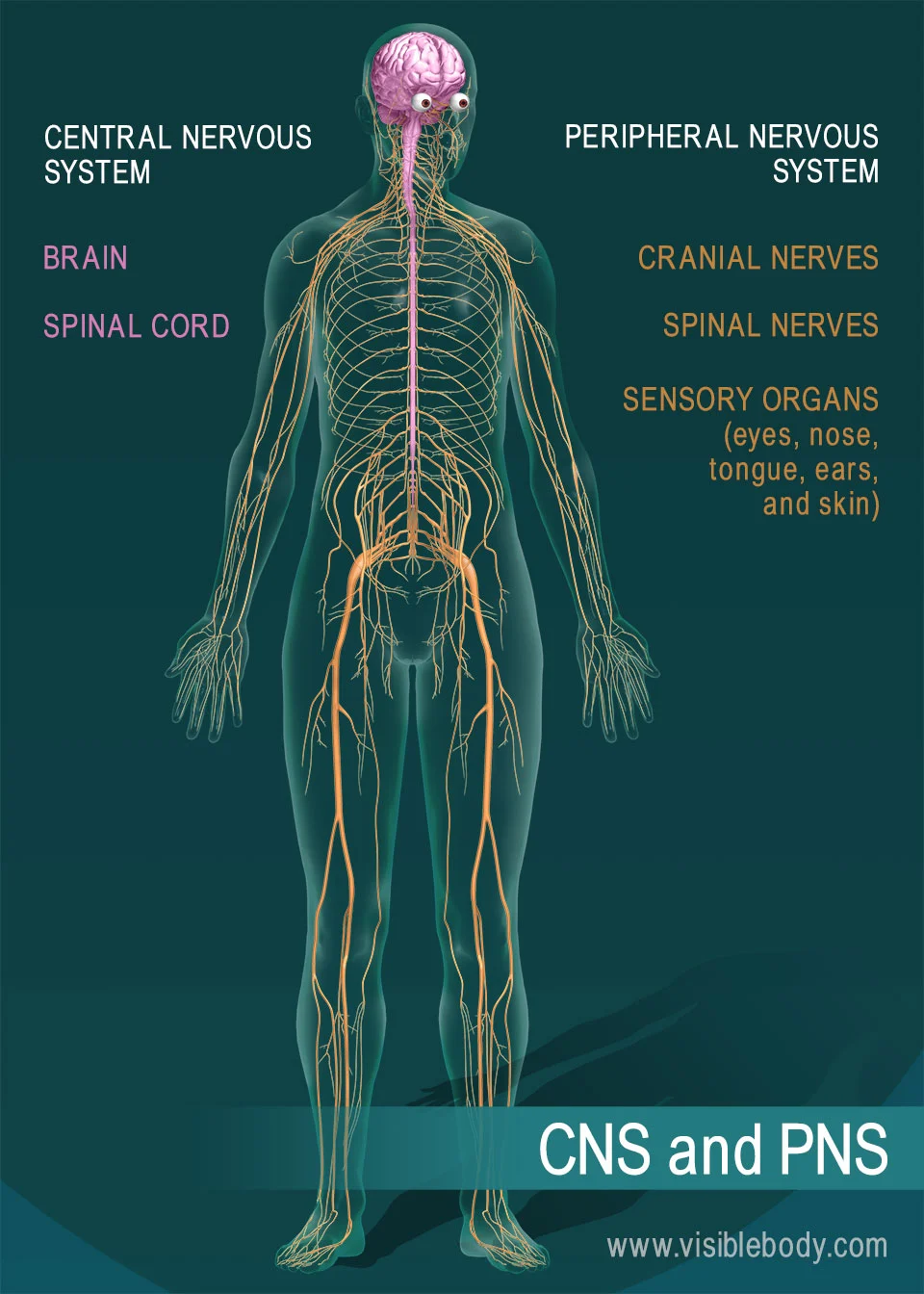
central nervous system
made of the brain and spinal cord
nervous system
Control bodily movements and is responsible for our: awareness, emotions, and will.
It’s made up of 2 main divisions: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
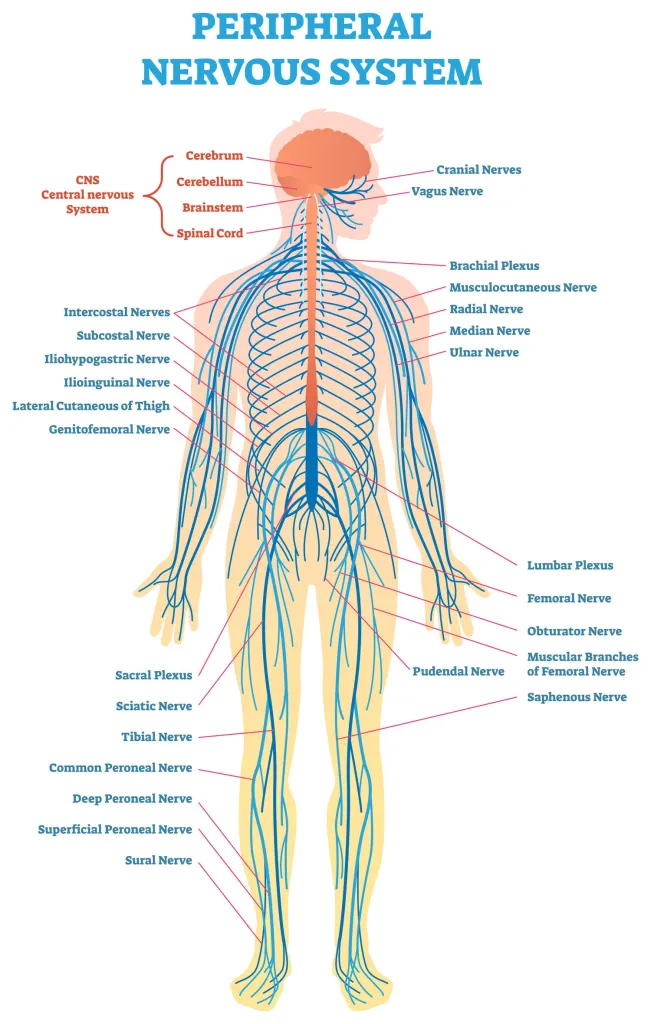
peripheral nervous system
Includes the sense organs (eyes, ears, and so on) and the nerves that branch off the central nervous system.
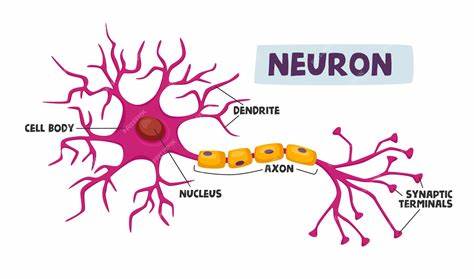
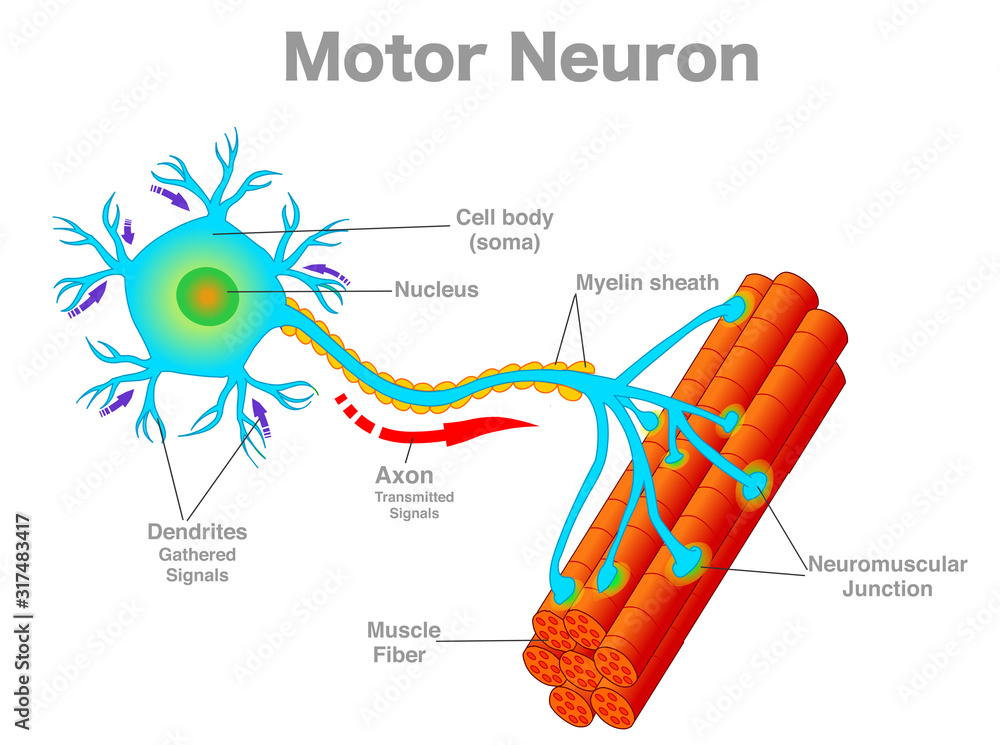
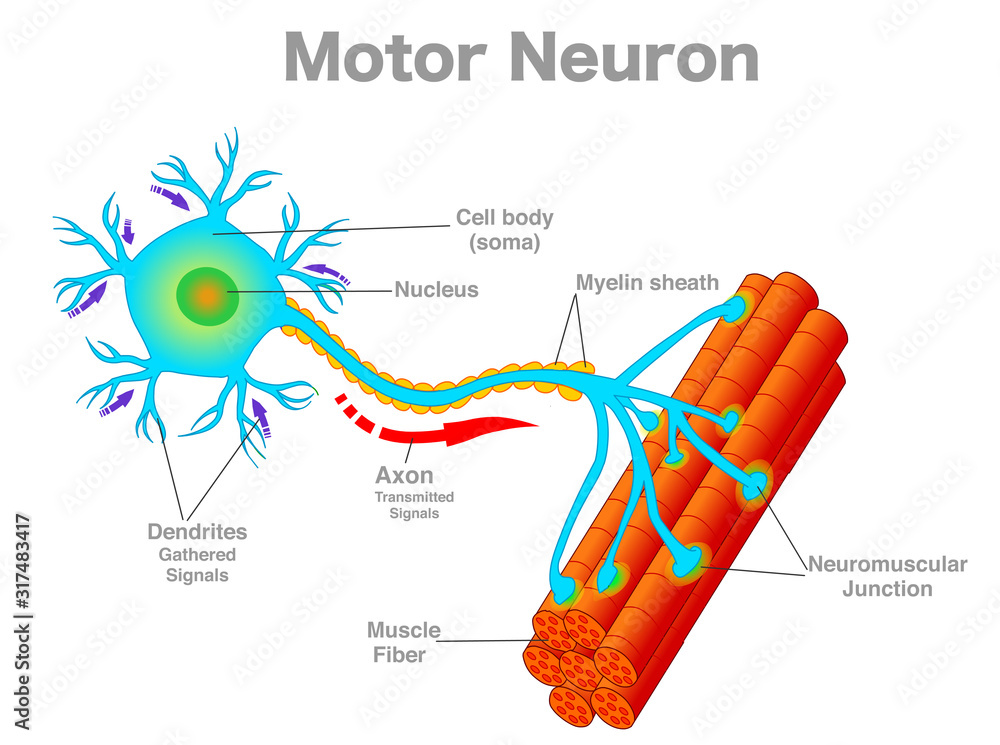
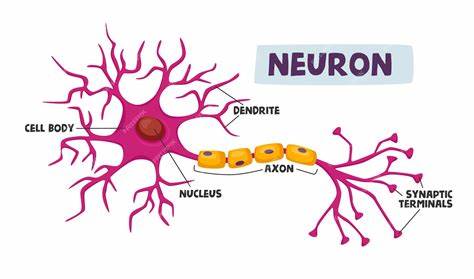
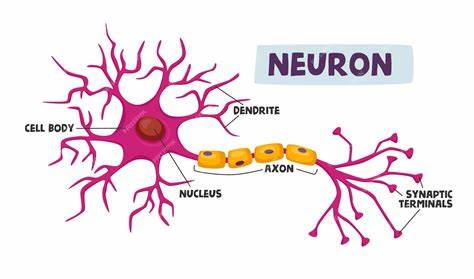
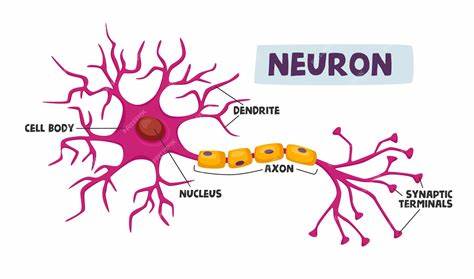
dendrites (memorize its location)
carry impulses toward the cell body
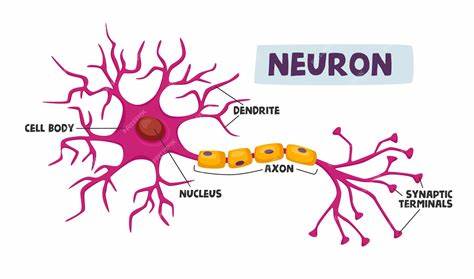
axons (memorize its location)
carry the impulses away from the cell body
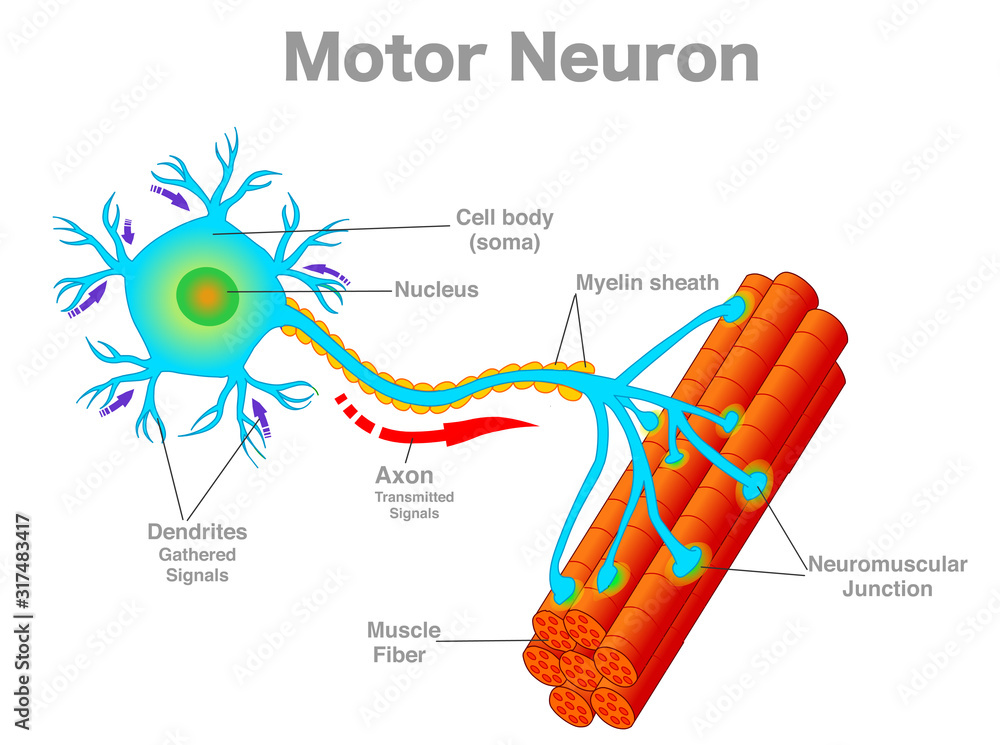
cell body (soma) - memorize its location
cell body (soma)
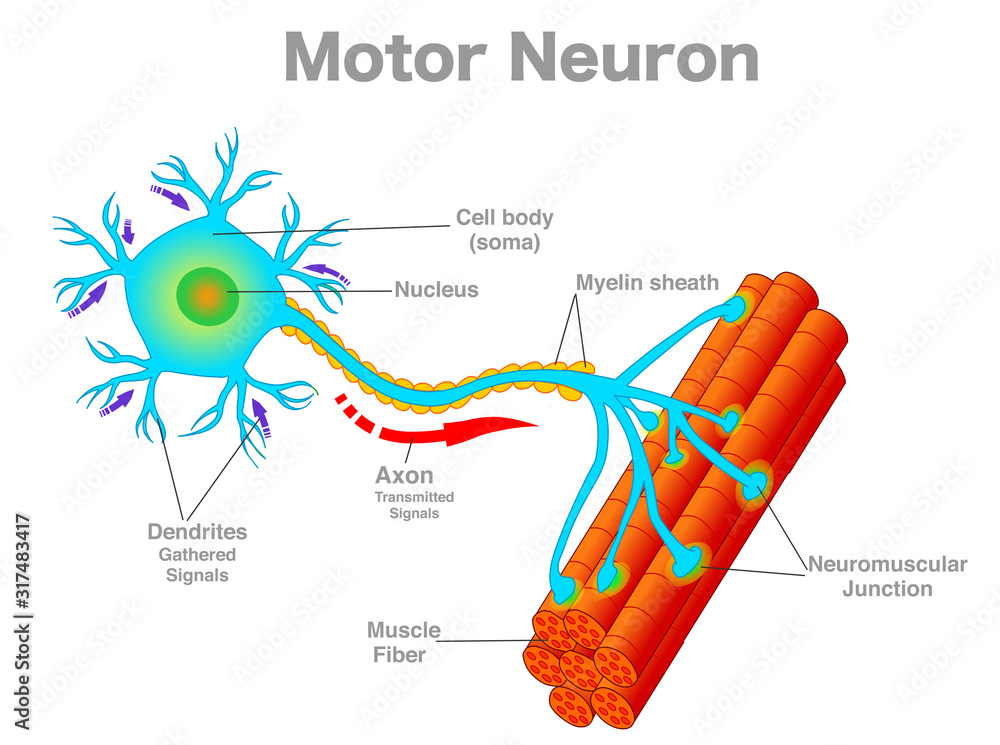
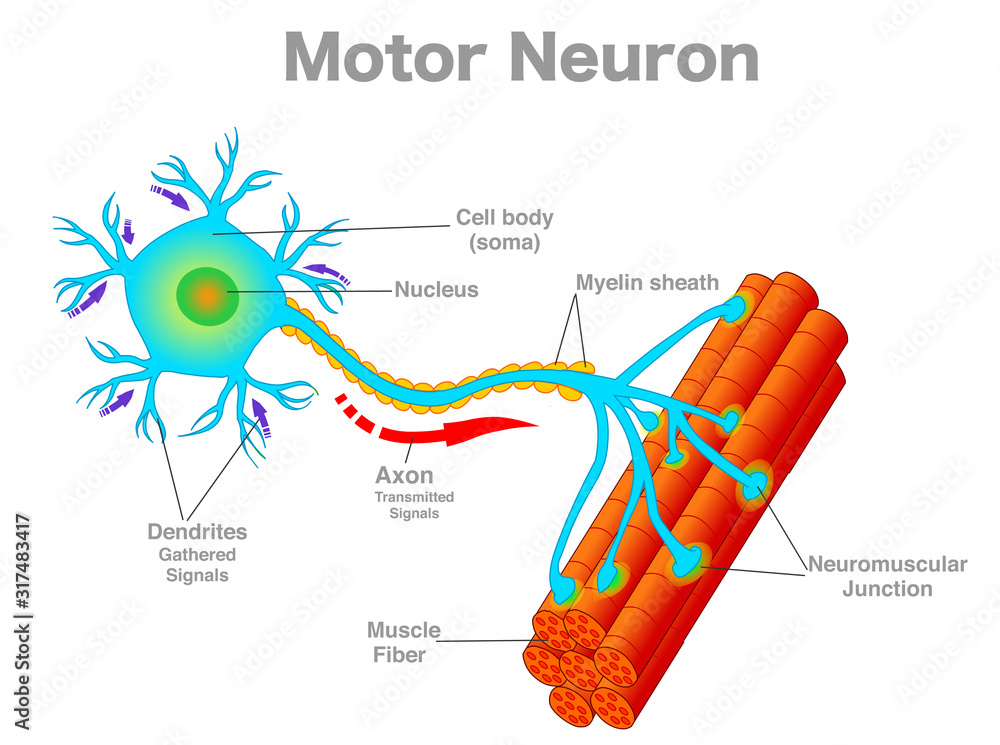
synapse (memorize its location)
The space where two neurons have an impulse jumping from one neuron to another.
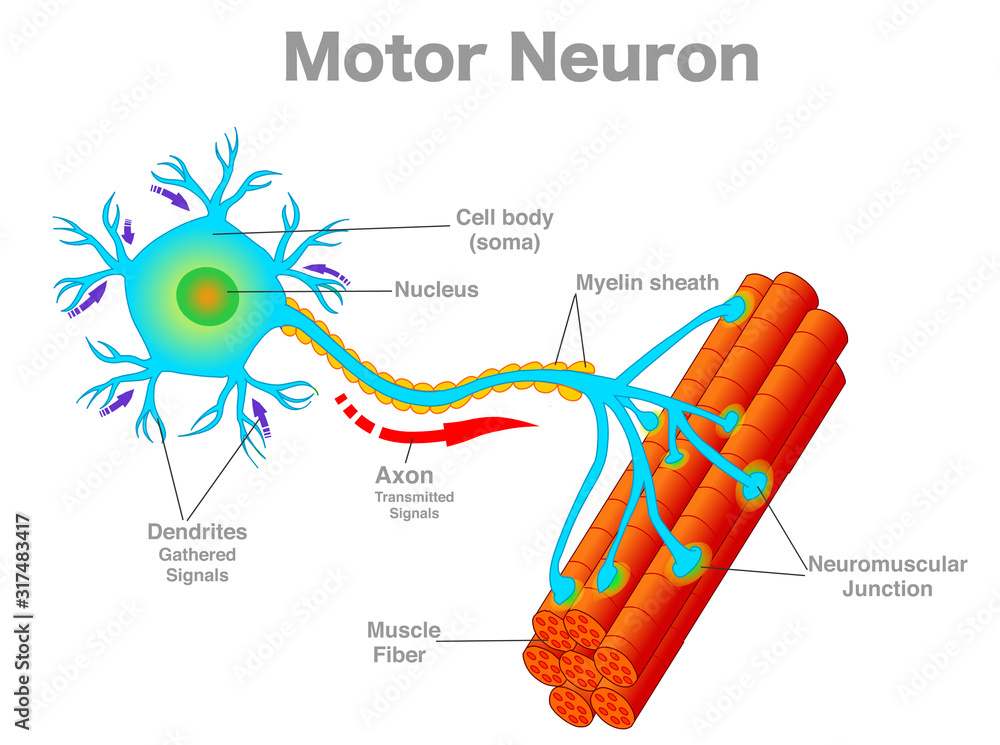
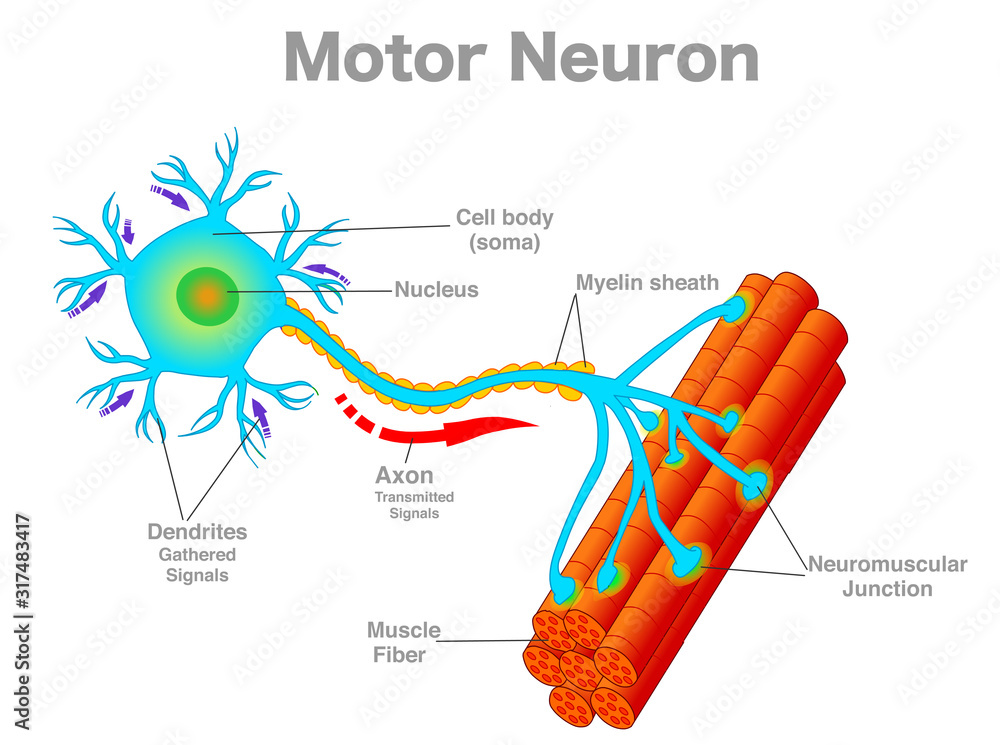
protective covering (myelin sheath) of nerve cell
In the central nervous system, the myelin sheath protects nerves in the brain, spinal cord and nerves leading to the eyes, known as optic nerves.
transmitting chemical
Serves to transmit an impulse from neuron to neuron.
nerves
long, thin branches of the nervous system that go to sensory organs, muscles and many other structures of the body.
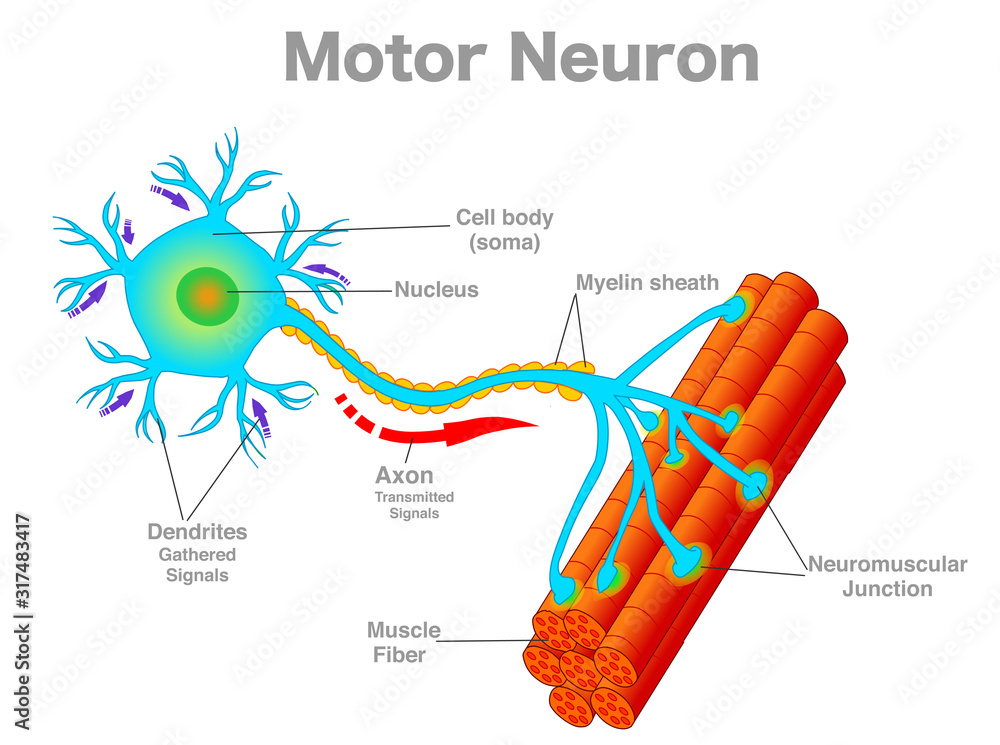
motor neuron
A neuron that is responsible for causing a muscle to produce movement
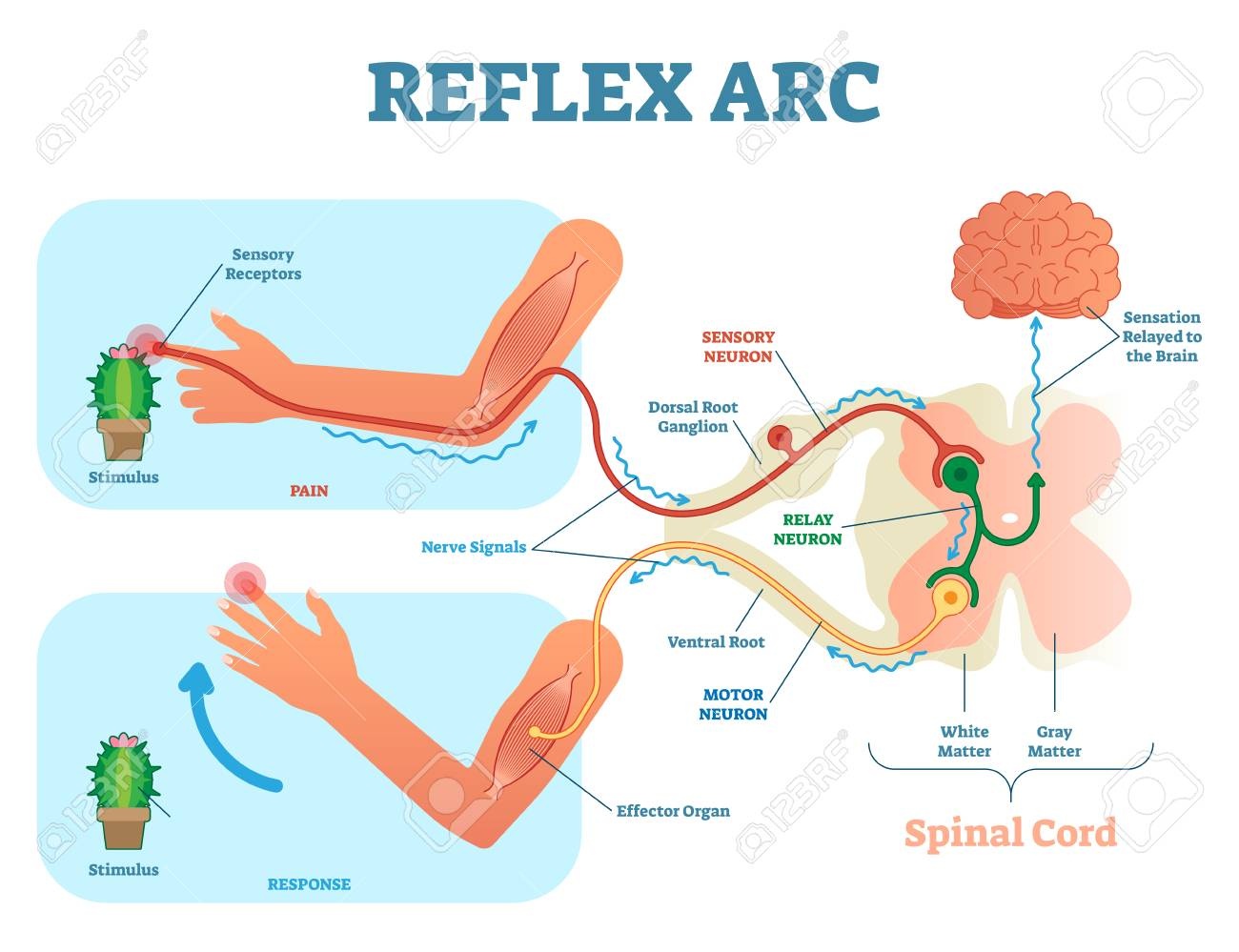
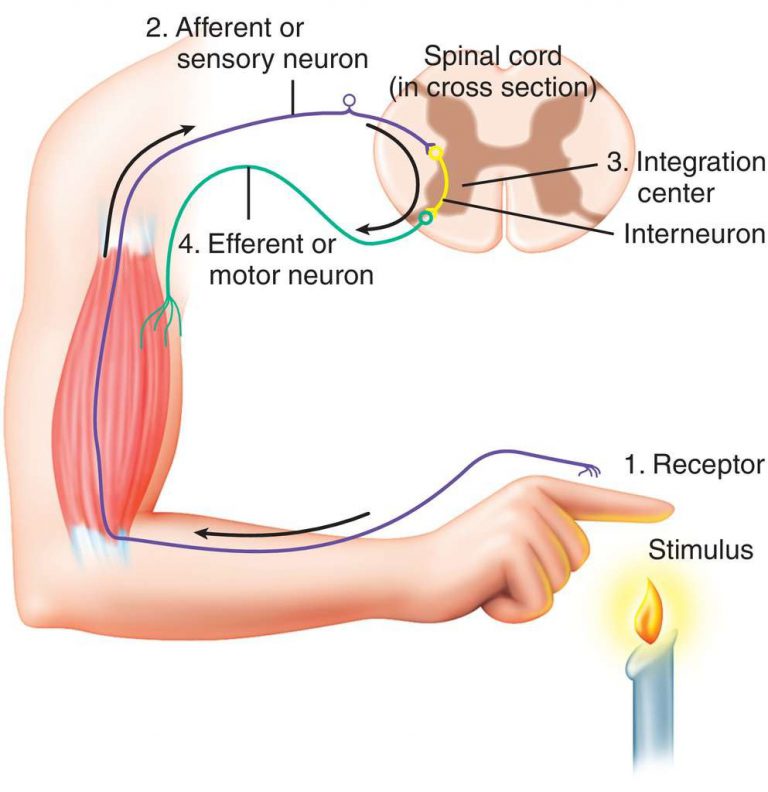
reflex arc
A series of neurons that receives a stimulus and then causes the body to react.
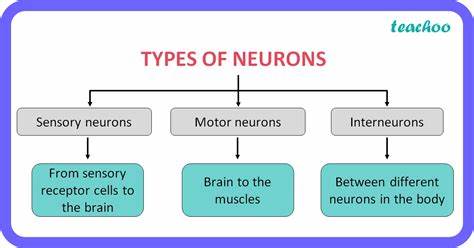
sensory neuron
The type of neuron responsible for receiving stimuli and carrying impulses to the central nervous system
reflex
An immediate, not learned, reaction to a stimulus.
interneuron
Acts as the go-between for the sensory neuron and the motor neuron.
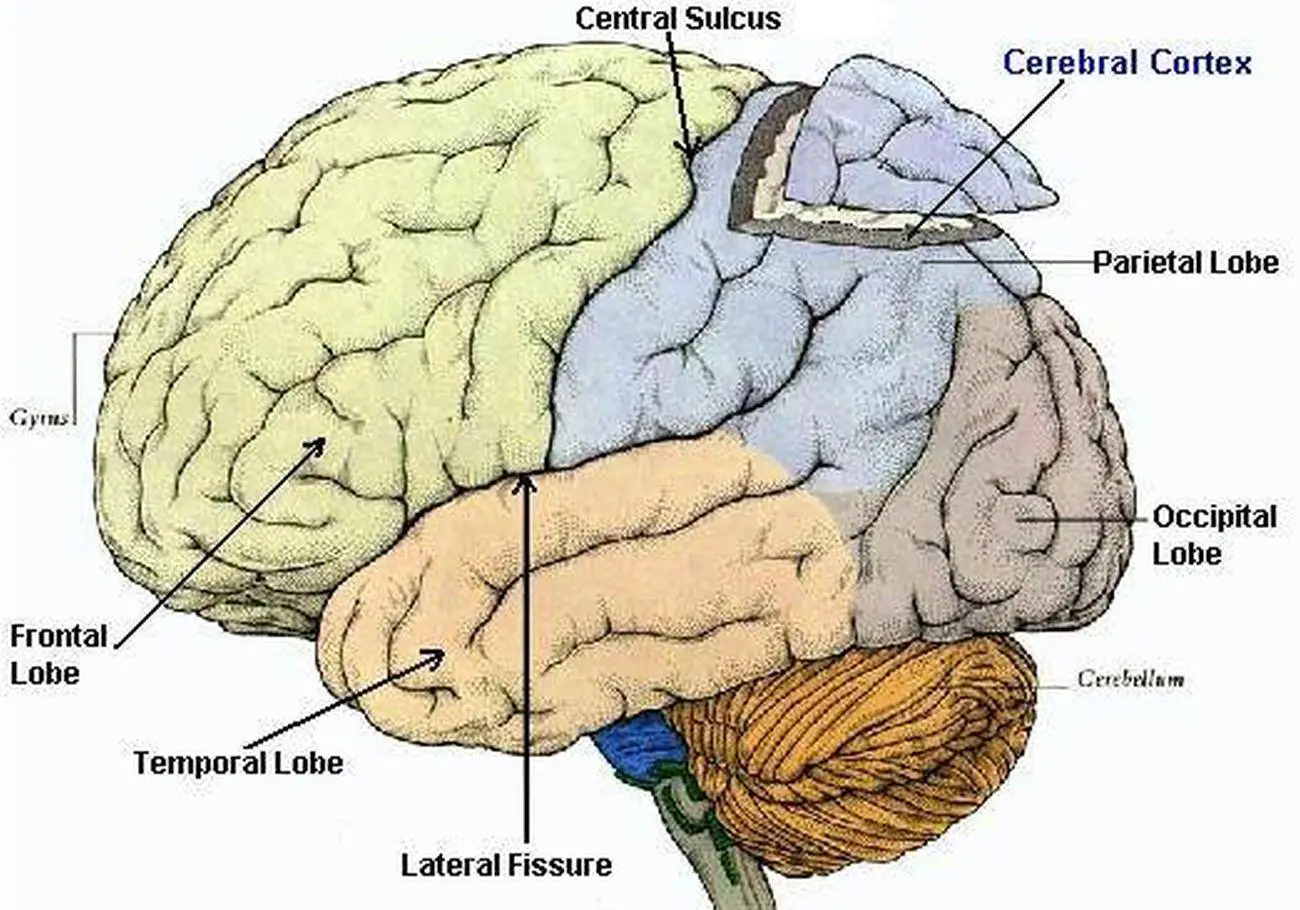
cranial nerves
Branch from the brain to various structures of the head, neck, and internal organs.
cerebral cortex
The outer layer of the cerebrum
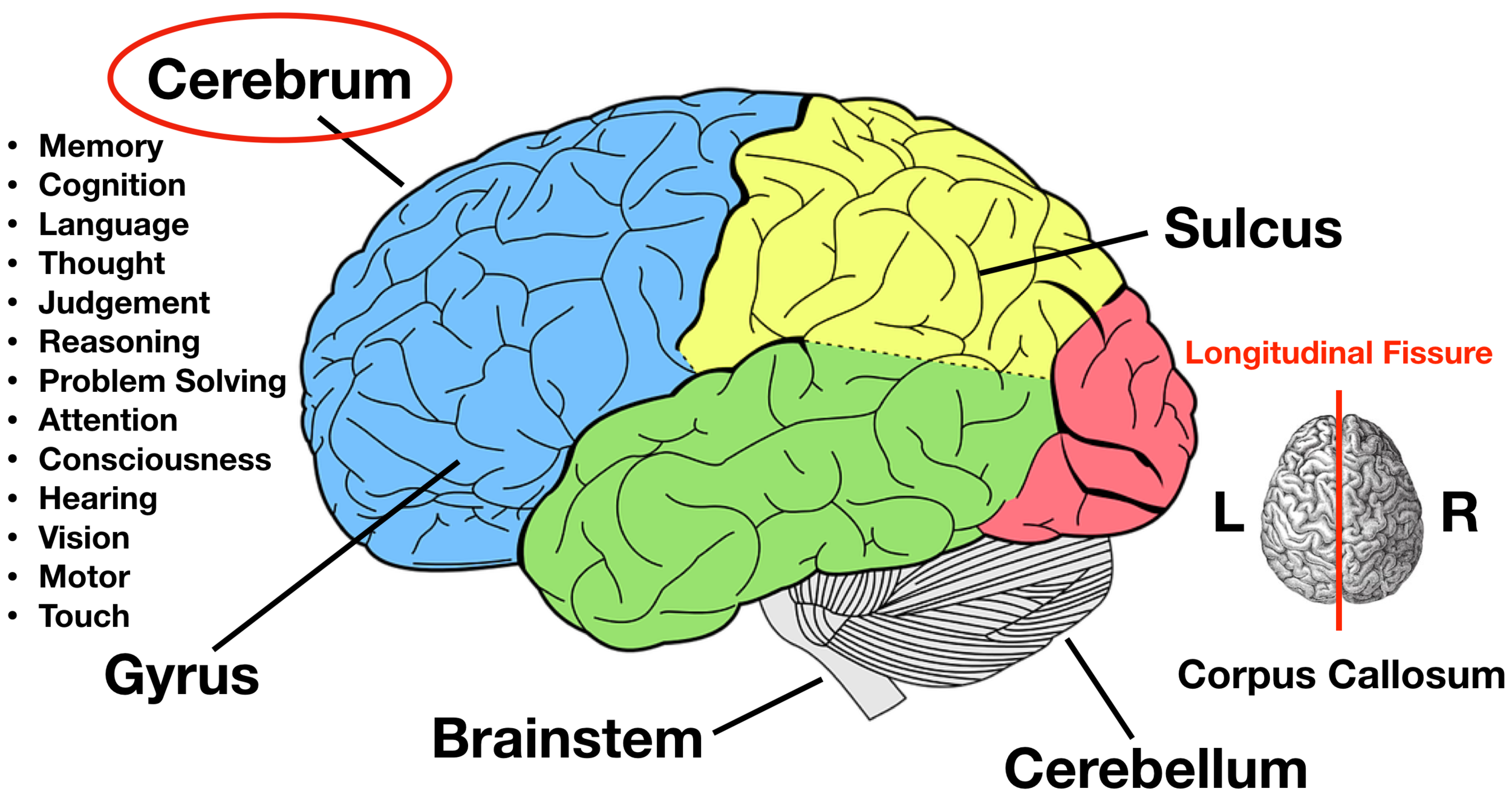
cerebrum
The largest portion of the brain
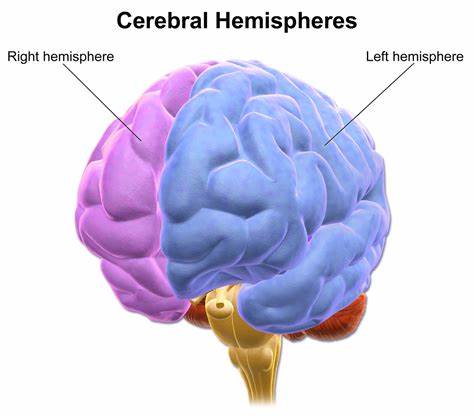
hemispheres of the brain
The divisions of the cerebrum are each called hemispheres.
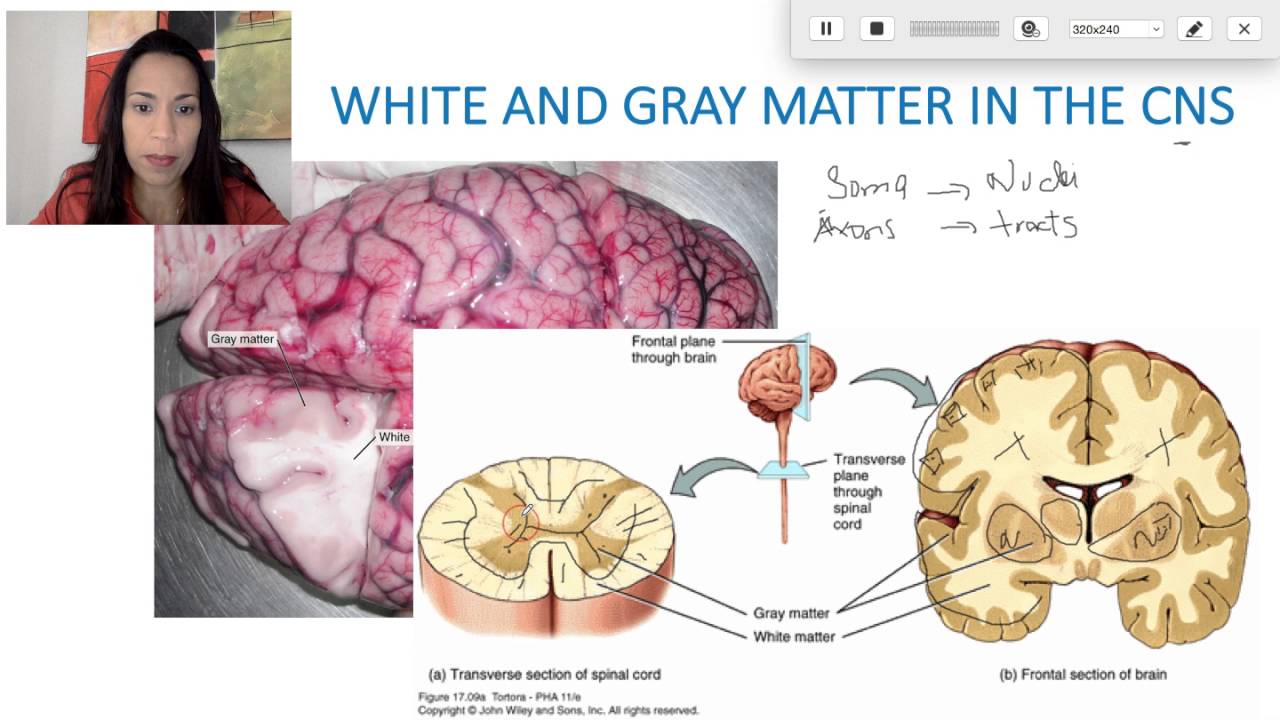
gray matter
Name given to the cerebral cortex because of its color. The gray is the color of the neurons and the red is the color of the blood that nourishes the brain.
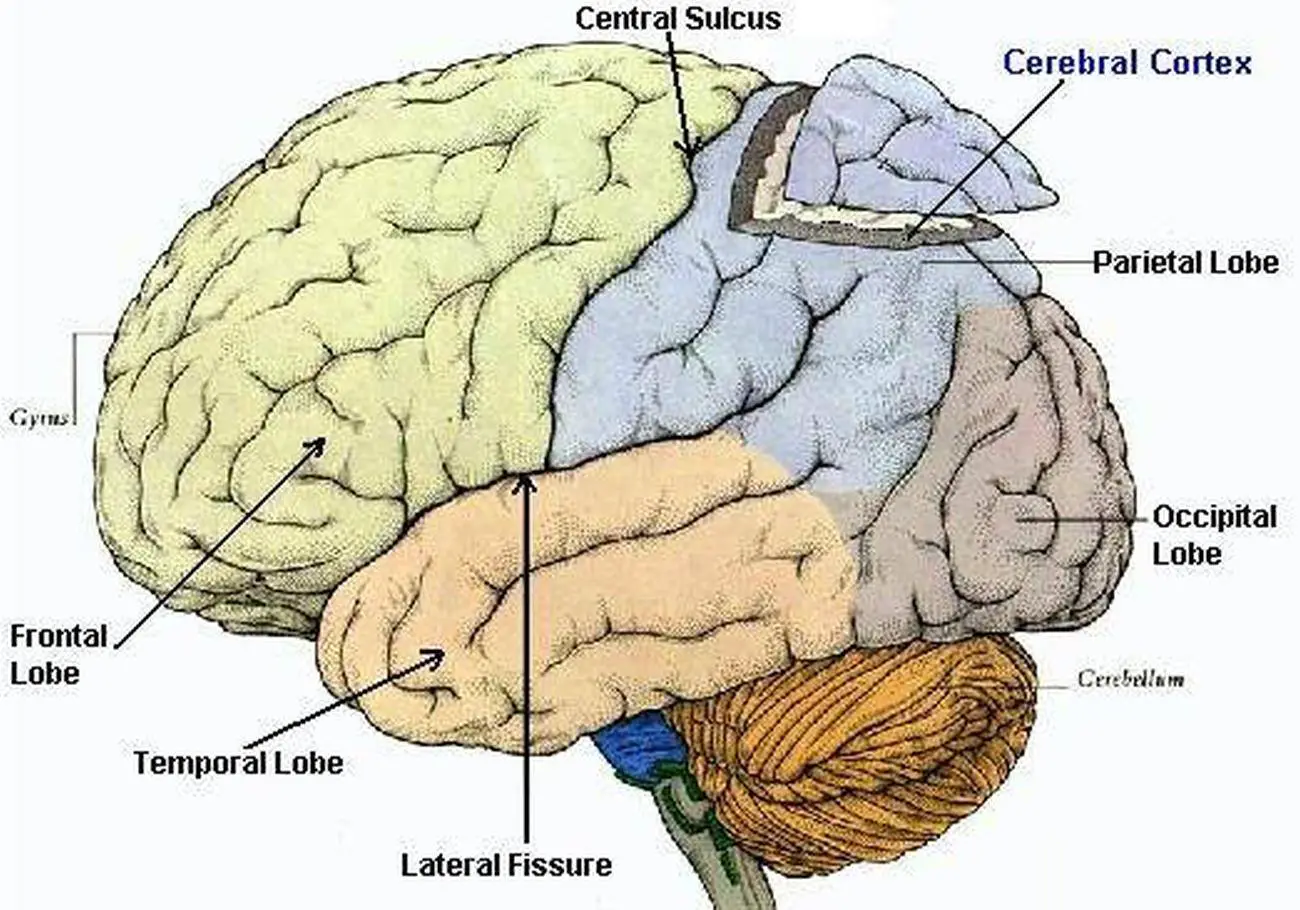
lobes
The 4 divisions of the 2 hemispheres of the brain. They are each responsible for different functions.
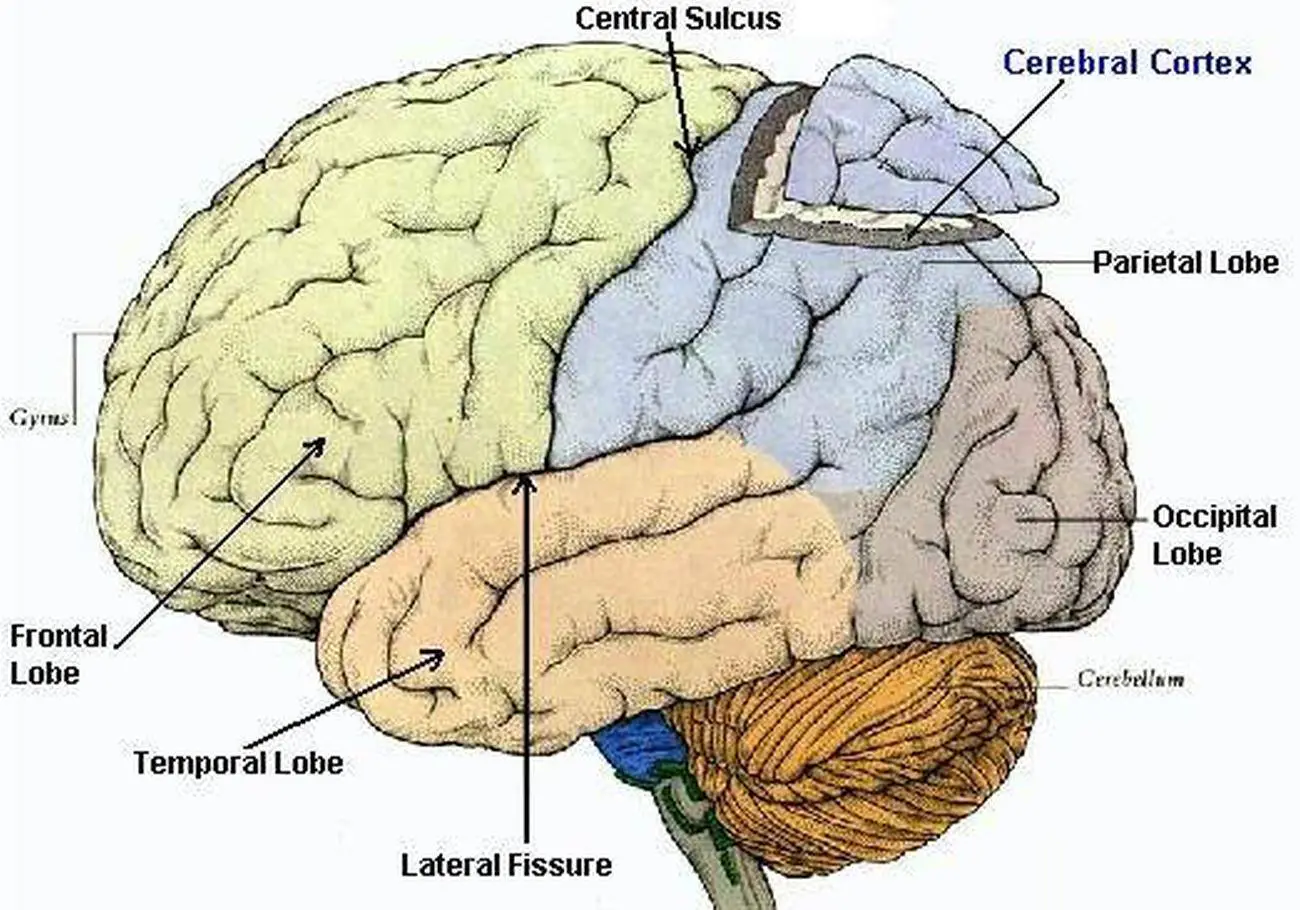
frontal lobes
control your consciousness and your primary body movements, also…
your awareness of what’s happening
your personality
your reasoning ability
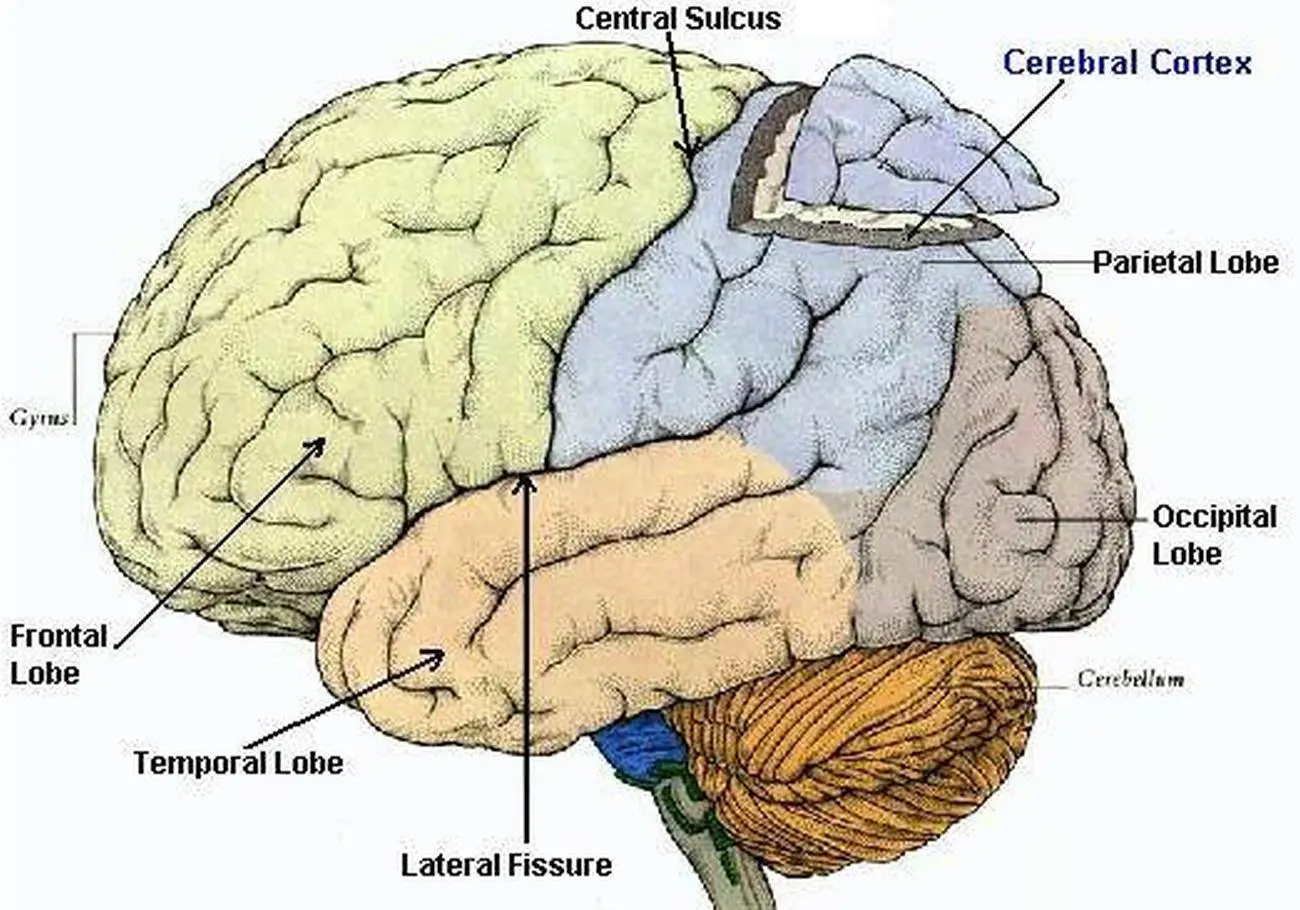
parietal lobes
Part of your brain that deals with sensations: pain, pressure, temperature, touch, and part of taste.
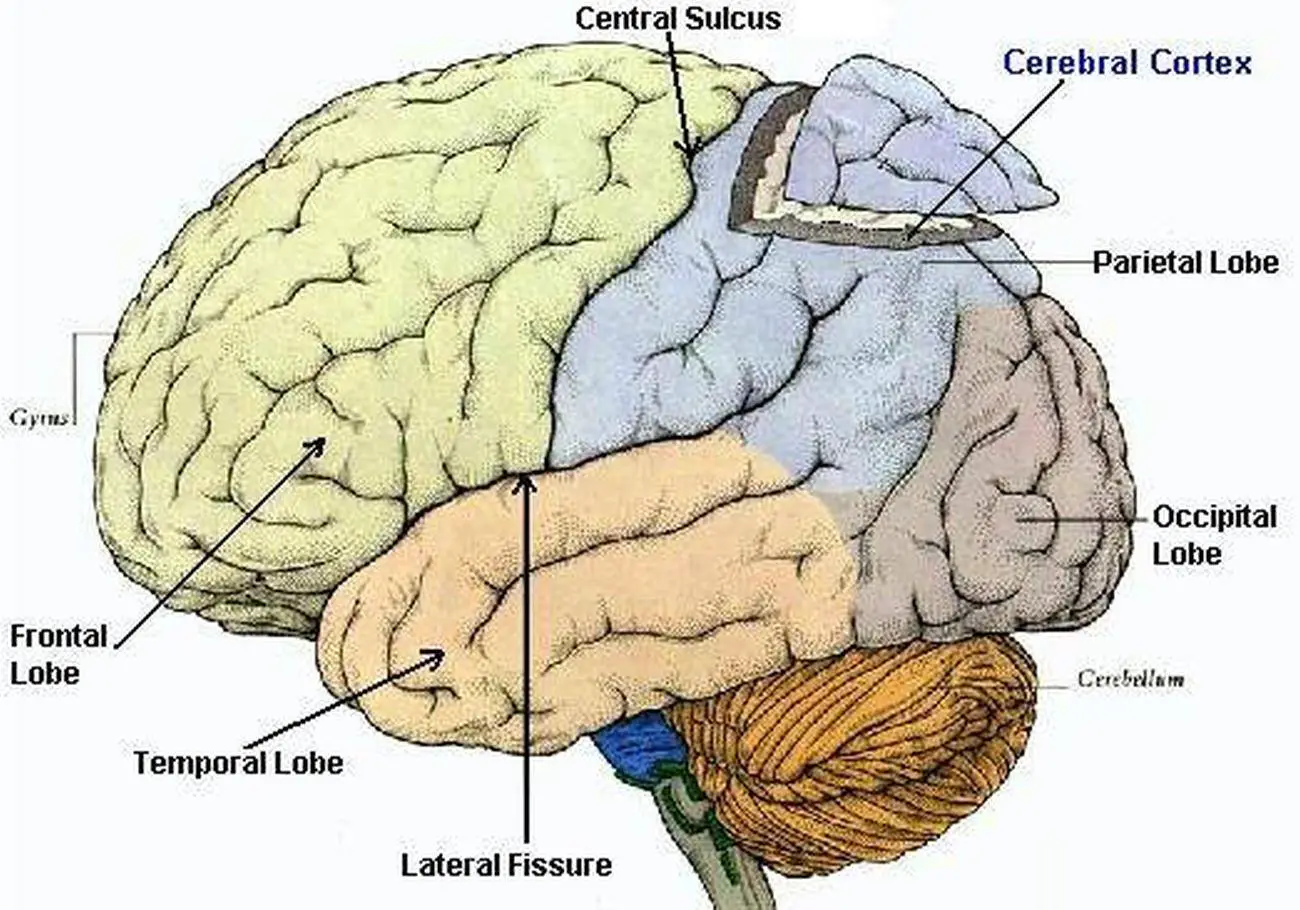
temporal lobes
Part of your brain that receives impulses from the ear and interpret them as sound. They are also responsible for remembering sound.
occipital lobes
Part of your brain that receives impulses from nerves of the eye and interpret them as vision. They also help you remember what you see.
psychoactive drugs
Have a primary effect on a person’s mental or emotional condition.
depressant
A psychoactive drug that slows mental activities.
stimulants
A psychoactive drug that increases a person’s mental activities.
hallucinogens
A psychoactive drug that causes the mind to make up things.
narcotics
Psychoactive drugs that dull the senses.
alcohol
A psychoactive drug that is a depressant and causes a person to react more slowly.
sedatives and biturates
Psychoactive drugs that are depressants and are commonly used in sleeping pills.
tranquilizers
A psychoactive drug that is usually given to calm a person.
amphetamines
A type of psychoactive drug that is a stimulant that causes the mind to work more quickly but not better.
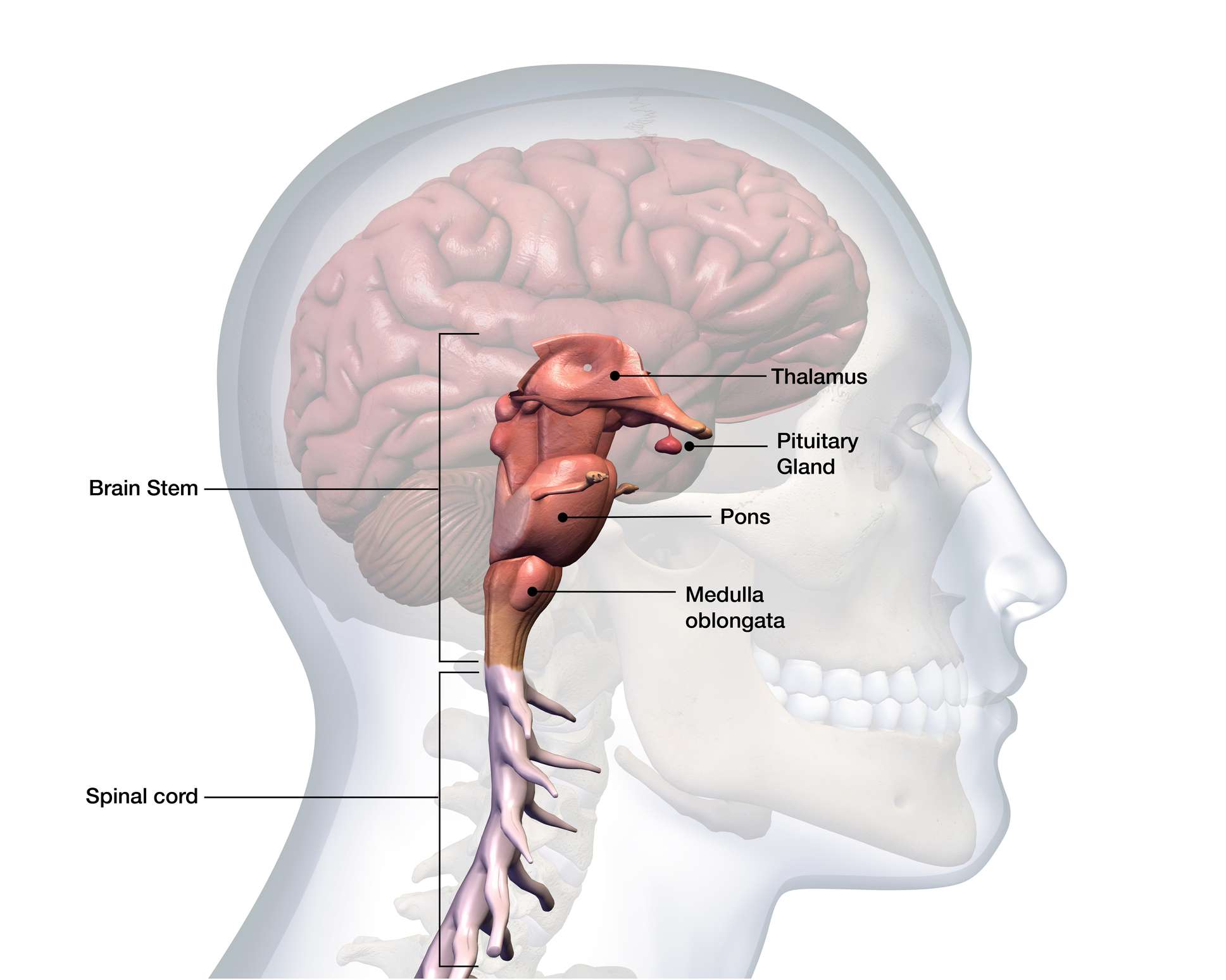
brain stem
helps to control heartbeat, breathing, and other involuntary activities
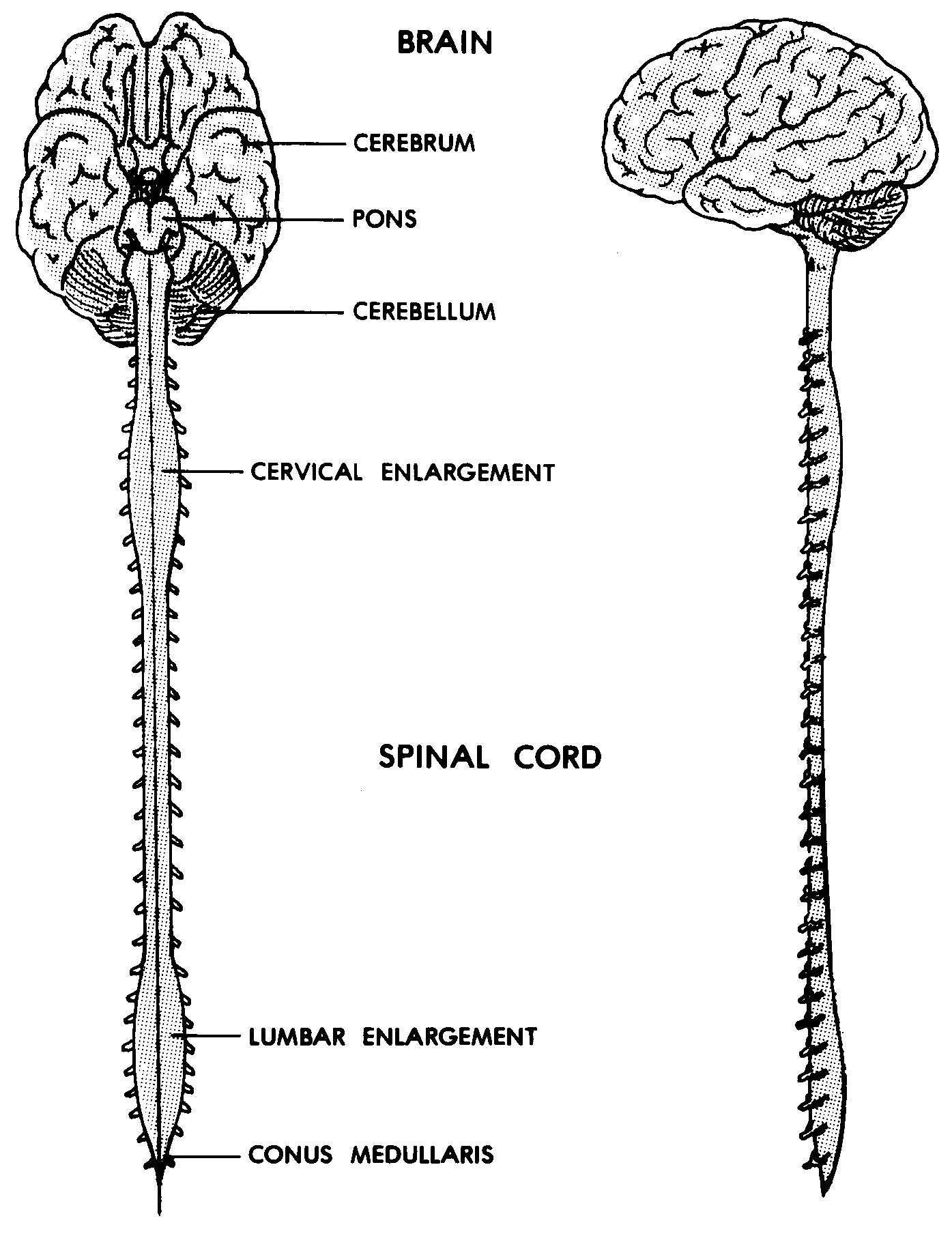
spinal cord
The continuation of the brain stem that extends down the back.
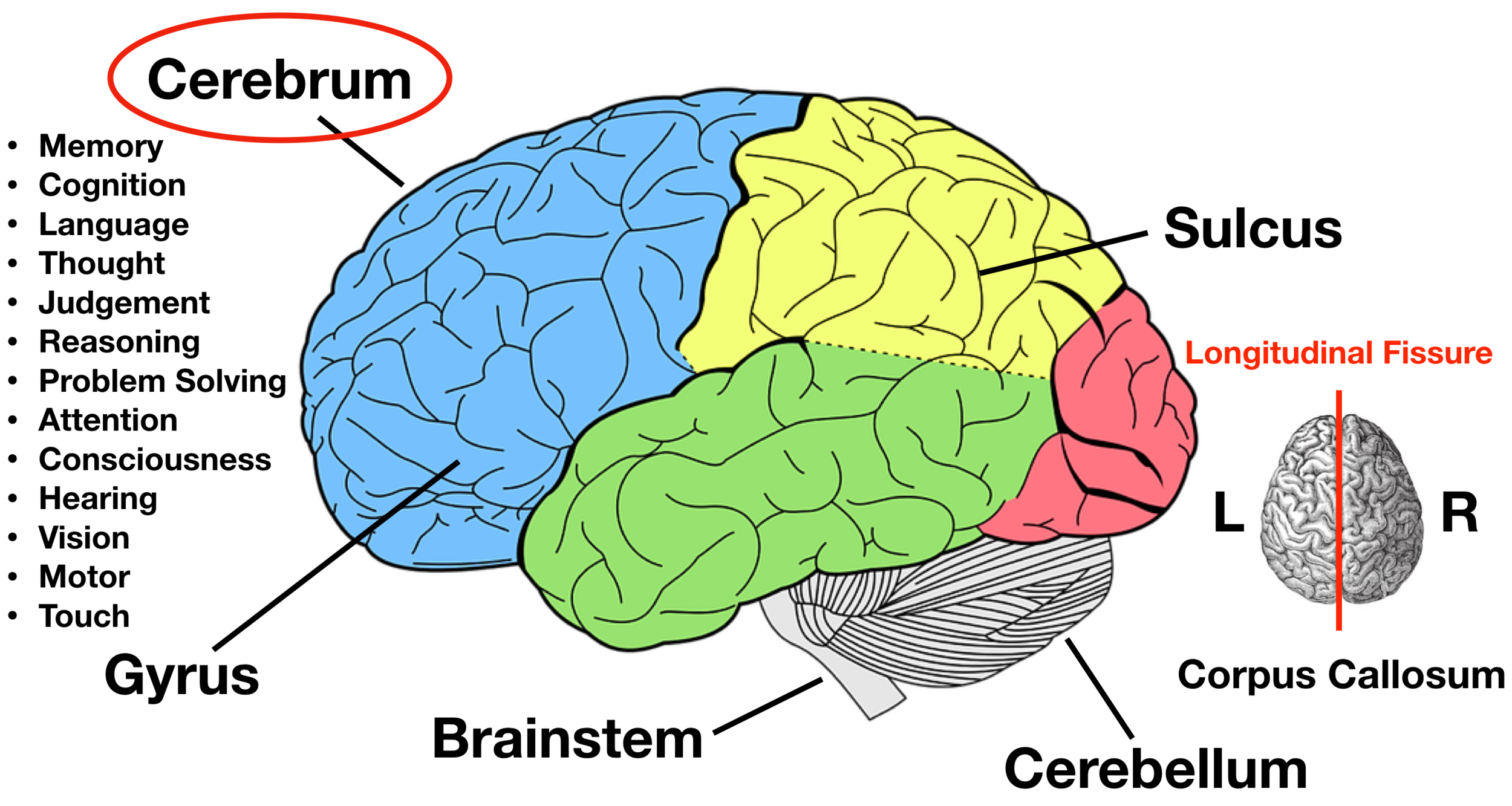
cerebellum
Part of the brain that monitors and controls body movements without your knowing about it.
examples: you making a decision to turn off a light, in turn, your cerebellum works out which muscles will need to stimulated to do the job.
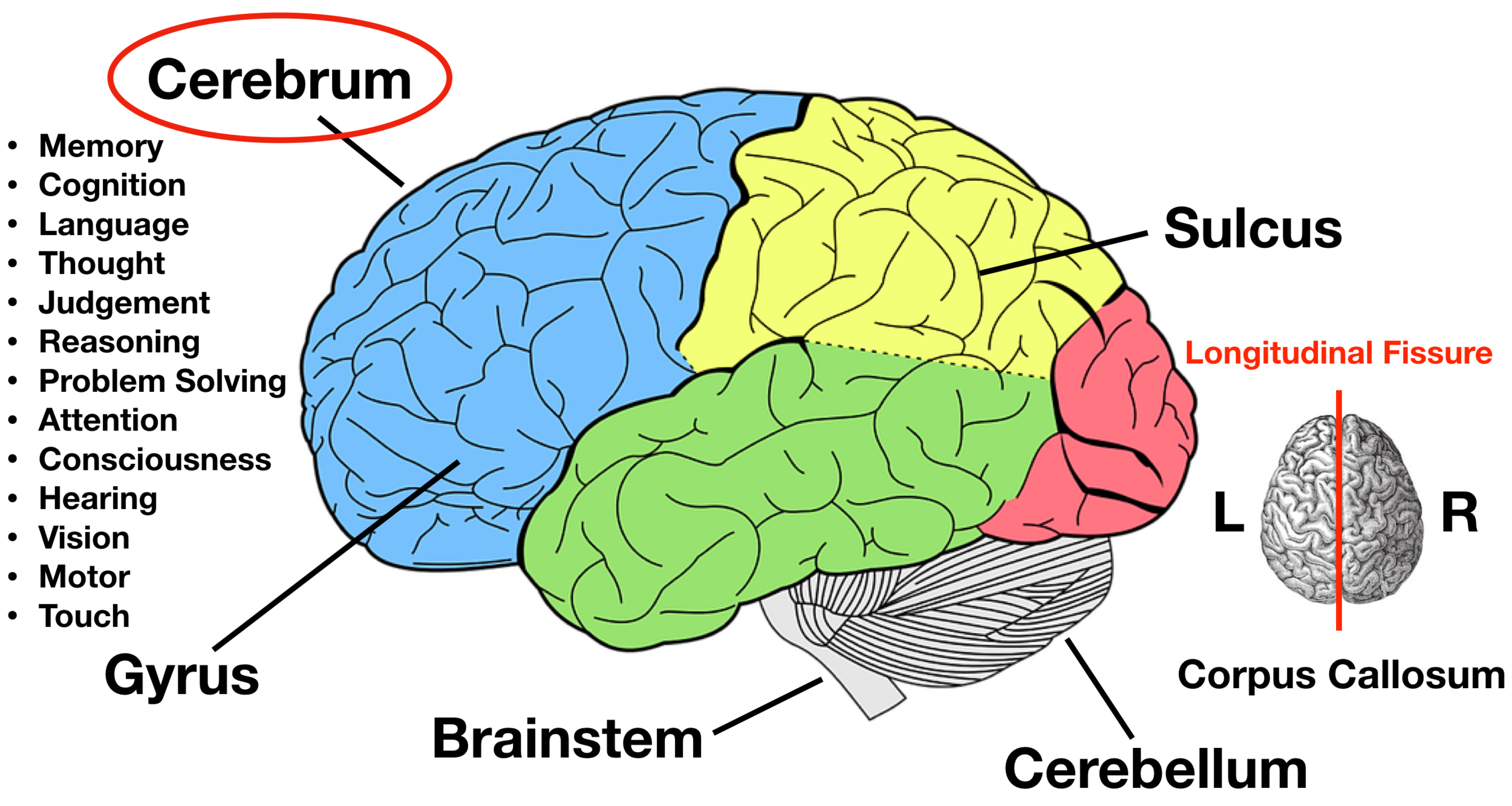
Which part of your brain is the largest?
the cerebrum
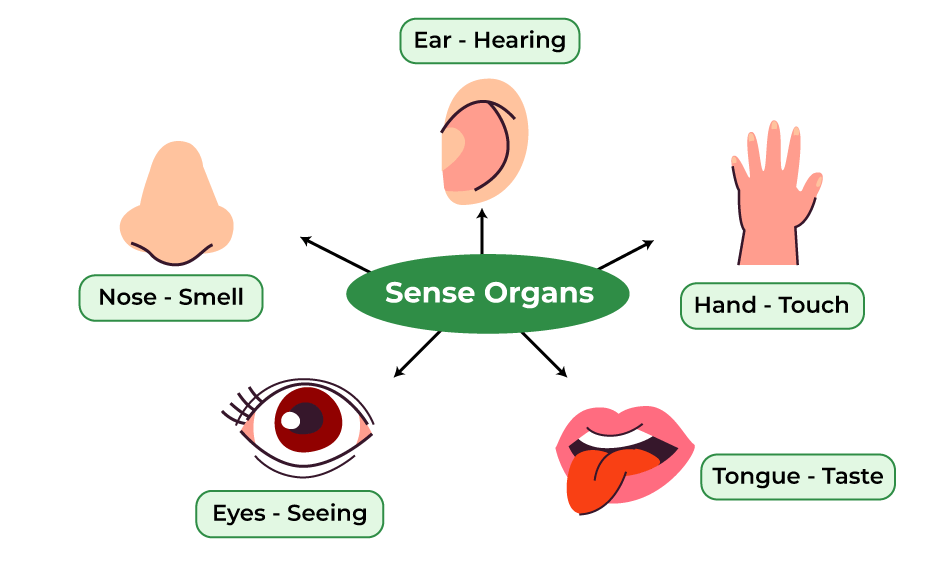
sense organs
Have special neurons that are sensitive to certain stimuli.
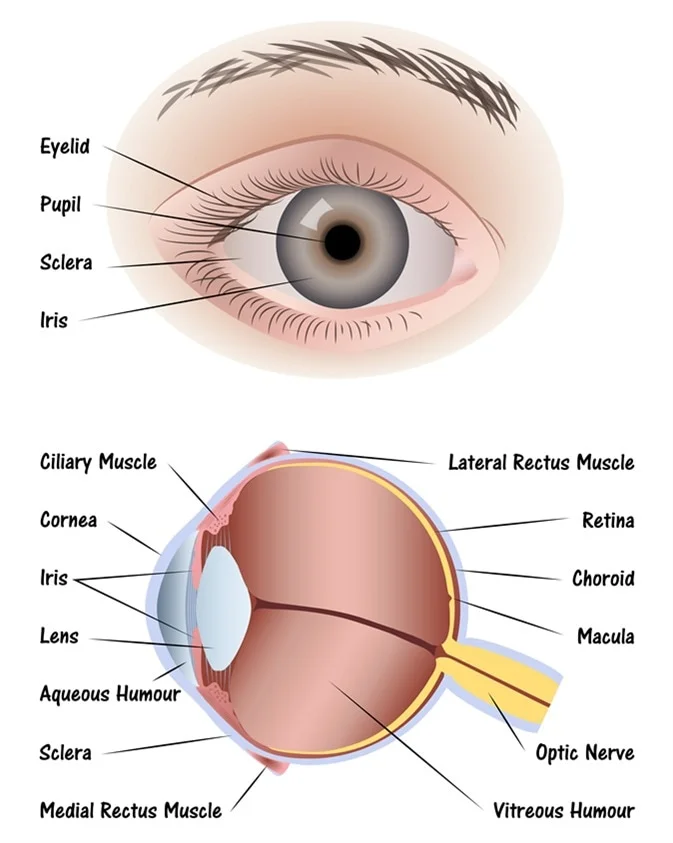
What controls the size of your pupil?
The muscles in the iris
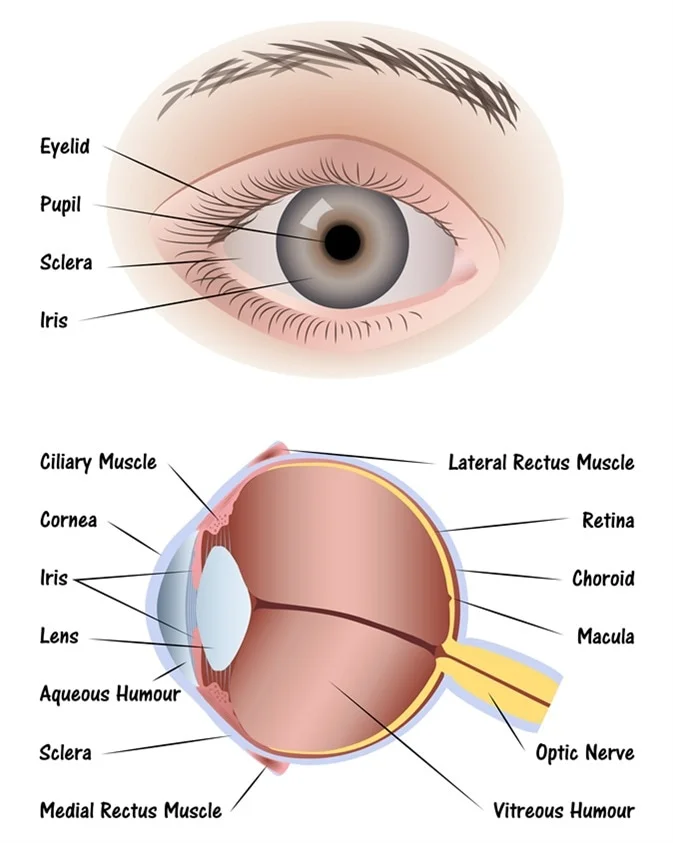
sclera (memorize its location - notice how it circles around the entire eyeball)
The tough outside tissue that is the “white of the eye”.
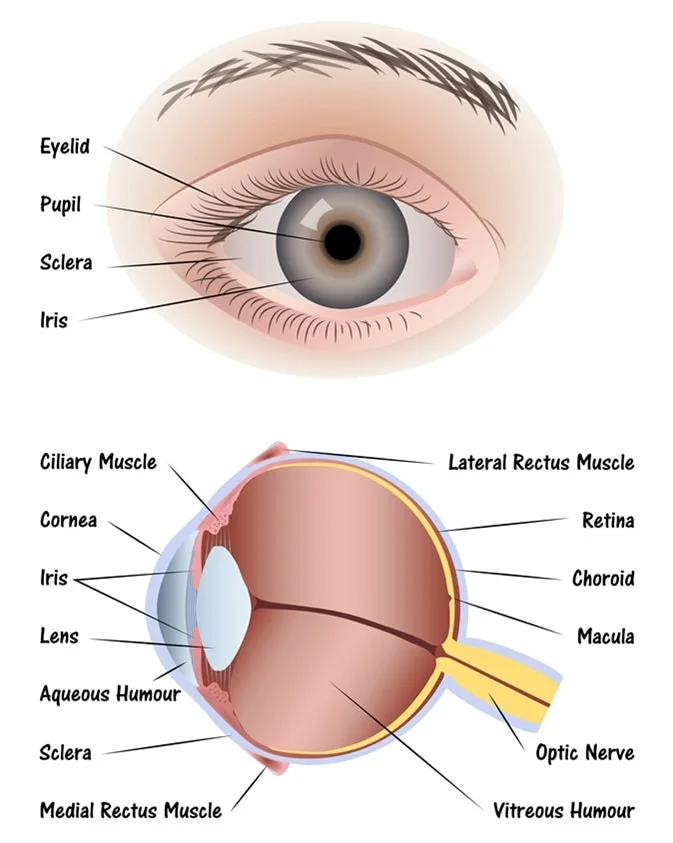
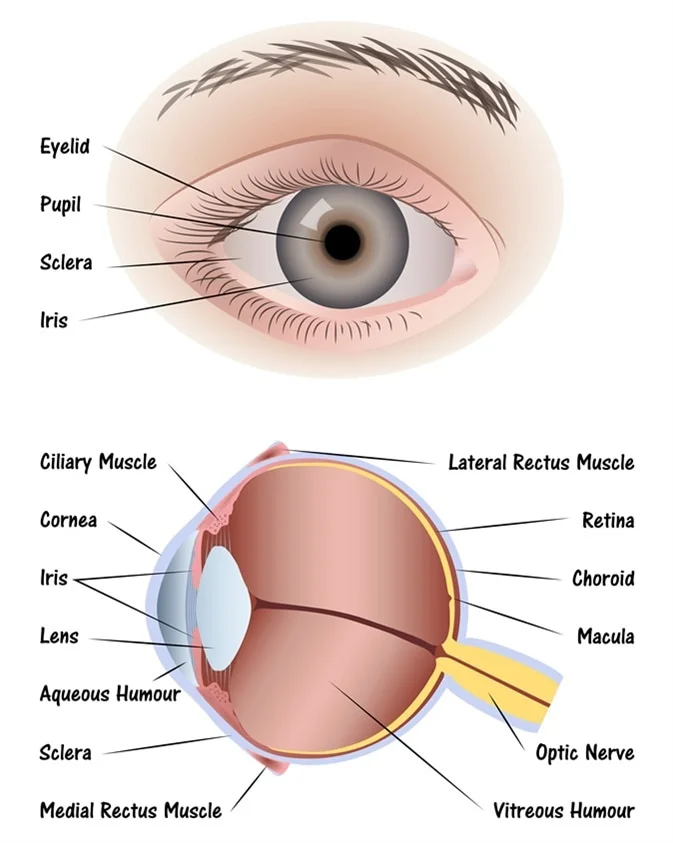
cornea (memorize its location - notice how it covers the entire outer front part of the eye you can see on a person)
Clear, lets light pass into the eye
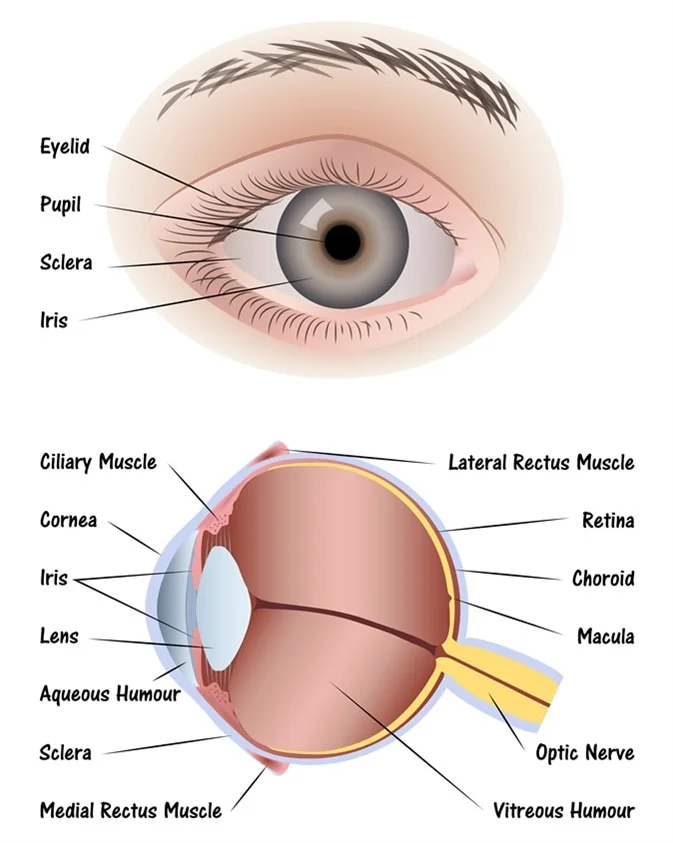
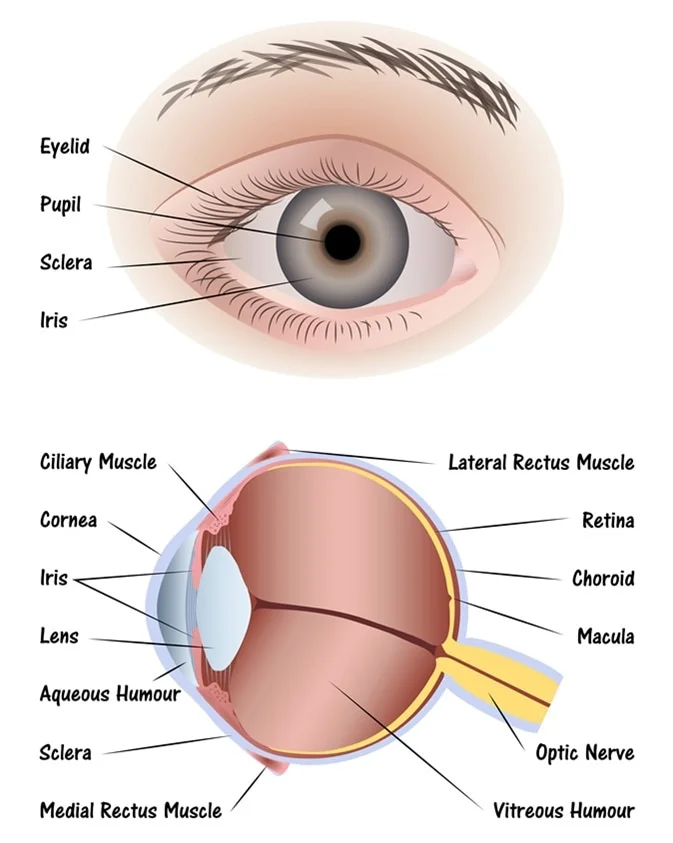
choroid
The middle layer of the eye.
iris (memorize its location - notice how to goes top and bottom, but leaves a space for the iris between it)
The colored part of the eye.
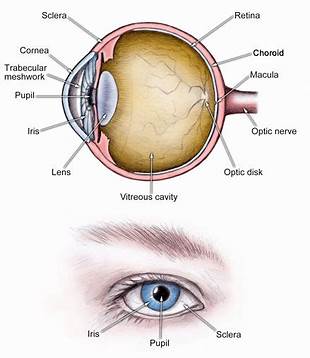
pupil (memorize its location)
The opening where light enters the eyeball. Its size is controlled by muscles in the iris.
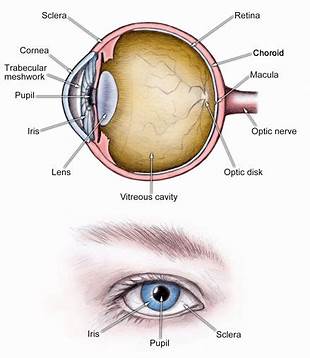
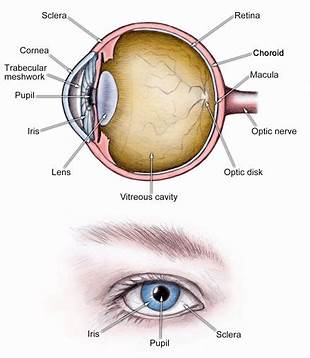
retina (memorize its location - it’s pointing to the white part. Notice the definition of the retina for its location as well.)
The inner layer of the eye that begins along the sides of the lens and continues around the back of the eye. It contains neurons that are sensitive to light.
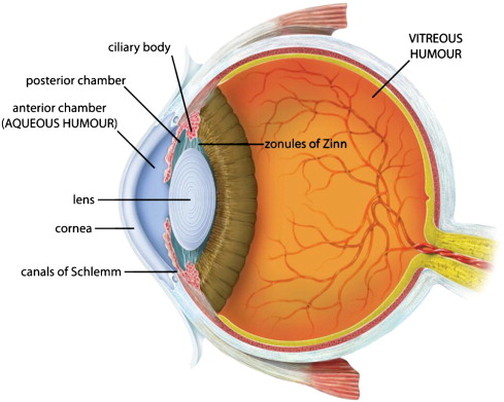
aqueous humor
A clear fluid in the eye that has nutrients that provide energy for the cells of the cornea.
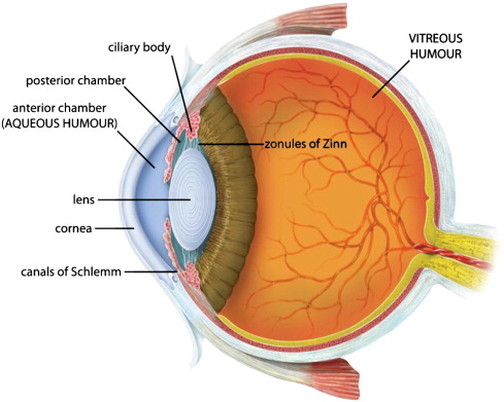
vitreous humor (memorize its location)
Clear and jelly-like, it helps to keep the eyeball round.
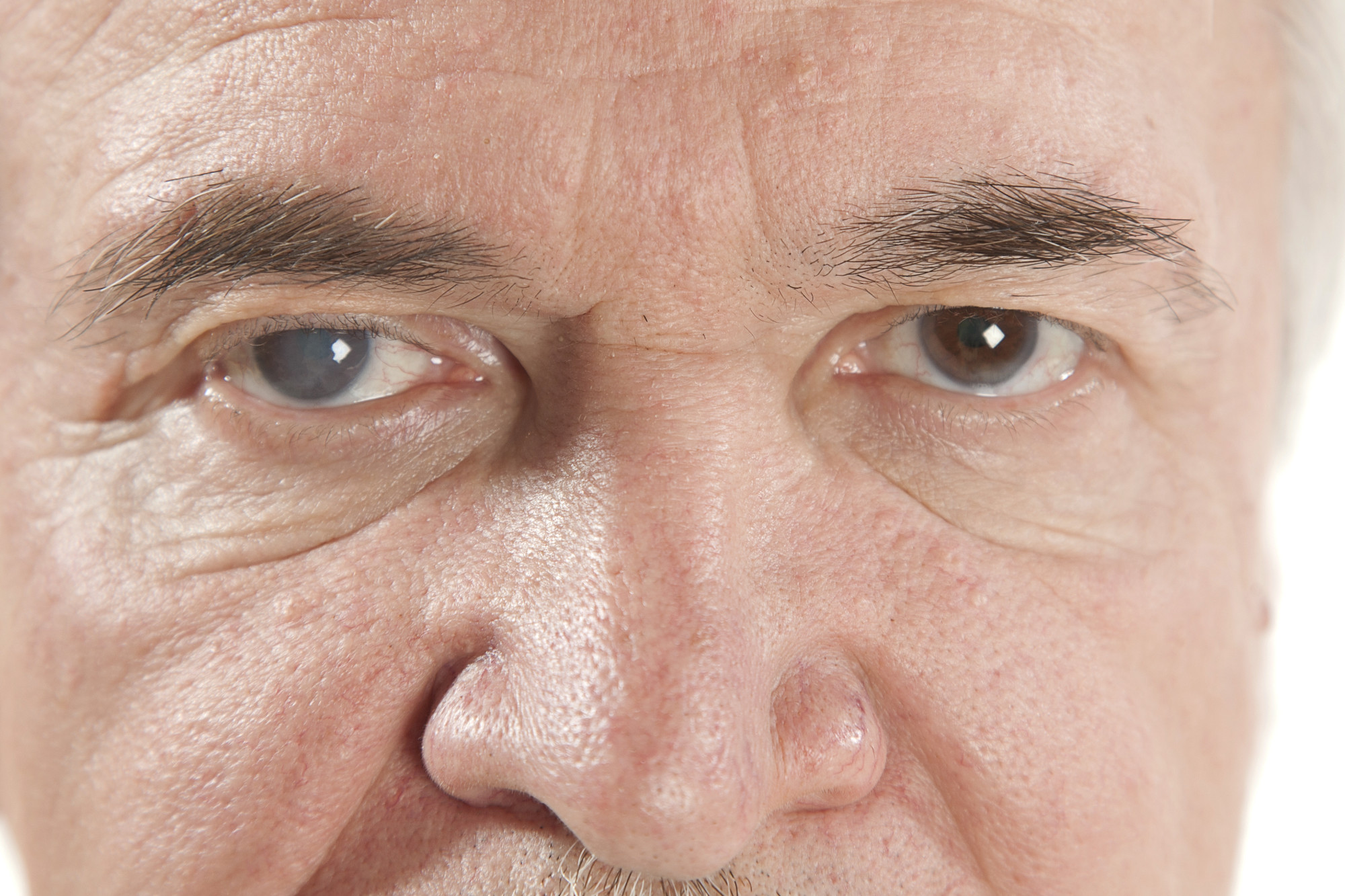

cataracts
An eye condition that stops light from passing through the lens of the eye. It’s usually caused by substances accumulating in the lens of the eye, making it cloudy. It can be fixed.
glaucoma
A build up of pressure in the eyeball
nearsighted
Someone who can only see things near. Things far away are blurry.
farsighted
Someone who can see things far away, but may have trouble reading a book that’s near their face.
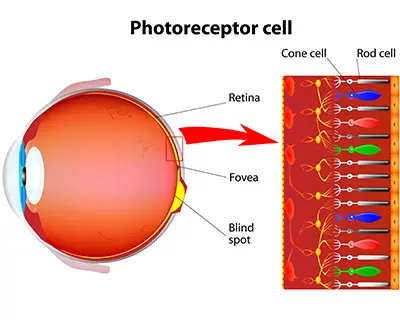
rods
Responsible for vision in dim light, but cannot identify colors.
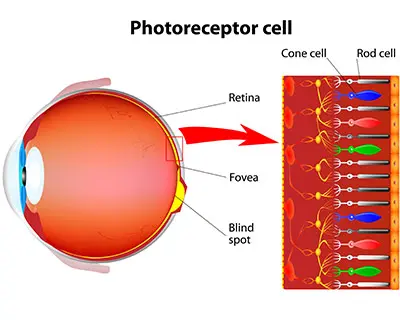
cones
Help you see colors when there is enough light.
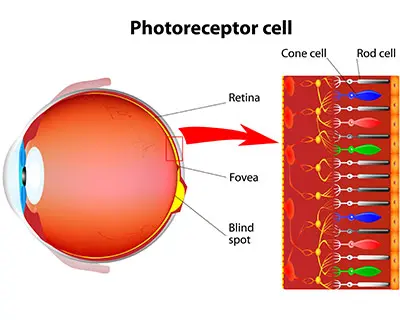
colorblind
A condition where someone’s cones do not work properly so they usually cannot tell the difference between two colors.
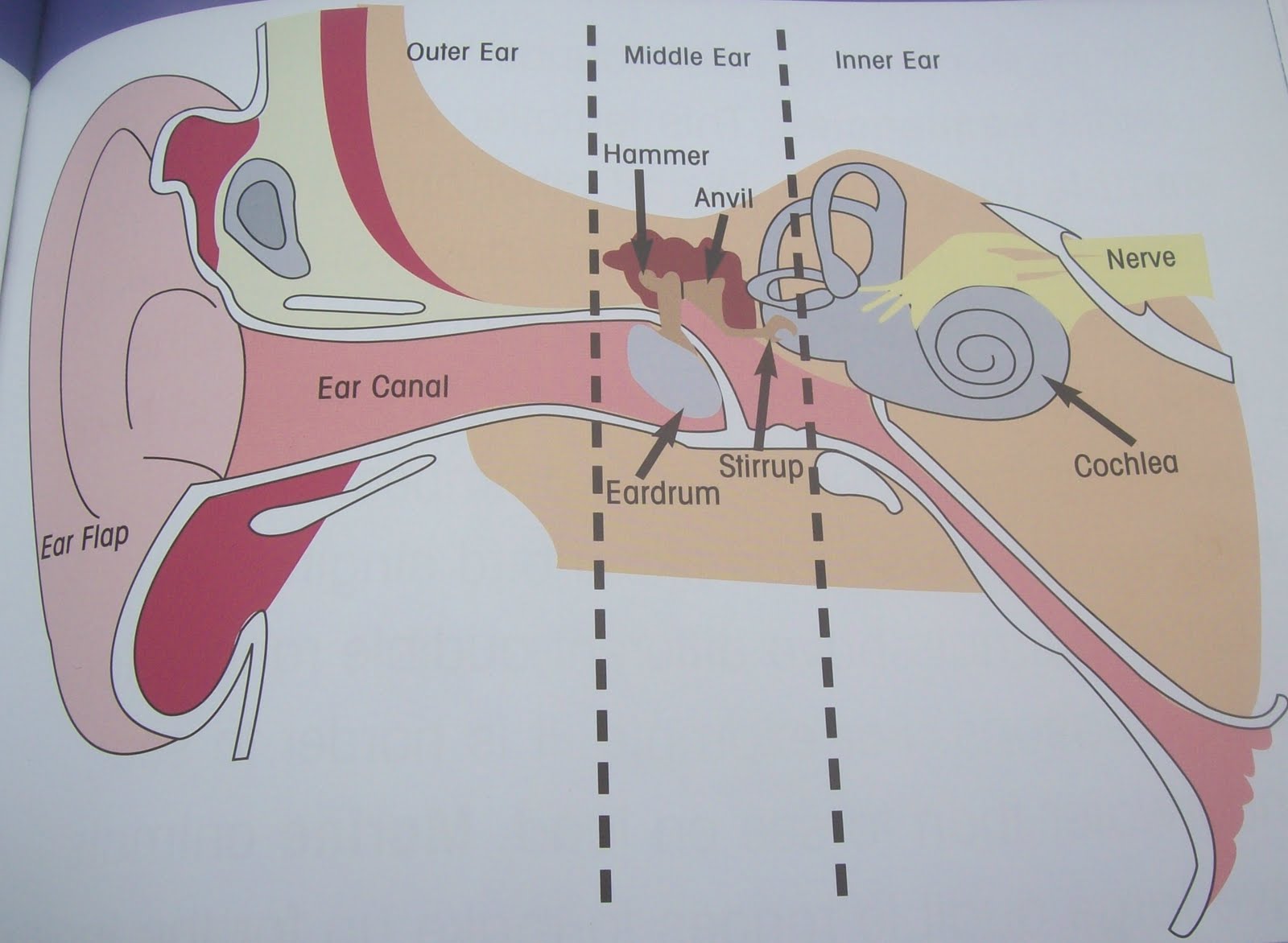
Where are all bones in the ear located?
In the middle ear.
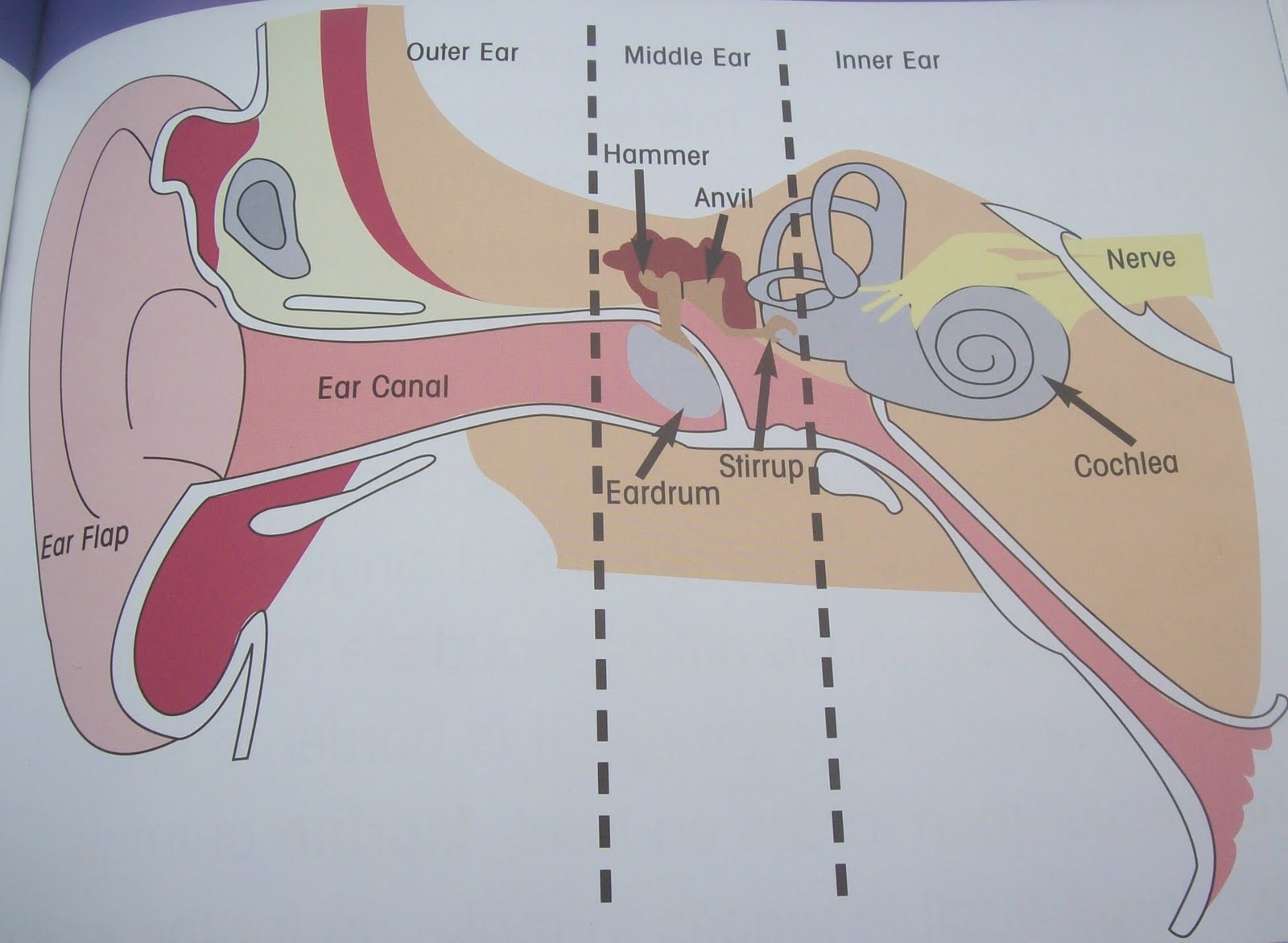
eardrum (Memorize its location)
A membrane that stretches over the opening to the middle ear. Sound waves hit it, causing it to vibrate.
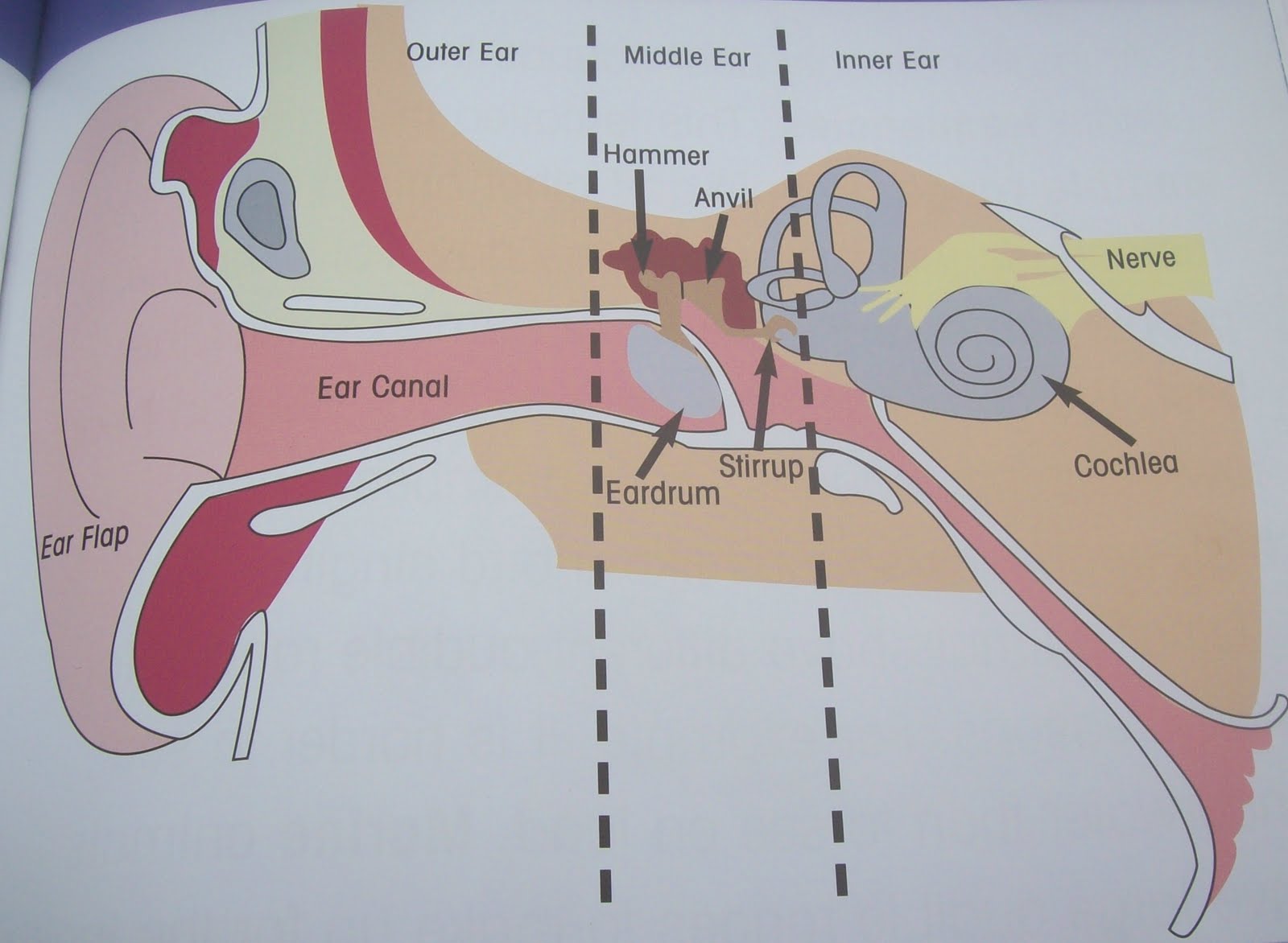
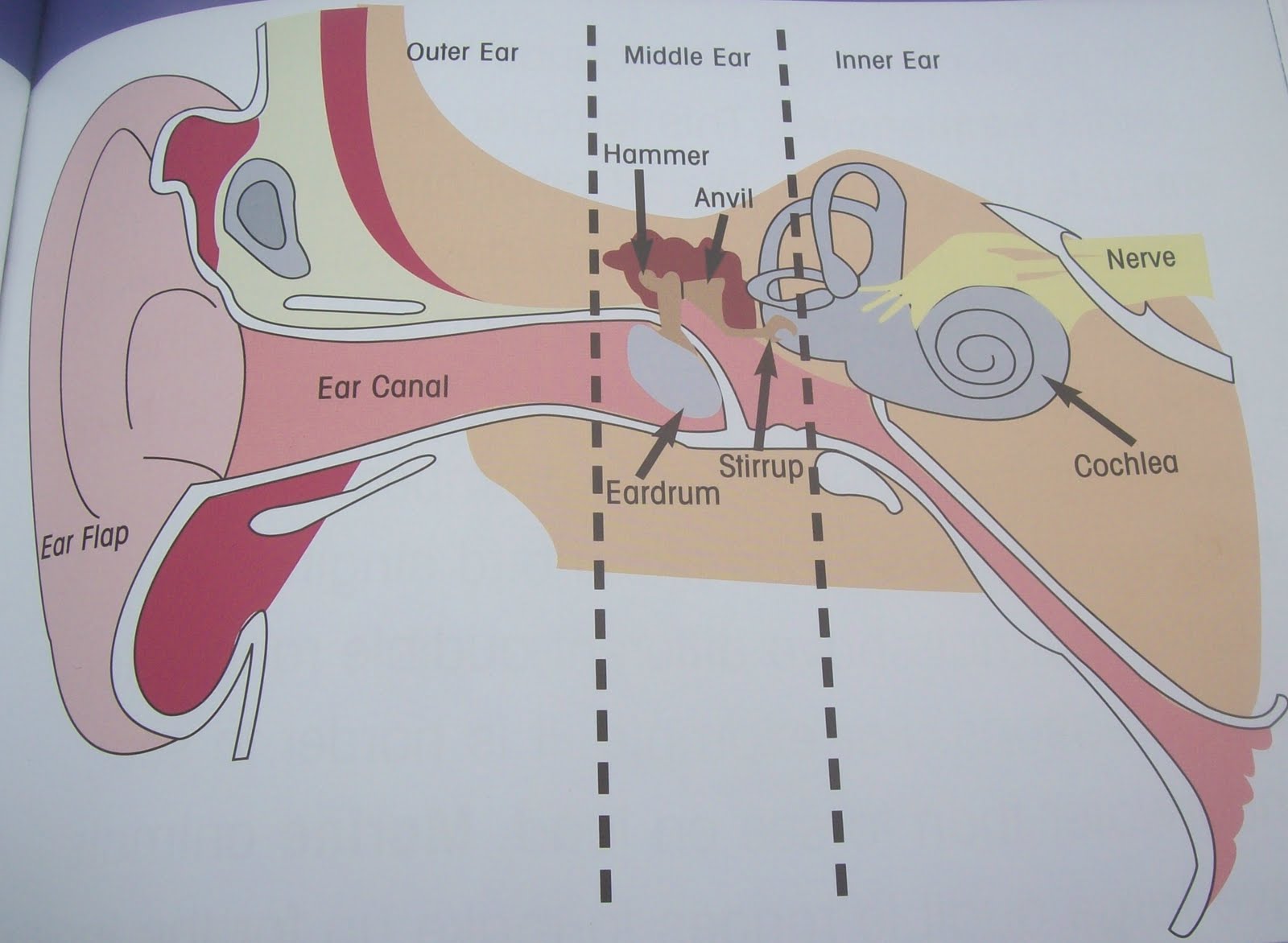
3 ear bones (memorize their locations)
hammer, anvil, and stirrup
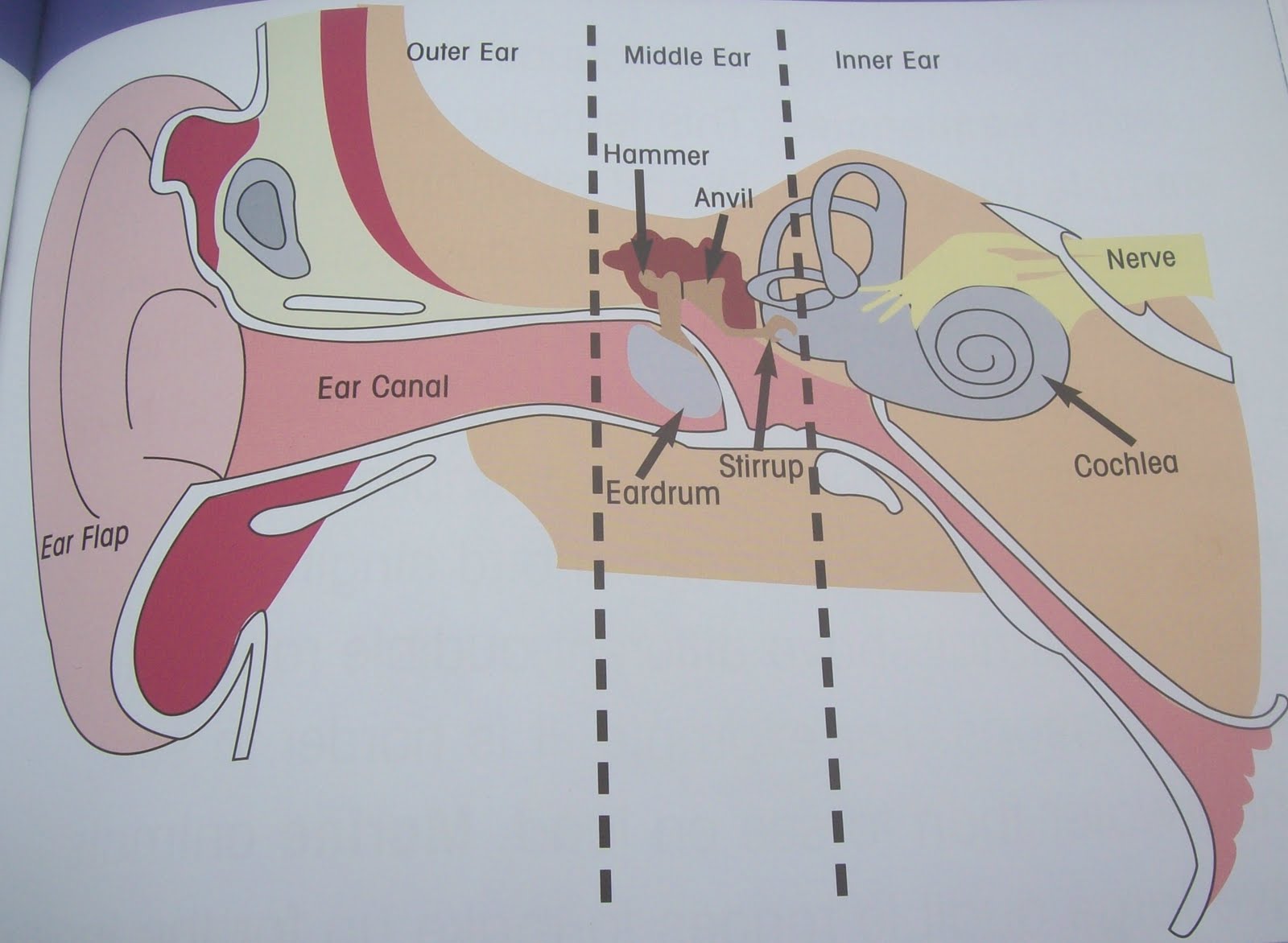
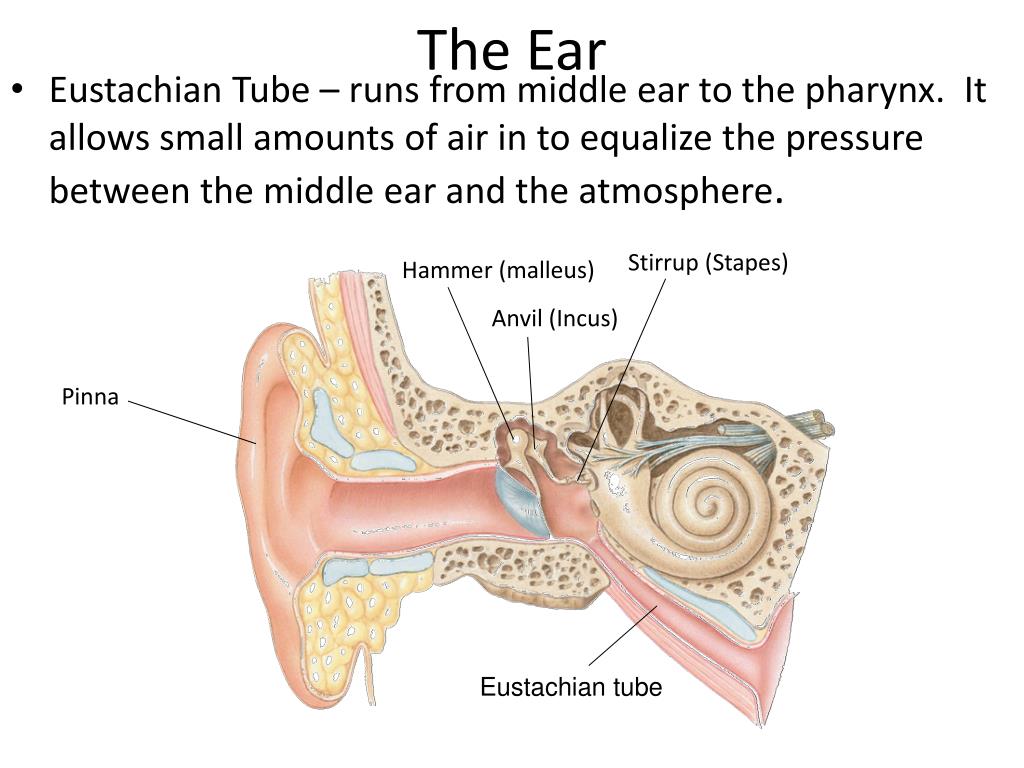
eustachian tube (memorize its location)
Leads from the middle ear to the pharynx. It’s normally closed, but when there is a significant change it opens up to make pressure on both sides of the eardrum equal.
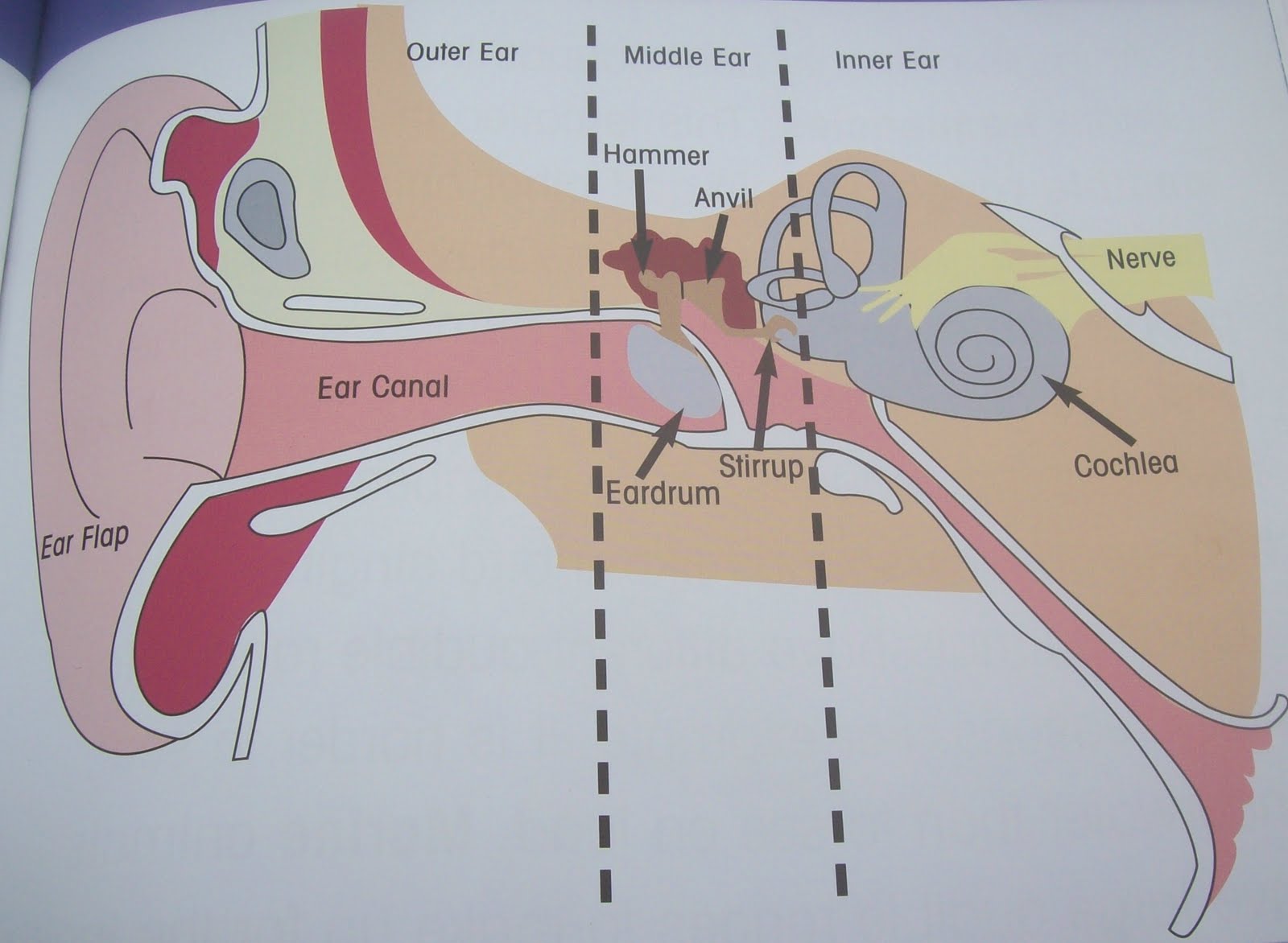
cochlea (memorize its location)
Contains fluid. When vibrations from the eardrum pass through the ear bones, the stirrup vibrates the membrane-covered opening, which pushes against the liquid in the cochlea. These vibrations form waves in the fluid that causes hairlike neurons to bens. When these neurons bend, they start nerve impulses that travel to the brain. The brain interprets the impulses as sound.
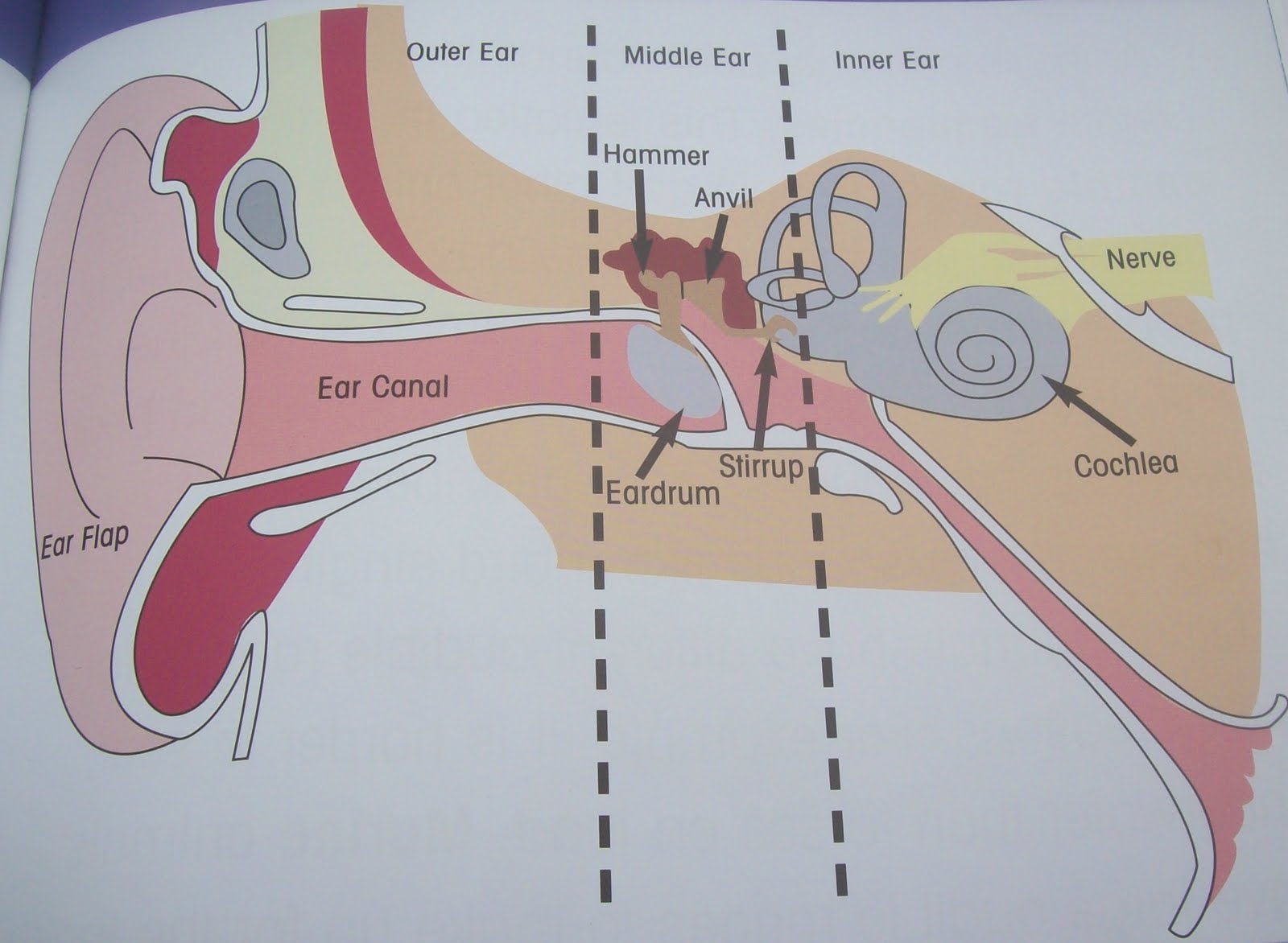
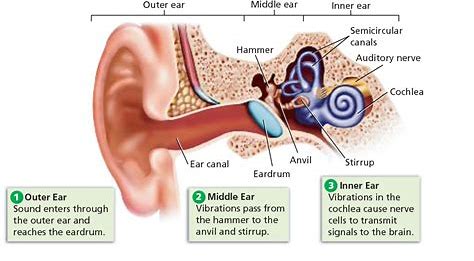
semicircular canals (memorize its location)
The parts of the ear which enable one to balance while riding a bike.
hormones
A chemical messenger made in an endocrine gland and carried by the blood.
Made in one tissue and transported to the tissues they affect.
Highly specific in their functions
vestigal organ
An organ that no longer functions.
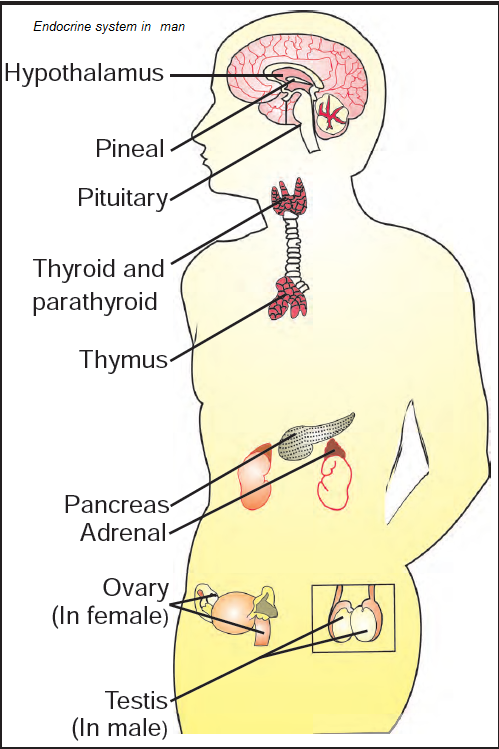
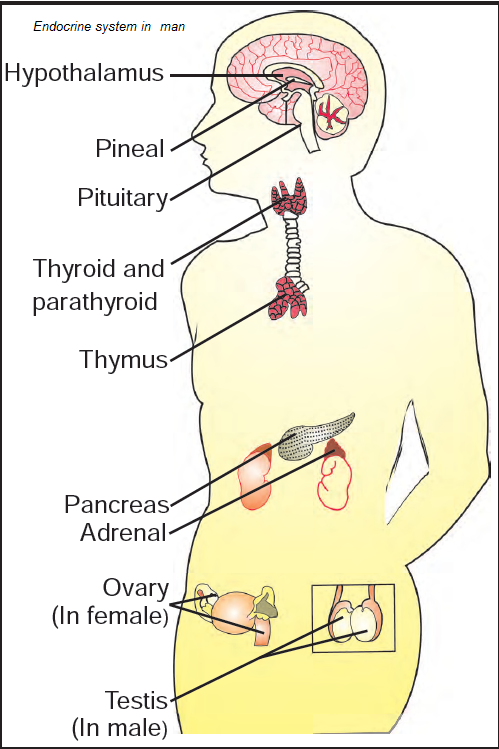
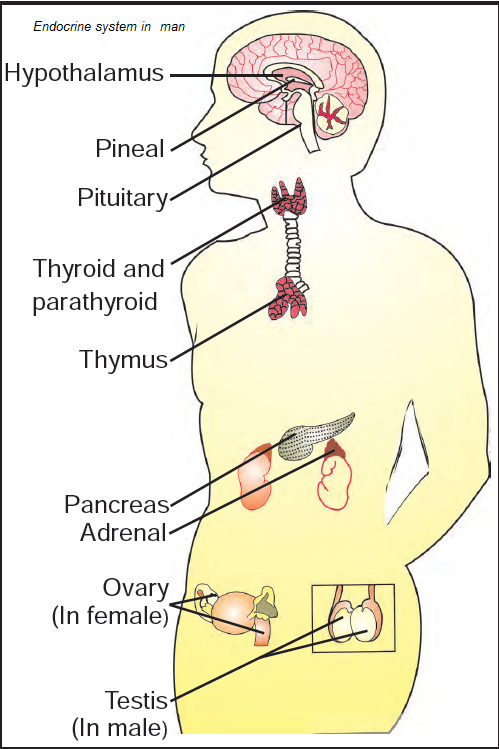
pancreas
Contains a gland that is responsible for forming insulin. But it is also part of the digestive system.
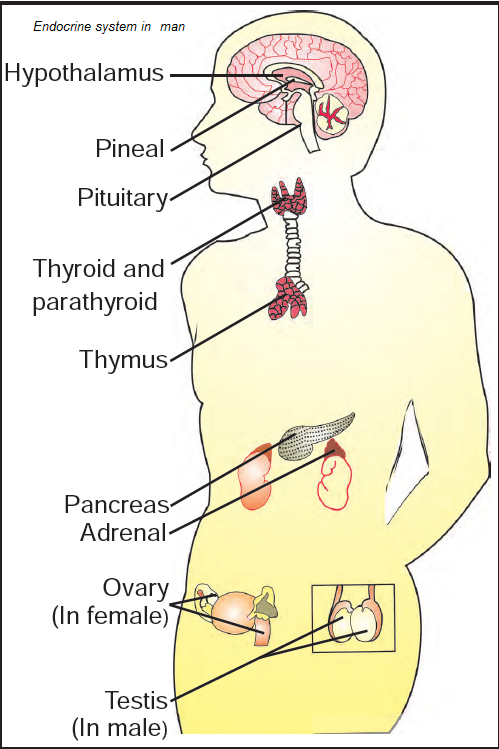
pituitary (gland)
It secretes a greater number of hormones than any other endocrine gland. Many of the hormones that it secretes stimulate other endocrine glands to produce their hormones. It sometimes known as the master gland.
growth hormone
Produced by the pituitary gland, this hormone stimulates bones, muscles and various other tissues to grow.
insulin
a hormone that helps regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
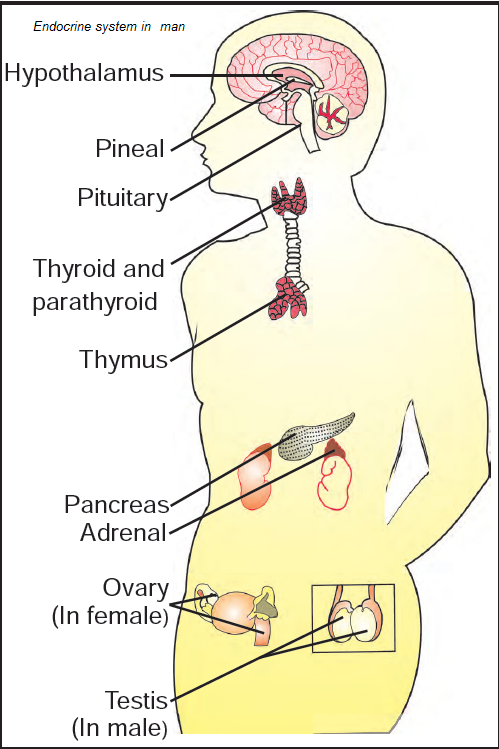
adrenal glands
Sits on top of the kidneys. They’re also known as glands of emergency. They produce the hormone epinephrine.
epinephrine
The hormone that prepares the body for emergencies. (Also known as adrenaline, and “fight or flight” hormone.)
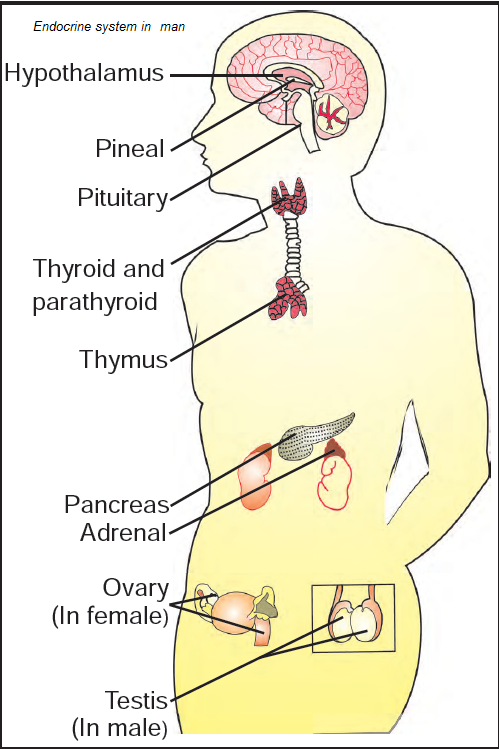
thyroid
A gland that controls the body’s metabolic rate (the body’s rate of activity).
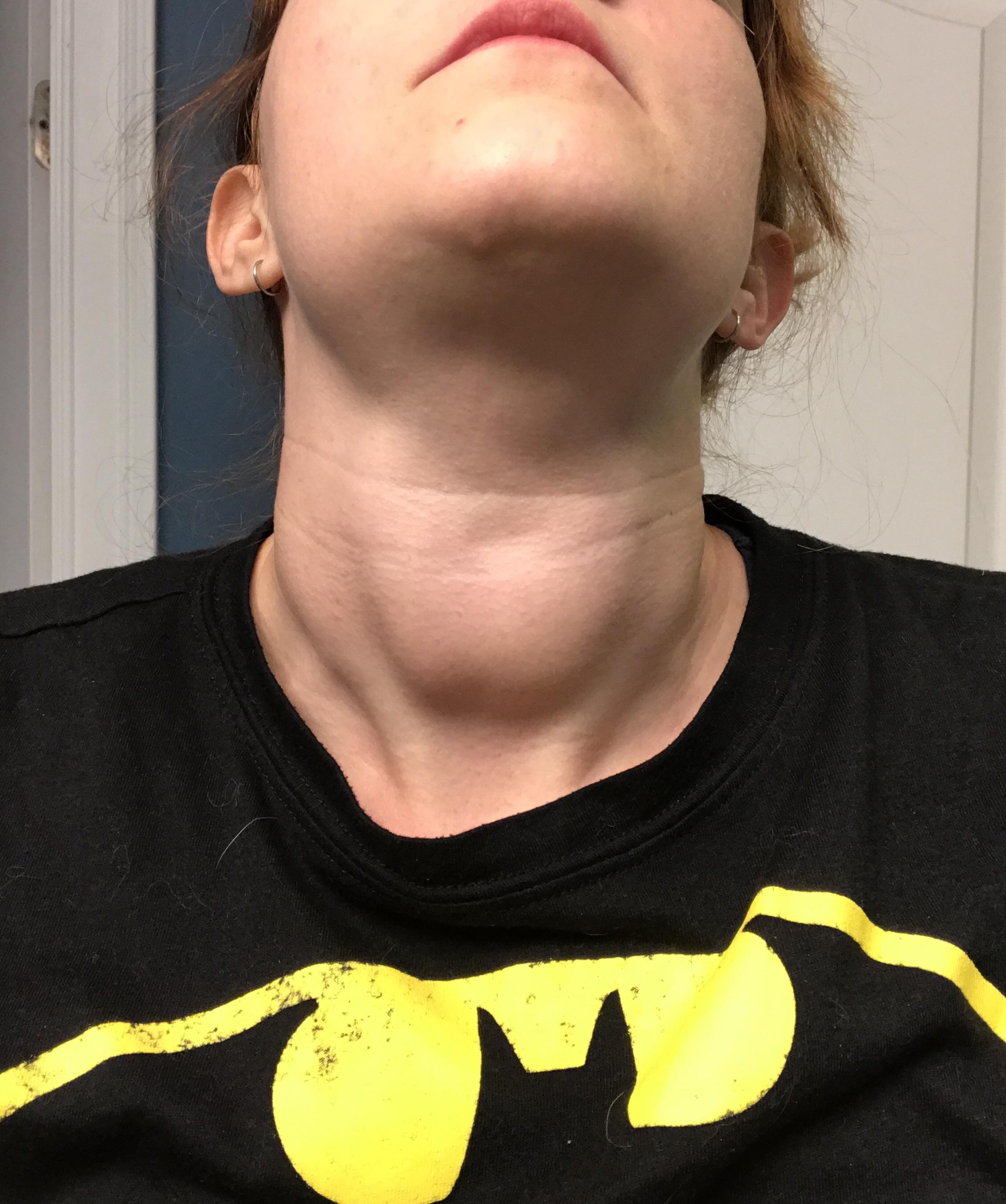
goiter
Swelling of the neck caused by his thyroid growing, trying to make thyroxine and it can’t because there’s a lack of iodine in his diet. This can affect a person’s metabolism (their body’s rate of activity.)
puberty
The period in life in which the reproductive organs cause the body to mature.
What transports endocrine chemicals?
circulating blood
Iodine
A component of the hormone thyroxine, and without thyroxine metabolism will be lower and a goiter may occur. Foods high in iodine are things like milk, cheese, shrimp, whole grain bread, and iodized salt.
What kind of cell has axons and dendrites?
the neuron
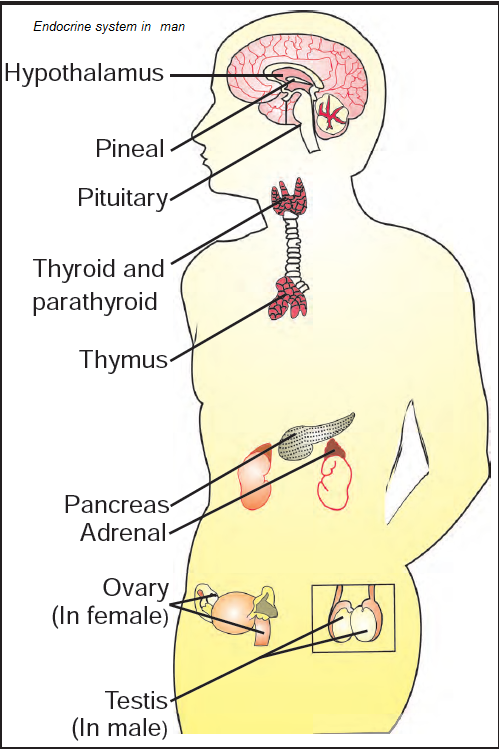
Endocrine glands
The pancreas, pituitary gland, adrenal glands, thyroid gland, ovaries and testes that secrete hormones and enzymes.
How does a reflex work when you touch a hot object?
The impulse is transmitted by a sensory neuron from the skin to the spinal cord, where it passes to an interneuron. The interneuron passes the impulse to a motor neuron, which carries the impulse to a muscle. The muscle receives the impulse and contracts.