Febrile Neutropenia
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What are the factors that increase the risk of infection in patients with Solid tumors?
Neutropenia
Disruption of anatomic barriers
Obstruction due to primary or metastatic tumor
Procedure and devices
Miscellaneous factors
Neutropenia definition
Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) of 500 or ANC that is expected to decrease to 500 during the next 48 houts
Profound neutropenia def
Occasionally used to decscribe neutropenia in which the ANC is 100
Functional neutropenia
Normal neutrophil count but hematologic malignancy results in qualitative defects of circulating neutrophils
Fever def
A single oral temperature measurement of >38.3 degrees C (101 F) or a temp of >38 C (100.4) F sustained over a 1 hour period
Axillary temp discouraged
Avoid rectal temp to prevent colonizing gut organisms from entering
What are the causes of fever in neutropenic patients, both microbiologically and non-microbiologically?
Decreased Production |
Peripheral Destruction |
Peripheral Pooling |
Decreased Neutropenia Production

Peripheral Destruction
Peripheral Pooling Causes
Overwhelming bacterial infection
Hemodialysis
Cardiopulmonary bypass
What is the duration of neutropenia cut-off to determine high risk vs low-risk patients?
High risk | Low Risk |
|
|
What are the comorbidities/conditions that classify patients as high risk.
Presence of any active uncontrolled comorbid medical problems, including:
Signs of severe sepsis or septic shock
Oral or gastrointestinal mucositis that interferes with swallowing or causes severe diarrhea
Gastrointestinal symptoms, including abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, or diarrhea
Intravascular catheter infection, especially catheter tunnel infection
New pulmonary infiltrate or hypoxemia
Underlying chronic lung disease
Complex infection at the time of presentation
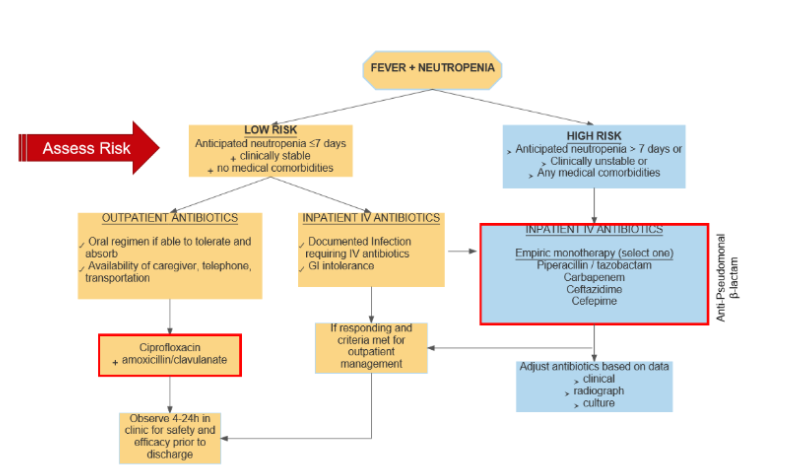
empiric treatment regimen for a high and low-risk febrile neutropenia patient.
Fluoroquinolones good
When should you consider antifungals in neutropenic patients? Which ones should be considered?
For high risk patients only; add after 4-7 days if continued fever
AmpB and caspofungin are options
How do you determine duration of treatment in febrile neutropenic patients?
In clinically or microbiologically documented infections, the duration of therapy is dictated by the particular organism and site
For others, continue abx for at least the duration of neutropenia or longer if clinically necessary
When should you consider antimicrobial prophylaxis? Design an empiric prophylaxis regimen for these patients.
Fluoroquinolone prophylaxis should be considered for high-risk patients with expected durations of prolonged and profound neutropenia (ANC <100 cells/mm³ for > 7 days)
Levo and Cipro considered mostly equivalent,
But Levo is preferred in situations with increased risk for oral mucositis-related invasive viridans group streptococcal infection
FQ resistance should be monitored
Prophylaxis is not routinely recommended for low-risk patients who are anticipated to remain neutropenic for > 7 days
is Addition of a gram-positive active agent to fluoroquinolone prophylaxis reccomeended?
generally not recommended