chapter 7 - sensory systems
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
what type of senses are provided by the action of mechanoreceptors
touch and pressure
hearing and equilibrium
what are the 3 types of touch and pressure receptors
baroreceptors, tactile receptors, proprioceptors
baroreceptors detect…
internal pressure change
tactile receptors detect…
external touch, pressure, vibration
proprioceptors monitor…
body position to provide sensory input for balance and control for body movements
vertebrate tactile receptors are widely dispersed in the…
skin
vertebrate tactile receptors in the skin include… (2)
free nerve endings and nerve endings enclosed in accessory structures
name two types of insect tactile receptors
trichoid sensilla and campaniform sensilla
name 3 types of vertebrate proprioceptors
muscle spindles, golgi tendon organs, joint capsule receptors
muscle spindles monitor…
skeletal muscle length
muscle spindles monitor skeletal muscle length in order to prevent…
excessive movement at joints
golgi tendon organs monitor…
tendon tension
golgi tendon organs monitor tendon tension to prevent…
excessive muscle contraction
joint capsule receptors monitor…
pressure, tension, and movement
joint capsule receptors provide …
sensory input for balance
what is the insect proprioceptor known as
scolopidia
what is the role of scolopidia in some species
modified into tympanal organs sound detection
in vertebrate what is responsible for balance and hearing
ears
in invertebrates … organs are used for hearing and balance
different
what specifically allows fish and amphibians to detect body positive and movement
hair cells
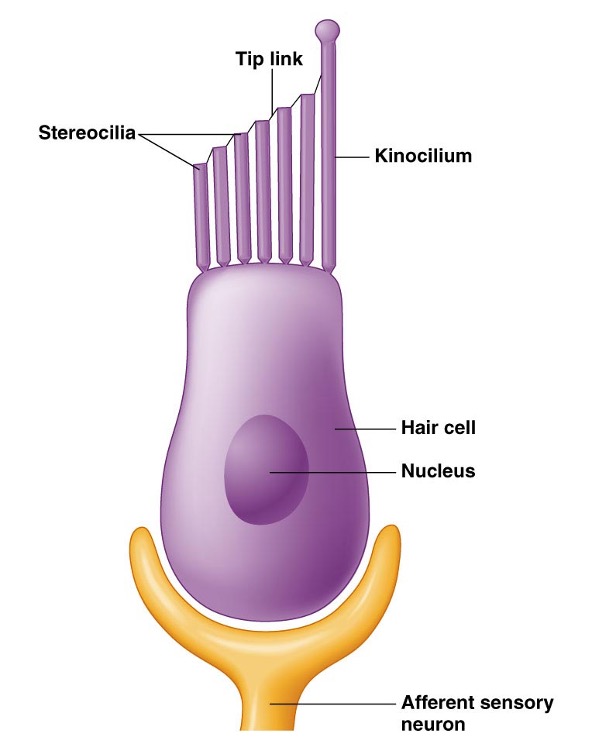
what are hair cells
modified epithelia cells
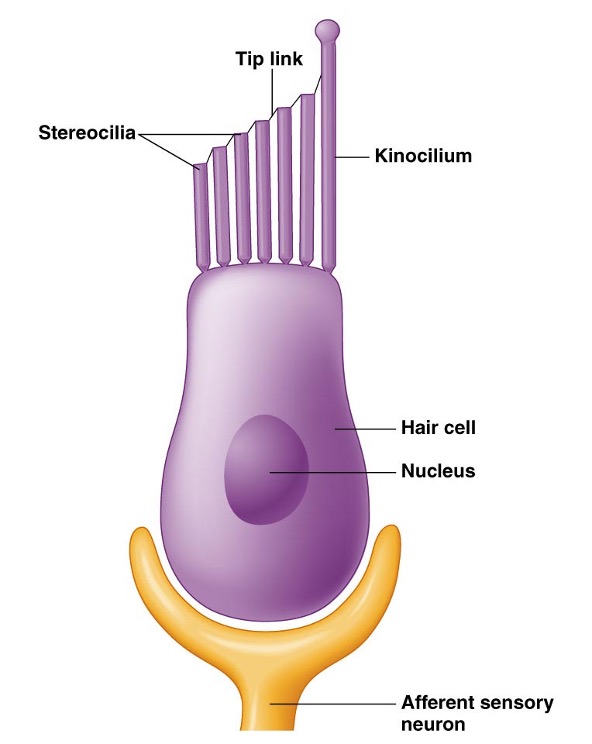
two key structures of hair cells
kinocilium (true cilium) and stereocilia (microvilli)
movement of … changes ion permeability
steorcilia
direction and degree of sterocilia bending affects…
number of open K+ and Ca+ channels → amount of neurotransmitter release → frequency of AP produced
what organ helps detect invertebrate equilibrium
statocysts
what are statocysts
hollow, fluid-filled cavities lined with mechanoreceptors
what do statocysts contain
statoliths
statoliths stimulate what
mechanoreceptors
three important organs for invertebrate hearing
trichoid sensilla, chordotonal organs, tympanal organs
name two important structures in fish and amphibians ability to detect body position and movement
neuromast and lateral line system
what is the neuromast
hair cell stereocilia embedded in cupola, detect water movement
what is the lateral line system
linear arrays of neuromasts in skin on sides of body and head
what are the three components of the ear in vertebrates
outer ear, middle ear, inner ear
what makes up the outer ear
pinna and auditory canal
what makes up the middle ear
interconnected bones in air filled cavity
what makes up the inner ear
fluid-filled sacs and canals
location of hair cells
the inner ear is important for detecting …
movement for balance
what are the components of the inner ear which are important for detecting movement for balance e
3 semi-circular canals w/ enlarged ampulla and 2 swellings (utricle and saccule)
3 semi-circular canals w/ enlarged ampulla detect…
rotational movements
utricle and saccule detect …
linear movements and head tilting
what is improtant for hearing in birds and mammals
lagena, extension of saccule forms cochlea with hair cells
macula detects…
horizontal and vertical linear movements and tilting of head
macula is found in …
utricle and saccule
cristae has hair cells in…. (2)
capula and ampullae of semicircular canals
cristae detect…
angular acceleration
frequency detection happens through
different areas of membrane stimulated, and high frequency stimulates at cochlea base while low frequency stimulates apex
amplitude detection happens through
loud sounds causing larger movements of basilar membrane, increase in depolarization of hair cells → increase action potential frequency
what are the two basic types of photoreceptors
ciliary and rhabdomeric
ciliary is a ….
single, highly folded cilium
rhabdomeric’s surface has …
microvillar projections
what two types of photoreceptors are found in vertebrates
rods and cones
how do photopigments produce photo-transduction
chromophore absorbs photo energy → dissociates with opsin → activates G-protein → causes formation of 2nd messenger → ion channels open/close → change membrane potential to stimulate or inhibit NT release
vertebrate retina have several types of neurons
horizontal, bipolar, amacrine
these neurons in the vertebrate retina are all involved in processing…
visual signals from rods and cones to the ganglion cells of the optic nerve
do rods exhibit convergence
yes
many rods synapse with one…
bipolar cell
many bipolar cells synapse with one…
ganglion cells
each ganglion cell has a … receptive field
large
convergence in rods provides…
low resolution and high sensitivity
do cones exhibit convergence
no
each cone synapse with one…, bipolar cell synapses with one…
bipolar cell, ganglion cell
each ganglion cell has … receptive field
small
cones provide … resolution but … sensitivity
high, poor
what allows for color vision in vertberates
detection of different wavelengths from different types of cones
most mammals are …. which means they have .. cone types
dichromatic, 2
humans are … which means they have … cone types
trichromatic, 3
birds, reptiles, and fish are either …, … or ….
tri-, tetra-, or pentachromatic
mantis shrimp are… which means they have … cone types
dodecachromatic, 12
accommodation is the process by which an…
eye changes its focal length
accommodation allows the eye to produce a …
focused image of objects at different distances
polychaete worms change their focal length by changing the …. , which alters the size of the eye and thus the distance between the lens and the retina (accommodation)
volume of liquid in the eye
invertebrates and vertebrates alter focal length by …(accommodation)
moving the lens and the retina
lizards, birds, and mammals alter their focal length by changing the …. (accommodation)
shape of the lens
to focus on nearby objects, the ciliary muscles …, which … the width and … the tension on the suspensory ligament, causing the lens to become more rounded
contract, increases, loosens
to focus on distant objects, the ciliary muscles…, this … the width of the ciliary muscles, … the tension of the suspensory ligaments, which pulls on the lens and flattens it
relax, reduces, increasing
what are the two types of receptors for temperature
central thermoreceptors and peripheral thermoreceptors
central thermoreceptors are found in the … and monitor …
hypothalamus, core internal temperature
peripheral thermoreceptors are found on the … and monitor …
skin, environmental temperature
what are the two types of peripheral receptors
warm sensitive and cold sensitive
what receptors are useful for painfully hot stimuli
thermal nociceptors
what do pit vipers and bird snakes use to detect heat radiating objects
pit organs
pit organs can detect …. degrees C changes (humans can only detect 0.5 degree C changes)
0.003
what type of animals have magneto-sensory neurons
nematodes
what type of animals use Earth’s magnetic field to help them navigate (2)
migratory birds and homing salmon
sea turtles have magnetite in … around the brain
dura mater
in the retina of some vertebrates they have ….
crypto-chrome
what are the Ampullae of Lorenzini
a series of pits found on the noses of sharks and rays acting as poly-modal receptors that detect both electrical and mechanical stimuli
what type of animals have Ampullae of Lorenzini
shark and rays
platypus “bill” has both … and …
electroreceptors and mechanoreceptors