Plant Biology Exam 1
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Binomial name (scientific name)
Genus specific epithet
Theophrastus
considered the first botanist
Linnaeus
developed the binomial naming system
ophyta
phylum
opsida
class
ales
order
aceae
family
kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
taxonomic hierarchy in order
Archaebacteria (archea)
unicellular, prokaryotic,
ex: methanogen bacteria
Eubacteria
“typical” bacteria and blue green algae
unicellular, prokaryotic
Eukaryotes
only domain with nuclues
contains the 4 kingdoms (fungi, plant, animal, protist
Fungi
multicellular eukaryote
Polyphyletic = several independent lineages
heterotrophic = need outside source of food
Plant
one of the four kingdoms of eukaryotes
multicellular, eukaryotic
autotrophic
Animals
one of the four kingdoms of eukaryotes, multicelluar, eukaryotic, heterotrophic,
protists
one of the four eukaryotic kingdoms
eukaryotic, unicellluar, and multicellular
Cladistics
tool for determining nautral relationships
based on shared, derived characteristics
Cladogram
treelike diagram of descent
branch represents the common ancestor
node represents a divergence between two lines of
herbarium
Collections of preserved plants and fungi
systematically arranged
repository
area of collections and records
germplasm
algae
Diverse polyphyletic group
several independent lineages
One of the major plant groups
refers to a life style and form rather than a single lineage
Rhodophyta
red algae
chromophyta
brown algae
chlorophyta
green algae
Zygomycota
black bread molds
ascomycota
cup fungi
basidiomycota
club fungi
fungi we put in salads
Bryophytes
Polyphyletic? they may or may not be
These plants don’t have xylem or phloem (plumbing system)
Bryophyta
Mosses
Hepaticophyta
liverworts
Anthocerophyta
Hornworts
Bryophyta
Mosses, type of bryophyte
Hepaticophyta
Liverwort, type of bryophyte
Anthocerophyta
hornworts, type of bryophyte
Ferns
Polyphyletic?
They growth without seeds (they reproduce through
Polypodiophyta
Lycophyta
Equisetophyta
Psilotophyta
Polypodiophyta
fernsL
Lycophyta
Lycopods, type of fern
Equisetophyta
horsetails, type of fern
Psilotophyta
whisk ferns
Gymnosperms
Polyphyletic, flowering (not like your typical flower) plants and have seeds (naked) that develop on the surface of the plant’s reproductive structures
Pinyphyta, cycadophyta, Gnetophyta, Ginkgophyta
Pinophyta
confiers (pine trees) type of gymnosperm
Cycadophyta
Cycads; sago palm, type of gymnosperm
Gnetophyta
Ephedra, Gnetum, Welwitchia, type of gymnosperm
Ginkgophyta
Ginkgo, type of gymnosperm
Angiosperms
Magnoliophyta
Monophyletic
Single Lineage
Flowering plants
largest gorup
most recent
very diverse
most successful
2 major groups, monocots and eudicots
Monocots
one seed leaf
Poaceae, araceae,, orchidaceae, liliaceae
Eudicots
2 seed leaves
Lamiaceae, solanaceae, rosaceae
Basal angiosperms
both monocots and eudicots
primitive features
Eudicot ex: Ranunculaceae (buttercup family)
Poaceae
grass family, monocot (angiosperm)
Araceae
Palm family, monocot (angiosperm)
Orchidaceae
Orchid family, monocot (angiosperm)
Liliaceae
Lily family, monocot (angiosperm)
Lamiaceae
Mint family, eudicots (angiosperm)
Solanaceae
Nightshade, tobacco, potato, tomato, eudicots (angiosperm)
Rosaceae
rose family, apple, rose, blackberry, eudicots (angiosperm)
Genetics
Heredity
systematics
evolutionary relationshipsC
Cytology
cellular structure and interactions
Anatomy
internal plant structureMo
Morphology
external plant structure
Plant physiology
plant functionP
pathology
plant diseases
ecology
environmental interactions
Economic botany
the relationships between people and plants, how people use plants with a little anthropology thrown in
Phytosociology
the study of plant -not people-communities and the relationships between species of plants
Ethnobotany
how indigenous populations make use of plants
Biometeorology
a newish subfield that relates plants with environment
Plant ecology
ecology of vascular plants on land and in wetland ecosystems
Phycology
study of algae
horticulture
cultivating plants
agronomy
soil management and study as it relates to crop management
Paleobotany
fossils
plant taxonomy
categorizing plant species, usually using DNA analysis
Paleoclimatology
how many plants have contributed to the atmosphere through history, and how plants are historical indicators of climate
Palynology
study of where a body has been laying in a particular spot, and forensic botany
Bryology
study of mosses and liverworts
Dendrology
study of woody plants
Lichenology
study of lichens
Pteridology
study of ferns
Xyology
study of the structure of wood
Forensic botany
using plants in legal, usually criminal investigation
Biotechnology
genetic modification of living organisms to produce useful products
Matter
occupies space and has mass
composed of elements
Organic Compounds
compounds containing carbon
Polymer
chains of repeating identical or similar molecular subunits (monomers
Dehydration Synthesis
forms polymers from monomers by getting rid of an H and an OH
Hydrolysis
breaks down polymers into monomers, cuts with water
Carbohydrates
sugars, composed of C, H, and O in the ratio of C1 H2 O1
Monosaccharide
single sugar molecule
simple sugar
Glucose, fructose
Disaccharide
two sugar molecules bonded
Sucrose = glucose + fructose
Polysaccharide
complex carbohydrates
Polymers of monosaccharides
Starch and cellulose
Starch
polysaccharide that is bonded in the same orientation
glucose polymer, ex: potatoes
the potato is the energy storage for the potato plant to be used in the winter
Cellulose
polysaccharide that is bonded in an alternating pattern
Inulin
fructose polymer, energy storage in carbs
ex: onion, garlic
Structure of carbohydrates
cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin
Hemicellulose
gluey, bind microfibrils
gums e.g., gum arabic (stabilizer)
important in binding fibers in paper
variable composition - short, branched glucose chains
structure of carbohydrates
Pectin
galacturonic acid polymer
Jelly
agar and carrageenan (allows commercial ice cream to melt slower than homemade ice cream)
structure of carbohydrates
Lipids
Composed of C, H, O, not in a 1:2:1
have little or no affinity for H2O
Fats
Saturated molecules
No double bonds between carbons in fatty acids
straight chain
solid at room temp
butter and coconut oil
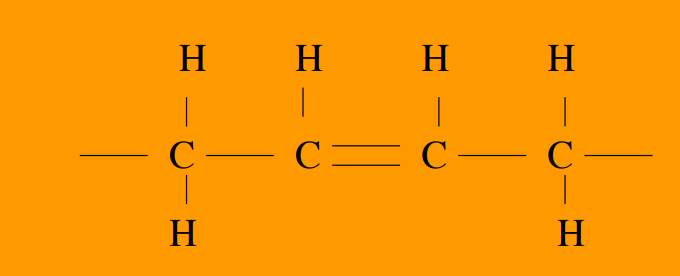
Oils
unsaturated molecules
one of more double bonds between carbons
bend chain
can be cis or trans
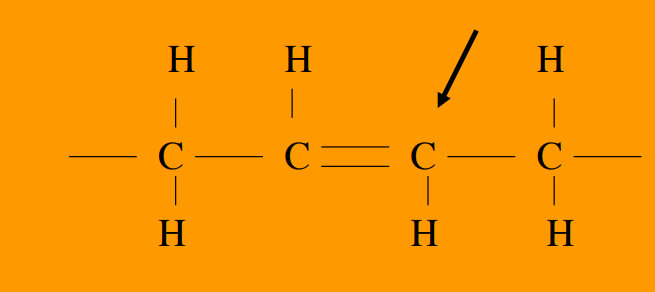
Trans fatty acid
doesn’t bend the fatty acid
it acts like a saturated fatty acid
produced by hydrogenating unsaturated fats
Phospholipid
Major structural units of cell membranes
glycerol + 2 fatty acid tails + phosphate unit (in head)
Hydrophilic head, and hydrophobic tail
Steroids
complex lipid
Complex molecules consisting of rings of Carbon atoms
Various Functions
membrane structure
hormones
Plants
Phytosterols
sold as health supplements
reducing cholesterol
Protein
Great diversity of functions
structure
storage of energy
contraction (muscle)
enzymes
Polymer of amino acids
Contains C, H, O, N, S
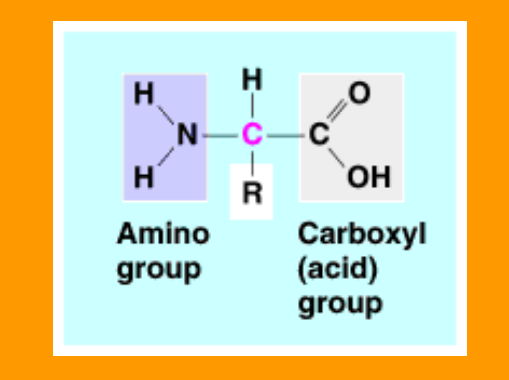
Amino Acid
Amino group + r-subunit + carboxyl group