chem/phys mcat practice exam 1
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
competitive inhibition
inhibitor binds to same active site as substrate. Vmax stays the same and Km increases
uncompetitive inhibition
inhibitor binds to ES complex at an allosteric site. Km decreases (because ES is constantly being drained out so we make more by binding more E to S), Vmax decreases
noncompetitive inhibition
inhibitor binds to allosteric site whether or not substrate is yet bound. Km stays the same, Vmax decreases
mixed-type inhibition
inhibitor acts as competitive or uncompetitive in terms of binding to an E or ES complex and how the Km is changed. but it binds at an allosteric site. Km will increase or decrease depending on if it acts as competitive or uncompetitive (E or ES binding). Vmax always decreses
axes of lineweaver-burk plot
x axis: -1/Km
y axis: 1/Vmax
linear
2:0 or 2:3
trigonal planar
3:0
bent (120 degrees)
2:1
tetrahedral
4:0
trigonal pyramidal
3:1
bent (109.4 degrees)
2:2
trigonal bipyramidal
5:0
seesaw
4:1
t-shaped
3:2
octahedral
6:0
square pyramidal
5:1
square planar
4:2
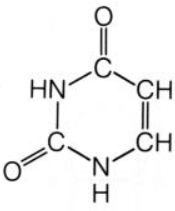
uracil
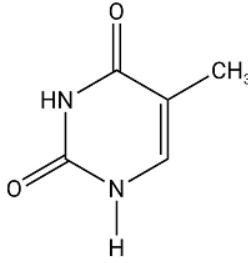
thymine
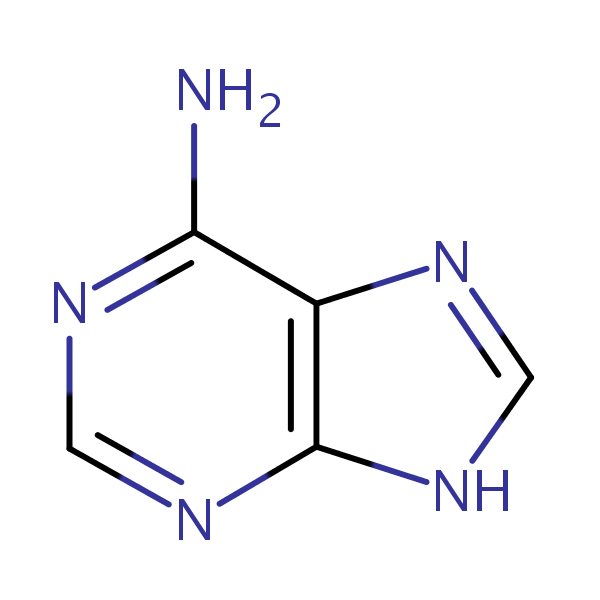
adenine
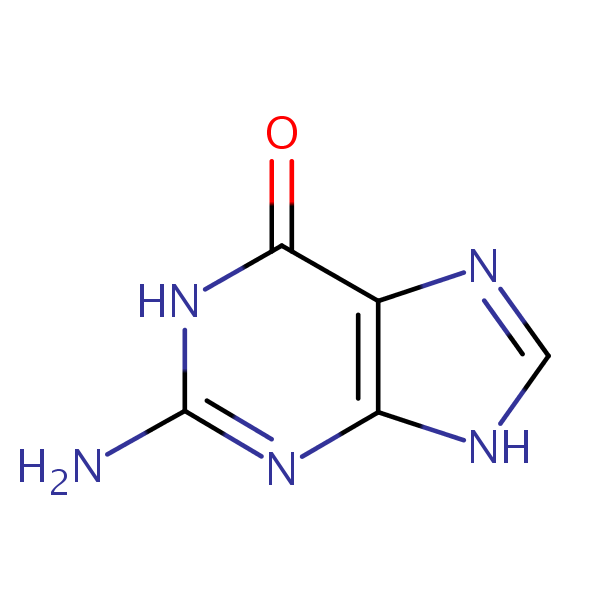
guanine
cytosine
equation to find electric field magnitude
E (units: v/m)= change in V (voltage) / D (distance)
equation for energy in a capacitor
E=(1/2)(QV) or E=(1/2)(CV²) Q=electric charge stored on the capacitor V= voltage across the capacitor C=capacitance of the capacitor
log(1)
0
log(2)
0.30
log(3)
0.48
log(4)
0.60
log(5)
0.70
log(10)
1.00
log(0.1)
-1.00
log(0.01)
-2.00
log(0.001)
-3.00
henderson-hasselbach equation
pH=pKa + log (A-/HA)
what is the delta G of this rxn: exothermic and decreased disorder
spontaneous at low temperatures, nonspontaneous at high temperatures
what is the delta G of this rxn: exothermic, increase in disorder
always spontaneous
what is the delta G of this rxn: endothermic, decrease in disorder
never spontaneous
what is the delta G of this rxn: endothermic, increase in disorder
spontaneous at high temperatures
what is the delta G of this rxn: requires energy at any temperature
nonspontaneous
converting energy, wavelength, frequency, and the speed of light
E=hv, c=λν
absorbance units
no units!
how to find concentration of enzyme at calculated absorbance
calibration/standard curve based on equation
what makes up a blank?
no reactants or products; just a solvent
relate energy to power and time
E=Pt
amplitude
how high a cosine or sine wave goes
period
a full cycle of a cosine or sine wave
phase difference
the x difference between two crests of the same type of wave
crest
the name for the top of a sine or cosine wave
constructive interference; what is it and what is its effect
occurs when there is no phase difference between 2 cosine or 2 sine waves; produces a third wave which combines their amplitudes
phase-shift
cosine or sine wave moving left or right, affecting whether the crest is up or down at a certain spot
deconstructive interference
occurs when there is a phase difference between 2 waves; subtract the amplitudes from each other
relationship between LDF forces and molecule size
larger molecules have more electrons, making their e- cloud more easily distorted, making it more more polarizable, leading to stronger LDF
acid dissociation constant equation
Ka=([H+][A-])/[HA]
how many C in propane
3
how many carbons in butane
4
acyl group
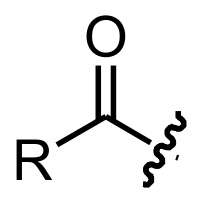
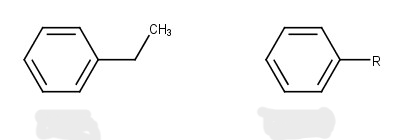
benzyl group
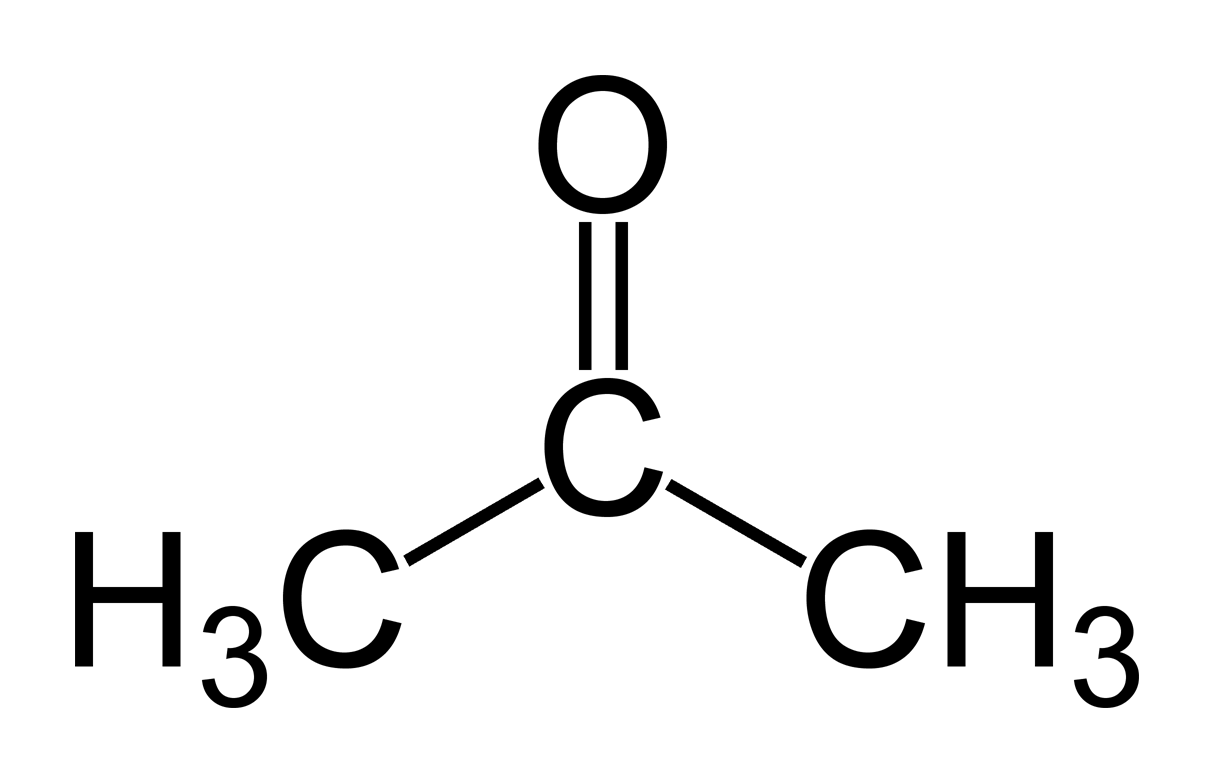
acetone
how are beta sheets held together
intermolecular hydrogen bonding between the C=O and N-H backbone portions
how are alpha helices held together
intramolecular hydrogen bonding
ionic radius periodic trend
decreases going up, increases with negativity (cations will shrink, anions swell)
relationship between Ka, pKa, and acidity
increased Ka = decreased pKa = releases proton more readily = stronger acid
positron decay (B+) ; same trend as electron capture
one proton is converted into a neutron, leading to net negative charge
alpha decay
emits 2 protons and 2 neutrons
B- decay
neutron is split into a proton (new element) and an electron. electron is emitted, so atom now has +1 charge
gamma decay
photon is released as energy
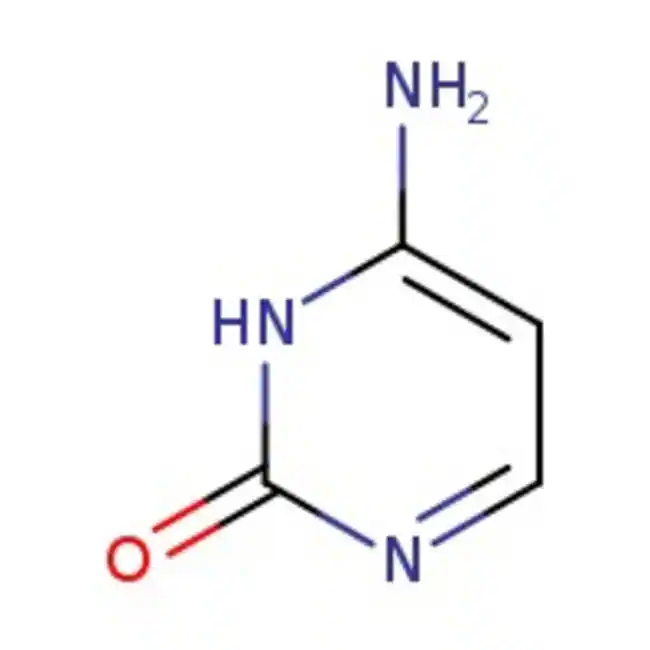
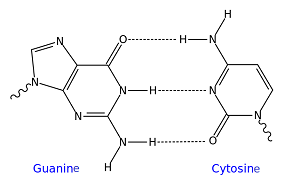
G and C hydrogen bonding
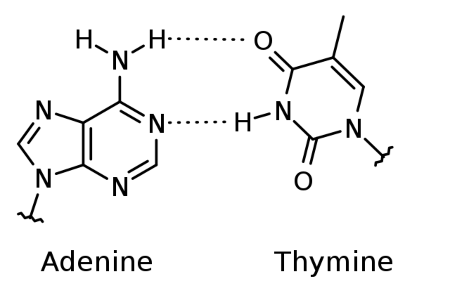
a and t hydrogen bonding
relate the electric field to voltage and distance (capacitor)
E = change in v/d
electric field within a conduction material at equilibrium
0