IB HL Biology - Subcellular Structure and function | unfinished
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Processes Of Life, Origin of Cells, and Cell types
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Nucleic Acids
DNA and RNA
Functions of nucleic acids
DNA - Storing and transmitting genetic information.
Monomer of nucleic acids
Nucleotide
Polymer of nucleic acids
Polynucleotide
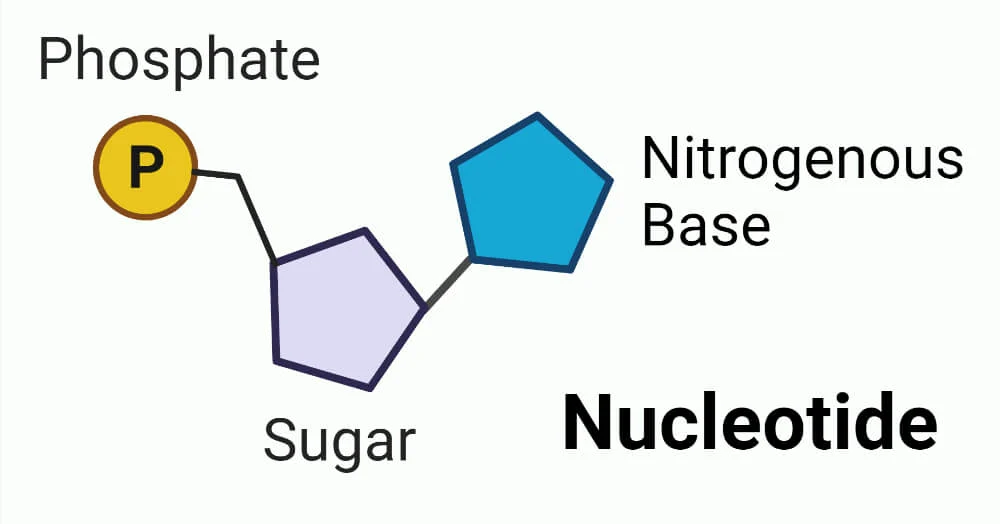
3 parts of a nucleotide
Phosphate group
Pentose sugars
Nitrogenous base
Elements found in nucleic acids
C, H, O, N and phosphorus
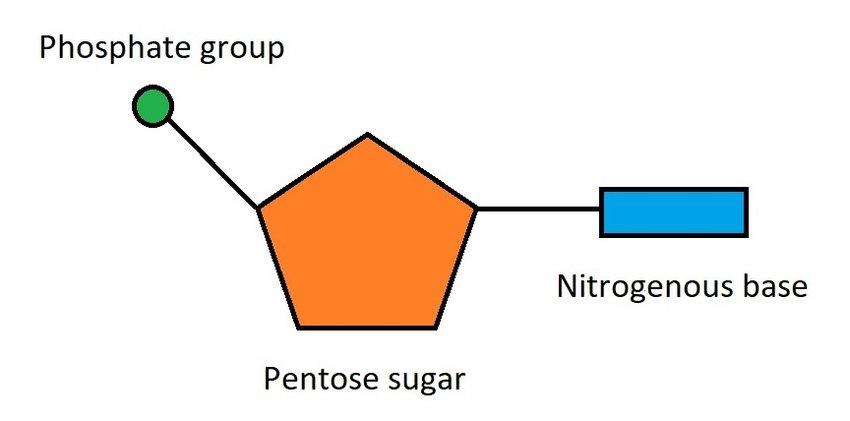
What is the circle?
Phosphate
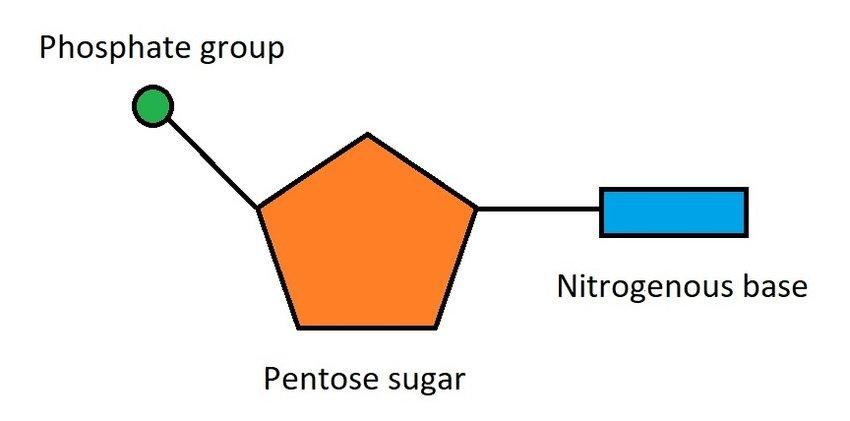
What is the pentagon?
Pentose sugar
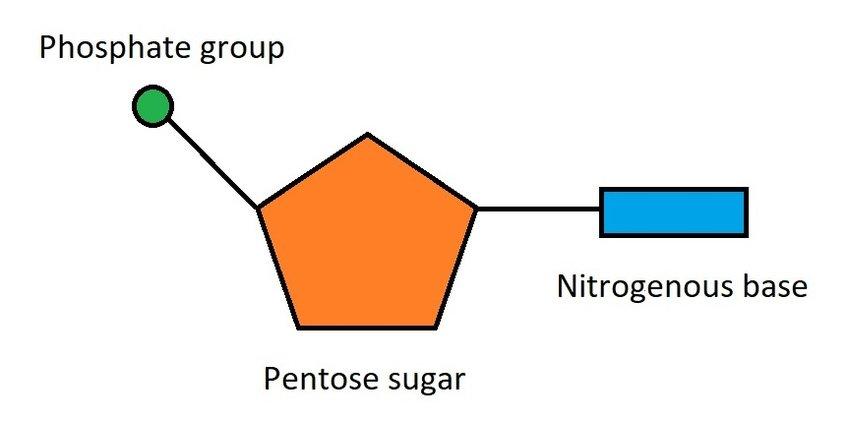
What is the rectangle?
Nitrogenous Base
The type of pathway that synthesizes polynucleotides
Anabolic
Type of reaction that occurs and what bond is formed during the polynucleotide reaction?
Condensation
Phosphodiester bond
connect neighboring nucleotides within that polynucleotide strands
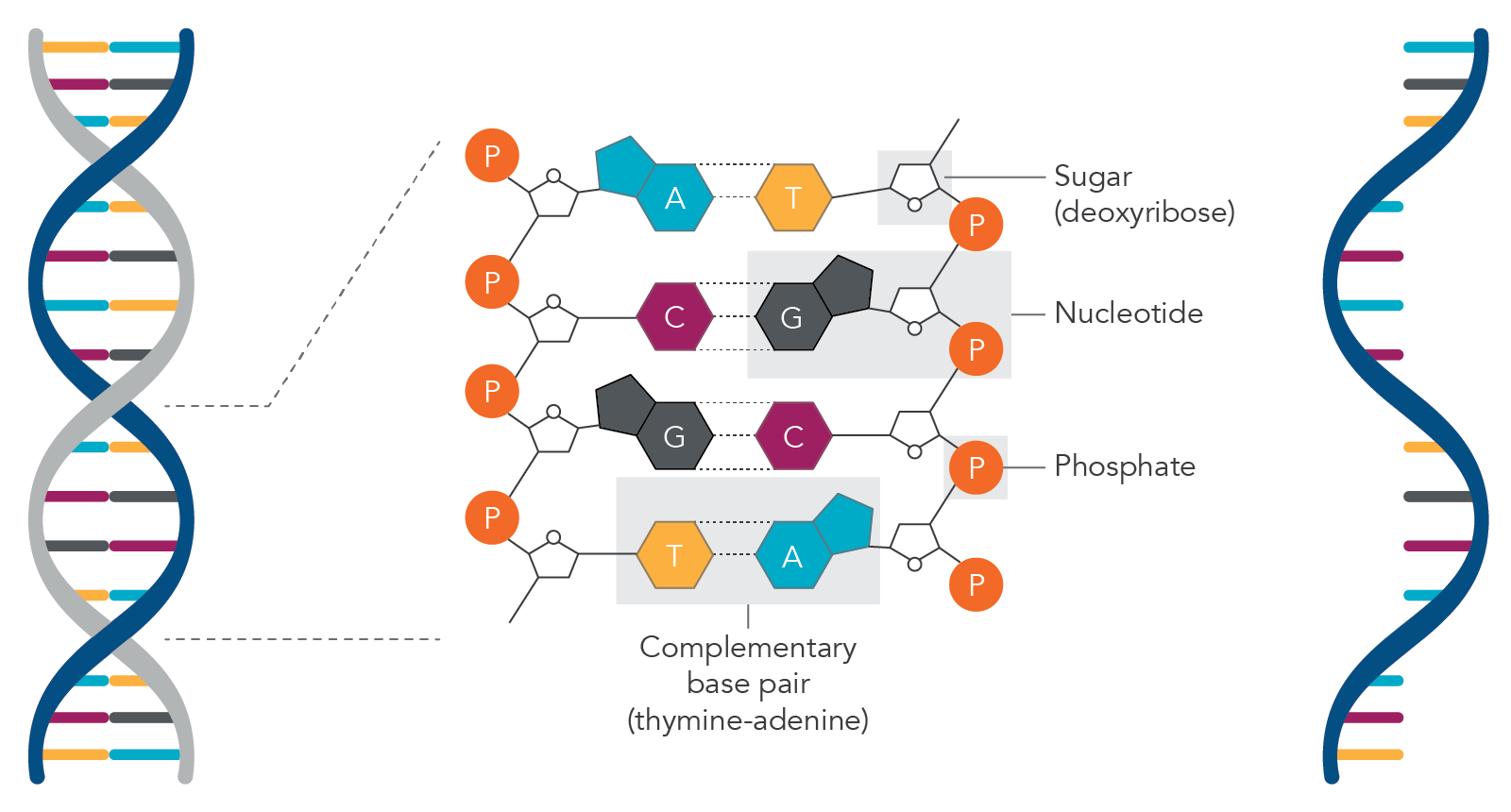
Sugar phosphate backbone including the type of bond involved
Repeating patterens of the pentose sugar, then phosphate along with the polynucleotide. Held together by phosphodiester.
2 pentose sugars found in nucleic acids. Molelcular difference.
Deoxyribose | has 2 -H on 2’ carbons | no oxygen | in DNA
Ribose | has -OH on 2’ carbons | in RNA
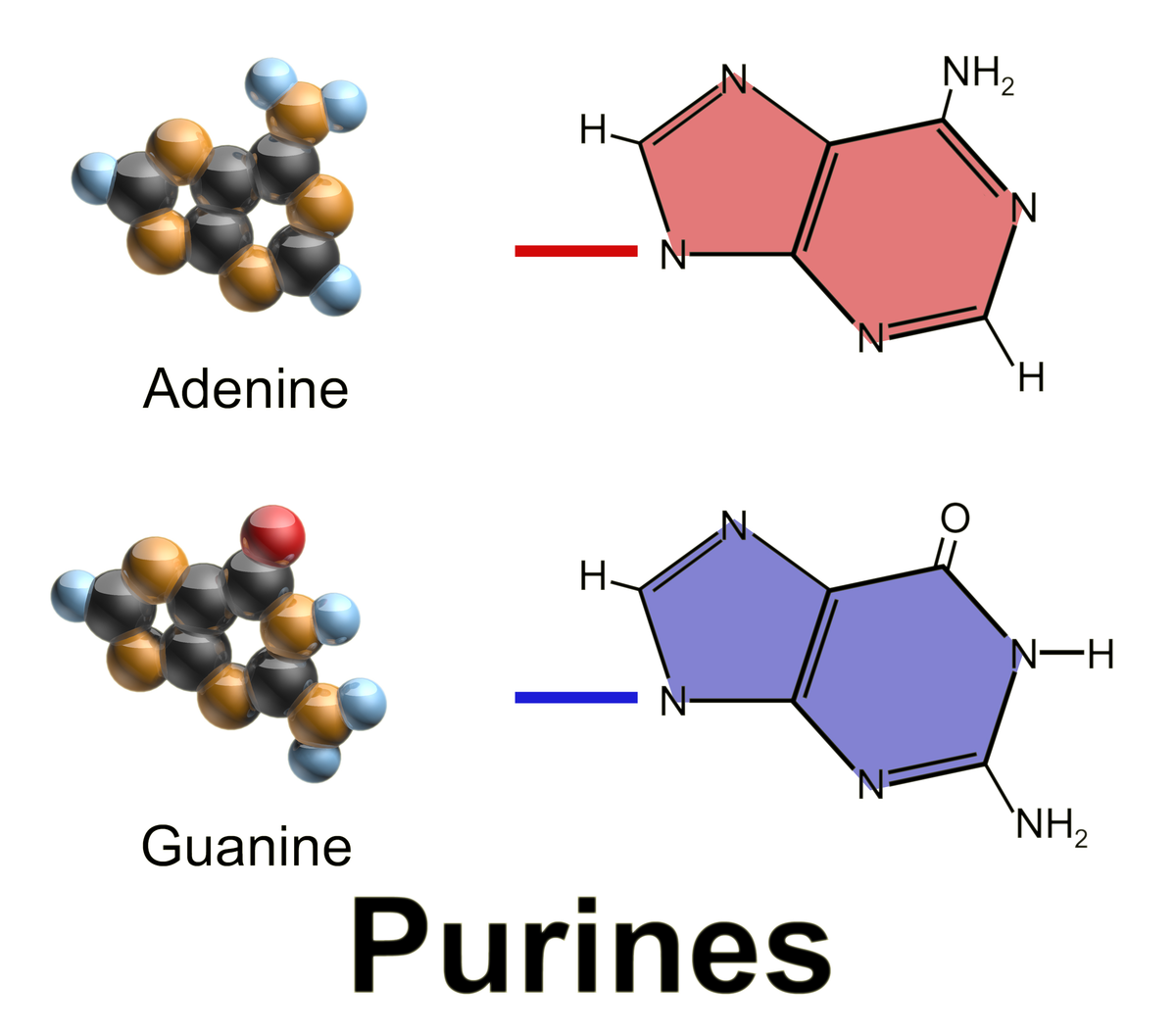
Purines
2 rings
Adenine
Guanine
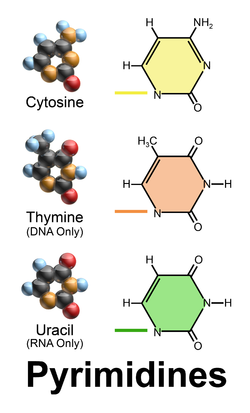
Pryrimidines
1 ring
Cytosine
Thymine
Uracil