microbio lecture 22 (ecology & symbiosis)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
symbiosis
Most of the interactions between species involve food in that they are either:
competing for the same food supply
eating one another (predation)
or avoiding being eaten (avoiding predation)
These interactions are often brief. However, when two species live in close association for long periods it can be classified as this
Often restricted to only mutually beneficial interactions
parasitism
In symbiosis, at least one member of the pair benefits from the relationship. The other member may be:
injured
commensalism
In symbiosis, at least one member of the pair benefits from the relationship. The other member may be:
relatively unaffected
mutualism
In symbiosis, at least one member of the pair benefits from the relationship. The other member may be:
may also benefit
mutualism examples
Wolbachia and insects
Vibrio and squid
Rhizobium and nitrogen fixation
wolbachia
Insect symbionts - A classic example of intracellular animal-microbe symbiosis
cosmpolitan - intracellular parasite that colonizes over half of the world’s insect species
vertical transmission - transmitted from mother to offspring through the germ line
feminization
genetic males that develop as females
parthenogenesis
development of unfertilized eggs
male killing
male offspring of infected females are killed
cytoplasmic incompatibility
an infected male and uninfected female cannot produce offspring
wolbachia
Releasing _____-infected mosquitos in Indonesia reduced dengue infection rates from 9.4% to 2.3%
____ obtain nutrients from their host through specialized transporters
Genes for the biosynthesis of purines and pyrimidines are conserved across _____
_____-infected insects have changes in the expression of nucleotide metabolism genes
When nutrients are limited, ______ infection is beneficial
vibrio
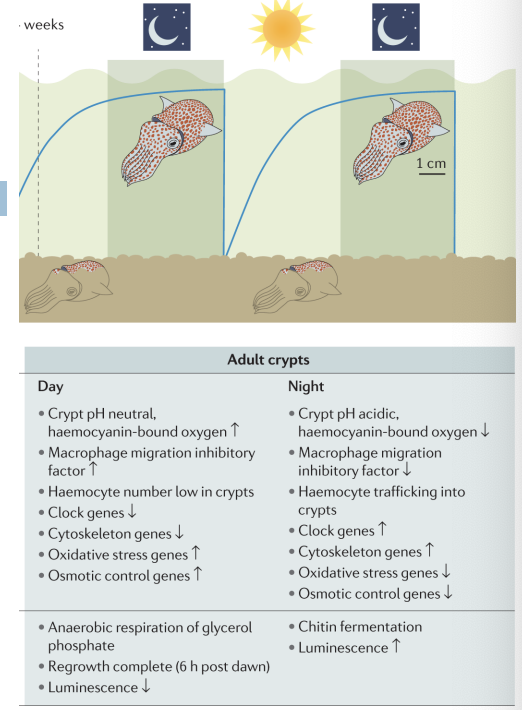
Bioluminescent bacteria - A classic example of extracellular animal-microbe symbiosis
bobtailed squid (euprymna scolopes) have light organs that project light at night but the bacteria is producing the light
horizontal transmission
Squid acquire Vibrio from their environment through ____ ______
Vibrio colonize crypts inside a light organ
Squid eject the Vibrio from the crypts in the light organ every morning and reacquire bacteria throughout the day
factors that control who colonizes and persists
Dispersal:
The movement of microbes between environments determines which microbes are available to colonize
Host interactions contribute to microbial dispersal
Selection:
Host filtering excludes or recruits microbes through the immune system and changes to the host environment
Diversification:
Once they colonize, microbes can evolve into new species
Ecological drift:
Random processes may cause some microbial populations to vanish
Priority effects:
The first microbe to colonize influences subsequent colonization
host specificity and host filtering
Squid secretes chitobiose, a chemoattractant, in mucus at the entrance to the light organ
Host immune system excludes other bacteria
Presence of bacteria initiates cellular changes in the host
phylosymbiosis
“microbial community relationships that recapitulate the phylogeny of their host”"
Microbial dispersal, microbial selection/host filtering, microbial diversification, ecological drift, and priority effects can lead to ______
MAMPs
Vibrio luminescence peaks at night, when squid are hunting
Vibrio _____ (the friendly version of PAMPs) drive expression of the cry blue light receptor gene in the squid (a clock gene)
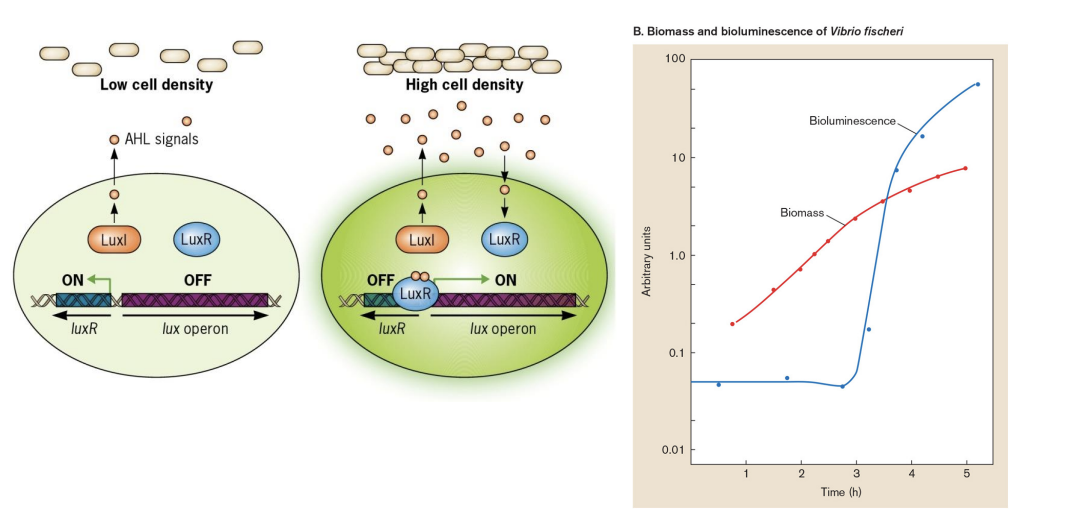
quorum sensing
regulates bioluminescence
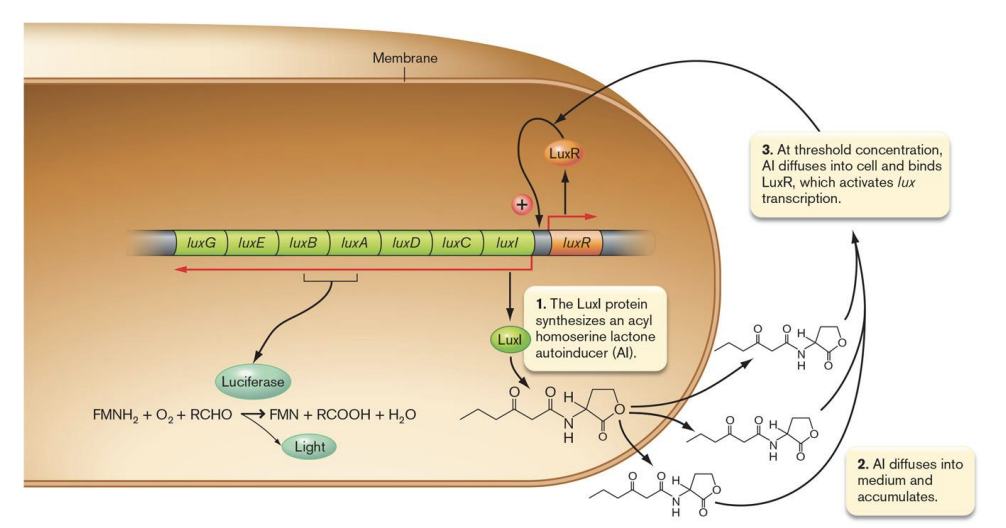
vibrio
______ presence is necessary for light organ development
______ secretes TCT (tracheal cytotoxin), which triggers tissue reorganization
cell surface fraction, LPS, peptidoglycan
how does Vibrio contribute to host development?
Fractionated culture supernatant of Vibrio by reverse-phase HPLC found a familiar molecule
Trachael cytotoxin (TCT) is a toxin secreted by Bordella pertussis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae
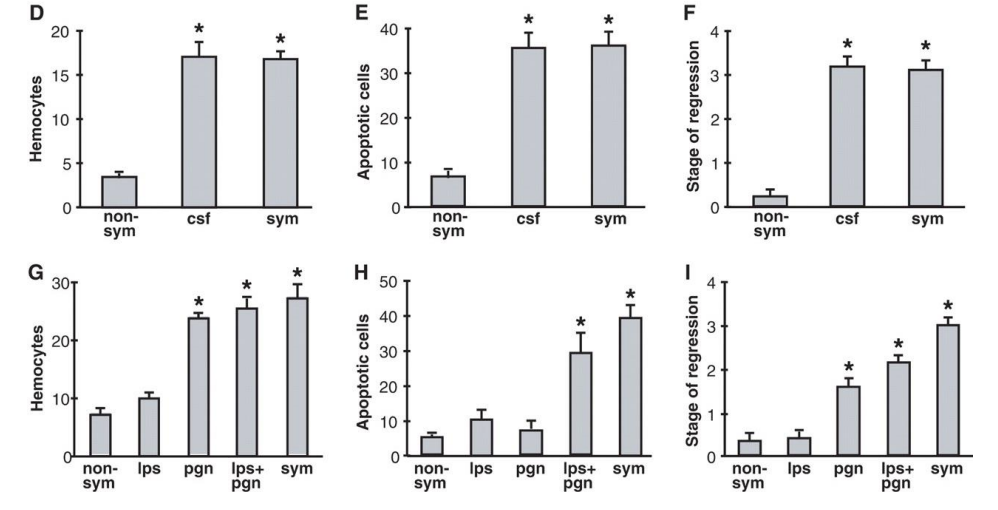
TCT
is a toxin secreted by Bordella pertussis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae
adding this to developing squid resulted in full development of light organ
rhizobium
Nitrogen fixing bacteria:
Perhaps the most agriculturally important mutualistic interaction between bacteria and plants
These bacteria are essential for the cultivation of leguminous plants such as peas, beans, and alfalfa
nitrogen fixation
Normally, plants and water leach nitrogen from the soil.
To compensate, farmers fertilize or rotate crops like corn with legumes (alfalfa, soybeans, peas, etc.). Legumes associate with bacteria that fix nitrogen from the air.
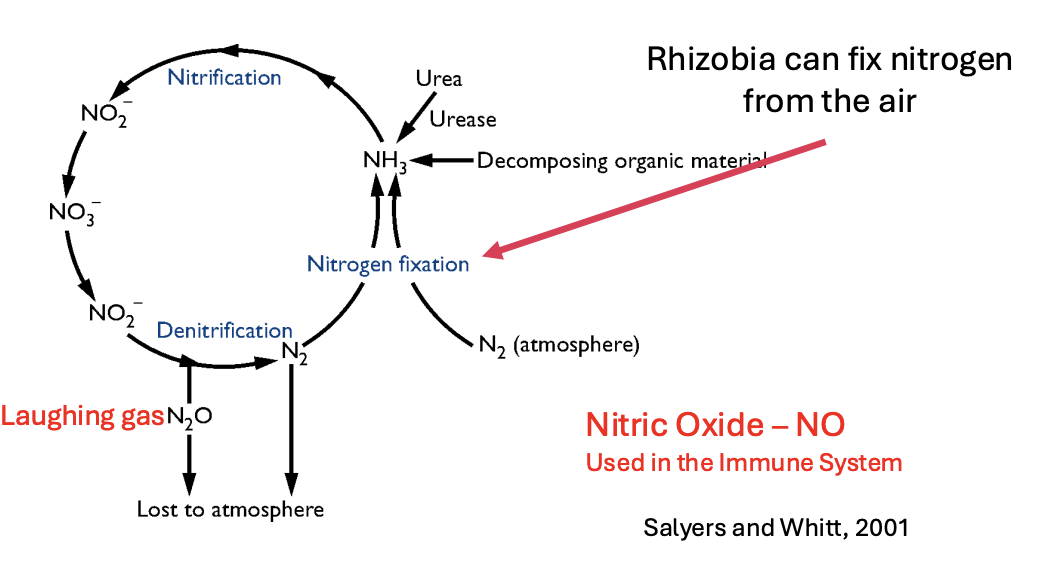
rhizobium
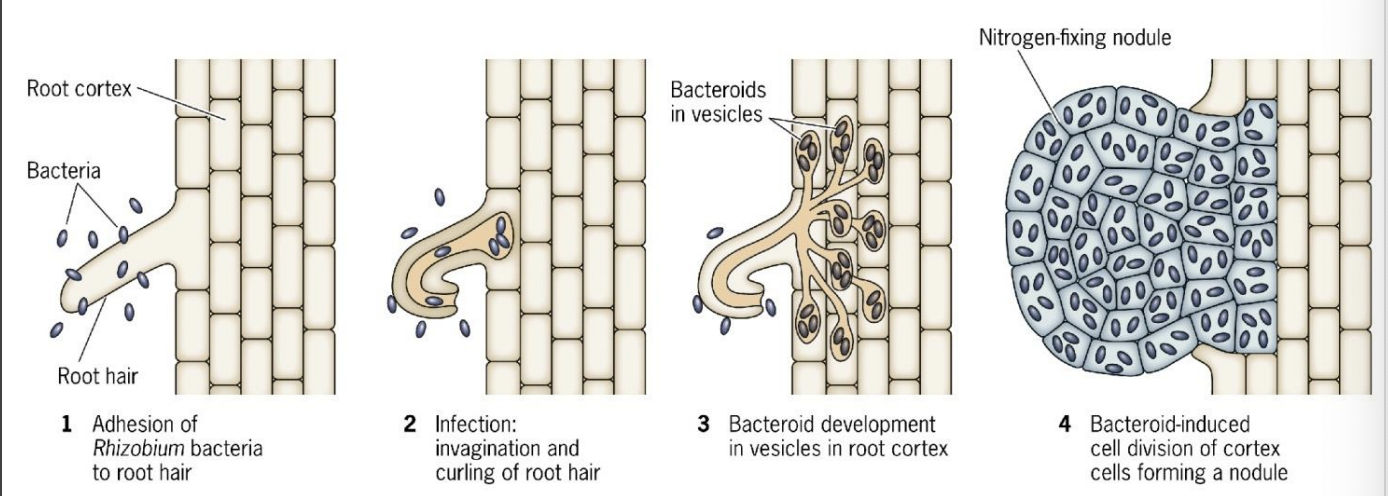
Gram-negative motile rods
Associate with the roots (and sometimes stems) of leguminous plants in a species specific manner
Enter the root via the root hairs
Invade plant cells and differentiate into semi-dormant nitrogen fixing state (bacteroids).
Interaction between bacteria and root leads to the formation of nodules-groups of plant cells containing high numbers of bacteroids
nodule formation: recognition
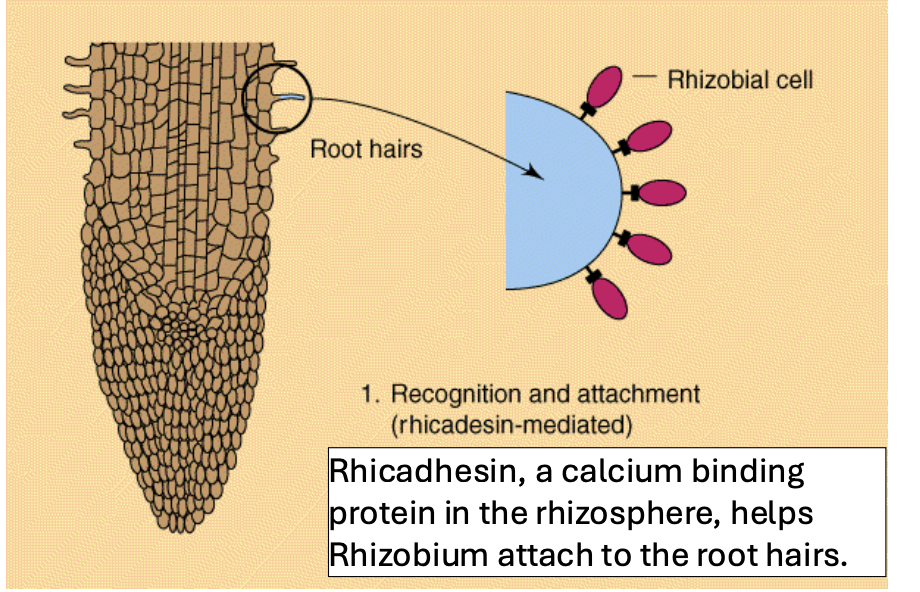
rhicadhesin
a calcium binding protein in the rhizosphere that helps Rhizobium attach to the root hairs during recognition (nodule formation)
Nodule Formation: Invasion
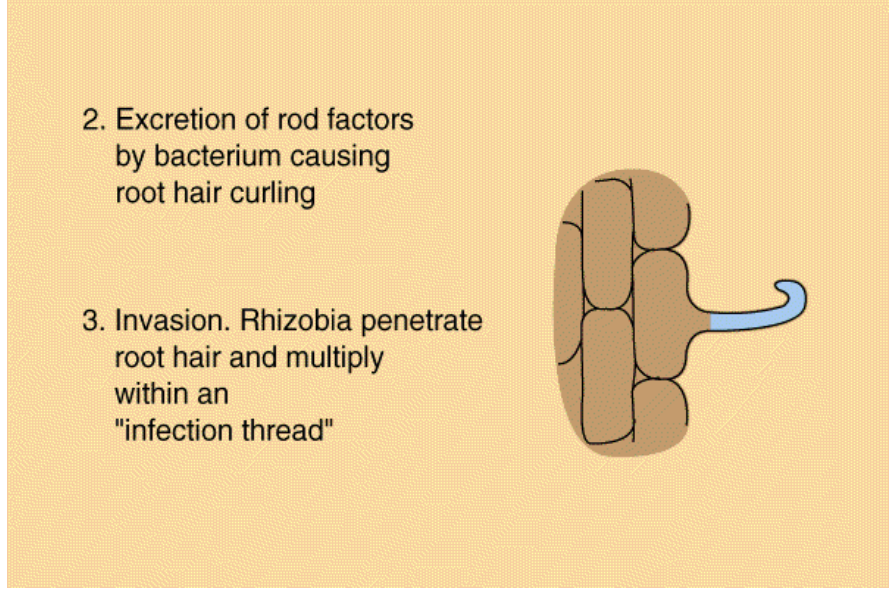
rod factors
excretion of these by bacterium causes root hair curling during invasion (nodule formation)
nod factors
A region of the sym plasmid of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae, which nodulates peas
The sym plasmid also contains genes that restrict infection to a particular host plant
nodA, nodB, and nodC are responsible for producing ____ ____, chitin-like molecules that induce root hair curling and nodule formation.
The addition of exogenous ___ ____ is sufficent to induce nodule formation in the absence of bacteria.
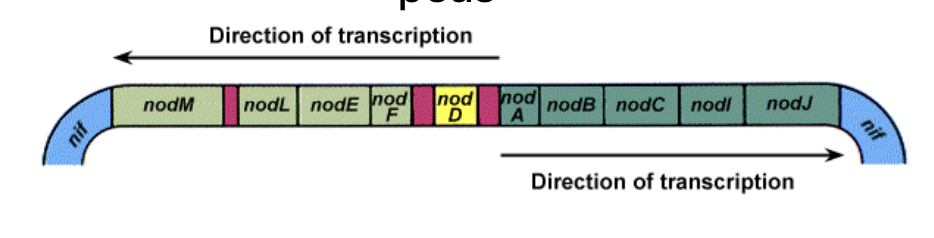
nodD
this product controls transcription of the nod genes, which mediate interaction with the plant root hairs
→ activates transcription of the nod genes by bending DNA at the promoter and thus enhancing RNAP binding and transcription
this is activated by activated by inducers including plant flavonoids
flavonoids
____ are complex organic molecules that are secreted in large quantities by the roots of leguminous plants. They are involved in growth regulation and attracting pollinating animals among other activities
rhizobium-infection
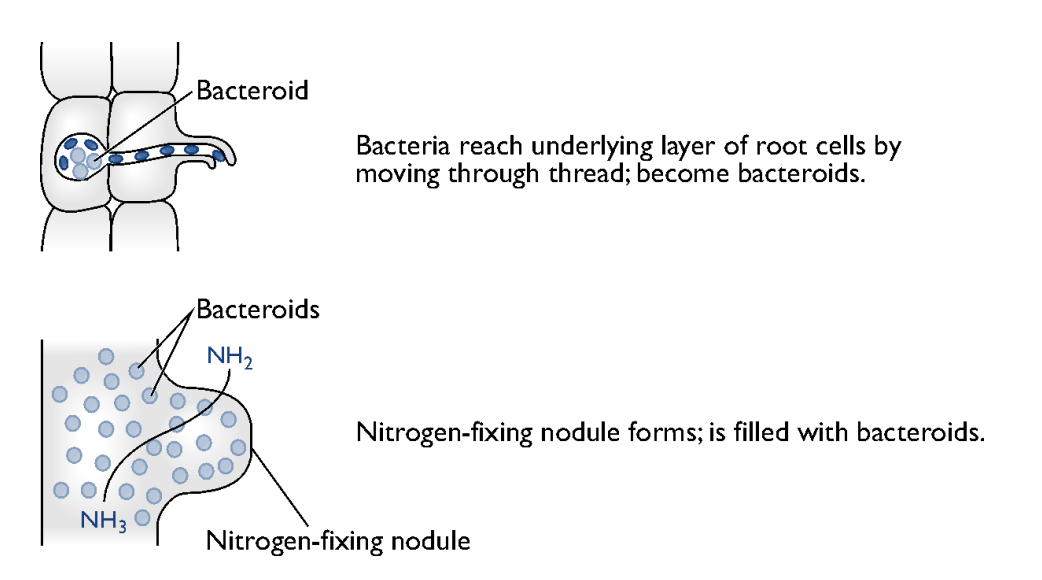
nodule formation
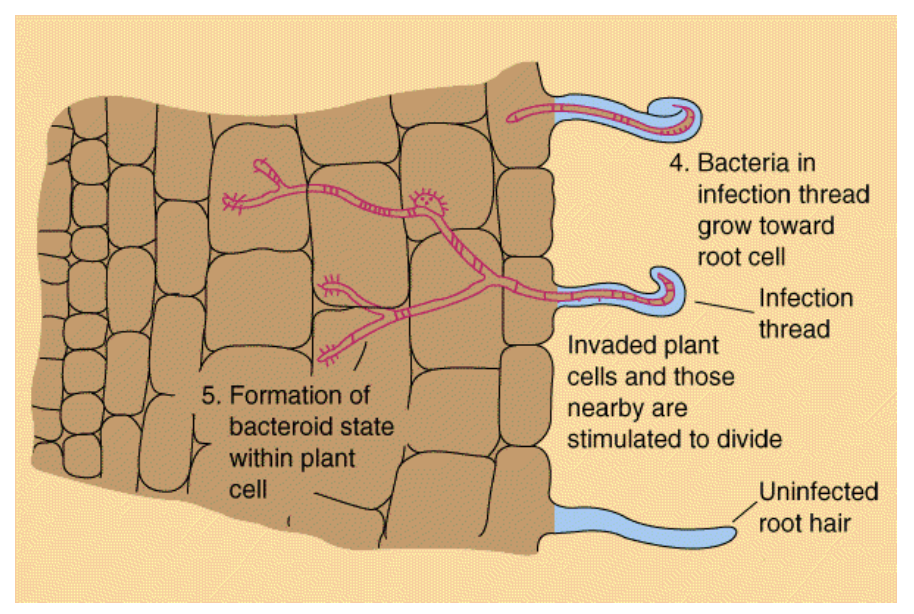
nodule formation
adhesion of Rhizobium bacteria to root hair
Infection: invagination and curling of root hair
Bacteriod development in vesicles in root cortex
Bacteroid-induced cell division of cortex cells forming a nodule
leghemoglobin
Nodules are red due to _____:
In culture Rhizobium are only able to fix N2 under microaerophilic conditions
Although the bacterium needs some O2 for nitrogen fixation, its nitrogenase is inactivated by high levels of O2
O2 levels are kept low by the O2 binding protein _____, a plant produced, iron containing protein found in healthy nodules
microaerphilic
In culture Rhizobium are only able to fix N2 under ______ conditions
bacterium, plant
What does each partner get?
_____: plant provides a steady source of carbohydrates and organic acids
____: gets nitrogen in a form it can use (Amides and Ureides) from the bacterium. This gives the plant a significant growth advantage in nutrient poor soils. This advantage is so great, seed companies sell soybean seeds already innoculated with Rhizobium