Ch.3 - DNA and Ch.4 -Tissues
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What type of cells found in skeletal muscle tissue? Where is it found?
Muscle fiber/Skeletal Muscle cells
Found; skeletal muscles
What structures does skeletal muscle tissue have? Voluntary or involuntary?
Striated and multi nucleated (large, visible cells)
Voluntary
What is the function of skeletal muscle tissue?
Movement, protection, and generates heat
What type of cells found in cardiac muscle? Where is it found?
Cardiocytes; single nucleus
Found; heart/blood vessels
What unique structure does cardiac muscle tissue have?
Intercalated disc: produce synchronized contractions for blood pumping
What is the function of cardiac muscle tissue?
Move blood and maintain blood pressure
What type of cells found in smooth muscle tissue? Where is found?
Smooth muscle cells; single nucleus
Found; skin, blood vessel walls, stomach
What are the functions of smooth muscle tissue?
Move food, urine, and reproductive secretions
Control diameter of blood/respiratory vessels and
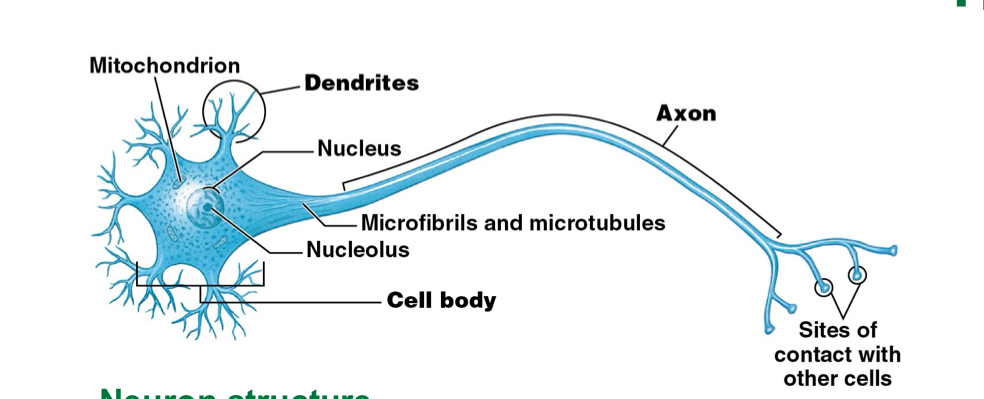
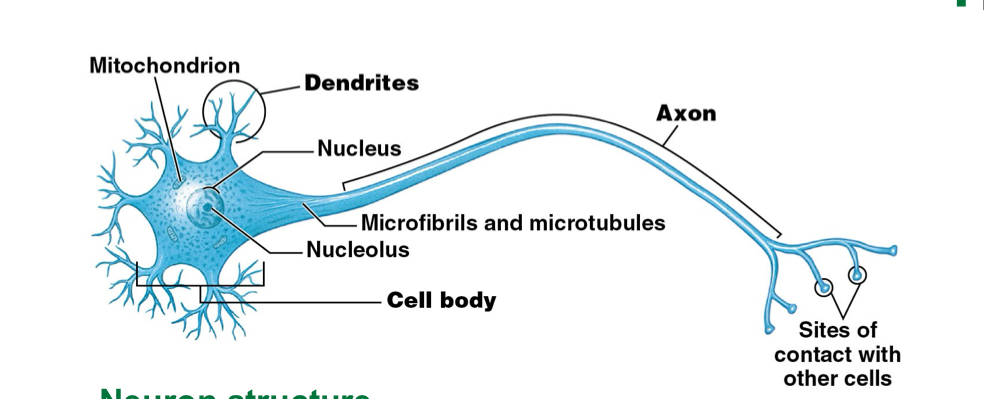
What are the structures of a neuron?
Dendrites; shorter
Axon; longer
Cell body
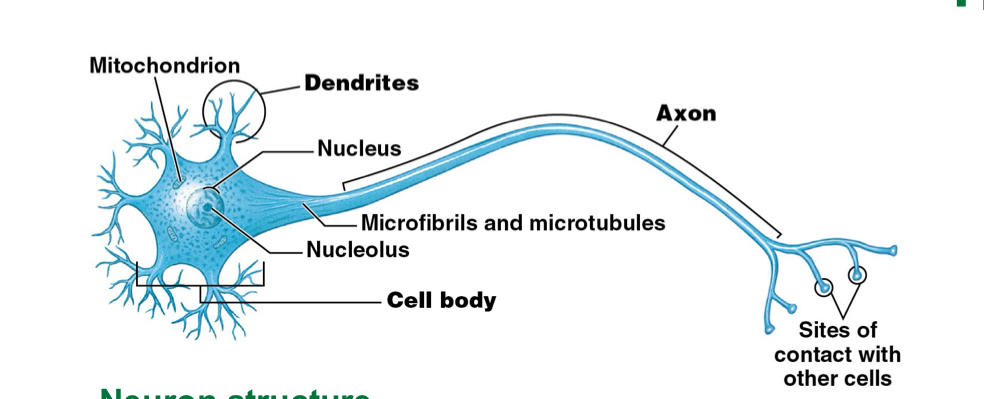
What is the function of dendrites? Axons?
Dendrites: receives information
Axons: sends information to other cells
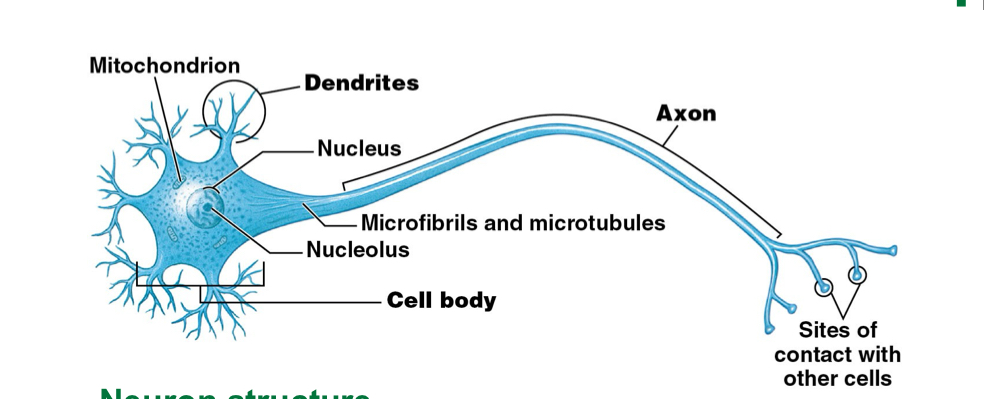
What doe the cell body contain? What is its function?
Nucleus (lacks centrioles, CANNOT divide)
Function: control center and processing
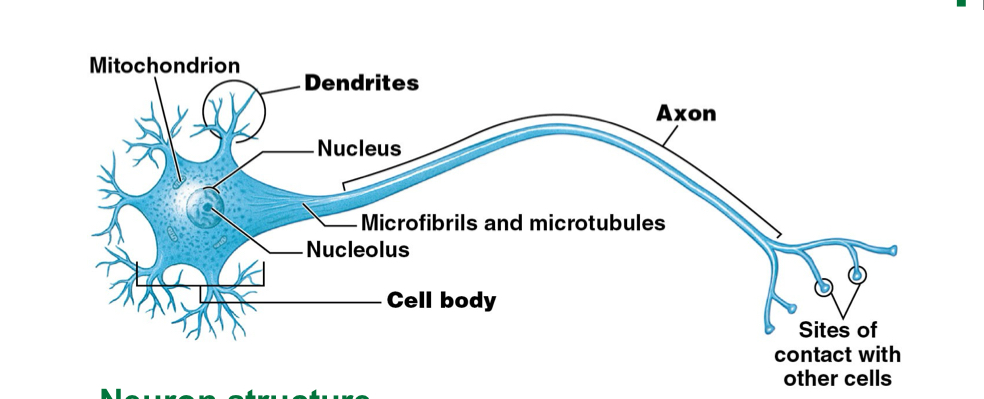
What are the two types of cells found in nervous tissue?
Neuron cells
Glial cells/ Neuroglia
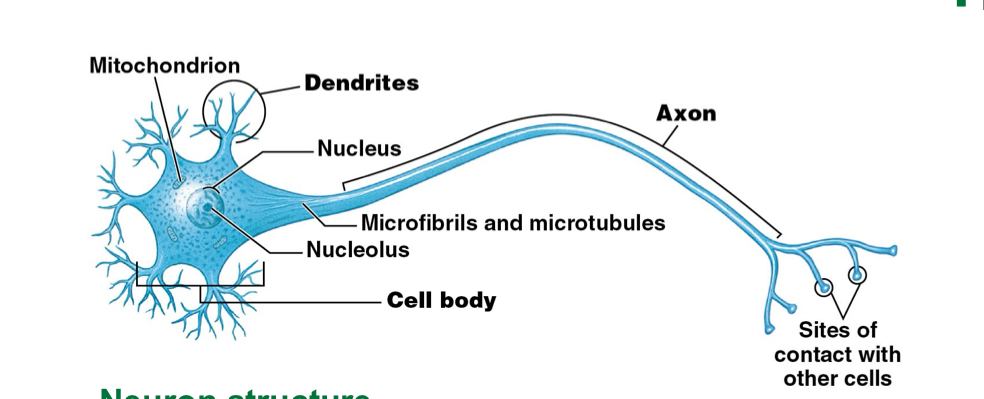
What is the function of the neuron cell?
Transfer and process information
Longest cells in body
What is the function of the neuroglia or glial cells?
Maintain physical structure
Repair framework
What are the characteristics of epithelial tissue?
Avascular layers (no blood vessels)
Cover exposed surfaces
Line internal cavities
Gland cells
What is a gland versus a gland cell?
Gland: many gland cells
Gland cell: 1 cell
What cells are glands usually made up of?
Cuboidal cells; secretory
What are the two types of glands?
Exocrine glands
Endocrine glands
How do exocrine glands secrete? Example?
Secrete directly onto external surface/duct
sweat
How do endocrine glands secrete?
Secretes to interstitial fluid
THEN, distributed by blood vessels
What are the 3 types of exocrine gland secretion?
Merocrine secretion
Apocrine secretion
Holocrine secretion
How does merocrine secretion work? Example?
Product in vesicles will move to apical surface and release by exocytosis
Mucin/Mucus
Ex: salivary gland secretion
How does apocrine secretion work? Example?
A piece of
Places product on apical surface and pinches/breaks off releasing cytoplasm with secretory product
Mammary glands (merocrine + apocrine)
How does holocrine secretion work?
Whole, entire
Destroys cell by bursting, releasing secretions
sebaceous gland (hair)
cells recovered using stem cells
What is the apical surface of a cell?
In contact with Lumen (outside space)
Microvilli/Cilia attached
What is the base of a cell? Which are the two types?
Base: attached to underlying tissue
Basal (basement membrane): bottom side
Lateral: side of cell
What does polarity of a cell refer to?
Some parts of cell exposed to outside, others not
What are the functions of epithelial tissues?
Provide physical protection
Control permeability (secretion)
Provide sensation
Neuroepithelium
Produce specialized secretions
What are the five intracellular connections?
How cells sticks together
Hemidesmosomes
Tight junctions
Adhesion belts
Gap junctions
Desmosomes
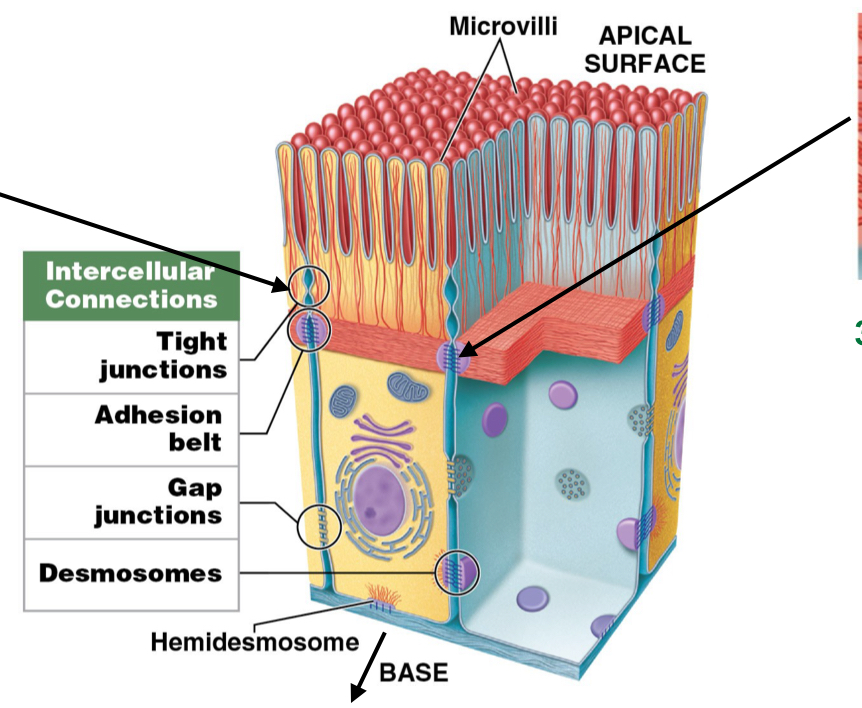
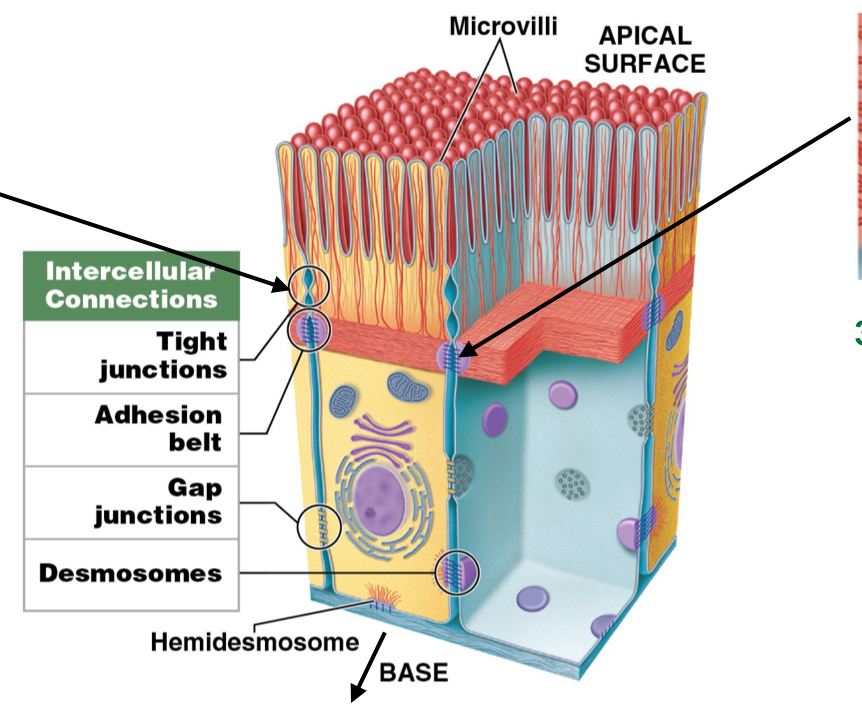
What is the function of hemidesmosomes? Are they attached to cytoskeleton?
Anchor cell membrane of epithelium TO basement membrane
attached to cytoskeleton
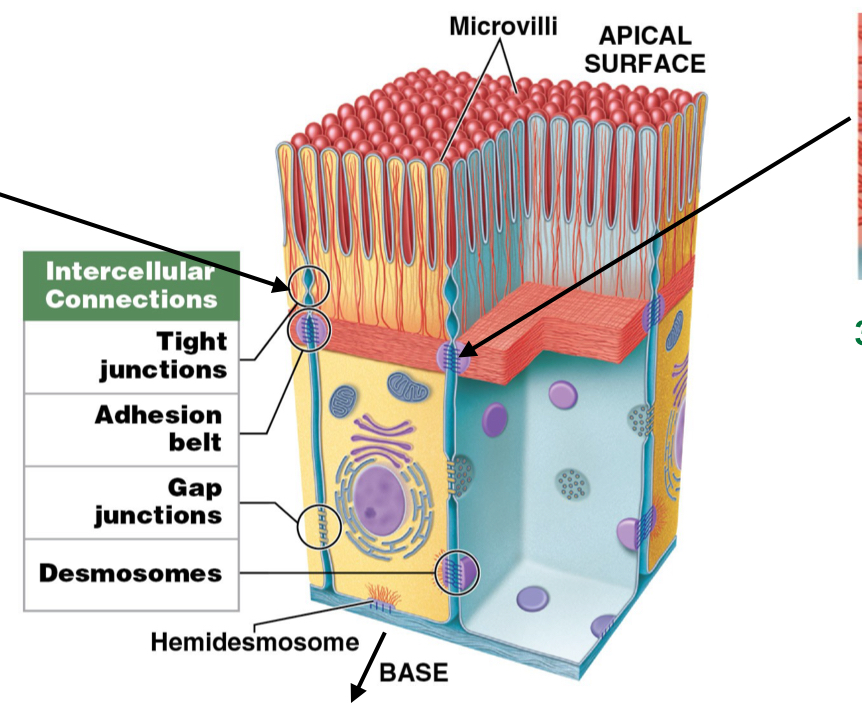
What is the function of tight junctions? Are they attached to cytoskeleton?
Interlocks cell membranes of different cells to each other on APICAL SURFACE
not attached to cytoskeleton
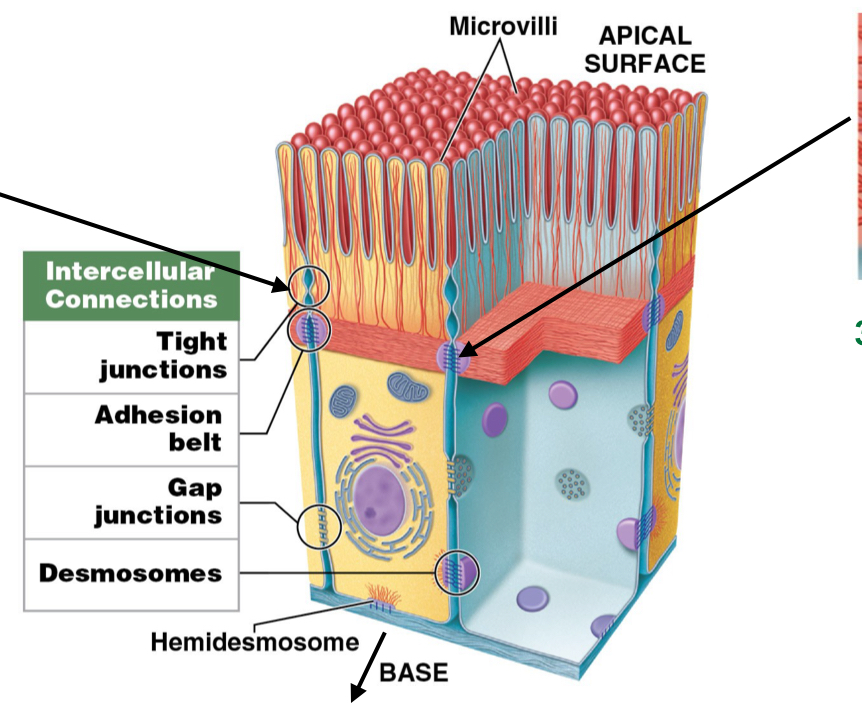
What do tight junctions prevent when two cells are joined together?
Prevents passage of water and solutes between cells (waterproof)
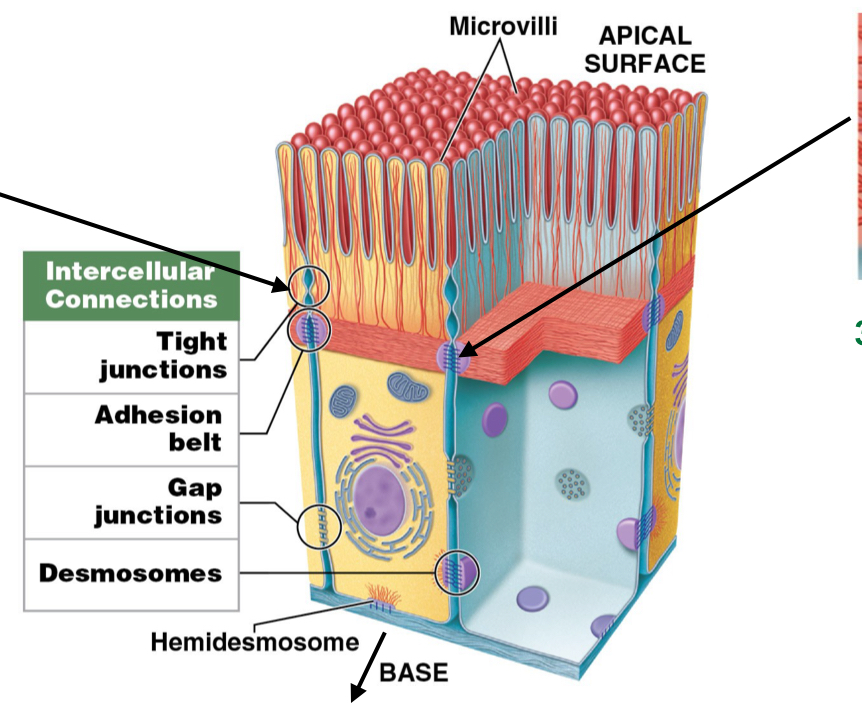
What is the function of adhesion belts? Are they a part of the cytoskeleton?
Strengthen apical region of cells by reinforcing tight junctions
Attached to terminal web (cytoskeleton)
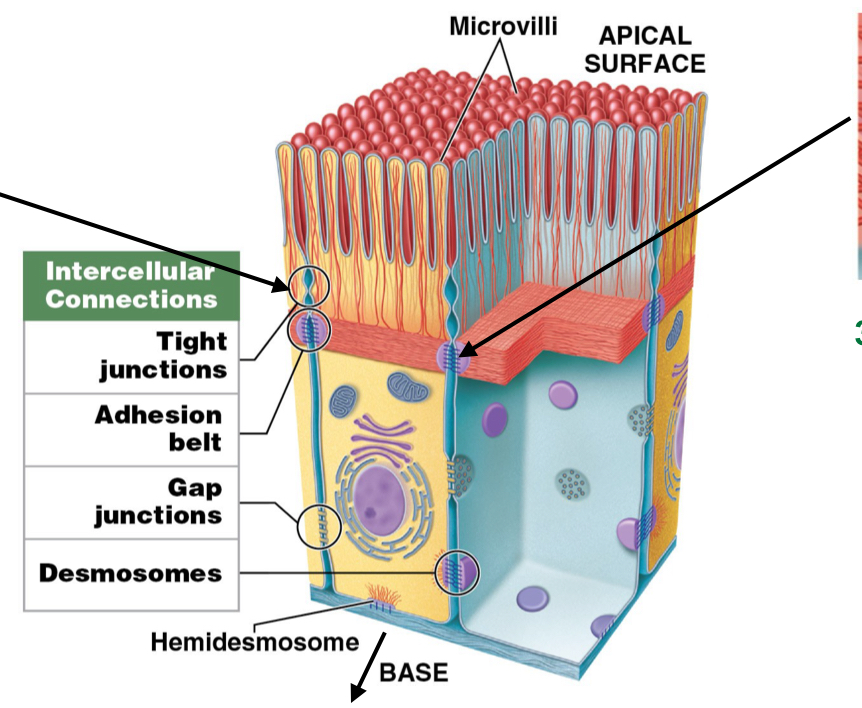
What is the function of gap junctions?
Assist chemical communication to coordinate secretion or beating cilia
How do gap junctions form?
Held together by interlocking transmembrane proteins: Connexons
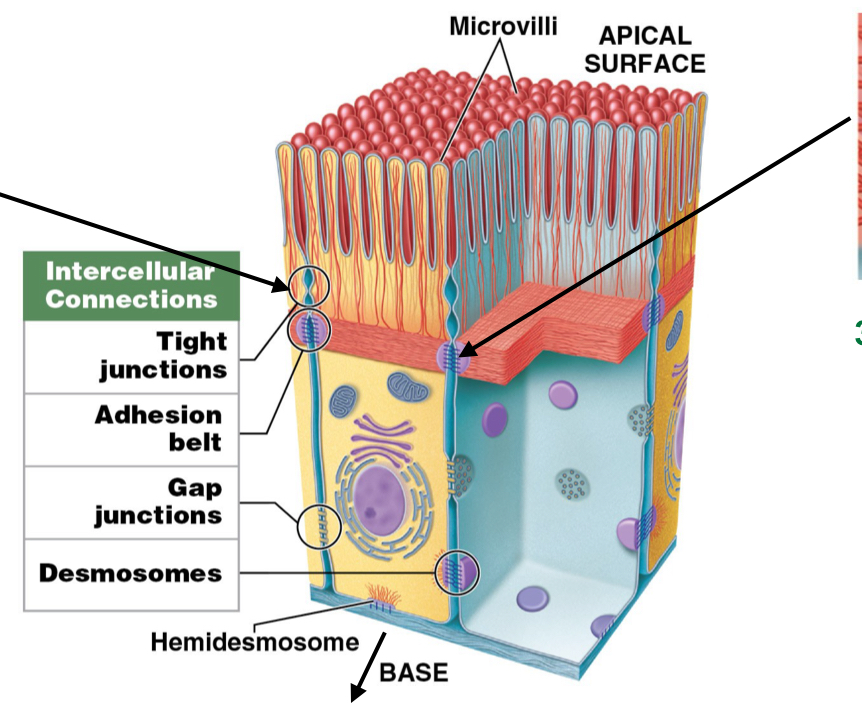
Where are gap functions found?
Intercalated discs in cardiac muscle
assist in beating/contractions of heart
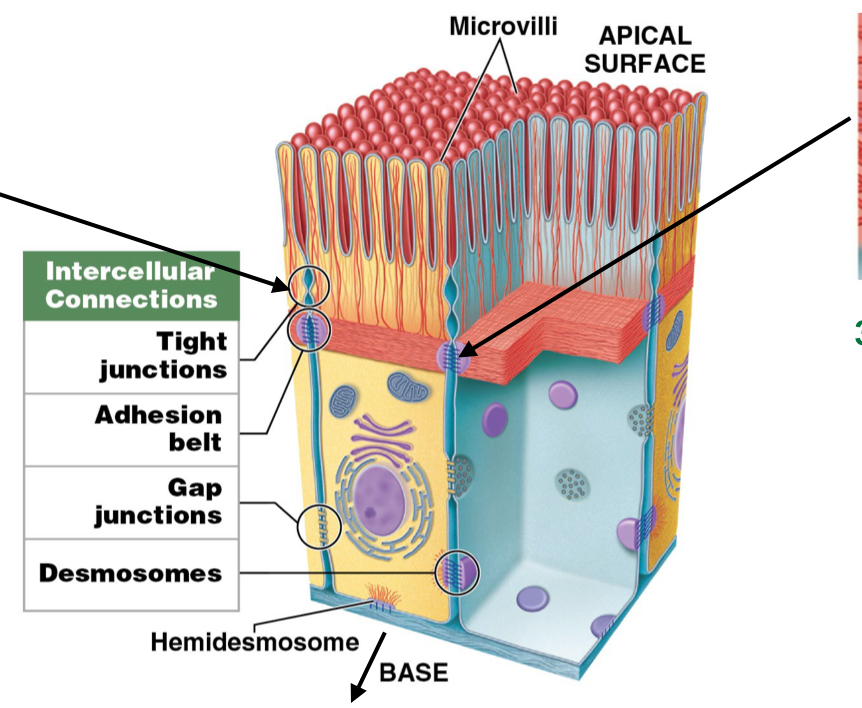
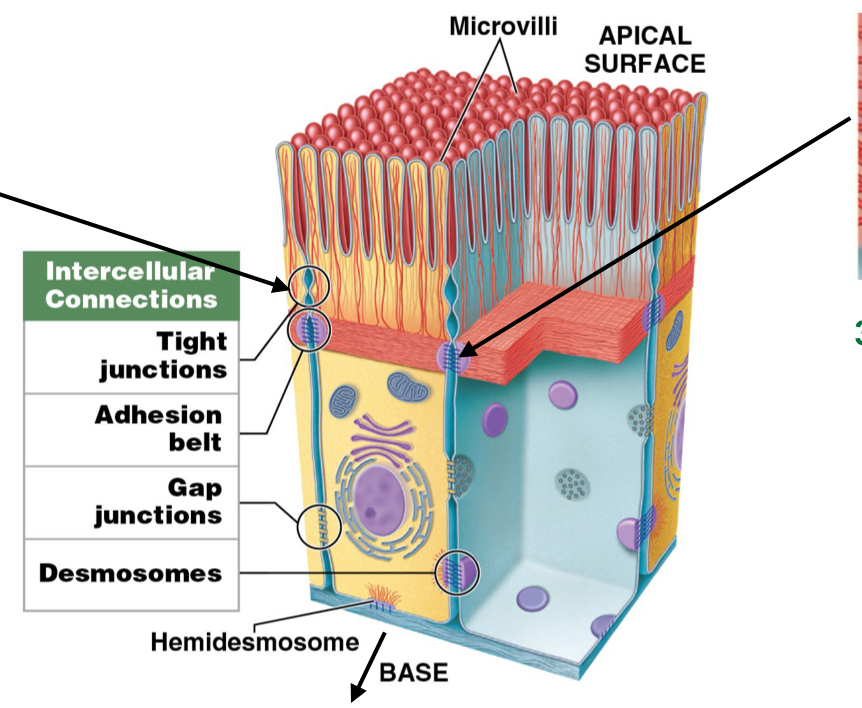
What is the function of desmosomes? What do they use to do so?
Provide attachment by interlocking lateral side of cell (attach cells to each other)
Use CAM, Cell Adhesion Molecules (glue)
What is mesothelium?
Simple Squamous epithelium
Lining ventral body cavity (pericardial, pleural)
What is endothelium?
Simple squamous epithelium
Lining heart and blood vessels
What is the function of simple squamous epithelium? Where is it found?
Function: absorption, diffusion, reduction of friction
Found; peritoneum, lungs
Where is keratinized stratified squamous epithelium found?
Packed with keratin, layer of dead cells
Found; skin, hair, nails
Where is nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium found?
Found; lining of oral cavity, vagina, esophagus (lots of friction)
What is the function of simple cuboidal epithelium? Where is it found?
Function: absorption and secretion
Found; lines kidneys and thyroid gland
What does stratified cuboidal epithelium exist as?
Rare
Exists as sweat glands and mammary glands
What is unique about transition epithelium? Where is it found?
Stretch or relax
Different kinds of cells
Found; bladder, ureters
What is the functions of simple columnar epithelium? What structure does it have?
Functions: absorption and secretion
Microvilli: for absorption OR Cilia: for movement of mucus
Where is simple columnar epithelium found?
Stomach, intestines, gallbladder
Where is pseudostratifed columnar epithelium found? What do they have?
Found; trachea
Have cilia: movement
What other cells may stratified or pseudostratified columnar epithelium have?
Goblet cells: secrete mucin/mucus