Comprehensive HPV and Cervical Cancer Screening & Pathogenesis
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is the global prevalence of HPV?
HPV is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections worldwide. The WHO estimates that ~80% of sexually active individuals will be infected at some point in their lifetime.

Describe the progression of HPV infection.
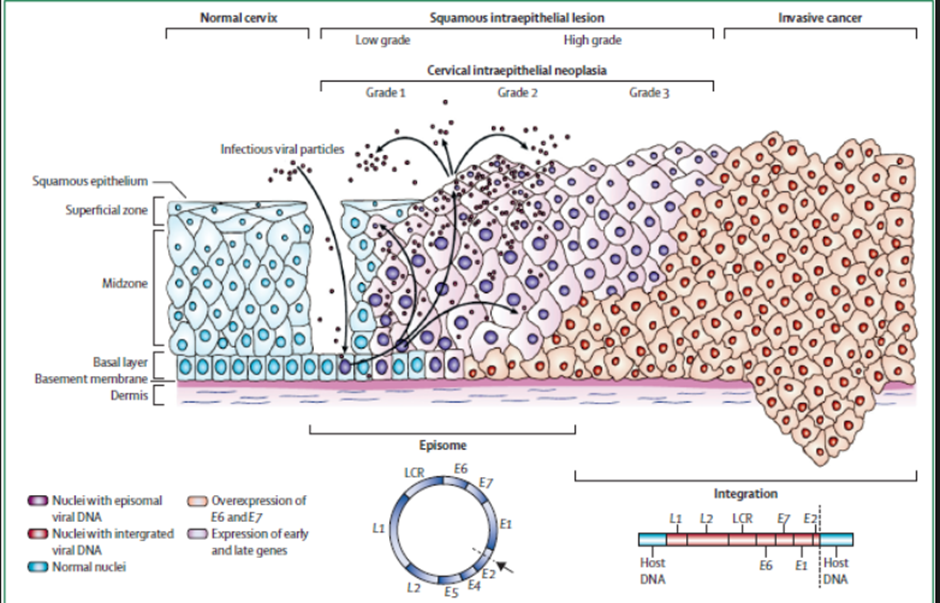
1. Infection - Virus infects cervical epithelial cells. 2. Transient infection - Immune system clears virus (regression). 3. Persistent infection - Leads to CIN (Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia). 4. Invasion - Breach of the basement membrane → invasive cervical cancer.
Which high-risk HPV types cause ~70% of cervical cancers?
HPV 16 (most carcinogenic, highest progression risk) and HPV 18.
How do E6 and E7 cause cancer?
E6 binds and degrades p53, preventing apoptosis and DNA damage repair. E7 binds and inactivates pRb, removing cell-cycle checkpoint → uncontrolled proliferation.
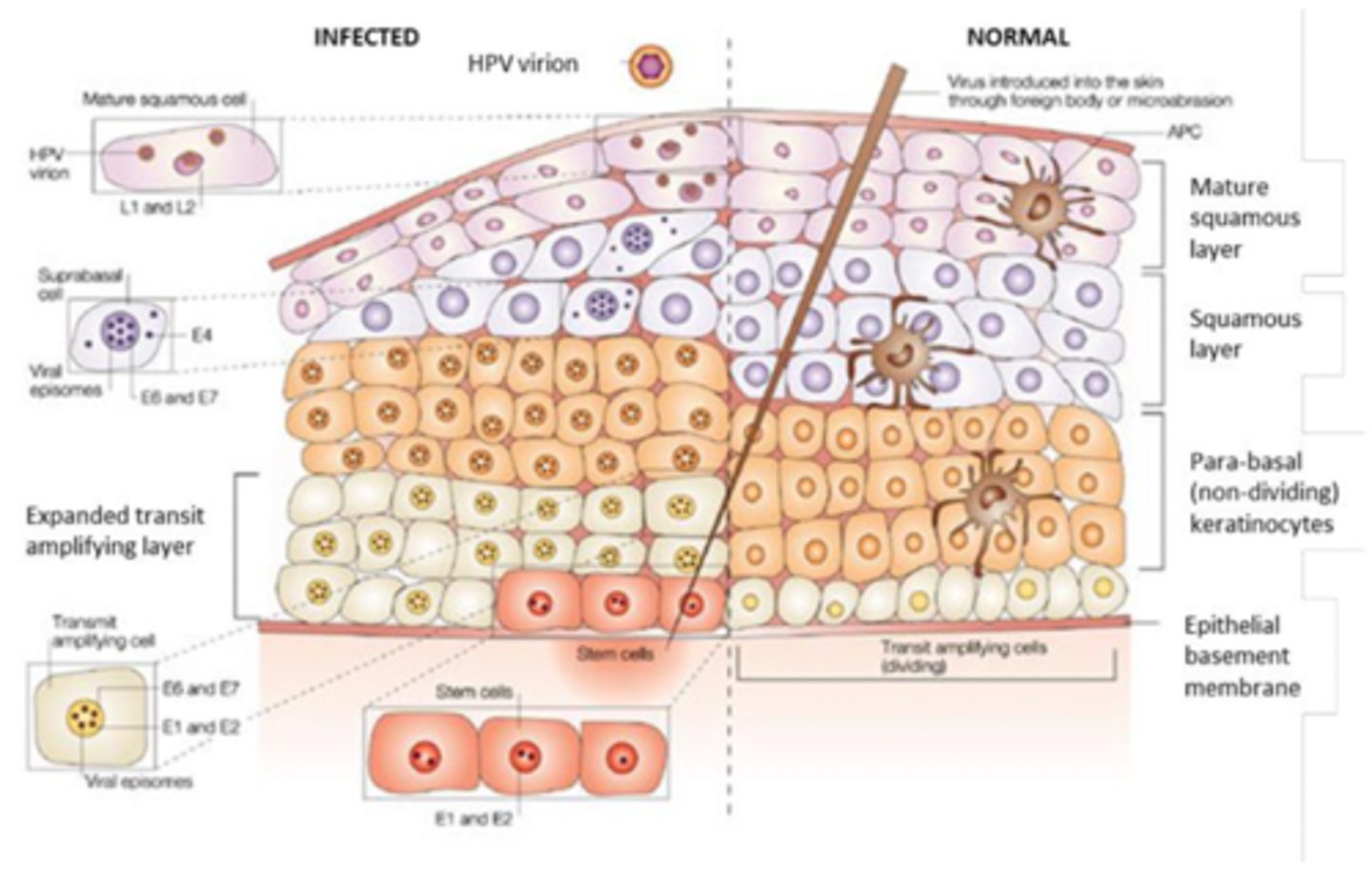
What is the significance of viral integration?
In early infection, HPV DNA is episomal (circular). In cancer, HPV DNA integrates into the host genome, leading to permanent, high-level expression of E6 and E7.
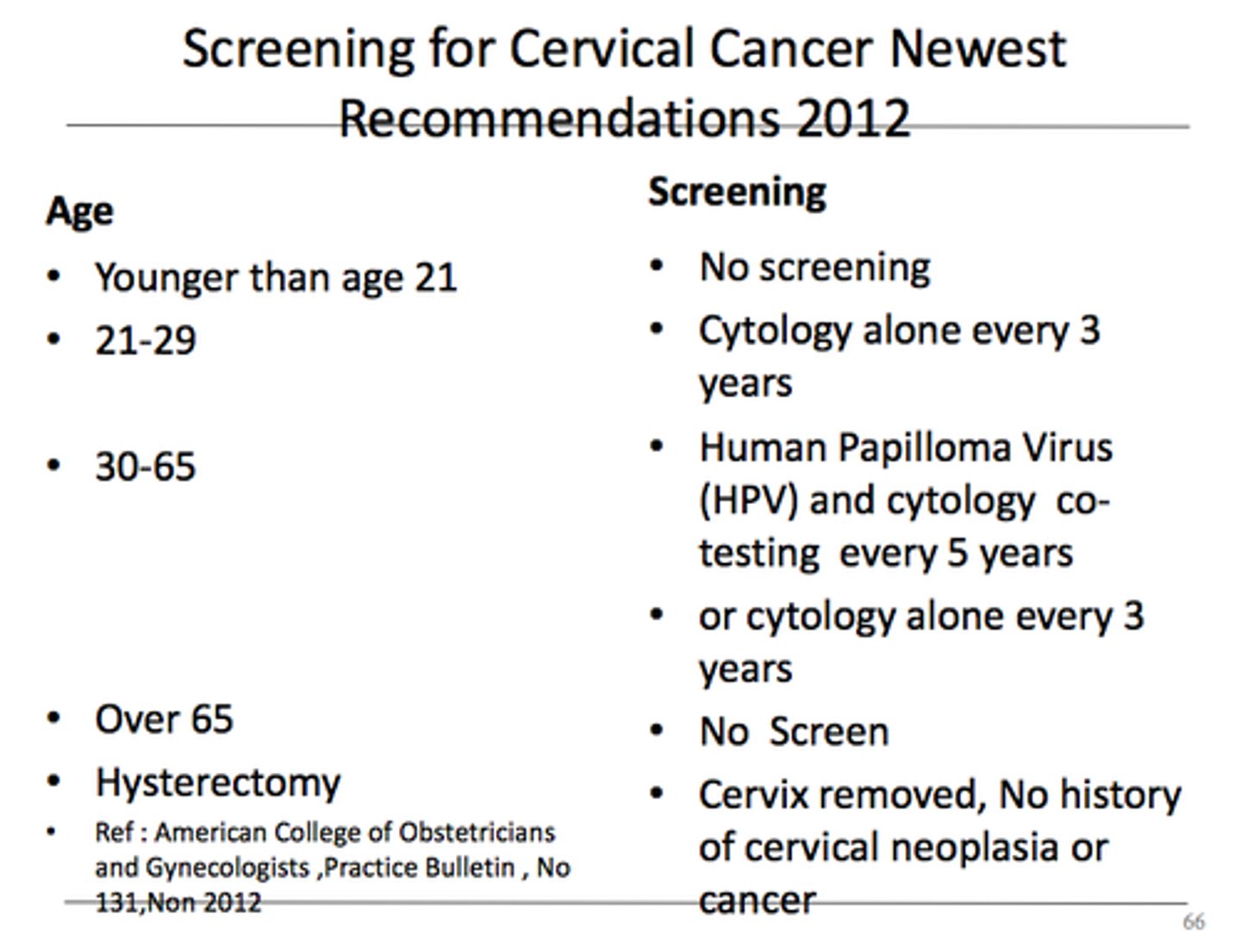
What is the UK screening workflow for cervical cancer?
1. HPV test first. 2. HPV negative → routine recall (3-5 years). 3. HPV positive → cytology triage. 4. Abnormal cytology → colposcopy. HPV 16/18 positive patients may be referred directly to colposcopy.
How does HC2 detect HPV?
HC2 is a signal amplification assay where RNA probes bind HPV DNA to form RNA-DNA hybrids, which are captured by antibodies and detected via chemiluminescence.
What is the main disadvantage of HC2?
HC2 does not provide genotyping; it detects high-risk HPV presence but cannot identify specific types (e.g., 16 or 18).
Why is PCR used in HPV testing?
PCR is used for target amplification, providing very high sensitivity, allowing HPV genotyping, and detecting low viral loads.
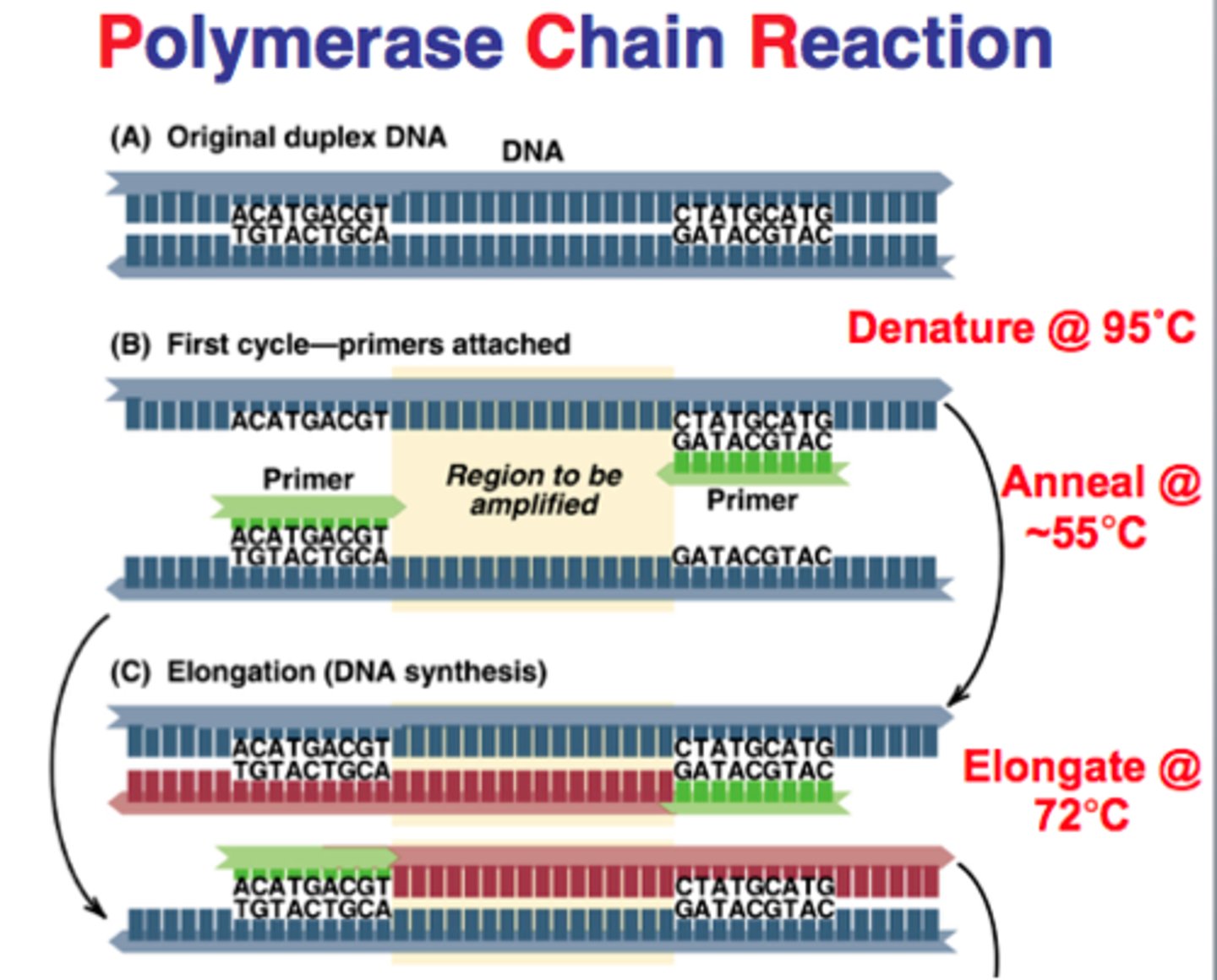
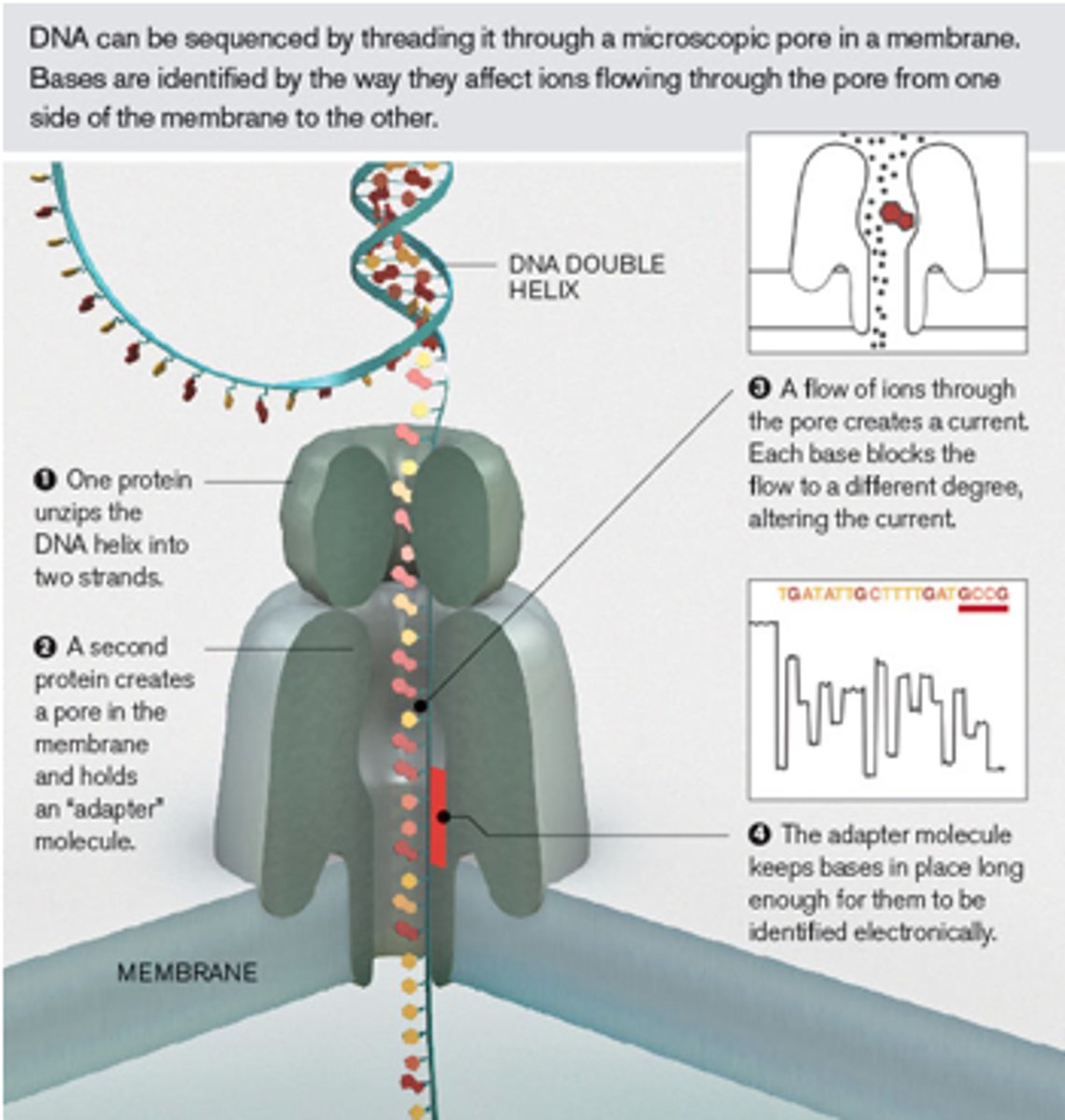
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)?
Advantage: High-throughput NGS can process massive amounts of genetic data simultaneously, providing detailed molecular insight. Disadvantage: Requires complex bioinformatics and has an extended turnaround time.
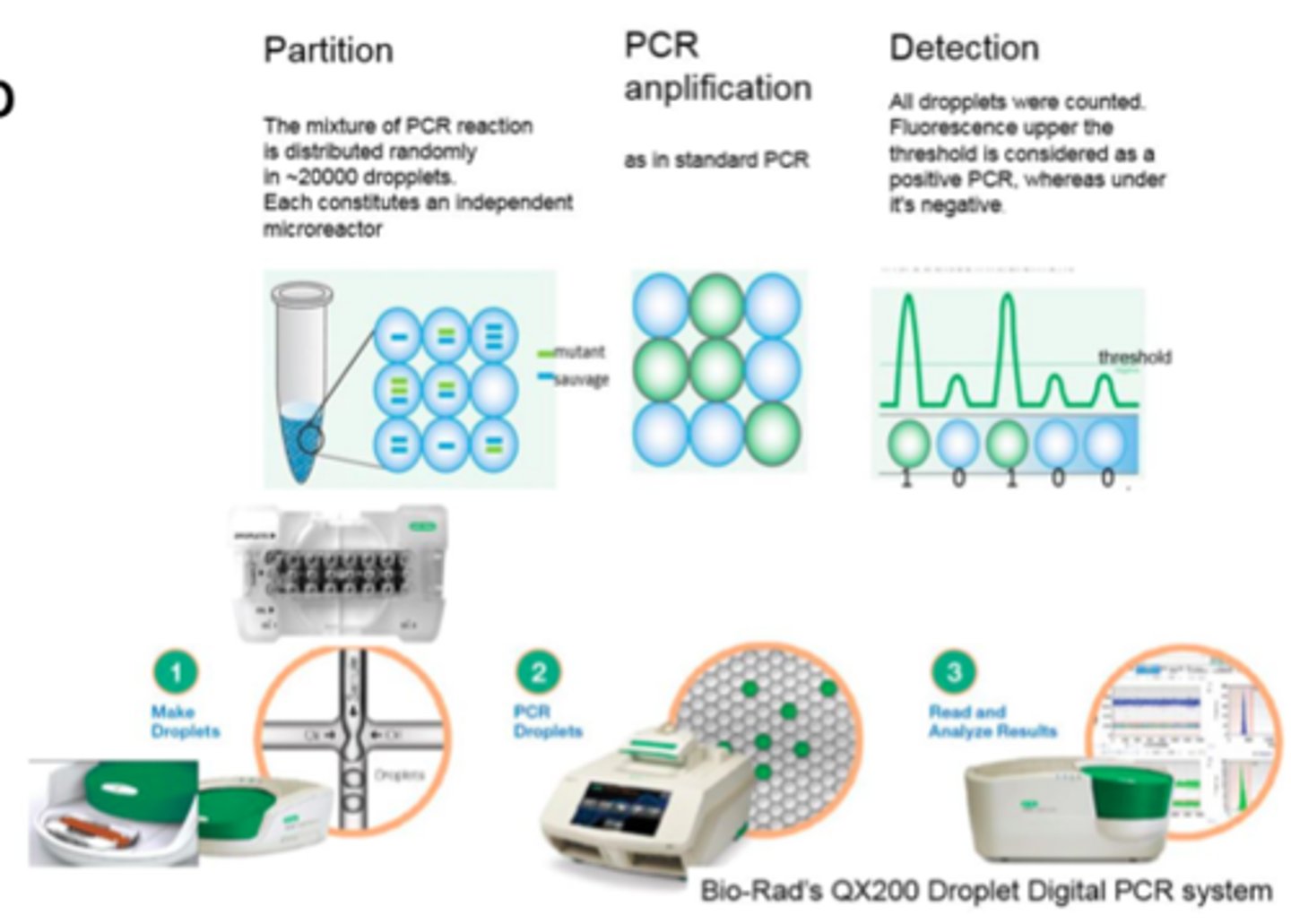
What is ddPCR?
Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) partitions the sample into thousands of oil droplets where PCR occurs in each droplet, allowing for absolute quantification of viral copy number.
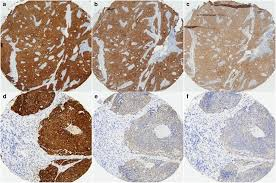
Why is p16 a surrogate marker for HR-HPV?
E7 inactivates pRb, causing the cell to overproduce p16. Strong, diffuse brown staining indicates active hrHPV-driven cell-cycle dysregulation.
What is the role of L1 Virus-Like Particles (VLPs) in vaccines?
E7 inactivates pRb
Cell compensates by overproducing p16
Strong, diffuse brown staining indicates active hrHPV-driven cell-cycle dysregulation
p16 reflects the cellular effect of HPV, not the virus itself.
What are the differences between HPV vaccines?
Bivalent: HPV 16, 18; Quadrivalent: 16, 18 + 6, 11 (warts); Nonavalent (Gardasil 9): 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52, 58 + 6, 11.

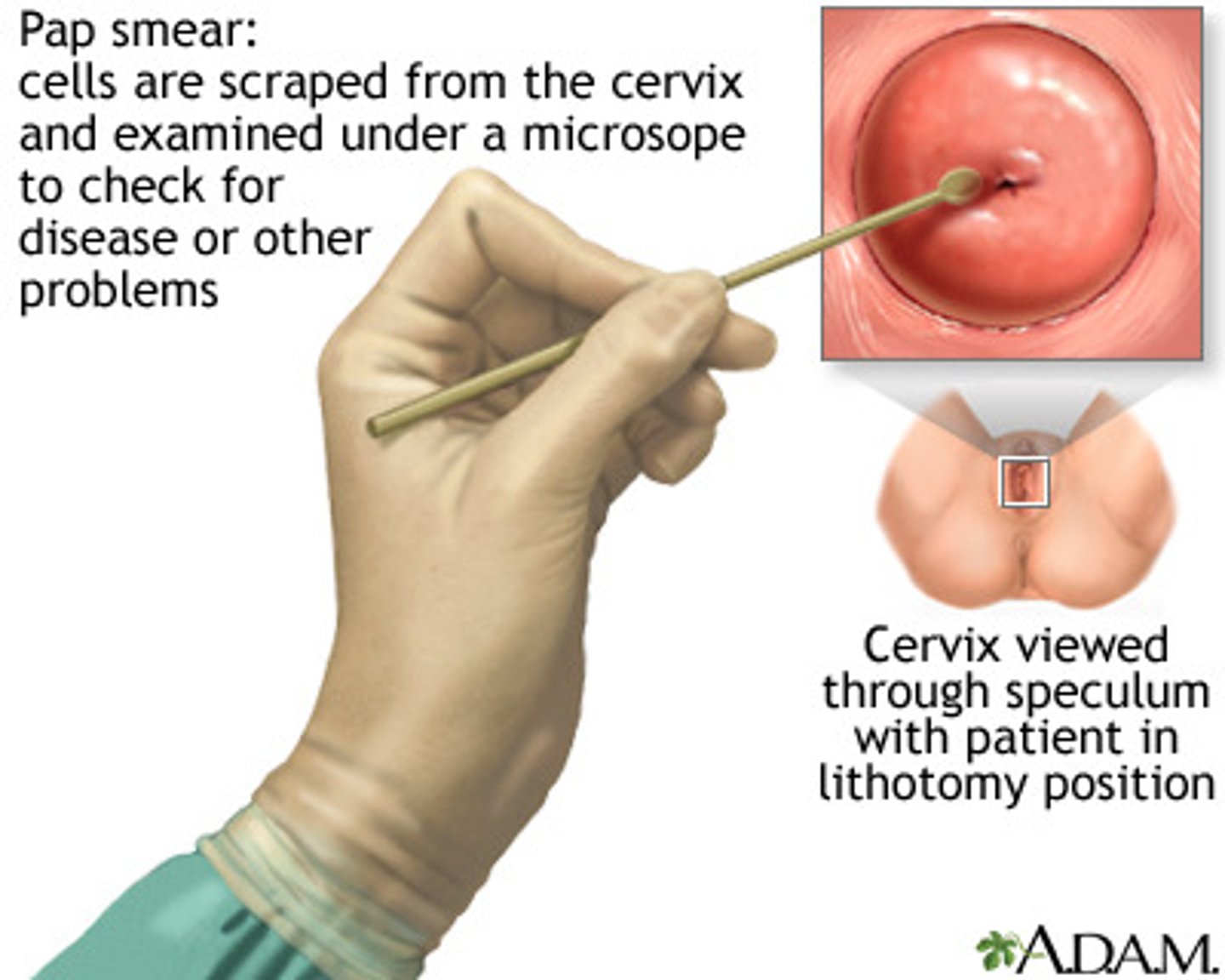
What are the advantages of HPV testing over cytology?
1. Objective (machine-read, not subjective). 2. Higher sensitivity. 3. High negative predictive value (HPV negative = very low cancer risk for years).
What are the disadvantages of HPV testing?
1. Lower specificity (detects transient infections → anxiety/overtreatment). 2. Higher cost than cytology.
What should be done if hrHPV is positive but cytology is negative?
Repeat testing at 12 months to allow time for immune clearance.
What is the one-line exam strategy for HPV testing?
Sensitivity/viral load → PCR or ddPCR; Whole-genome detail → NGS; Clinical triage/activity → p16 IHC.