Anatomy of the Urinary System
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is the structure below the pelvic floor called?
The perineum.
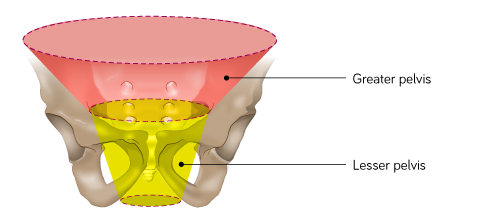
What two regions can the pelvis be separated into?
Greater (false) pelvis and Lesser (true) pelvis
What 7 structures make up the male reproductive system?
Testes
Epididymides
Ductus deferentes
Seminal vesicles
Ejaculatory ducts
Prostate
Bulbourethral glands
What 4 structures make up the female reproductive system?
Vagina
Uterus
Fallopian tubes
Ovaries
What is the role of the kidneys?
Excrete waste products
Filter blood and produce urine
Controls water volume, ion concentrations and acid/base balance of blood
Outer layer of tissue in the kidney is the _____
Cortex
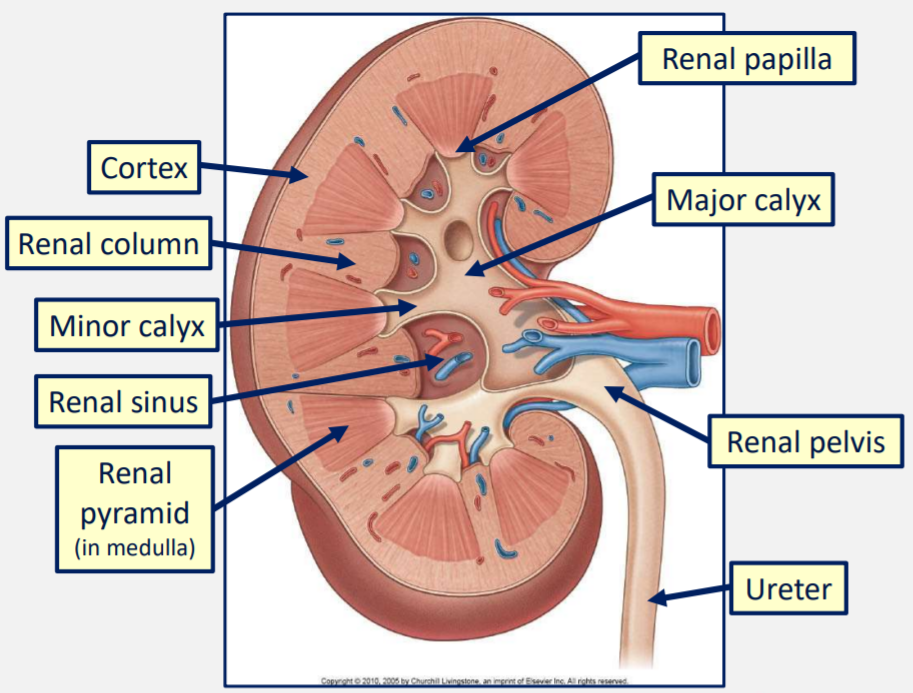
Inner layer of tissues in the kidney is the ______
Medulla
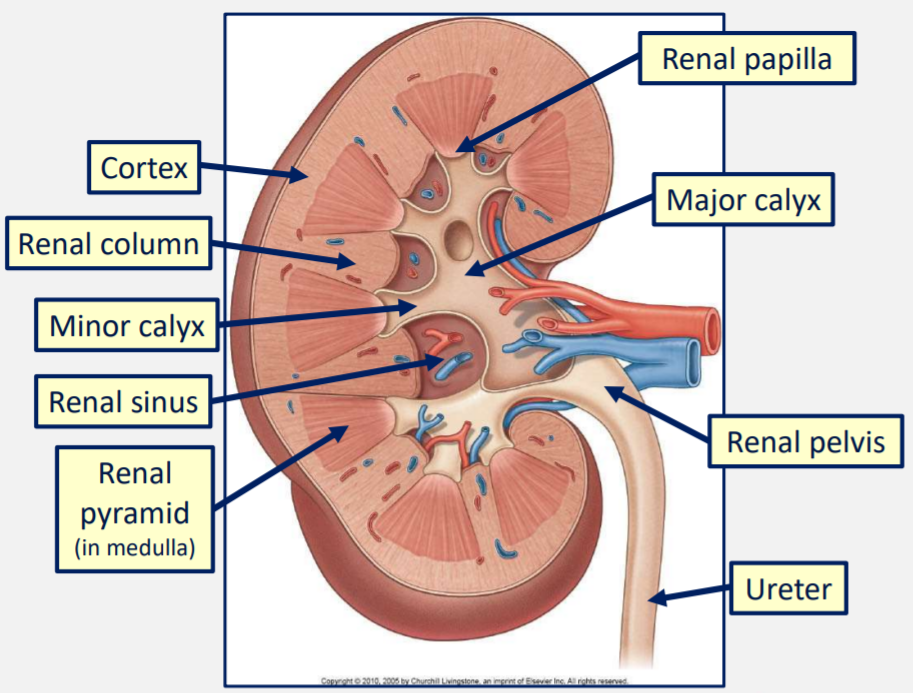
The pyramids of the cortex in the kidney drain into _____________
Minor calyces
2-3 minor calyces then drain into each of the 2-3 major calyces
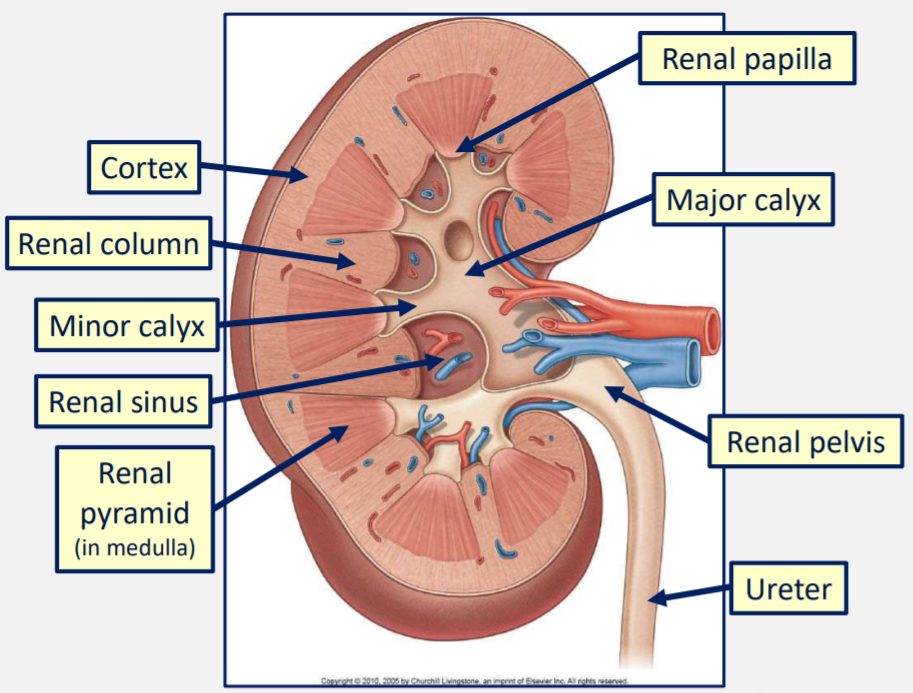
What do the major calyces of the kidney drain into?
The renal pelvis
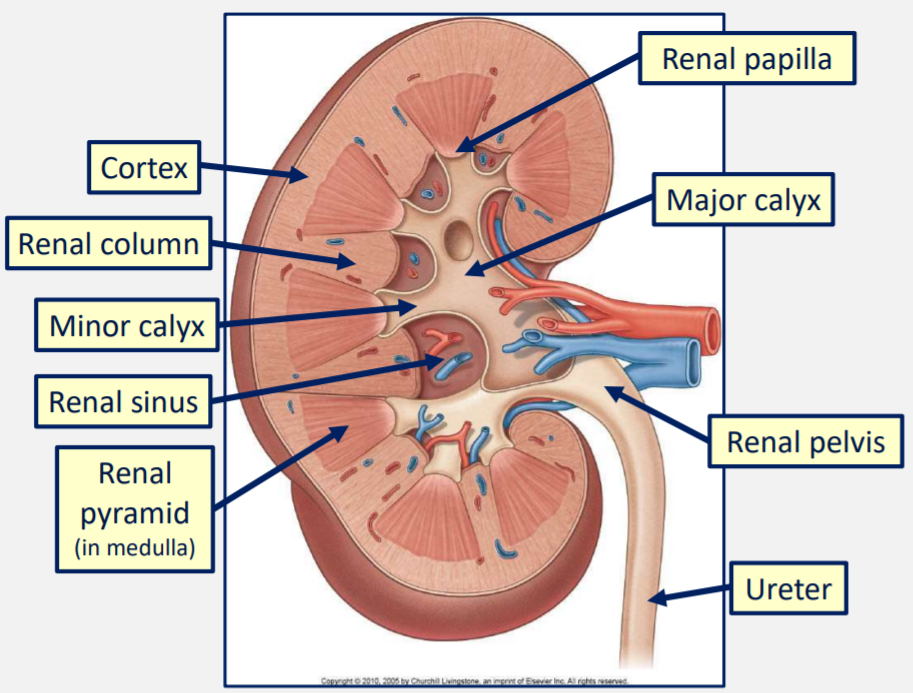
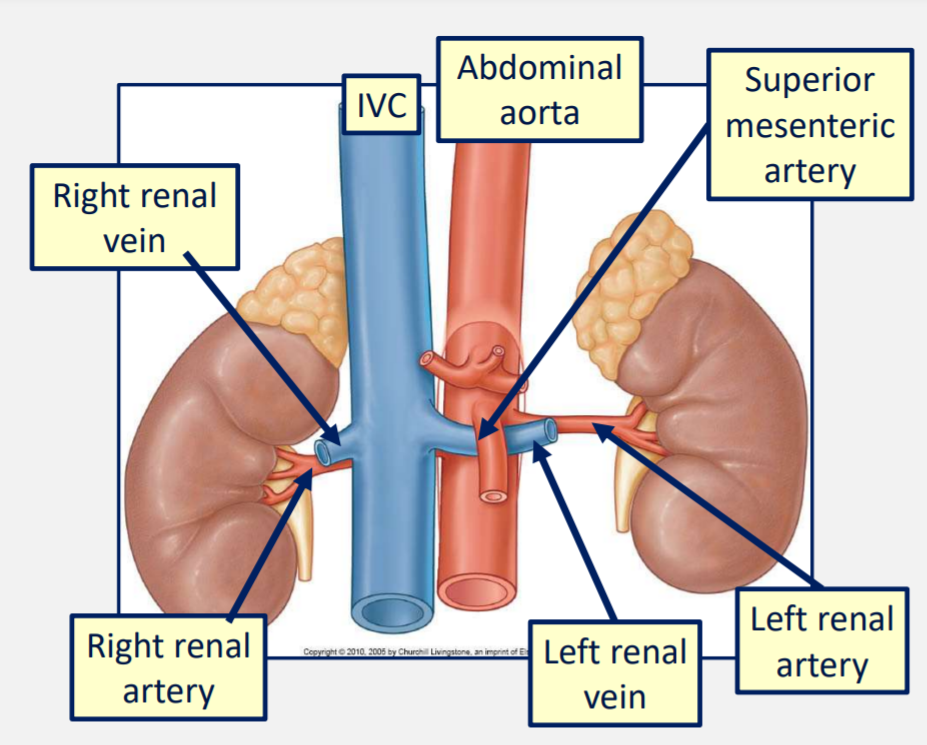
What structures are found at the hilum of the kidney?
Renal vein
Renal artery
Ureter
Lymphatics and sympathetic
Blood being filtered passes through The Nephron. What structures make up the Nephron in a kidney?
Blood passes through knots of capillaries called glomeruli.
Glomeruli are contained within Bowman’s capsule.
Filtrate then passes through the proximal convoluted tubule.
Then it passes through the Loop of Henle
Filtrate then passes through the distal convoluted tubule
Then filtrate enters the collecting duct
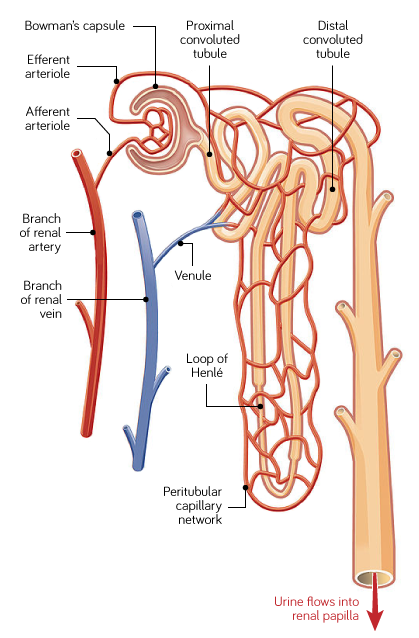
What is the purpose of the glomeruli and Bowman’s capsule?
Allows for almost all the constituents of plasma to be filtered out the blood.
Expect for large proteins (>64kDa) and any cells.
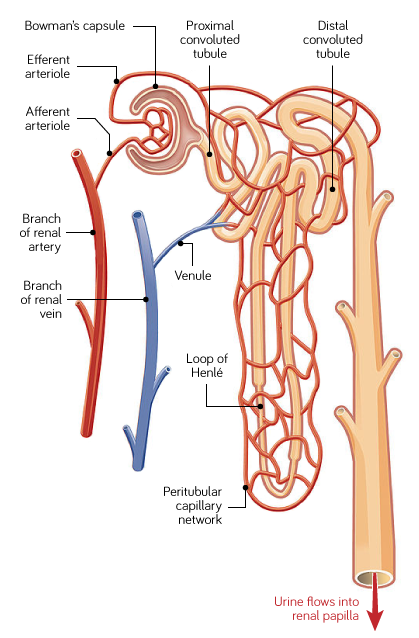
What occurs in the proximal convoluted tubule?
Any substances which are ‘useful’ to the body are reabsorbed (e.g. ions and glucose)
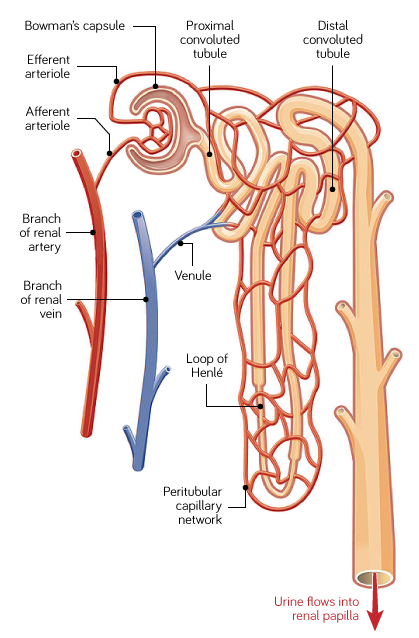
What occurs in the Loop on Henle?
Water is reabsorbed from the filtrate
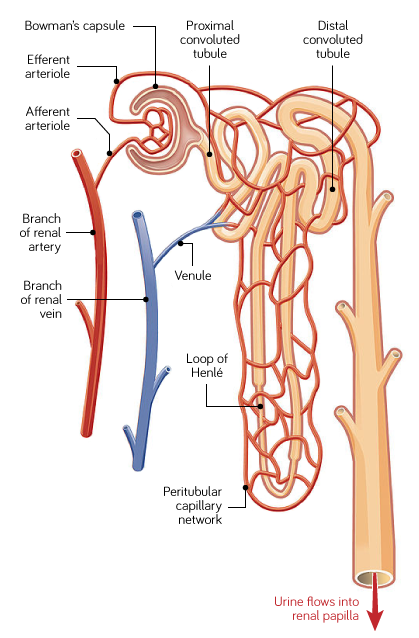
What occurs in the distal convoluted tubule?
Waste products that were not filtered out are secreted into the lumen of the nephron
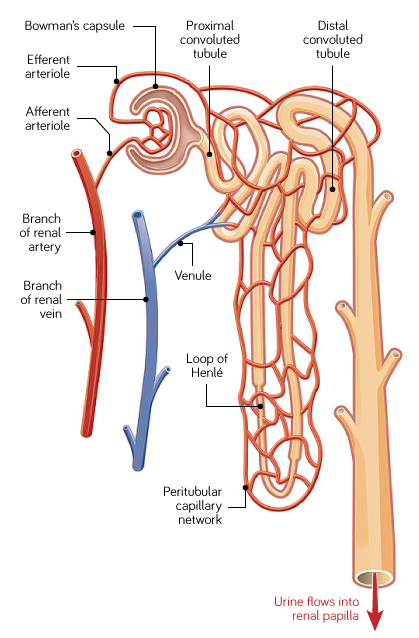
What is the role of the collecting duct?
To absorb water and ions back into the blood.
Absorption of water in the collecting duct determines how much urine is produced as water absorption at the other structures is constant (e.g. Loop of Henle)
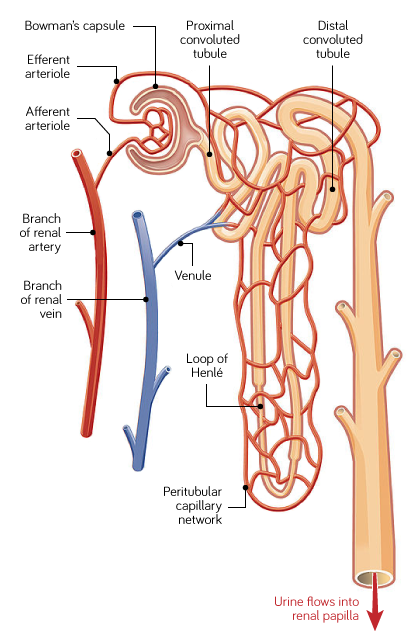
How is water reabsorption in the Collecting duct controlled?
Antidiuretic hormone (released by posterior pituitary) makes the collecting duct more permeable to water
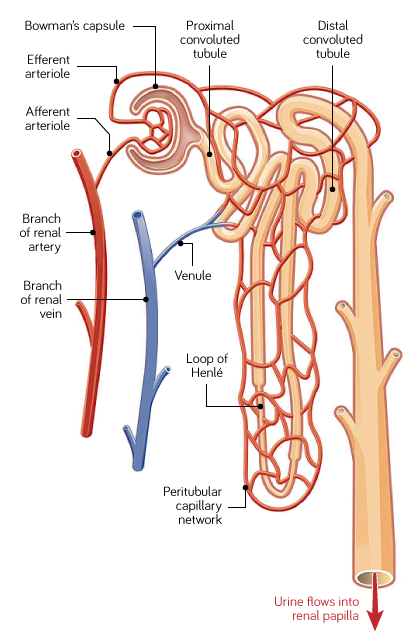
At what level do the renal arteries branch off the abdominal aorta?
Just below the level of L1
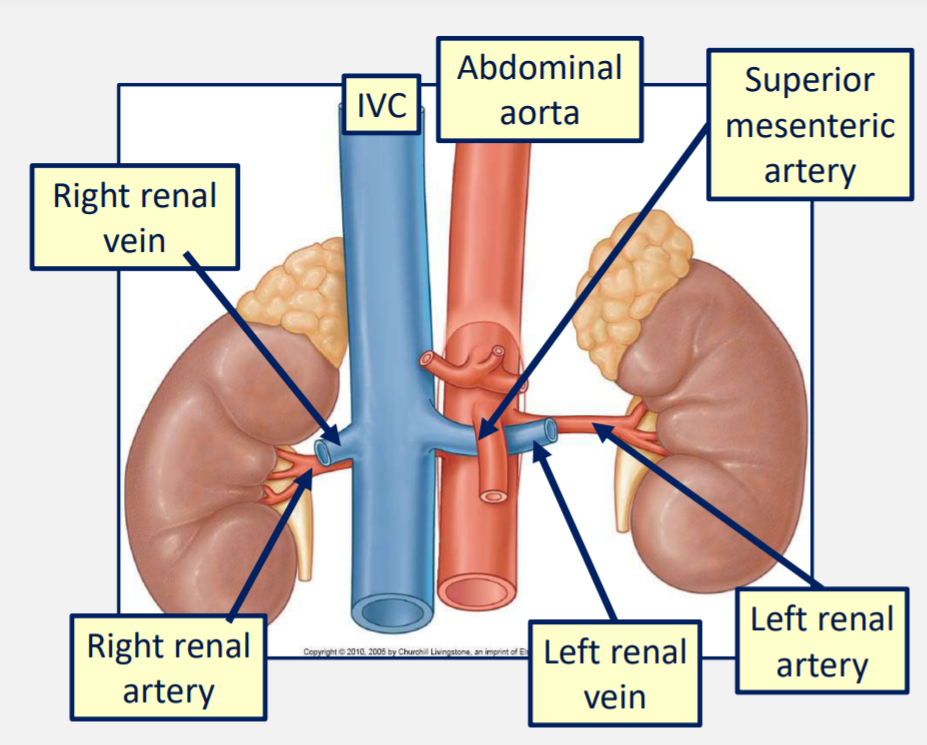
The renal arteries divide further into what vessels?
Afferent arterioles which feed into the glomeruli.
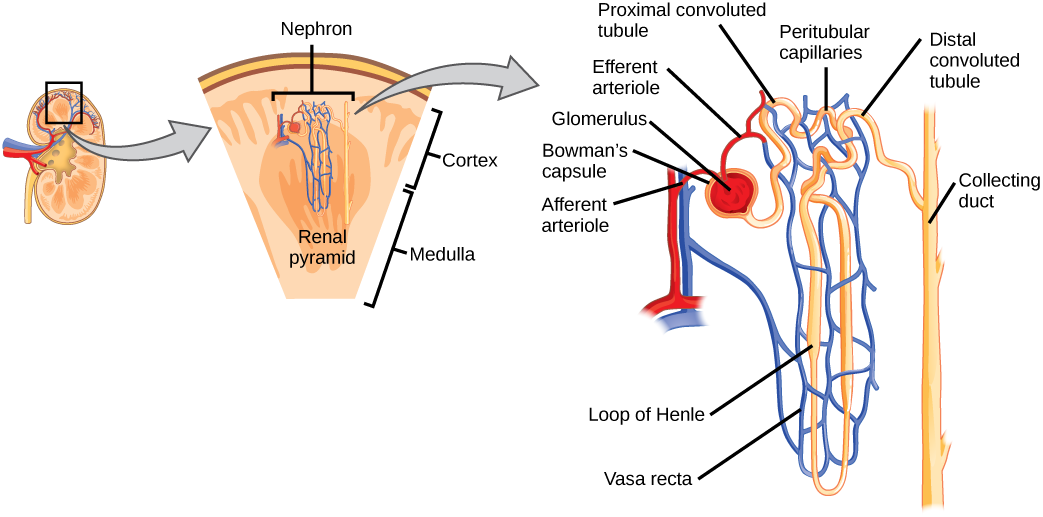
After the glomeruli, the capillaries converge and form what vessels?
Efferent arterioles which wrap around the nephron.
When efferent arterioles wrap around the loop of Henle, they are called what?
Vasa recta.
What do the efferent arterioles (and vasa recta) drain into?
Renal veins which then empty into the inferior vena cava.
The kidneys lie behind what structure which coats most abdominal organs and structures?
The peritoneum.
They lie retroperitoneally
What vertebral levels do the kidneys sit at?
Level of T12 to L3
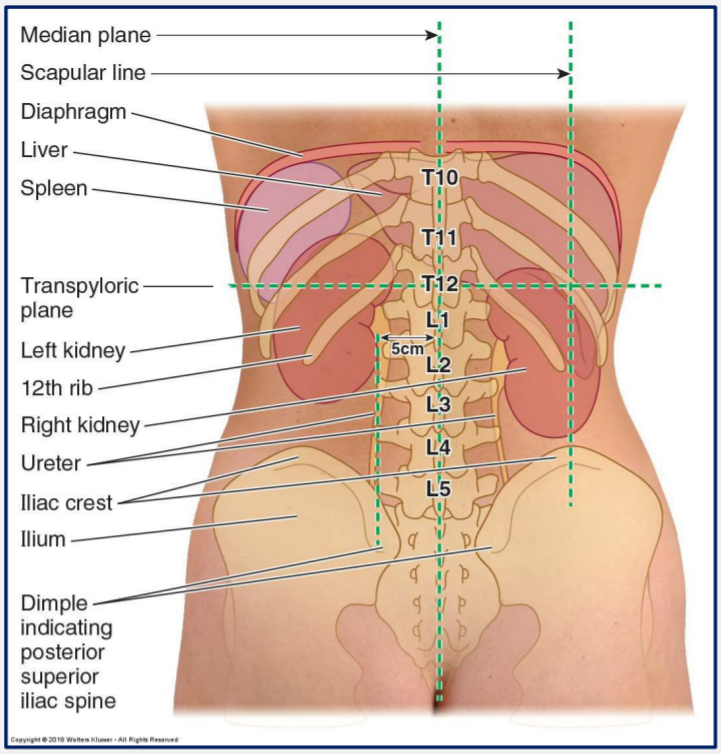
The kidneys are partly protected by which ribs?
Ribs 11 and 12
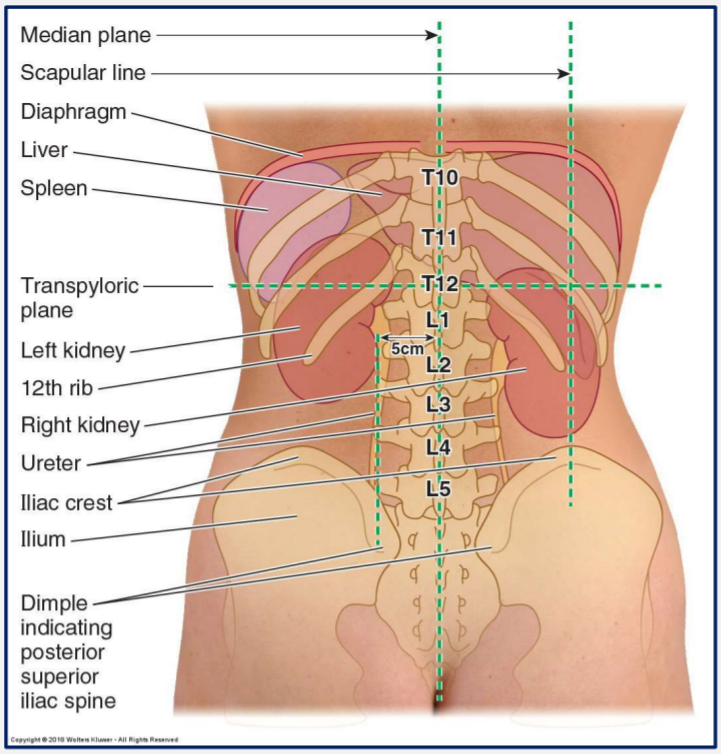
Which kidney lies lower than the other and why?
Right kidney usually lies lower than the left.
This is due to the large right lobe of the liver
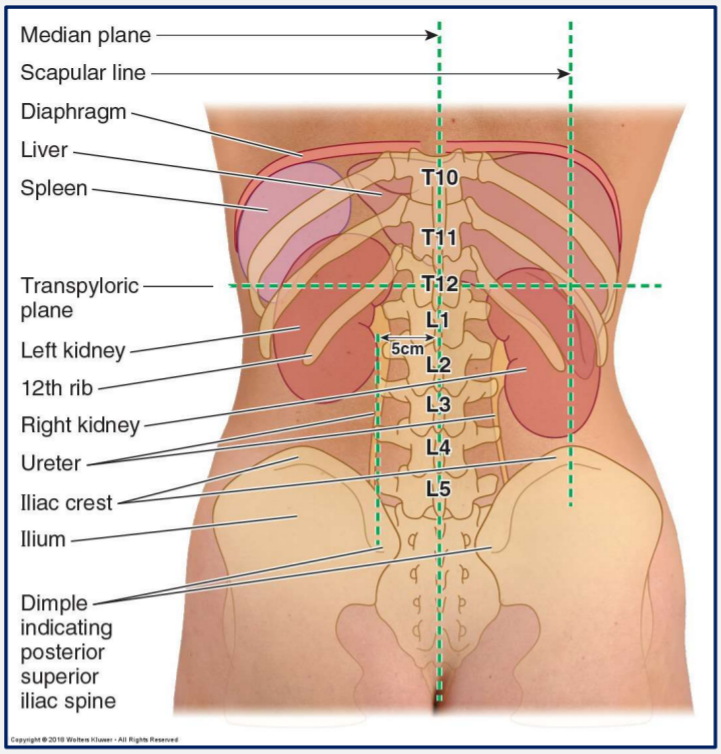
What glands sit on top of each kidney?
Adrenal glands
What are the adrenal glands also known as?
The suprarenal glands (as they are superior to the renal)
What 3 hormones are secreted by the adrenal cortex?
Cortisol
Aldosterone
Sex hormones
What 2 hormones are secreted from the adrenal medulla?
Adrenaline (epinephrine)
Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine)
What are the left and right ureters?
Muscular tubes which empty urine from their respective kidneys are carry it to the urinary bladder.
How many layers of smooth muscle make up the ureter walls?
Three layers of smooth muscle fibres which spiral around the tube.
There are three narrow regions of the ureters. What are these three regions?
1) Junction between ureters and renal pelvis
2) Where ureters cross the brim of the pelvic bone
3) Entrance of ureters into bladder.
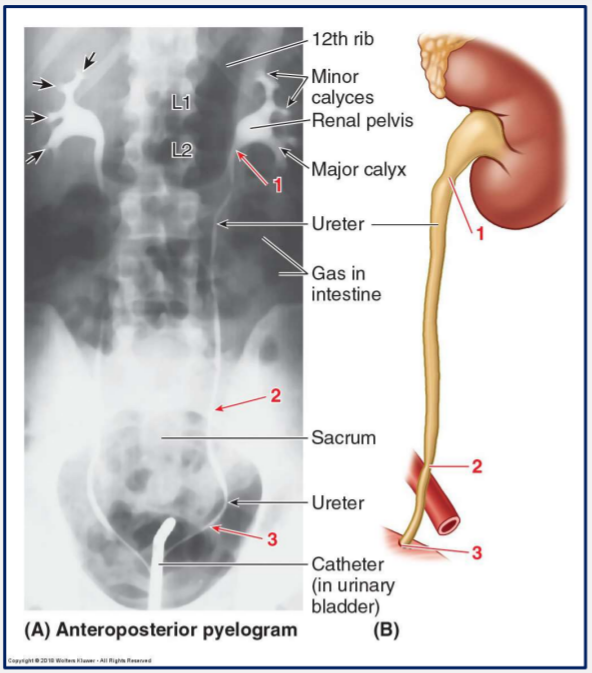
The bladder is completely empty after urination due to strong muscle contractions squeezing it.
True or False?
False.
Bladder always contains some urine. Usually a minimum of around 50ml
What are the three muscular layers of the bladder wall?
Internal layer
Middle layer
External layer
Together these form the detrusor muscle.
What do the three muscle layers of the bladder wall form?
________ muscle.
Detrusor muscle.
What type of epithelium lines the bladder?
Transitional epithelium or urothelium.
Why is transitional epithelium/urothelium special?
These cells can stretch and shift over one another as well as flatten.
This allows the bladder to stretch to accommodate for urine.
A distended bladder may only have 2-3 cell thick epithelium.
An empty bladder may have 5-6 cell thick epithelium.
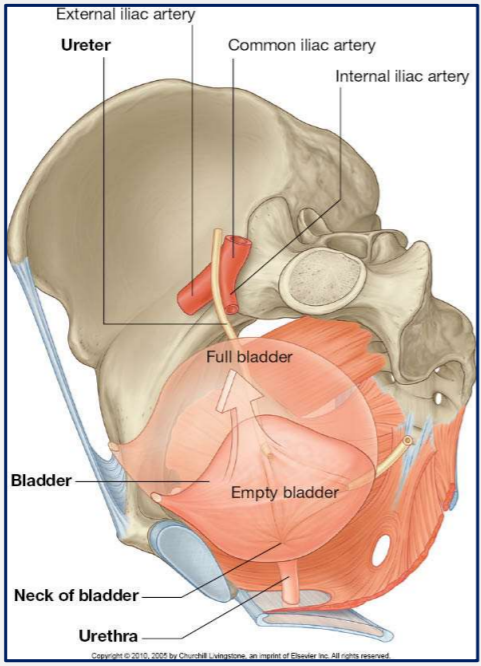
Where does the bladder sit in the body?
Anteriorly in the lesser pelvis and inferior to the peritoneum.
When full it extends superiorly
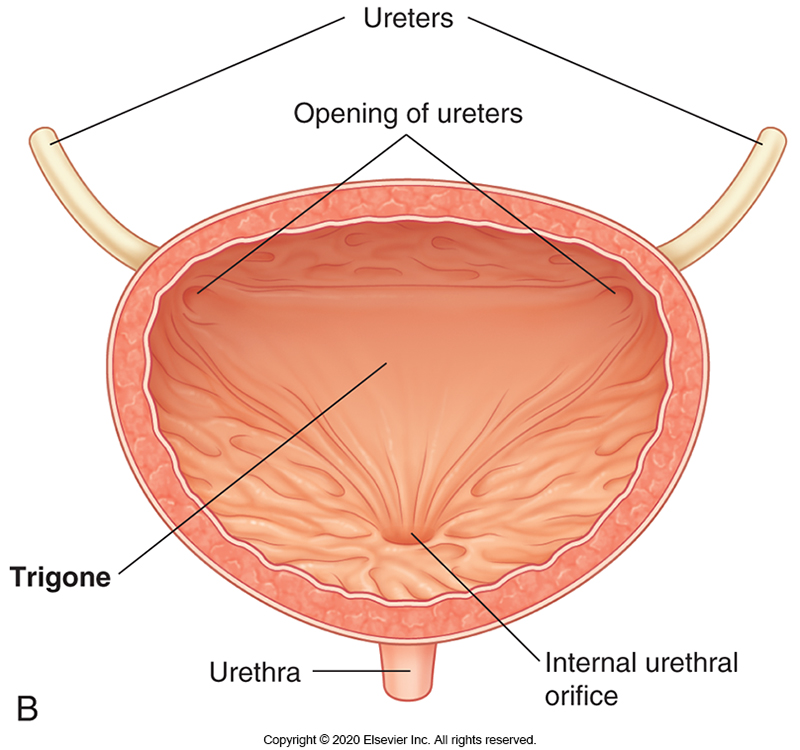
What is the trigone of the bladder?
Smooth triangular area formed between the ureteric orifices and urethral orifice.
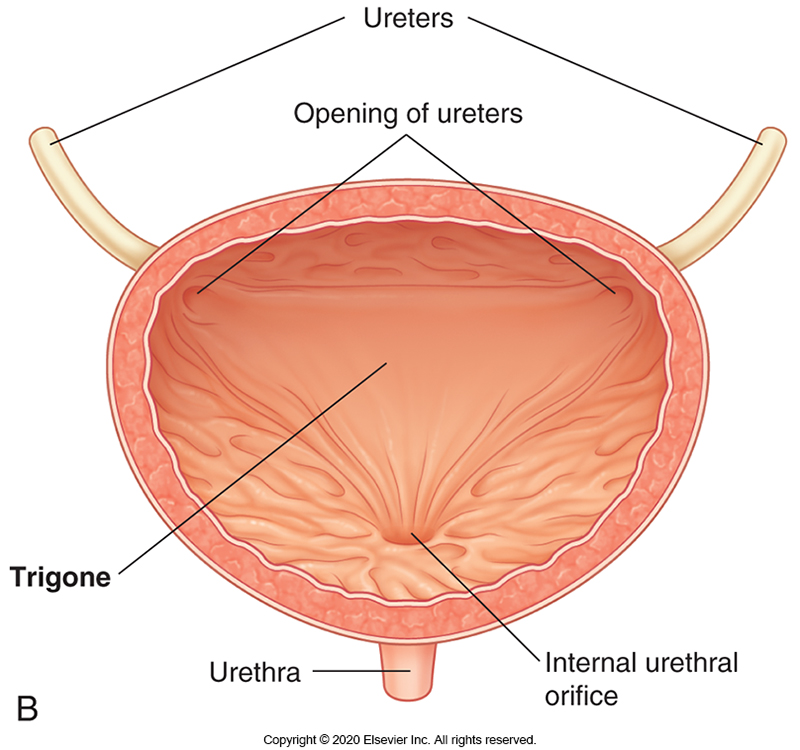
What are the ridges which line the inside of the bladder called?
Rugae
These flatten out when the bladder fills
What is the role of the internal urethral sphincter in males?
Prevents ejaculatory reflux of semen into the bladder.
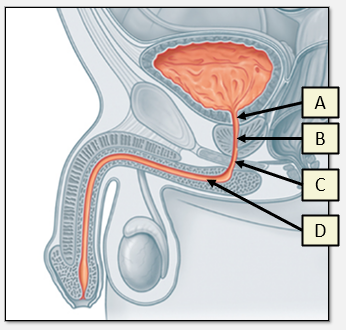
What four parts can the male urethra be separated into?
A) Pre-prostatic
B) Prostatic
C) Membranous
D) Penile
If kidney outflow is restricted by a kidney stone, pathogens can accumulate.
This can cause infection called __________
Pylenophritis
Infection of the kidneys
What are Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)?
Infections of the urinary tract which includes bladder, kidneys, urethra