Microanatomy of Skeletal Muscle Fiber
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
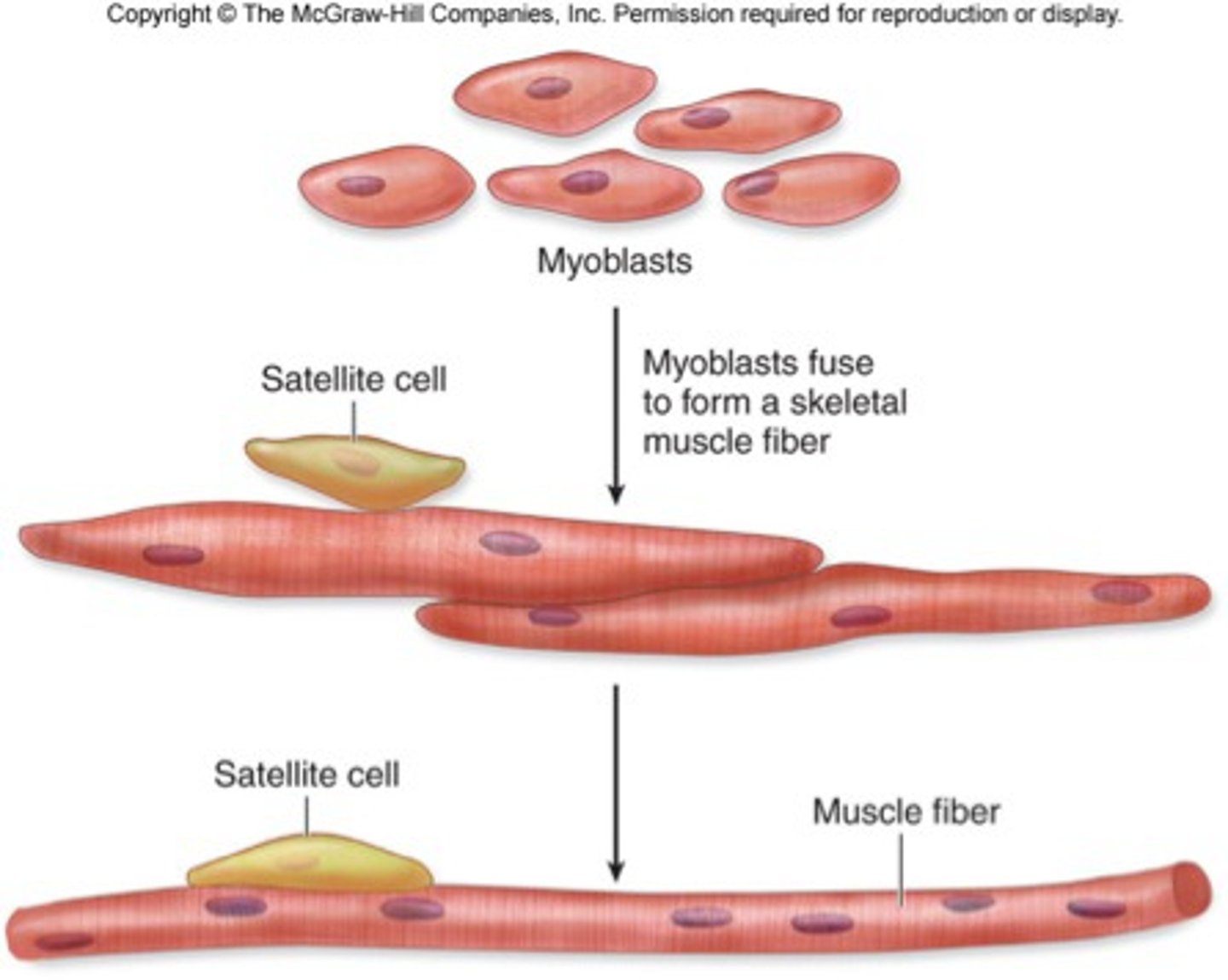
Myoblast
immature muscle cell that forms a muscle fiber
Skeletal Muscle Fiber contains
Mitochondria, Glycosomes, Myoglobin
Sarcolemma
plasma membrane of a muscle fiber
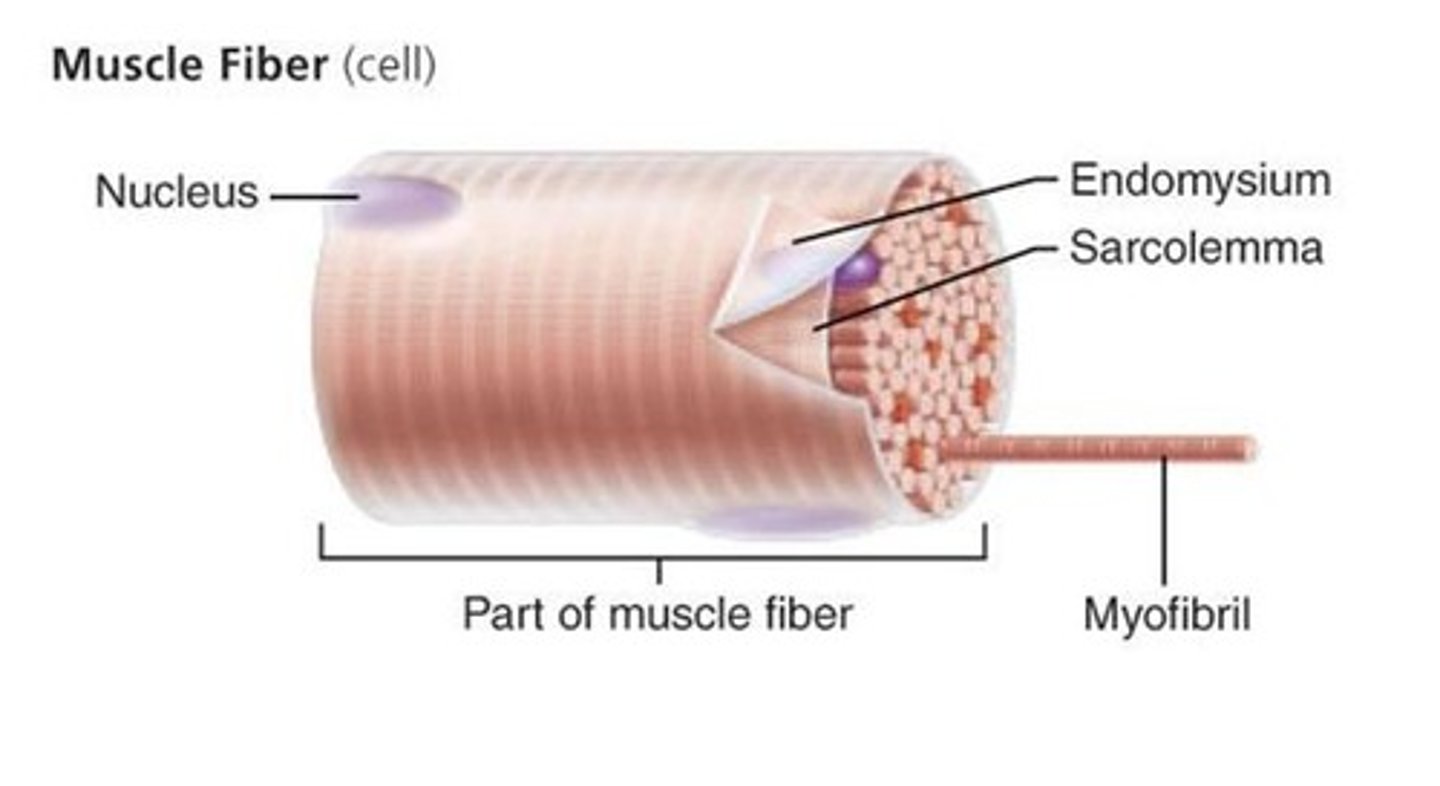
Sarcoplasm
cytoplasm of a muscle cell
Myofibrils
protein structures that make up muscle fibers
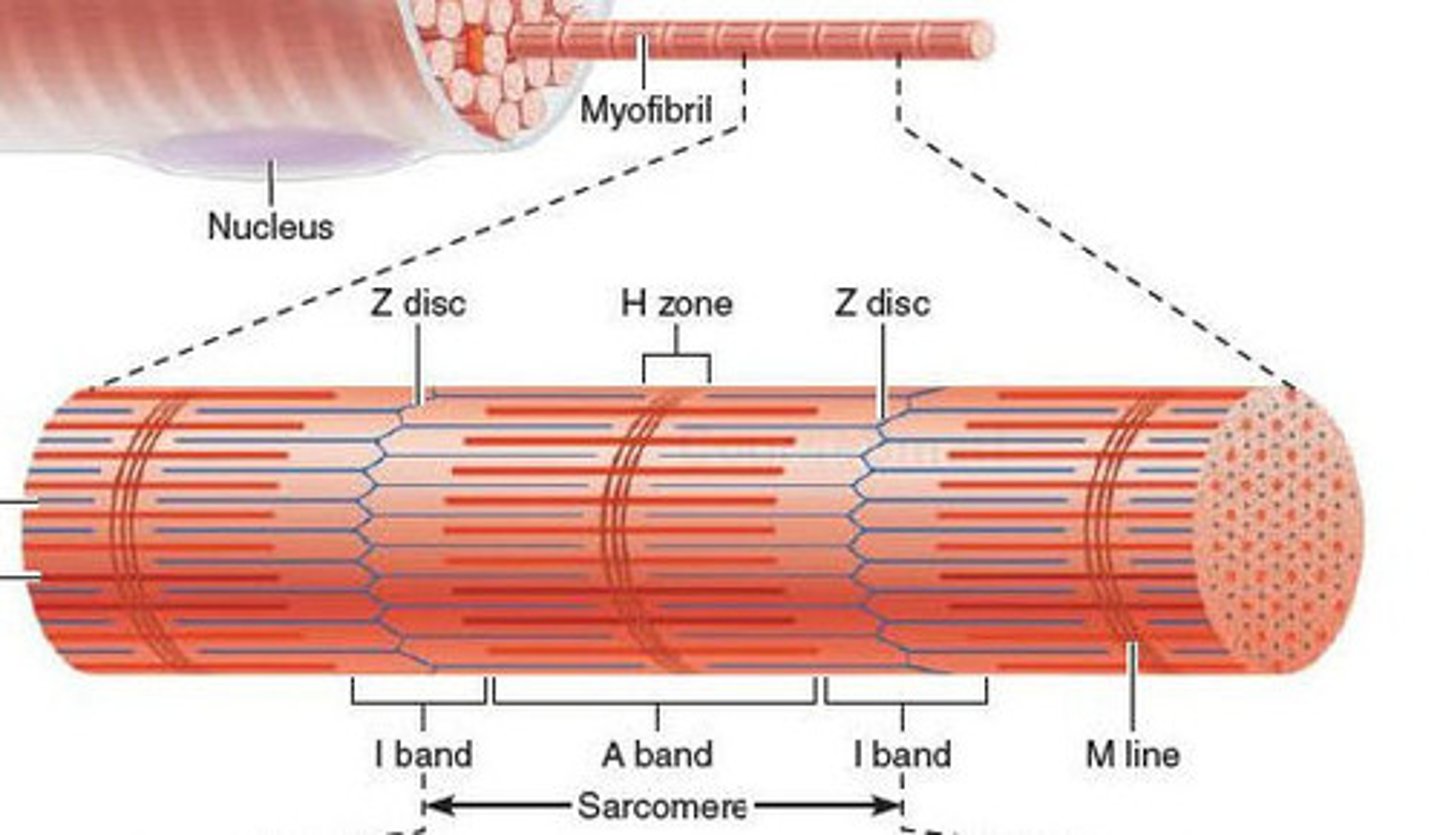
Striations
a repeating series of dark and light band
A bands
Dark regions
Sit between I bands
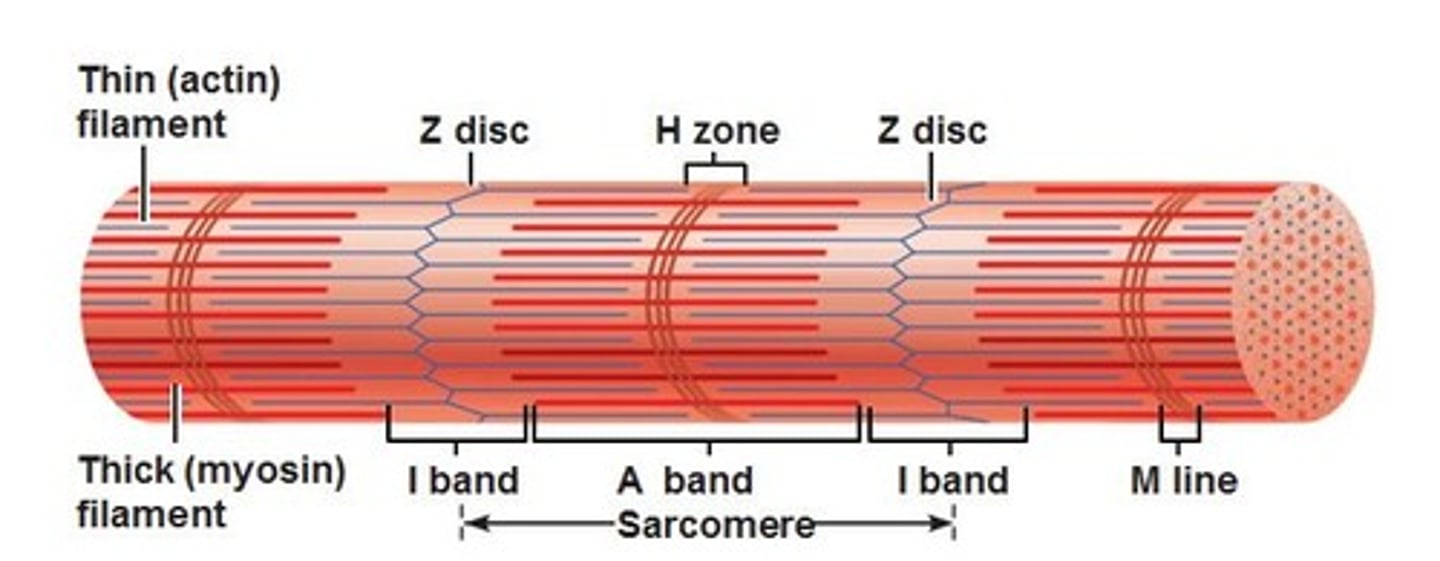
M Line
Bisects A Band vertically; Middle of sarcomere
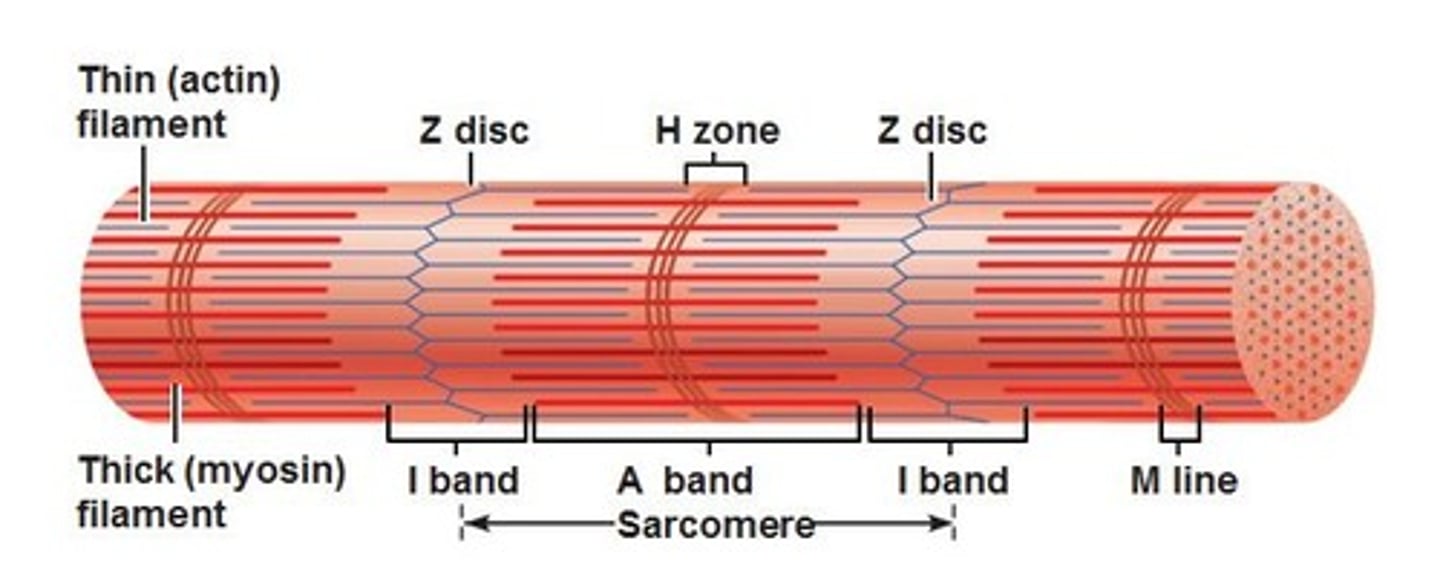
H Zone
thick filaments only
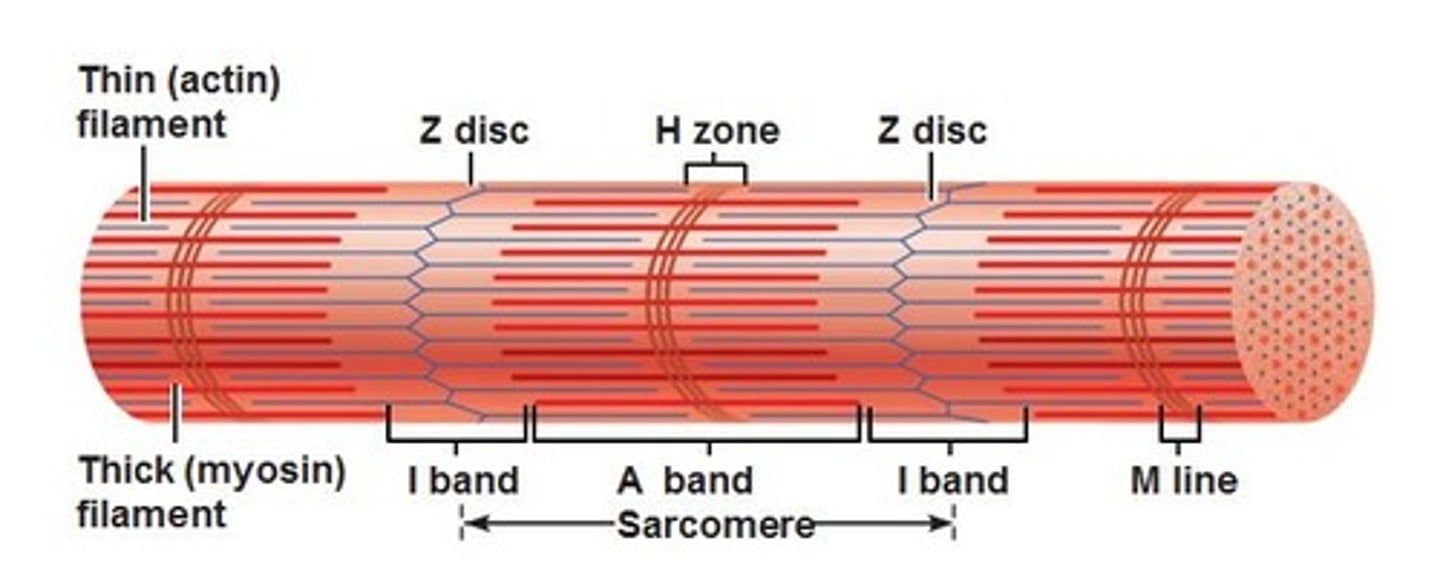
I band
light regions
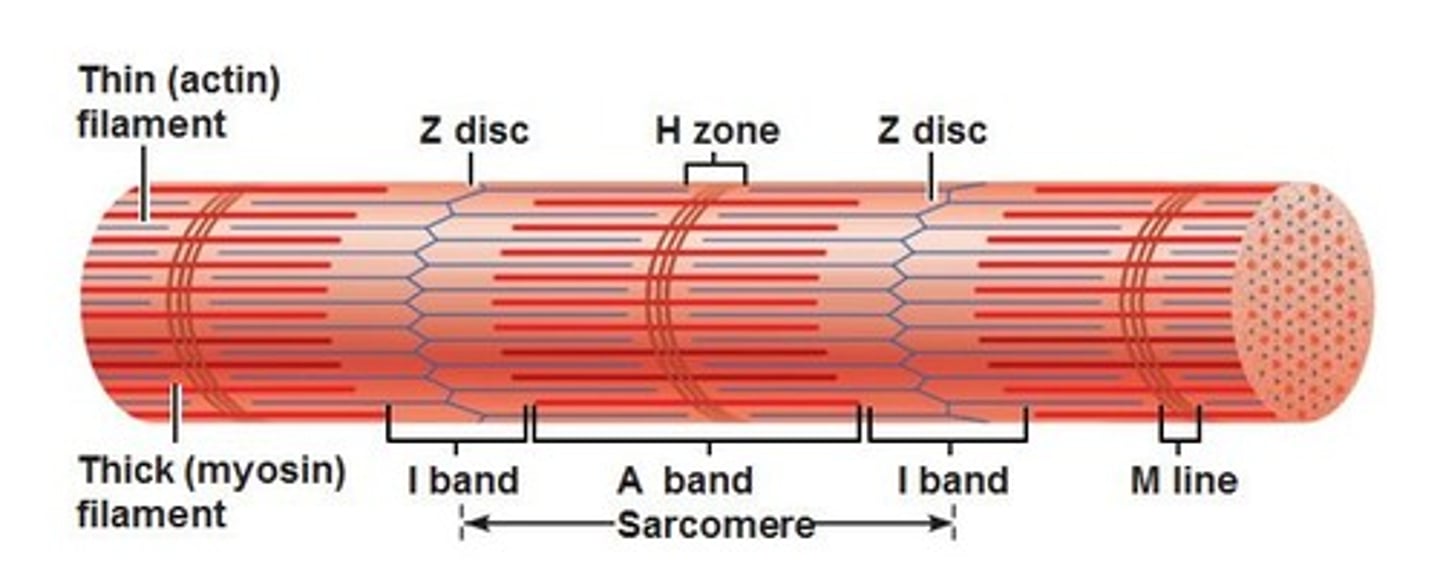
Z Discs
separate one sarcomere from the next
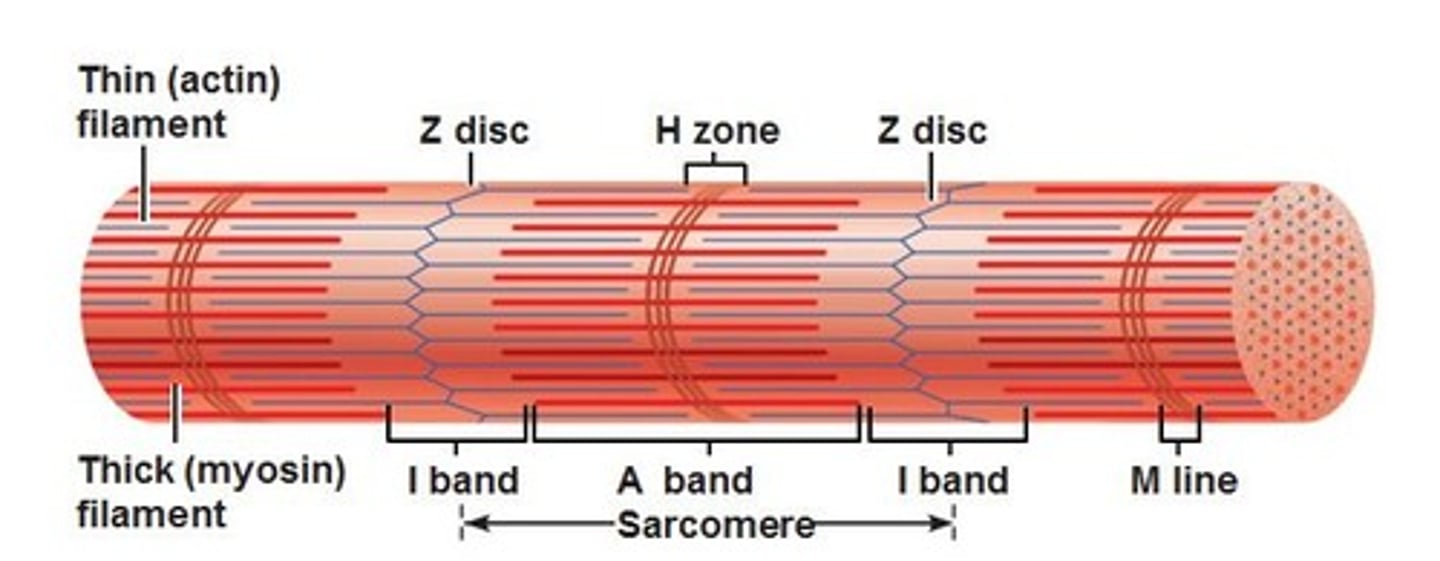
Sarcomere
Contractile unit of muscle; between Z discs
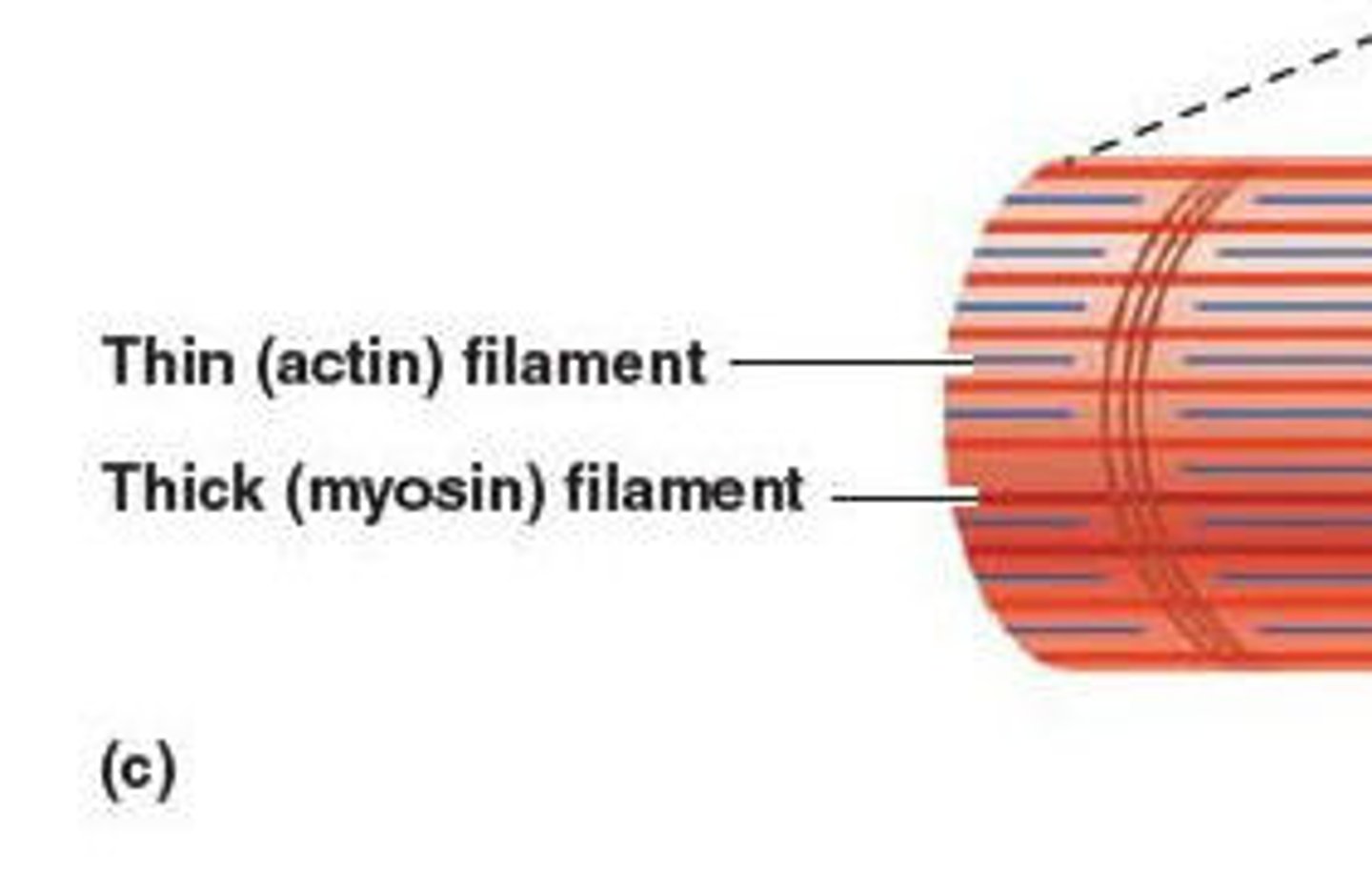
Myofilaments
actin and myosin
Actin
thin filaments
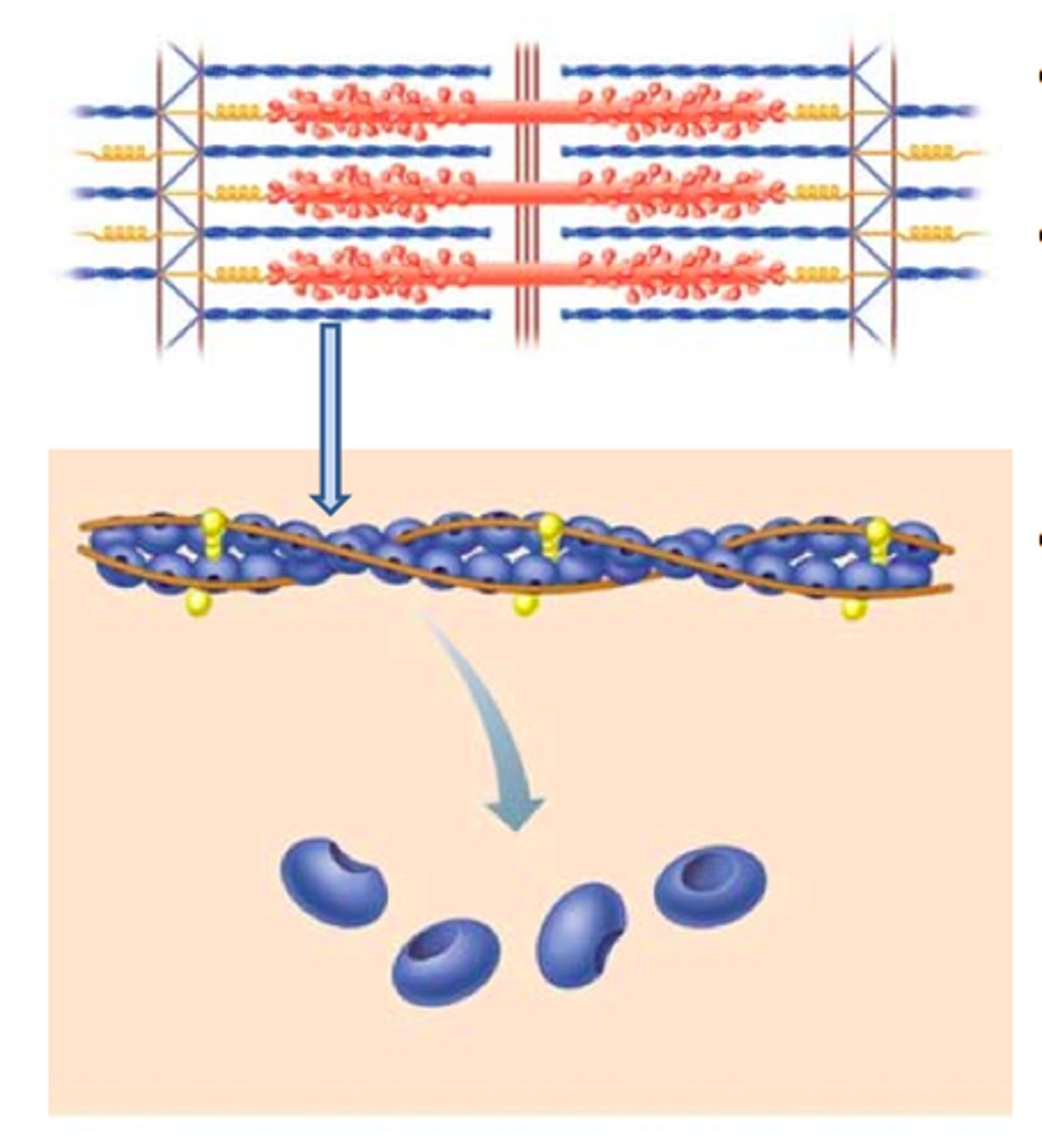
Actin acts as the
myosin binding site
troponin and tropomyosin
Ca2+ binding regulatory proteins
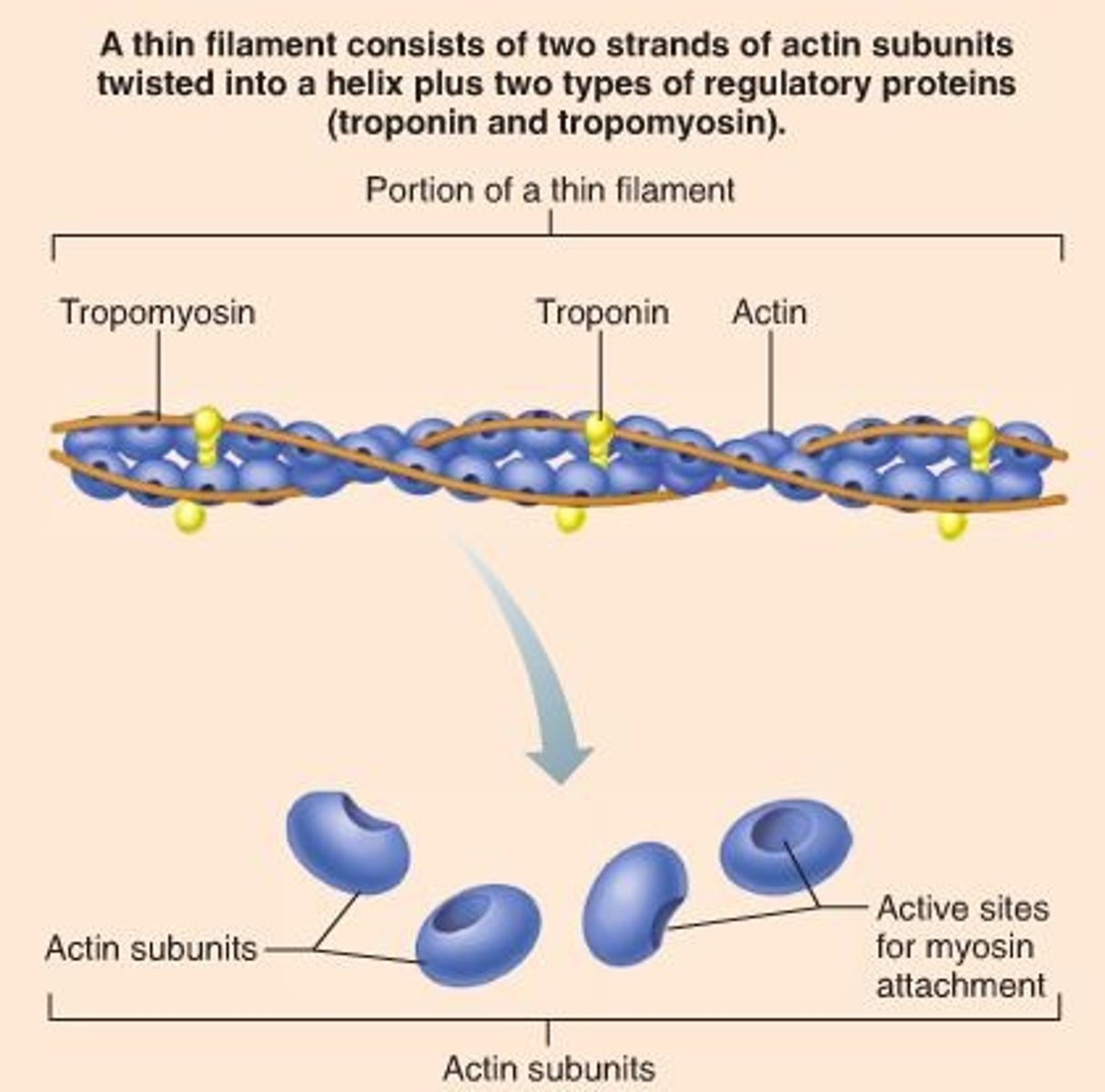
Thin filaments are anchored
to Z discs
Myosin
thick filaments
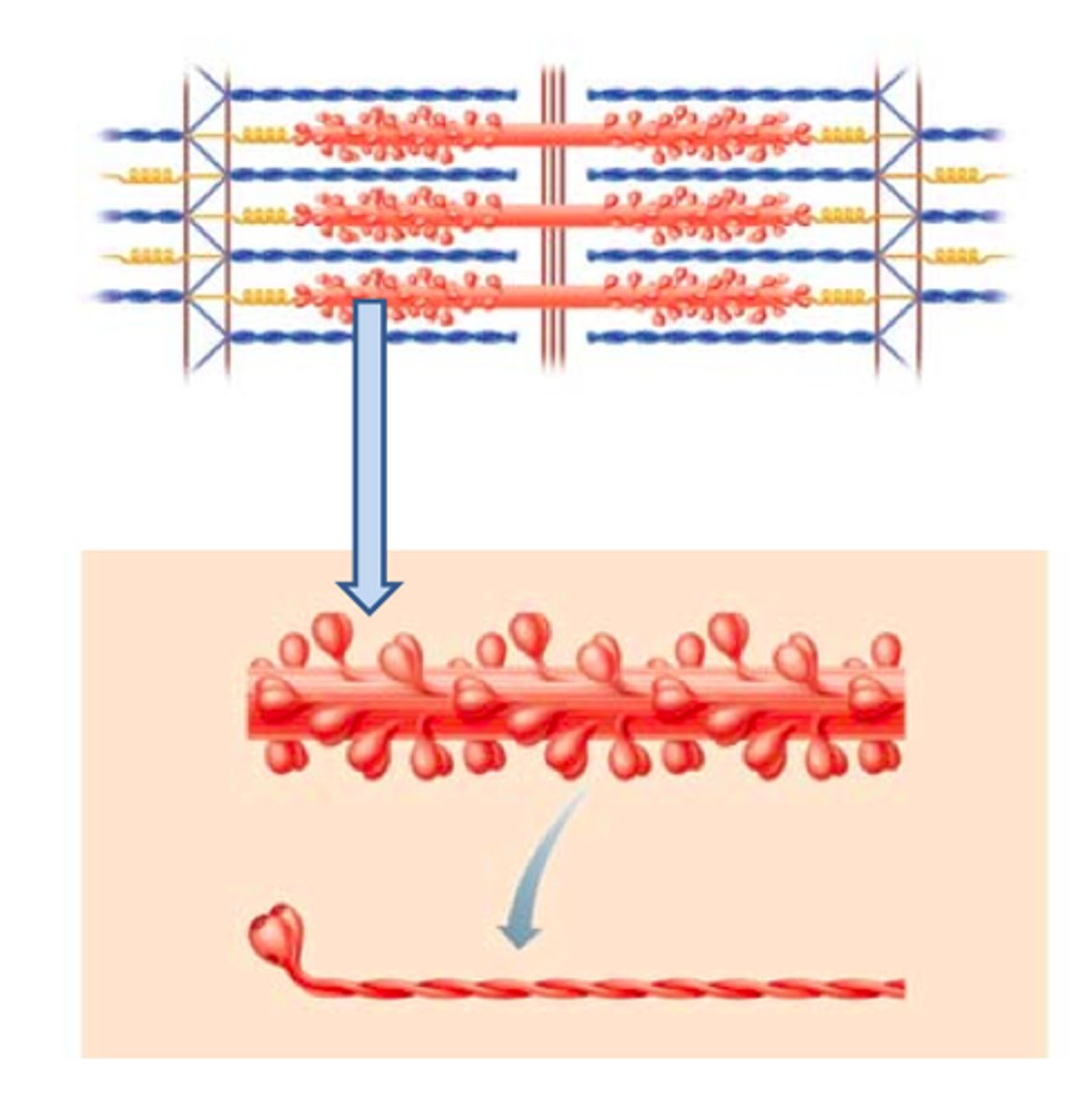
Myosin contains
globular heads
Heavy chains
form myosin tail
Light chains
form myosin globular head to bind actin subunits
Thick filaments are connected at
M line
Elastic filament
helps recoil after stretch
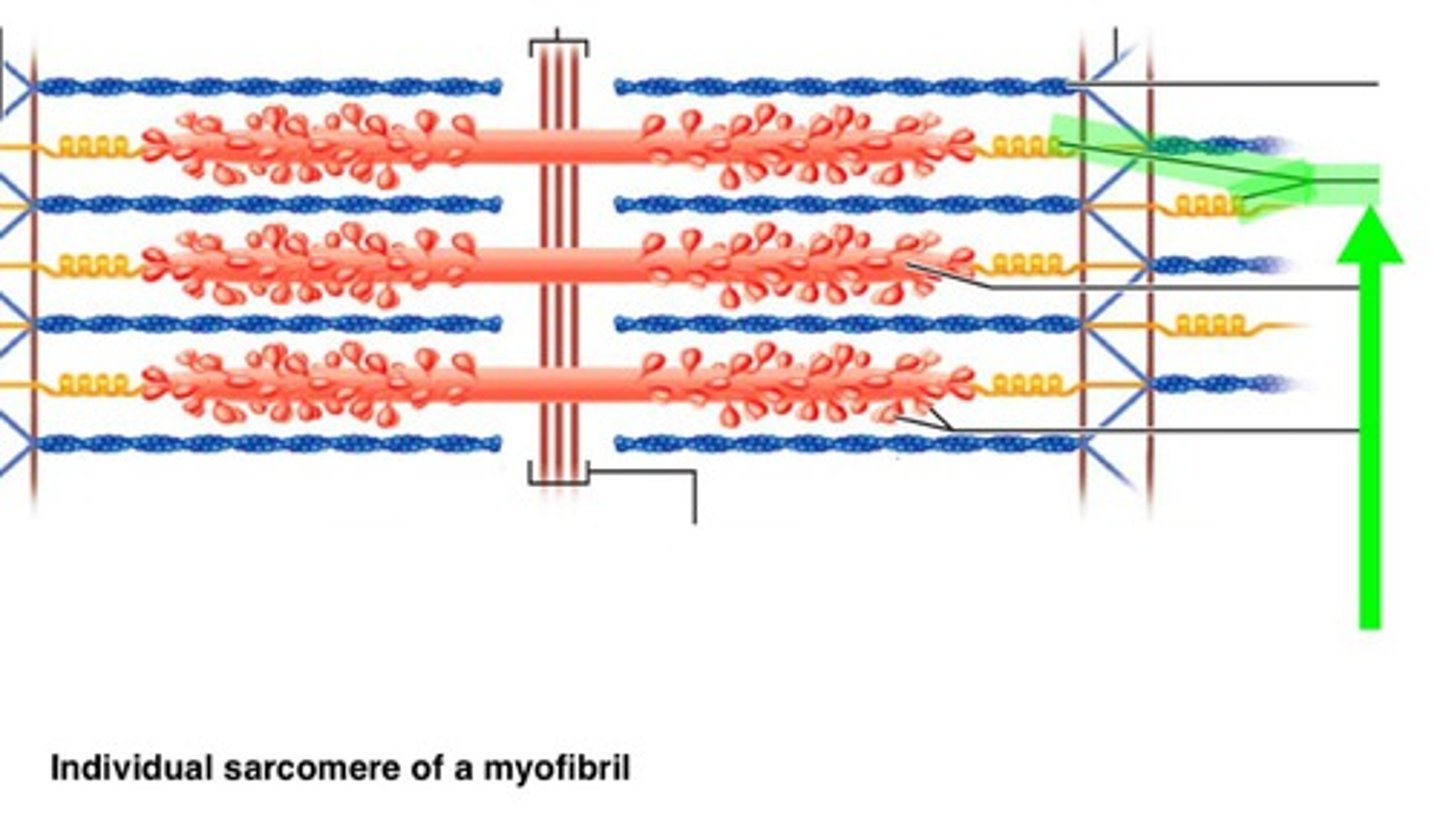
Dystrophin
Links thin filaments to proteins of sarcolemma
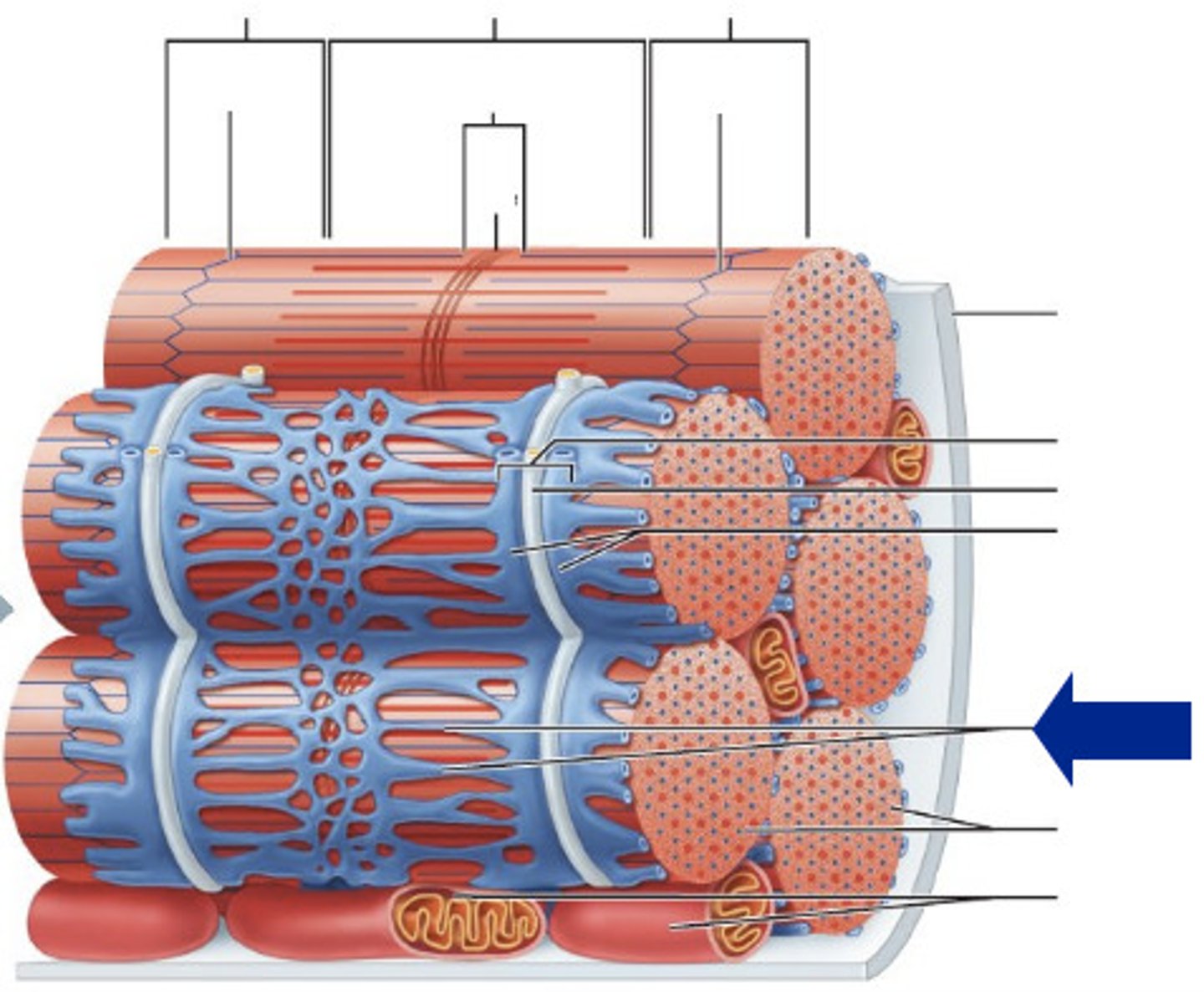
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Network of smooth ER
tubules surrounding myofibril
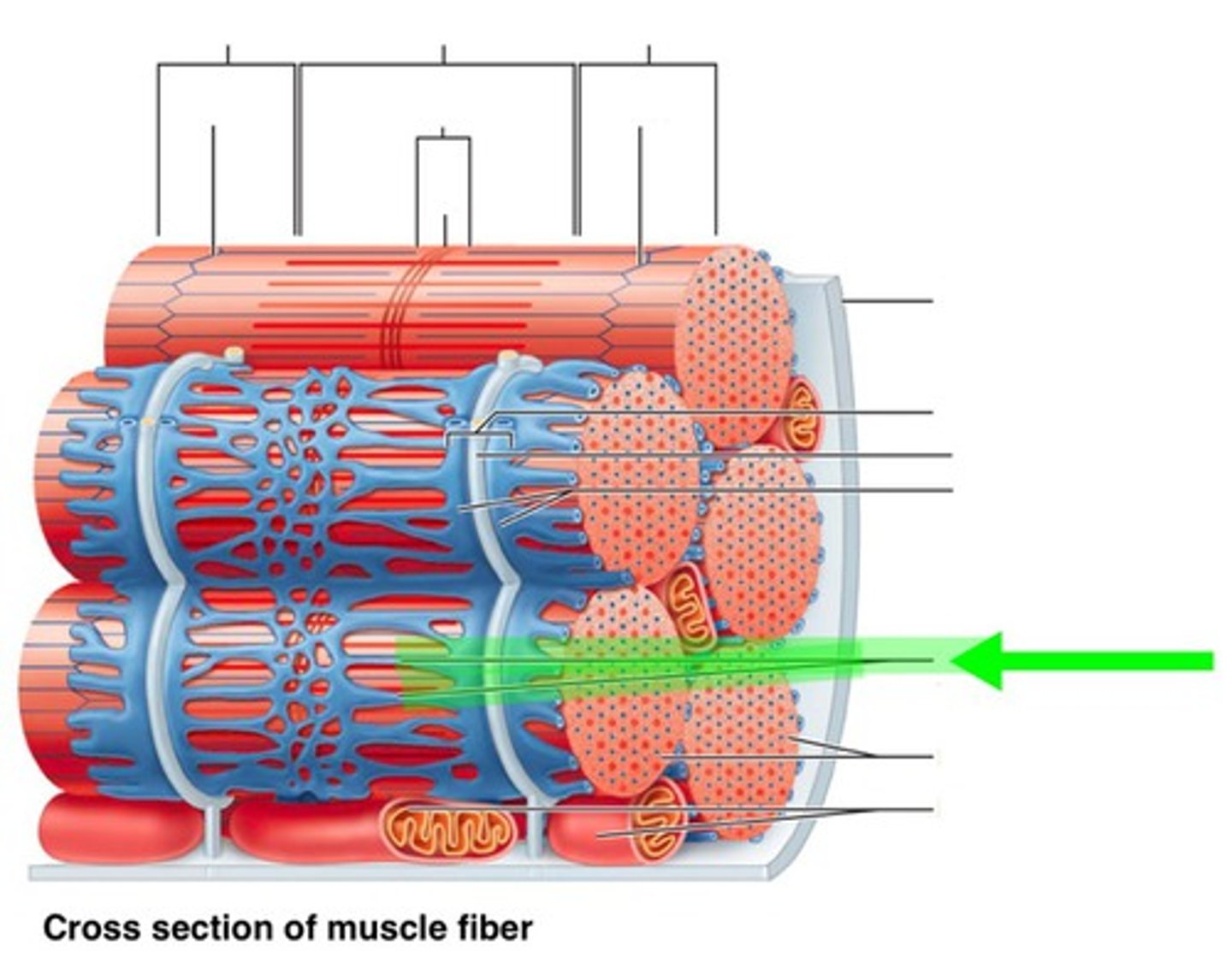
Terminal Cisterns
dilated end sacs of the sarcoplasmic reticulum
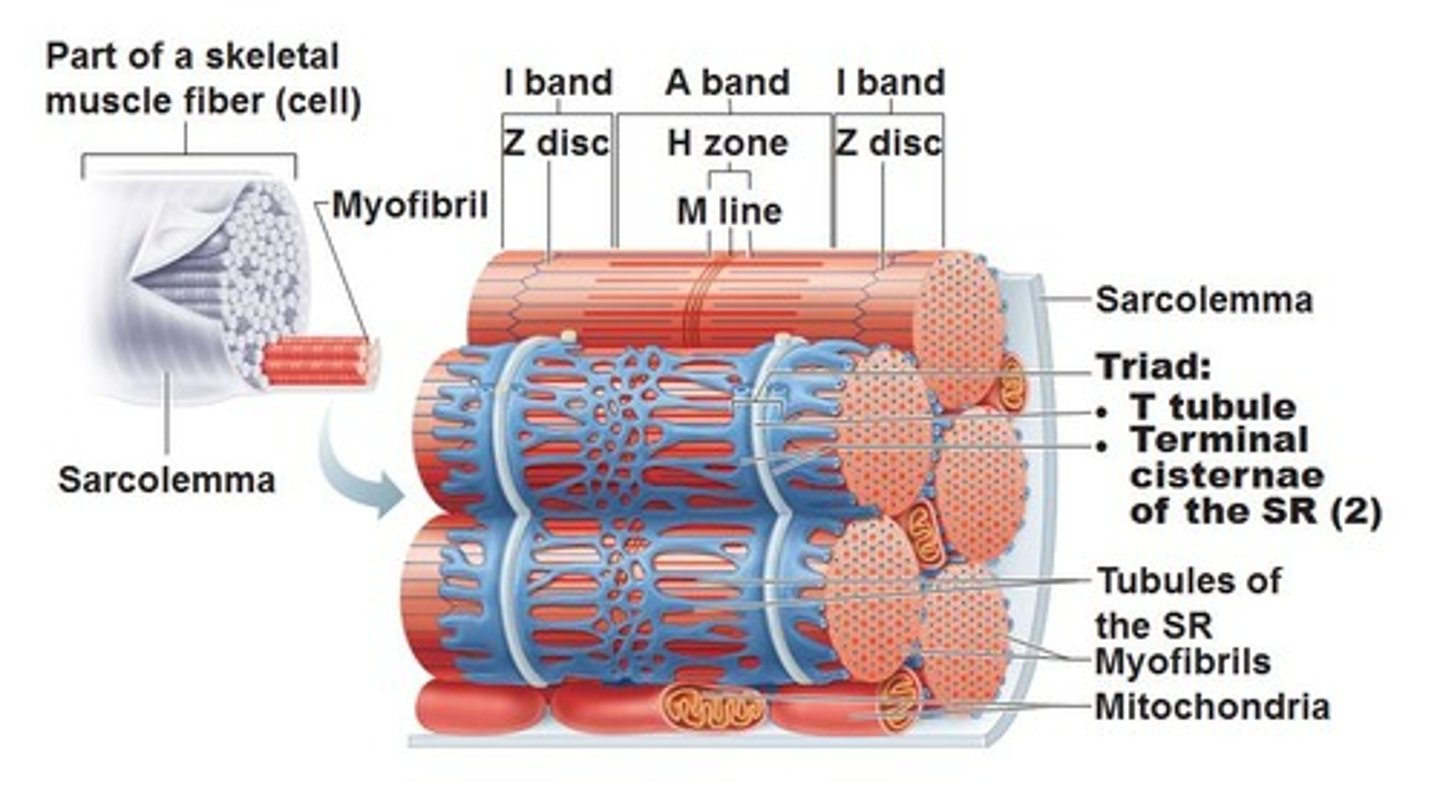
T-tubules
invaginations of the sarcolemma
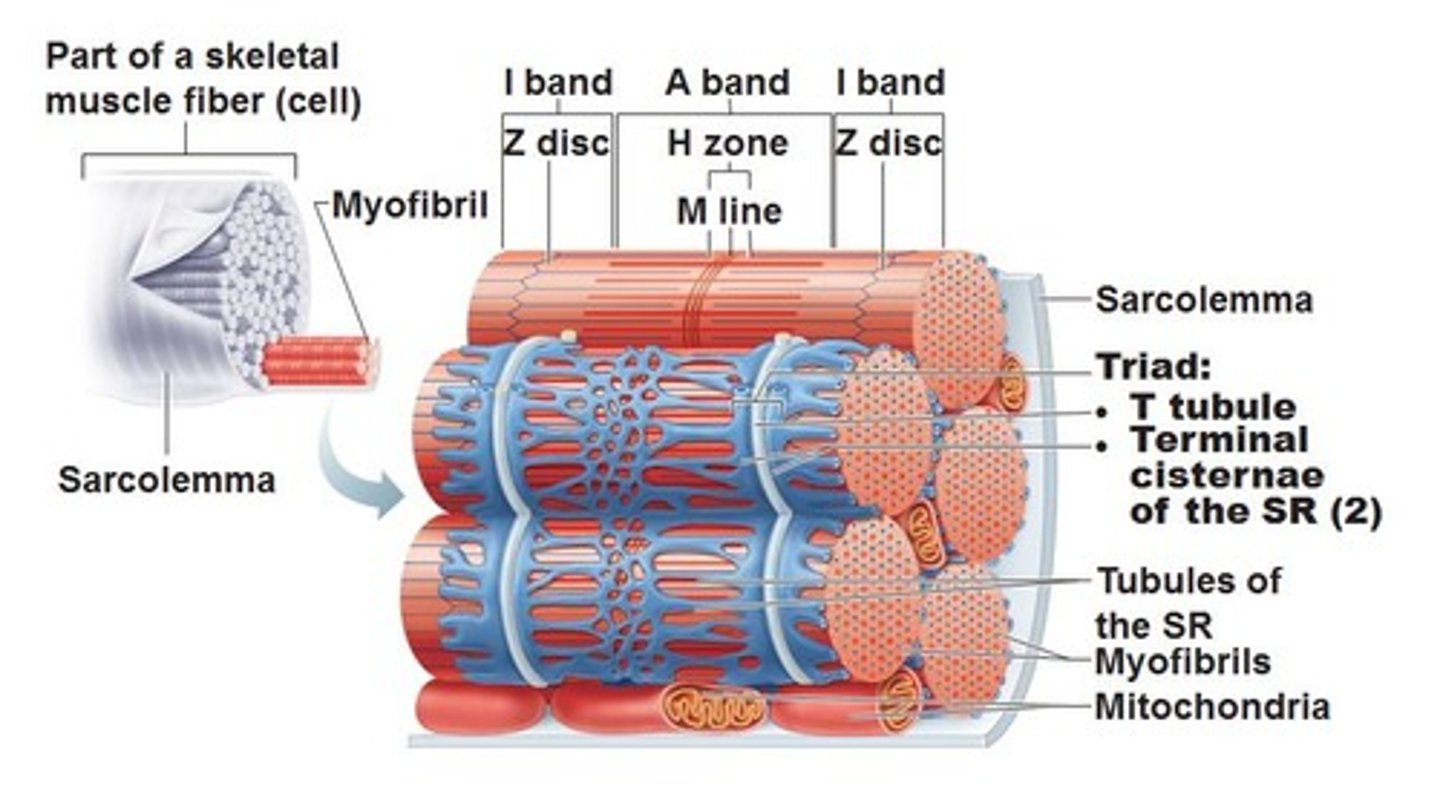
Triad
T-tubule with a terminal cistern on
either side
Triad relationship
T-tubules and SR membranes linked together by
integral proteins
T-tubule Funciton
Voltage sensor protein
SR Membrane function
gated Ca2+ channel