Unit 1 (Ch 4,5,6,7)
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
HMO
Health Maintenance Organizations
What is a health maintenance organization (HMO)?
An organization that provides complete comprehensive healthcare for the cost of the premium and a copayment for each visit.
What is one benefit of health maintenance organizations?
They prevent unnecessary visits and procedures.
What is required to see a specialist in a health maintenance organization?
You need to be referred to a specialist.
TJC
The Joint Commission
The Joint Commission
hospital accreditation.
- certifies that a healthcare institution meets certain minimum standards.
JCERT
Joint Review Committee on Education in Radiologic Technology
- establishes minimum educational standards, conducts inspections, and grands accreditation to programs (schools)
typical reason for patient or family members rudeness/tone
fear
who to contact for questions on orders
ordering physician
ASRT
American Society of Radiologic Technologists
- national professional organization for technologists in radiographic sciences
- describes the radiographer's duties and responsibilities
healthcare insurance and benefit systems
fee-for-service, health maintenance organizations (HMOs), Managed-care systems, Preferred provider organizations (PPOs), Federal health insurance (ACA, Medicaid, Medicare)
ACA
Affordable Care Act (obamacare)
- requires that companies with more than 50 FT employees provide health insurance
Medicaid
A federal and state assistance program that pays for health care services for people who cannot afford them.
Medicare
A federal program of health insurance for persons 65 years of age and older
Chain of Command
- executive board
- administration
- departments
- diagnostic, therapeutic, support, general
Diagnostic Departments
CT, ECG, EEG, MRI, Nuclear medicine, pathology (labs), Radiography, Sonography
Radiologist
were we get our orders, they decide the protocols
ARRT
American Registry of Radiologic Technologist
- establishes minimum standards for certification in various imaging specialties and radiation therapy
- registration exam for (RT) letters
how many Continuing Education hours
24 every 2 years
empathy
focus on patients needs constructively, being compassionate and understanding but still having the objective detachment.
Who sets our Code of Ethics
The ARRT - American Registry of Radiologic Technologists
Ethical analysis
method of evaluating situations in which the correct action is in question
1. identifying the problem
2. Developing alternate solutions
3. Selecting the best solution
4. Defending your selection
Moral agent
the person responsible for implementing the ethical decision
Standards of Ethics for Radiographers
created by ARRT
includes Code of Ethics and Rules of Ethics
Which ethical principles are best in our profession
Principle-based ethics
Principle-Based Ethics
Beneficence - goodness
Nonmaleficence - no evil
Veracity - truth
Fidelity - faithfulness
Justice - fairness
Autonomy - self determination
informed consent
necessary for any procedure that involves substantial risk or is considered experimental.
- need patient signature and witness (yourself)
If you have a patient who does not speak/understand English...
you should find a Medically trained interpreter
HIPPA
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability
- the right of privacy also includes the expectation of confidentiality
Tort
a civil wrong committed by one individual against the person or property of another
Criminal law
offenses against the state or society at large
Civil law
the rights and duties of individuals with respect to one another
the use of restraints without an order is
false imprisonment
Assault
the threat of touching in an injurious way
Battery
unlawful touching of a person without his or her consent
false imprisonment
unjustifiable detention of a person against his/her will
invasion of pricavy
intrusion into a patients private affairs, disclosure of private information, use of the patients name falsely or for personal gain
libel
written- malicious spreading of information that causes defamation of character or loss of reputation
slander
verbal - malicious spreading of information that causes defamation of character or loss of reputation
malpractice
professional negligence; an act of negligence in the context of a relationship between a professional person and a patient/client
Negligence
neglect or omission of reasonable care or caution. the radiographer is held to the standard of care and skill of the "reasonable radiographer" in similar circumstances
Types of Negligence
gross negligence, contributory negligence, and corporate negligence
gross negligence
reckless disregard for life or limb
contributory negligence
the behavior of the injured party contributed to the injury
corporate negligence
when the hospital as an entity is negligent
res ipsa loquitur
"the thing speaks for itself"
relates to foreign bodies being left in clients and instruments slipping during surgical procedures
doctrine of the "borrowed servant"
a physician may be liable for wrongful acts committed by hospital employees under the physicians orders
Respondeat Superior
the employer is liable for employees negligent acts that occur in the course of their work
vicarious liability
the liability by one person or agency for the actions of another
RIMS/RIS
Radiology information (management) system
- ordering and billing
- allows tech to access some pt information- room number, imaging reports and other diagnostic tests
- no info on pt health history or plan of care
7 C's of Malpractice prevention
1. Competence
2. Compliance
3. Charting
4. Communication
5. Confidentiality
6. Courtesy
7. Caution
Malpractice Claim Requirements
- the defendant (person or institution being sued) had a duty to provide reasonable care to the patient
- the patient sustained some loss or injury
- the defendant is the party responsible for the loss
- the loss is attributable to negligence or improper practice
Charting
defined as any records you are expected to add to a document
Chart
refers to an extensive compilation of a patient's medical care and information
Consequentialist
believes that an action is right if the outcome is good
-might argue that speeding is good if the outcome is good (arrived on time) and that it is bad if the outcome is bad (accident)
Nonconsequentialist
might argue that speeding is always bad because it is against the law and because it places you and others at risk
Hearing impaired
Speak slowly, be in front of patient, good lighting, quiet environment, speak in lower tone, repeat information as needed, speak clearly
Deaf
use a medical interpreter
speak to the patient not the interpreter
look at the pt when the interpreter is speaking
unconscious patients
speak to them as if they were conscious, explain what you are doing, be respectful, do not have other conversations over them
Aphasia
inability to speak
Ageism
discriminatory attitude toward the elderly that includes a belief that all elderly are ill, disabled, worthless, or unattractive
Therapeutic communication
a process in which the healthcare professional consciously influences a client or helps the client come to a better understanding through verbal and/or nonverbal communication. Uses strategies that convey acceptance and respect and encourage the patient to express feelings and ideas.
Kubler-Ross stages of grief
1. Denial -refuses to accept the truth
2. Anger - experiences frustration, outrage
3. Bargaining - attempts to earn forgiveness or mitigate loss
4. Depression - often acquiescent, quiet, and withdrawn
5. Acceptance - accepts the loss or impending death and deals with life and relationships on a more realistic, day-to-day basis
PASS
Pull, Aim, Squeeze, Sweep
RACE
rescue, alarm, contain, extinguish or evacuate
MSDS
Material Safety Data Sheets
- for hazardous materials; be on file and easily accessible
- OSHA requirement
Ergonomics
the study of the human body in relation to the working environment for the purpose of preventing injuries
Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs)
most common injuries reported by healthcare workers
- Repetitive motion injuries (RMIs)
- Repetitive strain injuries (RSIs)
- cumulative trauma disorders (CTDs)
Body Mechanics
the principles of proper body alignment, movement, and balance
- application minimizes the energy require to sit, stand, and walk
- proper body mechanics prevents injuries
most common cause of injury
lifting and twisting
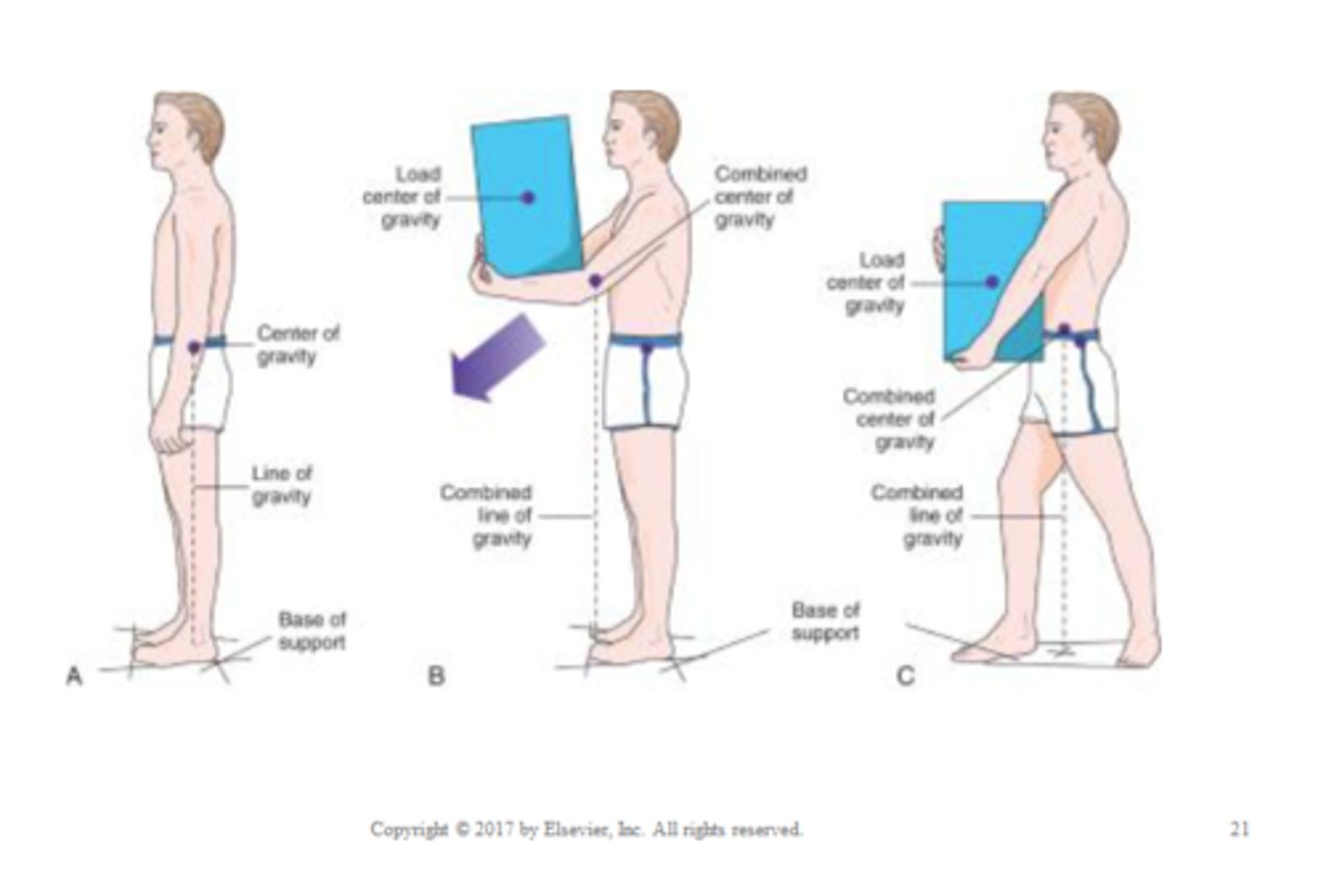
Base of Support
portion of the body in contact with the floor or other horizontal surface
- can be a horizontal line linking the points of contact
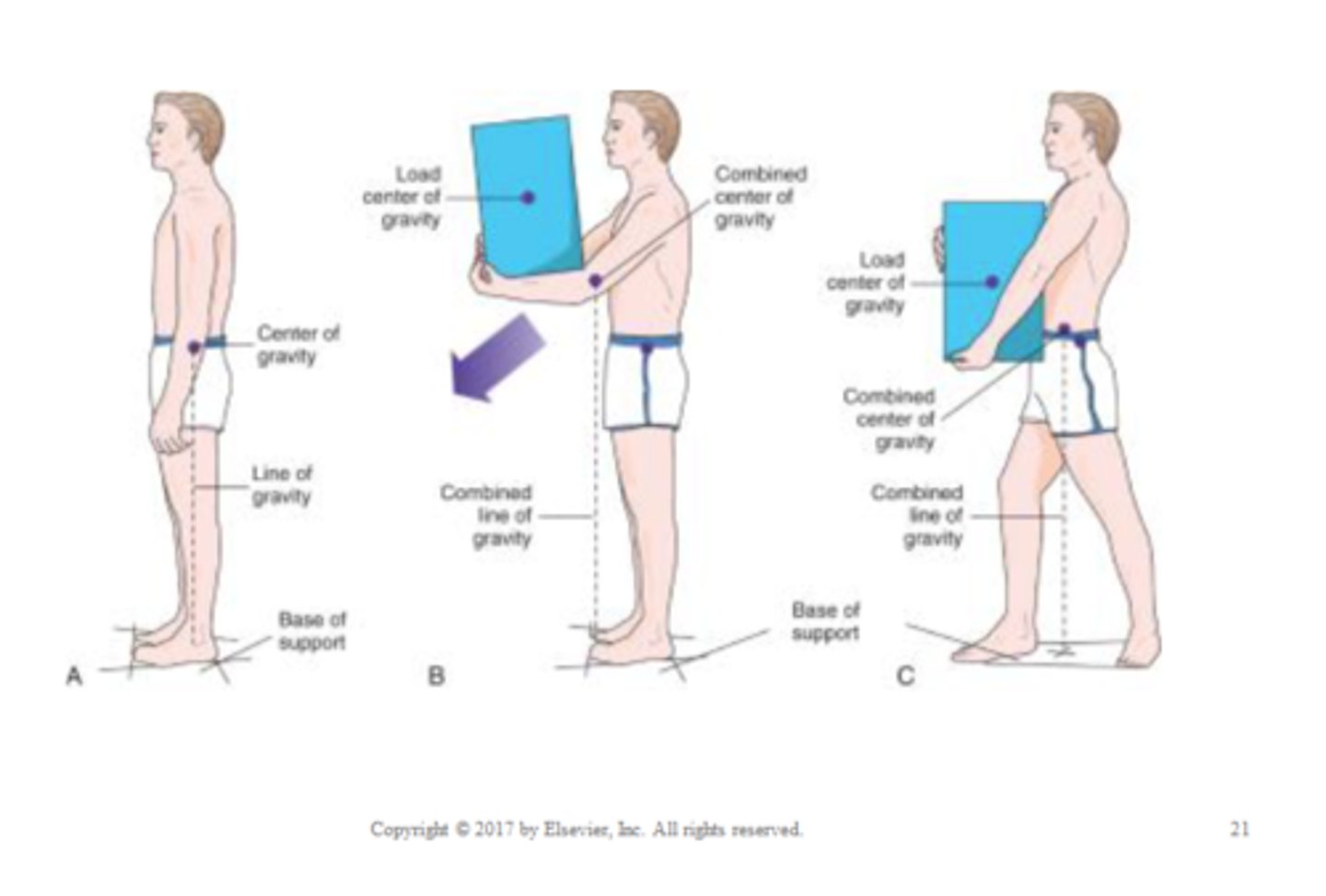
Center of Gravity
the point around which body weight is balanced
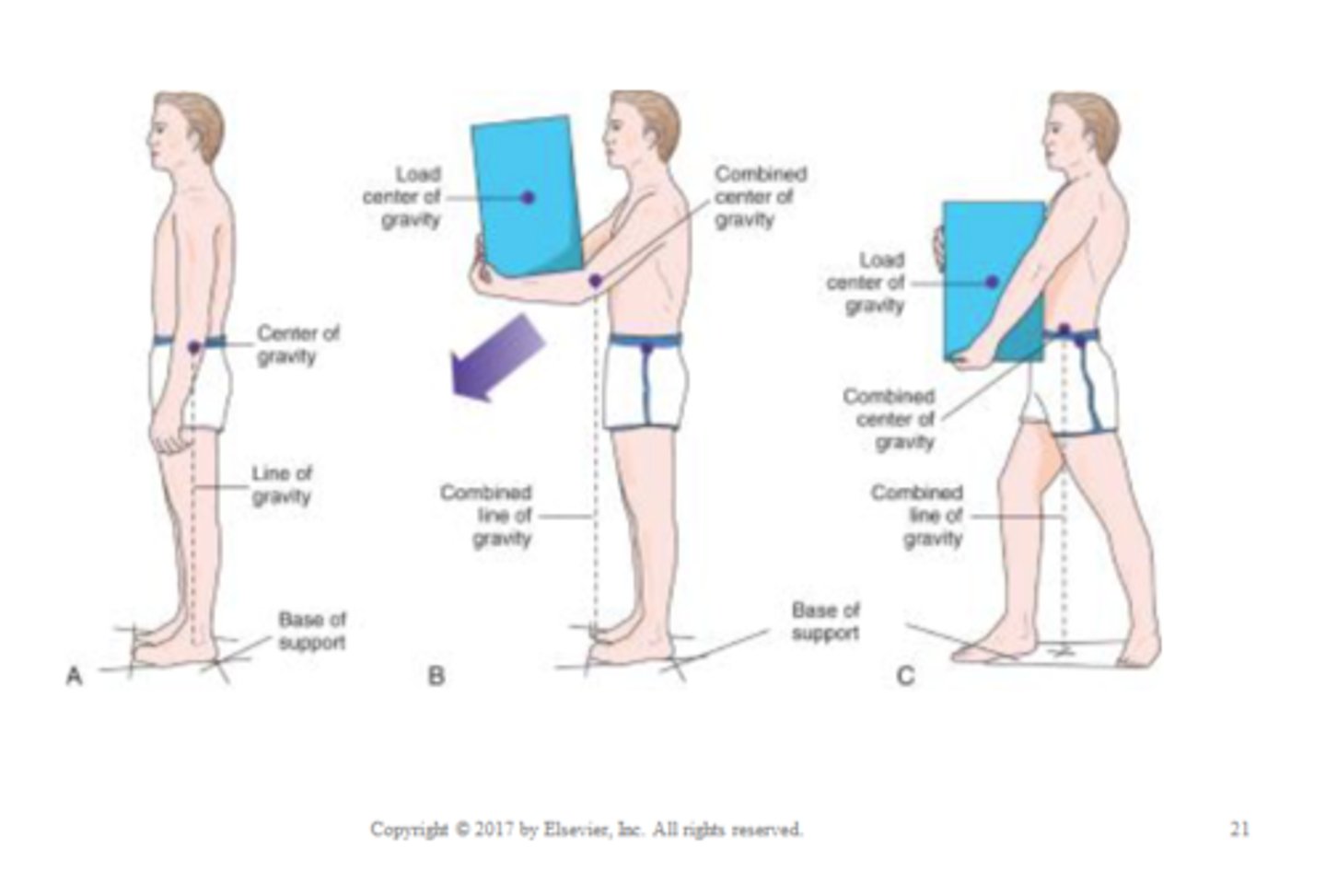
Line of Gravity
imaginary vertical line passing through the center of gravity
- the body is most stable when the line of gravity bisects the base of support
If you have issue with a member of another department you should...
follow you chain of command and notify YOUR manager/department supervisor
Crisis intervention
an approach in which the patient/client seeks help only when unable to manage alone.
- after emergency passes former lifestyle is typically resumed
preventative healthcare
healthcare system which attempts to promote well-being and avoid the need for medical intervention.
- encourages good nutrition, exercise, vaccinations, and health screening tests.
- potential health problems are identified before they manifest as illnesses
health-illness continuum
different points on line between optimal health and fatal illness