BIOL 2460 - EXAM 3 REVIEW - PARKS - MICROBIOLOGY
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/210
Earn XP
Description and Tags
🔑: ME: membrane PS: Protein Synthesis NA: Nucleic Acids MP: Metabolic Pathways AFD: Antifungal Drugs APD: Antiprotozoan Drugs AHD: Antihelminthic Drugs AVD: Antiviral Drugs AA: Alkylating Agents HM: Heavy Metals P: Peroxygens B: Bisbiguanides
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
211 Terms
1
New cards
Binary Fission Steps
G - growth and increase in cell size
R - replication of DNA
D - cytoplasmic division; cytokinesis
S - septum formation and daughter cell divisions
R - replication of DNA
D - cytoplasmic division; cytokinesis
S - septum formation and daughter cell divisions
2
New cards
Z-ring
formed during cytokinesis with the FtsZ protein to form a divisome
3
New cards
Divisome
promotes the formation of peptidoglycan and septum
4
New cards
Generation Time
time takes to double population
5
New cards
E. coli
20 min.
6
New cards
S. aureus
30 min.
7
New cards
B. subtilis
120 min.
8
New cards
M. tuberculosis
15-20hrs
9
New cards
Nn
number of cells at generation n
10
New cards
n
number of generations
11
New cards
N0
initial number of cells
12
New cards
Growth curve
closed system with finite nutrients
13
New cards
Lag Phase
cells grow larger and metabotically active (inoculum cells)
14
New cards
Log Phase
exponential; binary fission; cell replication > cell death
15
New cards
Stationary Phase
cells enter survival mode and < less susceptible to antibiotics; cell replication = cell death
16
New cards
Death Phase
cell replication < cell death; endospores; persisters
17
New cards
Persisters
surviving cells with slow metabolism (tuberculosis)
18
New cards
Sustainable Growth
Open system cultures have infinite resources
19
New cards
Chemostat
used to maintain a continuous culture in which nutrients are supplied at a steady rate
20
New cards
Direct microscopic cc
cells are counted under a microscope; CANNOT distinguish between live or dead cells; Known volume is transferred to a calibrated slide (Petroff-Hausser chamber) and cells are manually counted
21
New cards
Fluorescence Staining
cells are counted under a microscope or flow cytometer; Red stain binds to damaged cells to indicate DEAD cells
22
New cards
Coulter counter
detects electrical resistance change due to cell density; CANNOT differentiate live/dead
23
New cards
Viable plate counts
count of live cells; samples are diluted and grown on solid media;
24
New cards
Pour Plate Method
bacterial sample mixed with warm agar - > sample poured onto sterile plate -> sample swirled to mix, allowed to solidify -> plate incubated until bacterial colonies grow
25
New cards
Spread Plate Method
sample poured onto solid medium -> spread sample evenly over the surface -> plate incubated until bacterial colonies grow on the surface of the medium
26
New cards
Optical Density (turbidity)
Measured w/ spectrophotometer; light is passed through culture and is measured on other side
27
New cards
Alternate Patterns of Growth
fragmentation in cyanobacteria and budding in planctomycetes: Gemmata obscuriglobus
28
New cards
Biofilm Formation
1. Attachment of planktonic cells to a substrate
2. Attachment becomes irreversible; cells become sessile
3. Growth & division on substrate
4. Production of extracellular polymeric substance (EPS)
5. Attachment of secondary colonizers & dispersion of microbes to new locations
2. Attachment becomes irreversible; cells become sessile
3. Growth & division on substrate
4. Production of extracellular polymeric substance (EPS)
5. Attachment of secondary colonizers & dispersion of microbes to new locations
29
New cards
Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS)
Hydrated polysaccharide gel with other macromolecules and channels (sugar-gel)
EX: (rivers, pipelines, oral cavity) (cuts and wounds, lungs, intestines)
EX: (rivers, pipelines, oral cavity) (cuts and wounds, lungs, intestines)
30
New cards
Quorum Sensing
cell to cell communication
31
New cards
Autoinducer
small molecules are produced to induce various actions (positive-feedback)
32
New cards
Biofilm and Human Health
1. Cells in deep layers may
be metabolically inactive
2. EPS may slow diffusion of biocidal agents
3. Provide optimal environment for sharing of plasmids
2. EPS may slow diffusion of biocidal agents
3. Provide optimal environment for sharing of plasmids
33
New cards
Optimal oxygen concentration
ideal concentration of O2 (best for growth)
34
New cards
Minimum permissive oxygen concentration
lowest O2 concentration allowing growth
35
New cards
Maximum permissive oxygen concentration
highest O2 concentration allowing growth
36
New cards
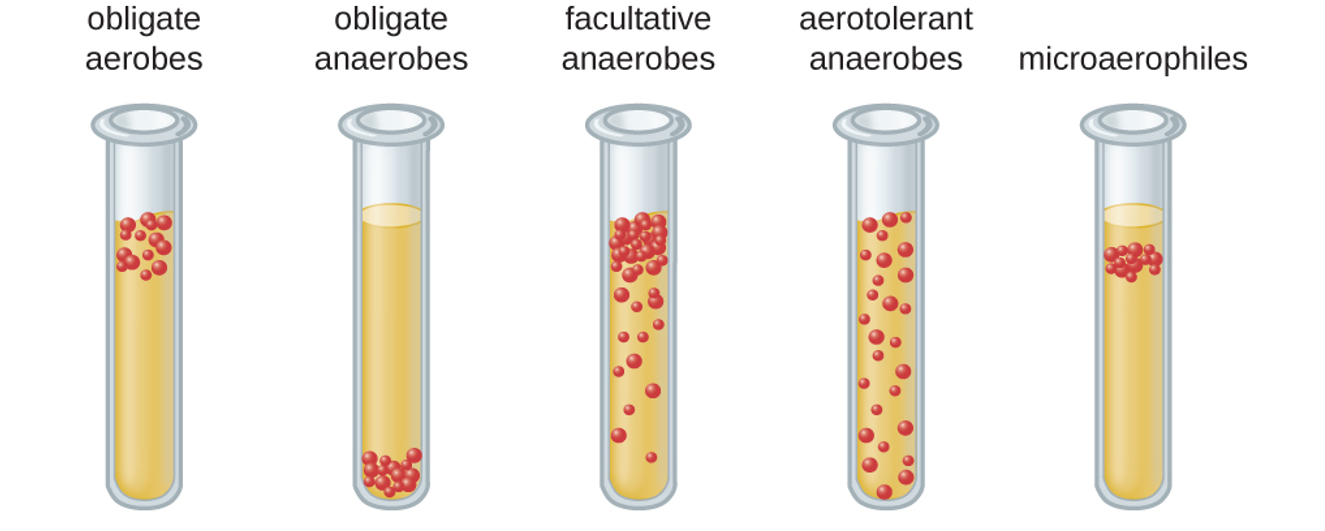
Obligate aerobes
must have O2; Micrococcus luteus
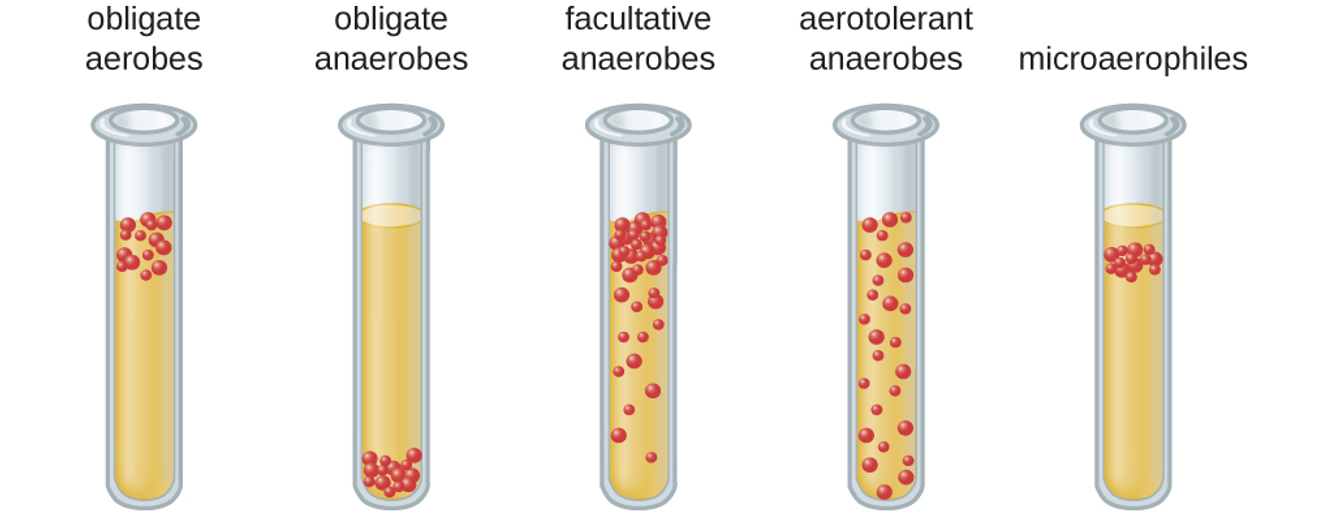
37
New cards
Obligate anaerobes
prefers other than O2; Bacteroides spp.
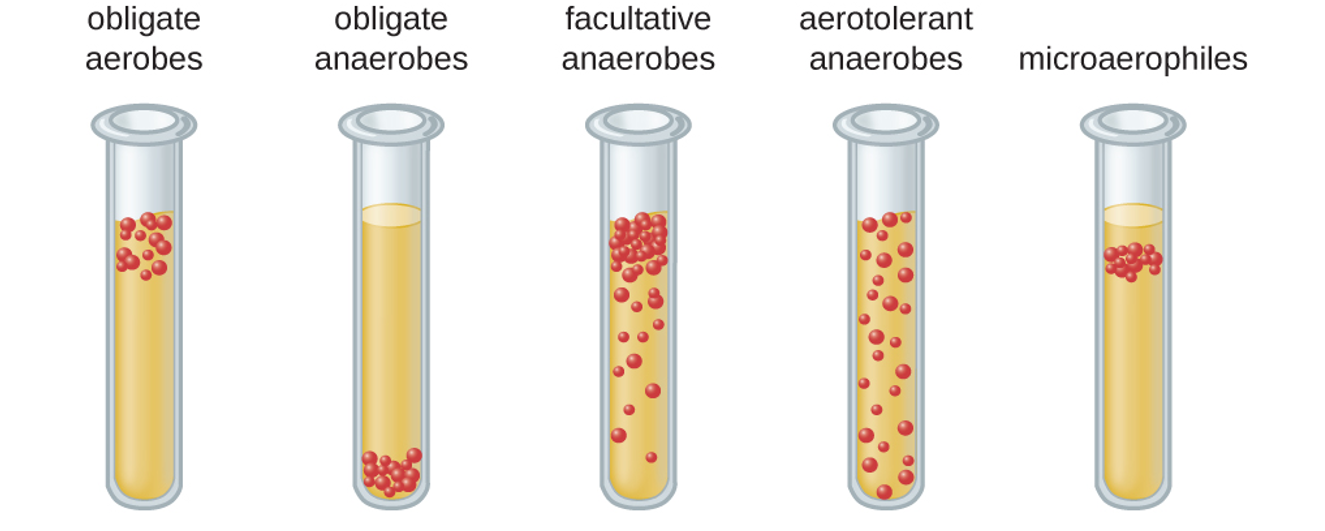
38
New cards
Facultative anaerobes
can do both; Staphylococcus spp.
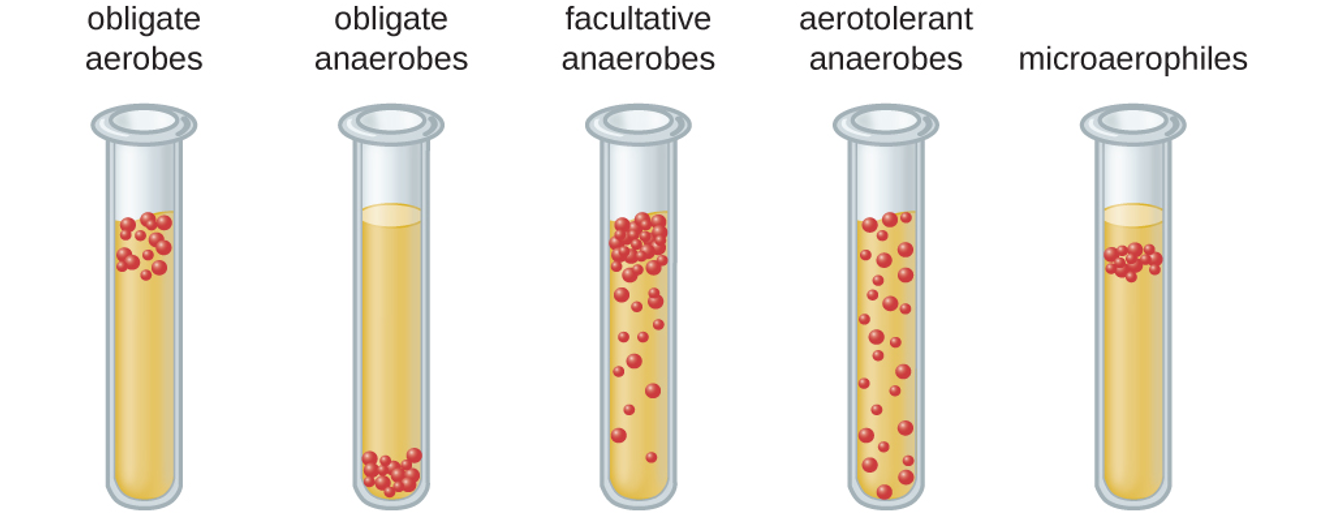
39
New cards
Aerotolerant anaerobes
tolerant to O2; Lactobacillus spp.
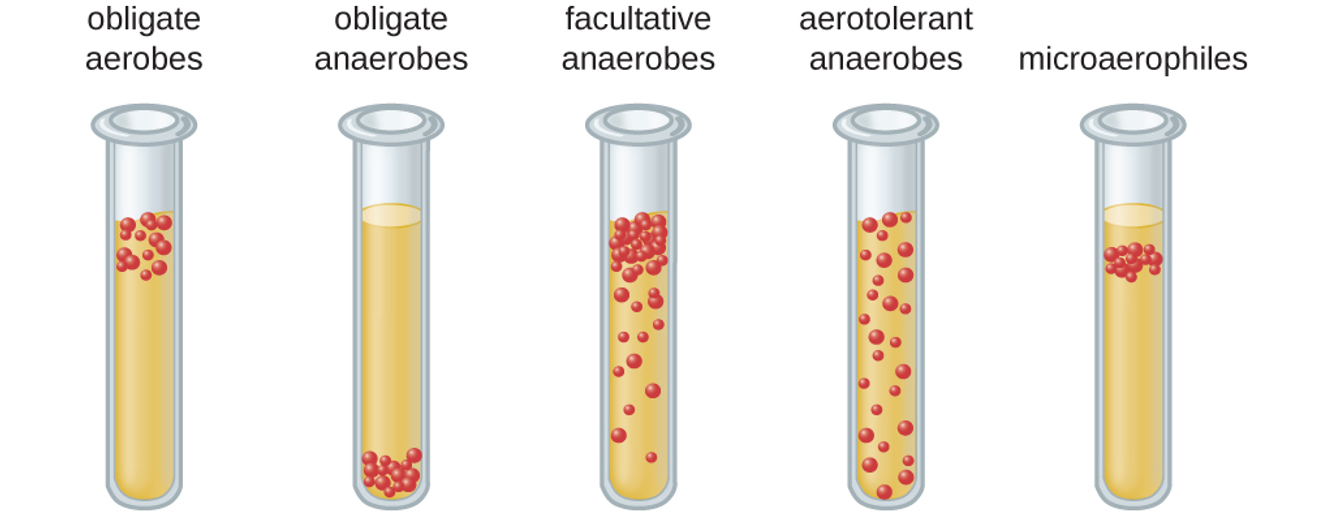
40
New cards
Microaerophiles
minimum O2; Campylobacter spp.
41
New cards
Fluid Thioglycolate Medium (FTM)
low % agar tube that has a gradient of O2
42
New cards
Aerotolerance
determined by location of growth
43
New cards
pH
acidic
44
New cards
Neutrophiles
~7 pH
45
New cards
Acidophiles
46
New cards
Alkaphiles
8-10.5 pH
47
New cards
Psychrophiles
48
New cards
Psychotrophs
4-20°C; make food go bad
49
New cards
Mesophiles
20-45°C; human microbe
50
New cards
Thermophiles
50-80°C; love heat, saturated
51
New cards
Hyperthermophiles
80-110°C; some survive @ > 121°C
52
New cards
Halophiles
Salt/solute lovers
53
New cards
Halotolerance
tolerate high salt (MSA & S. aureus)
54
New cards
Barometric pressure
ability to withstand great pressure; extremophiles
55
New cards
Barophiles
require high atmospheric pressure; unculturable; hyper or thermophiles (found on bottom of ocean)
56
New cards
Photoautotrophs
cyanobacteria and green sulfurs
57
New cards
Photoheterotrophs
purple non-sulfurs
58
New cards
Enriched media
Extra care of nutrients to grow certain micro and are hard to grow
59
New cards
Fastidious
organisms cannot make certain (exact) nutrients and hard to grow
60
New cards
Chemically defined medium
complete chemical composition known
61
New cards
Complex medium
contains extracts and digests of yeasts, meat, or plants; exact composition not known
62
New cards
Selective media
inhibit unwanted, promote growth of organism of interest
63
New cards
Enrichment cultures
promote growth of desired organism; only represents a fraction present
64
New cards
Differential media
distinguish colonies of bacteria by color change
65
New cards
Sterilization
fomite; removal/killing of ALL microbes; methods: (autoclave) Heat, Pressure, Filtration, and Chemical (sterilants); endospores and viruses
66
New cards
Sanitization
fomite; reduce microbial load; heat or chemicals
67
New cards
Disinfection
fomite; Inactivation/kill of microbes; vinegar and bleach; ≠ sterile
68
New cards
Antisepsis
living tissue; hydrogen peroxide, iodine, witch hazel, rubbing alcohol
69
New cards
Degerming
living tissue; washing hands, wiping with paper towel, etc.; soap and alcohol swab
70
New cards
BSL-1
sink for hand washing and door to close off lab; nonpathogenic E. coli and B. subtilis
71
New cards
BSL-2
UTA micro lab; BSL-1, PPE, self-closing door, eye-wash station, autoclave, or sterilizationS. aureus and Salmonella spp.; viruses: hepatitis, mumps, and measles
72
New cards
BSL-3
BSL-1 and 2; respirator, bio safety cabinets, hands-free wash sink, 2 sets of doors, directional air flow; indigenous or "exotic" pathogens; M. tuberculosis and B. anthracis; viruses: west nile virus and HIV
73
New cards
BSL-4
+BSL-3; full biohazard suit, change clothing on entry, shower on exit, decontaminate all material on exit, lab must have own air supply; "exotic" pathogens; viruses:
74
New cards
Critical
must be sterile; items used inside body; sterile tissue or bloodstream; surgical instruments, catheters, IV fluids
75
New cards
Semicritical
do not require high-level sterilization (membranous tissue, GI endoscope, RT equipment
76
New cards
Noncritical
do not require sterilization; stethoscope, bed linens, BP cuffs)
77
New cards
Decimal Reduction Time (DRT)
how much time it takes to kill 90% (1 log reduction) of population
78
New cards
Dry Heat
incineration; direct application of high heat (>250°C); Bunsen burner and bacteria incinerator
79
New cards
Moist Heat
penetrates cells with high temp in liquid/vapor; autoclave
80
New cards
autoclave
raise temp of water increasing boiling temp (~121°C) by raising pressure to 15 psi (endospores and thermophiles)
81
New cards
Pasteurization
"flash" heating foods to kill most microbes
82
New cards
HTST
milk heated at 72°C for 15sec, then bottled and refrigerated
83
New cards
UHT
milk heated at 138°C for 2 or more secs, then sealed in airtight containers for up to 90 days w/out refrigeration
84
New cards
milkborne organisms killed by pasteurization
C. jejune, Coxiella burnetii, Listeria monocytogenes, E. coli 0157:H7, M. tuberculosis, M. paratuberculosis, Salmonella spp. and Yevsinia enterocolitica
85
New cards
Refrigeration and Freezing
-static
86
New cards
Pascalization
high pressure used in food industry to kill microbes and prevent endospore formation (botulism)
87
New cards
Desiccation
drying or dehydration; to preserve foods by removing water
88
New cards
Lyophilization
freeze drying; rapid freezing then placed under vacuum
89
New cards
ionizing radiation
enters into cells and disrupts molecular structures such as DNA (x-rays and gamma rays)
90
New cards
non-ionizing radiation
doesn't penetrate glass, plastics, etc. can damage cells w/ direct exposure (UV irradiation)
91
New cards
sonication
High frequency sound waves to disrupt cell structure
92
New cards
filtration
use of barrier to physically separate microbes
93
New cards
membrane filtration
removes microbes from liquid samples
94
New cards
Phenolics
Denature proteins & membranes; triclosan(banned by FDA), lysol, and carbolic acid
95
New cards
Heavy Metals
binds inhibits proteins; MSCsZ
96
New cards
HM: Mercury
treated syphilis but banned due to neural toxicity
97
New cards
HM: Silver
used today to treat burn wounds, pediatric ophthalmic nenatorum, and in antibiotics
98
New cards
HM: Copper Sulfate
used as algicide to treat pools
99
New cards
HM: Zinc
mouthwashes, calamine lotion, baby powder, argyria
100
New cards
H: Iodine
oxidizes cellular components; commonly used as a iodophor (complex with organic molecule)