Cog exam 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
1
New cards
What is attention?
mental process that concentrates effort on a stimulus, limited resource
2
New cards
Why is talking on a cell phone while
driving more dangerous than talking with a passenger?
driving more dangerous than talking with a passenger?
requires more attention to focus on conversation
3
New cards
Selective attention
focusing on chosen event, limiting distractions
4
New cards
divided attention
focusing on two or more things at a time
5
New cards
automaticity
ability to perform process with little to no attention
6
New cards
mind wandering
attention wanders from current task
7
New cards
Spotlight attention
mental attention focusing mechanism for preparing to encode stimulus
8
New cards
Spatial Cuing Task (Posner): task & results
participants fixate on screen and respond when target is presented on either side of screen. Arrow on screen depicts location of target correctly or incorrectly
9
New cards
Significance of Posner's spatial cuing task
spotlight attention is mental and can be shifted before stimulus appears and is triggered by cognitive factors.
10
New cards
Visual Search (Treisman, CL2): method & results
participants indicate if target (green circle) is present in trials with feature search or conjunction search. Conjunction absent search increased rt most
11
New cards
Difference between feature and conjunction search
feature search had one distractor shape/color, conjunction search had two distractor shapes/color
12
New cards
Significance of Treisman visual search
two types of attention processes: quick, automatic process and slower, deliberate process.
13
New cards
Shadowing task
participant repeats what they hear in selective ear
14
New cards
dichotic listening
participant wears headphones where two messages play in either ear
15
New cards
Where does selective attention occur?
sensory and stm
16
New cards
Stroop task (CL3): task & results, implication
Participants report the ink colors of color names displayed. When ink colors and names contradict each other, stroop effect is observed and rt increases.
17
New cards
What is the stroop effect?
the delay in reaction time due to contradicting stimuli
18
New cards
How can one overcome stroop effect?
practice, focus on first or last letter of word
19
New cards
How does something become automatic?
repeated practice
20
New cards
Benefits of automaticity
faster, unconscious, doesn't require attention
21
New cards
disadvantages of automaticity
action slips and mind wandering
22
New cards
What are action slips?
unattended auto actions that are inappropriate for current situation
23
New cards
Hemineglect: What is this syndrome? From the perspective of attentional mechanisms, what
seems to be happening?
seems to be happening?
impairment in directing attention to half of perceptual world
24
New cards
What is Decay
the loss of information from memory
25
New cards
Brown & Peterson (CL4): experimental design & task, results, their interpretation
participants attempt to remember trigram of letters after doing distraction (subtraction) task. ability to remember trigram decreased with longer distraction task
26
New cards
Significance of Brown & Peterson study
info fades from stm if it can't be rehearsed
27
New cards
Waugh & Norman (probe digit) study, results & implications
participants heart list of sixteen digits, either one or four per second, had to remember which digit came after displayed digit
28
New cards
Significance of Waugh & Norman
interference (retroactive) is the main cause of forgetting from stm
29
New cards
Keppel & Underwood (thoughts on Brown-Peterson),
performance decreases on later trials due to proactive interference
30
New cards
Retroactive Interference (RI)
newer material interferes with recollection of older items
31
New cards
Proactive Interference (PI)
older material interferes with learning new items
32
New cards
Release from PI (Wickens)
when pi is decreased due to change in stimulus
33
New cards
free recall
people recall list in any order
34
New cards
serial recall
people recall list in original order
35
New cards
primary effect
accuracy of recall for early list positions because they are rehearsed more
36
New cards
recency effect
accuracy of correct recall on final list items because they are still in stm
37
New cards
Changes in serial position effects w/development (i.e., age/grade)
children increase in rehearsal as they age and primacy effect increases
38
New cards
2 properties/functions of rehearsal
recycles info in stm to maintain for longer periods of time and increases likelihood of info transferring to ltm
39
New cards
What is the capacity of STM?
15-20 seconds
40
New cards
chunks, recoding
chunking info together and remembering the group
41
New cards
Scanning STM: Sternberg task (CL5) – experimental design & task, results &
a series of letters were presented (1-6) for rehearsal, participant indicated if probe letter was present in previous series.
42
New cards
Sternberg task significance
people scan stm in serial exhaustive fashion at 38ms per item
43
New cards
Form of information in STM (i.e., types of codes/representations in STM)
verbal, semantic, visual, kinesthetic
44
New cards
Baddeley's model of working memory
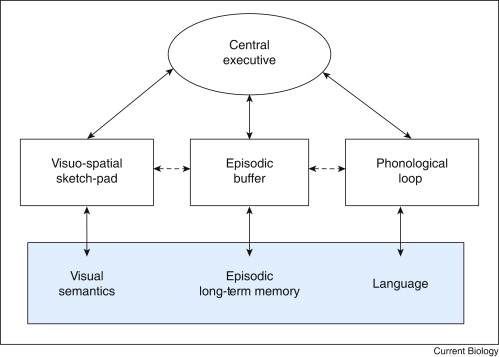
45
New cards
Characteristics of auxiliary systems (phonological loop and visuospatial sketchpad)
low level processing, domain specific, limited pool of resources, independent
46
New cards
Engle's model of working memory
working memory is the ability to control attention, everyone has different wm capacity
47
New cards
What is Broadbent's attention model?
sensory memory-blocking filter-perceptual analysis
48
New cards
What is the blocking filter?
blocks irrelevent info based on physical features
49
New cards
What is Treisman's attenuation model?
sensory memory-filter-dictionary
50
New cards
What is the dictionary?
blocks irrelevent info based on psychological info
51
New cards
What is Johnston and Heinz multimode model?
sensory memory-early filter-perceptual analysis-late filter
52
New cards
What is the early filter?
based on physical features
53
New cards
What is the late filter?
based on meaning, requires more capacity, slows processing speed