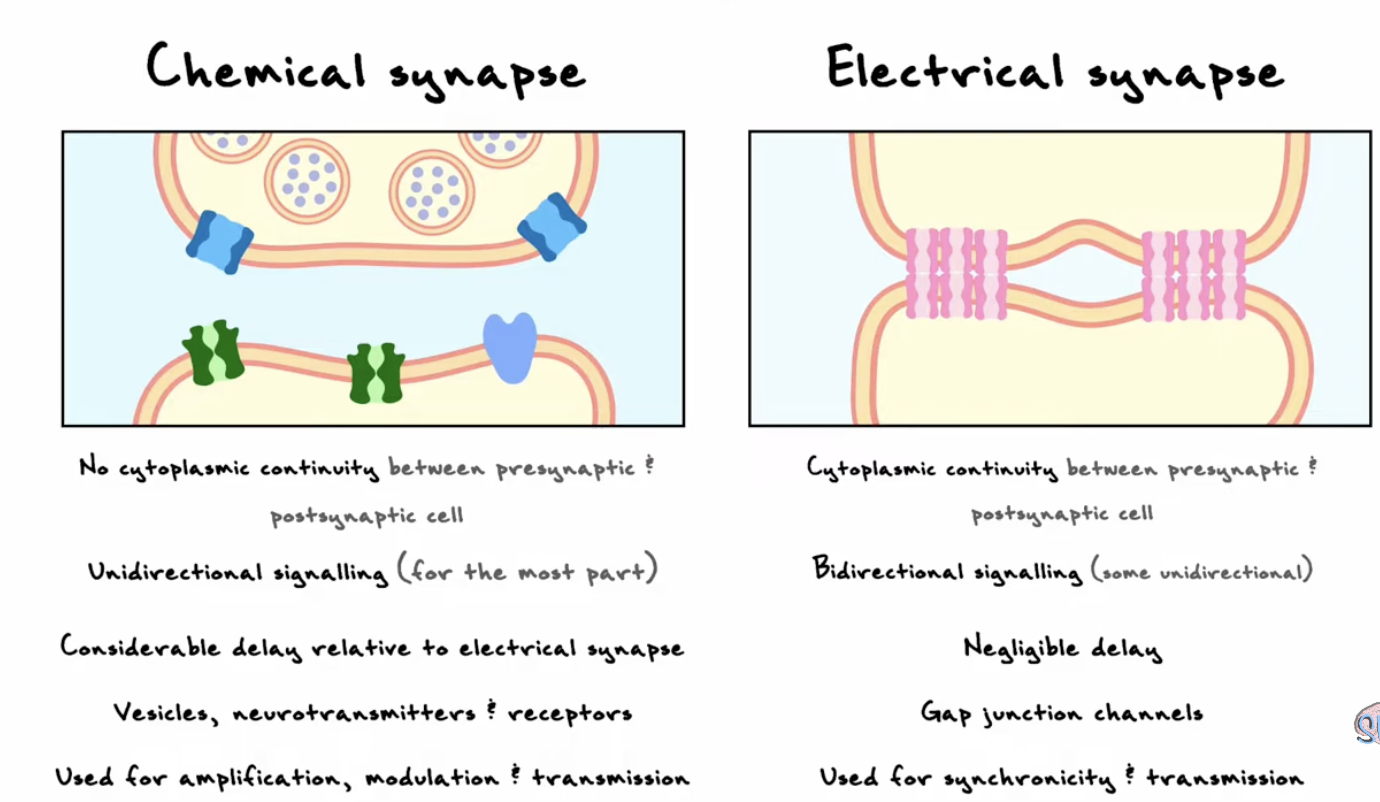
Electrical vs chemical synapses
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Where electrical synapses found
between neurons
between glial cells
Electrical synapses characterised by
cytoplasmic continuity between presynaptic and postsynapatic cell
How is this continuity facilitated by
Gap junction channels
two connexons
each made of 6 connexins
so one gap junction→ 12 connexins
diverse group of trans membrane proteins
have many types and different genes
each embedded in membrane of pre and post cell
Structure of pore
form large non specific pore
allows:
current, small peptides and anions and cations through
So can be bidirectional
However, due to diverse range of connexins
some are only unidirectional
Can close in response to
low pH
high Ca2+
phosphorylation
voltage
but depends on gap junction
Speed
no delay
due to it being continuous
instantaneous
Firing can be instantaneous→ e.g cardiac muslce
intercalated discs→ contain gap junctions
negligible delay means a signal that splits to go through multiple gap junctions can travel through at the same time
Synchronised
can be very beneficial, depending on the need of the body
Chemical synapses
no continuity
cleft is 5-10x larger than electrical synapse
unidirectional
delay→ 1ms (very noticeable compared to electrical)
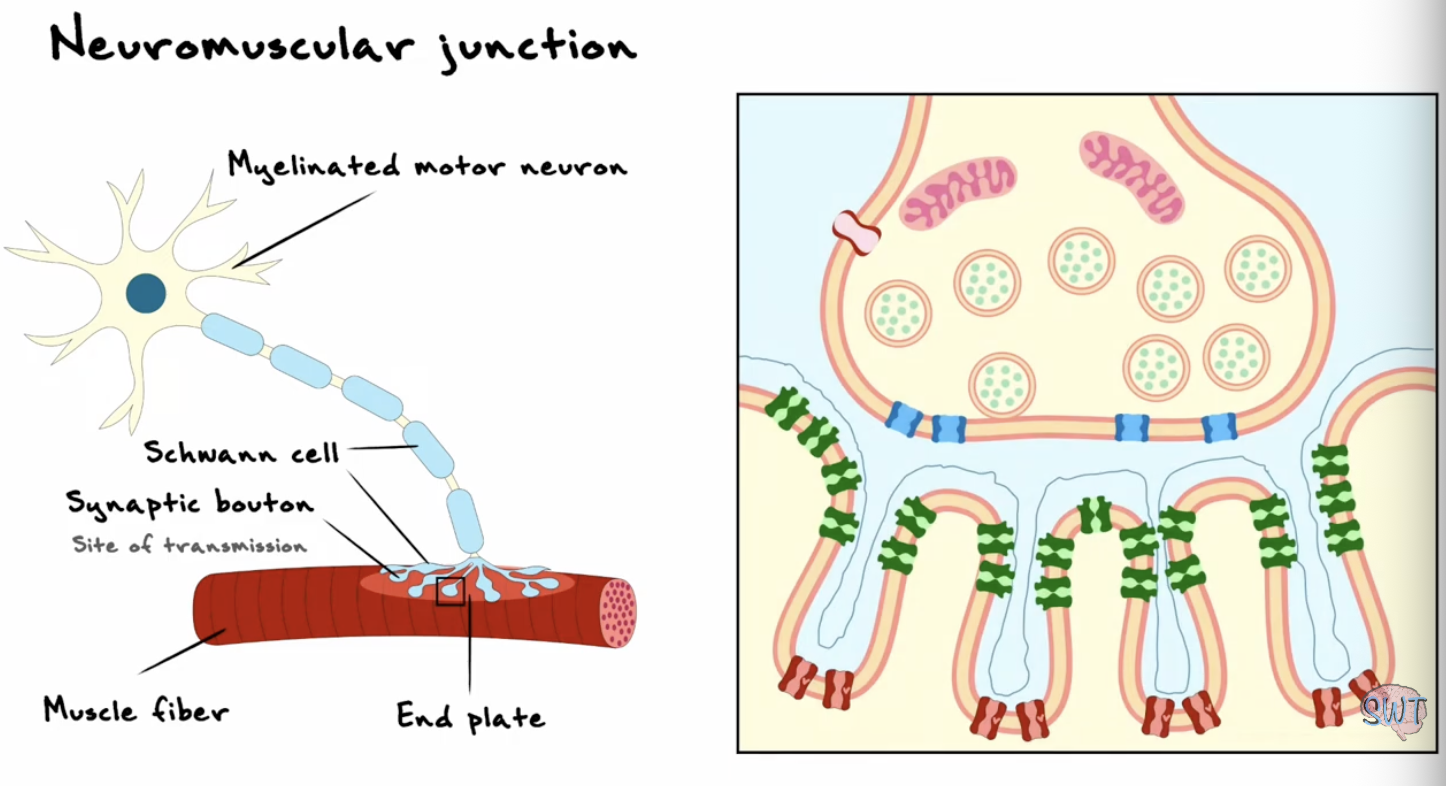
Why study the Neuromuscular junction to study synapses?
Size
Micrometer scale at the NMJ
vs nm scale in the brain
Simplicity
our neutrotransmitter : one receptor system
vs way more complicated systems in the brain
Accessibility
do not need to damage strucutre
THEREFORE: ideal for electrophysiologyical recordings
Neuromuscular junction features
myelinated motor neurone
wrapped in schwann cells
synaptic bouton→ site of transmission
also covered in scwann cells
form the endplate
on the muscle fibres
How is ACh packaged into vesicles
Choline into cell via symporter with Na+
acetyl-CoA made from glucose in mitochdonria
choline + acetyl-CoA → acetylcholine (ACh) using acetyltransferase (ChAT)
Vescicle proton pump H+ export
ACh into vescile through H+ symporter
Receptor for ACh in neuromuscular junction
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR)
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) features
pentameric ionotropic channel
2 alpha/beta/delta/gamma NMJ
CNS ones have different: 2alpha/3beta
Binding sites found between
two alpha subunits
neighbouring beta and delta subunits
How is the channel opened
two binding sites must have ACh
What happens when open
Na+ in
K+ out
can both flow due to large pore size
Ca2+ can also get through
channel is non selective
Why called nicotinic
nicotine can open it
it is an agonist
Antagonists
alpha-bungarotoxin
curare
bind and do not open it
Strucutre of post-synaptic→ end plate
invaginations→ increase SA
more nicontic receptors at the crests
sodium voltage gated in the trophs