Atomic Physics revision
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
how is the mass distributed in an atom?
most of the mass is concentrated in the nucleus — made up of the protons and the neutrons
the electrons in the outer shells contain little to no mass at all
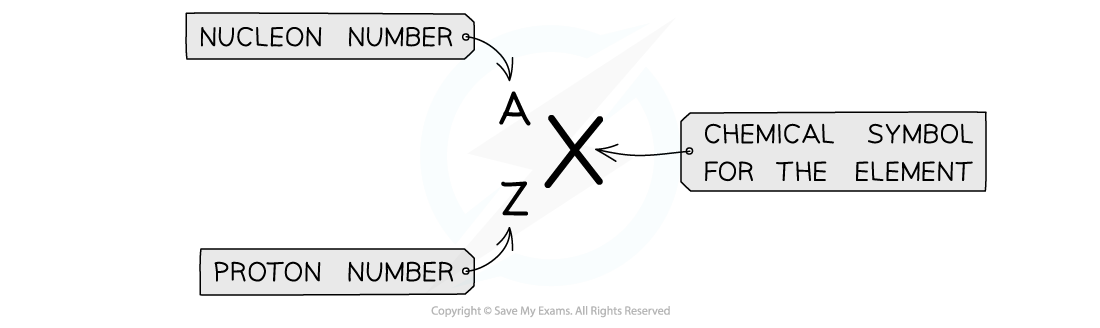
nucleon number / proton number of an atom:
A — nucleon number / mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons
Z — proton number = number of protons
what are the charges of the three particles that make up an atom?
Proton — 1.6 × 10-19 1
Electron — -1.6 × 10-19 1
Neutron — 0 0
describe an experiment that provides evidence for the nuclear model of an atom
alpha scattering:
alpha particles are positively charged so are repelled by positive nucleus
most of the particles passed through, un-deflected
thus proving, most of the atom is empty space
furthermore, alpha particles have a high momentum, so, to be deflected back they would’ve made contact with something of a high mass.
what is an isotope?
two isotopes of the same element have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons (i.e. same proton number but different nucleon number)
example: Carbon-12 and Carbon-13 are isotopes of eachother.
what is a radioactive decay?
is the process by which an unstable nuclei of an isotope changes to become more stable by emitting ionising radiation
they emit either alpha, Beta, or Gamma radiation
what makes the nuclei of an isotope unstable?
the nucleus holds too many or too little neutrons so must decay to become stable.
Alpha radiation
Penetrating power — poor = stopped by paper / only 2-3cm in air
Ionising power — strong
what is it? — Helium-4 nucleus with a +2 charge
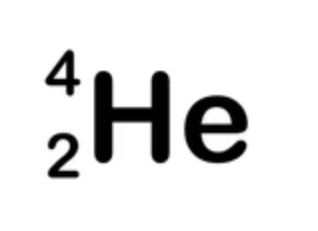
Beta radiation
Penetrating power — moderate = stopped by 2-3mm aluminium / ~50cm in air
Ionising power — moderate
what is it? — a fast moving electron with a charge of -1

Gamma radiation
penetrating power — strong = stopped by thick lead / infinite range in air
ionising power — weak
what is it? — highest frequency part of EM spectrum
nuclear fission vs nuclear fusion
Nuclear fission — one large, unstable, atom splits to form two smaller more stable atoms, releasing energy in the process. Usually the atom would absorb a neutron beforehand
Nuclear fusion — two smaller nuclei collide at a high speed causing them to join (fuse) to create a larger / heavier nucleus, releasing energy in the process.
what is the half life of a radioactive sample?
Is the time taken for the number of nuclei of a radioactive isotope to halve
Therefore, it is the time taken for the count rate on a Geiger-Muller detector to halve.
Name 4 sources of background radiation
iI is low level radiation that is always around us as it comes from naturally occurring unstable isotopes. As it is low level, it is also low-risk.
In the air — from radon gas that comes from the ground
In food and drink
In building materials / rocks beneath us
Cosmic rays (radiation from space) from the sun
name a use of alpha emitters.
In smoke detectors:
alpha particles ionise air particles causing a current to flow in the smoke detector
if smoke attaches to the air particle, the alpha particle is unable to ionise the particle
the current therefore falls and an alarm goes off
name 3 uses of gamma rays
1) To diagnose cancer:
rays pass through body easily and so can be detected
they are weakly ionising so don’t cause much damage to the patient
2) To treat cancer (radiotherapy):
involves a high dose of gamma rays that kill the cancer cells, stopping them dividing
3) to sterilise food / equipment:
high dose of gamma rays kills bacteria cells on food / equipment
doesn’t involve high temperatures so is good for food and plastic instruments.
name a use of Beta particles
Thickness gauge (quality control in factories):
beta is partially blocked by paper
if paper is too thick when it is being made, detector will pick up less radiation warning the factory that the paper is too thick
if paper is too thin when it is being made, detector will pick up more radiation, warning the factory that the paper is too thin.
what effect does a low dose of radiation have on living cells?
low doses cause minor damage without killing the cells.
However, this can lead to mutant cells that don’t work correctly.
Long term exposure to low doses increases the risk of mutant cells which divide uncontrollably.
This uncontrollable division of mutant cells then forms what we call a cancer
name 4 safety precautions and why we take them when dealing with radioactive sources
use gloves and tongs — reduces risk of contamination by radioactive particles as you are not physically touching the material
minimise exposure time — reduces the total dose you get and, in total, the time you are exposed to its emissions
maintain distance from the material — to allow most of the radiation to be absorbed by the air before it reaches you.
store in a thick lead-lined box — thick lead absorbs all types of radiation so it can be used as a shielding from the radioactive material.