Chapter 6: Thick/Thin, Color, Markings (dealing with epidermis)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
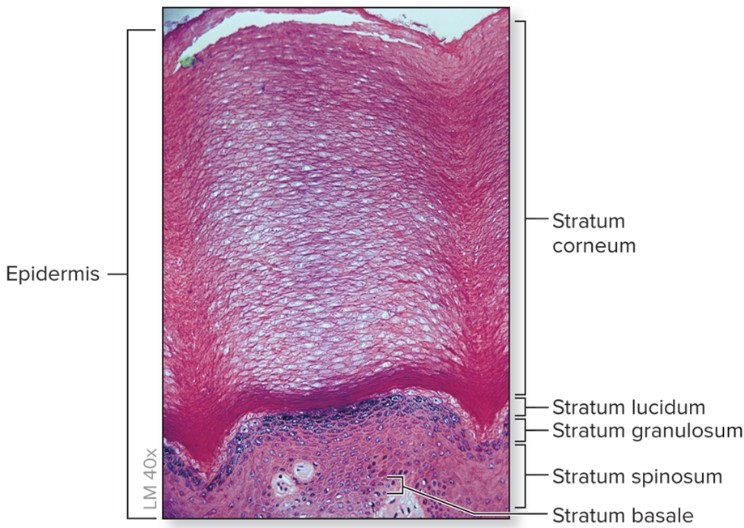
What is thick skin?
palms of hands, soles of feet
contains all five layers of epidermal strata
sweat glands but no hair follicles or sebaceous glands
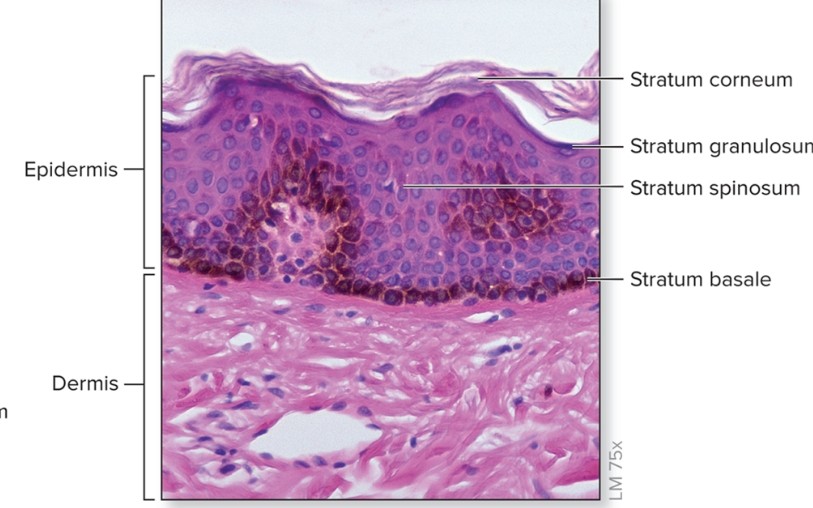
What is thin skin?
covers most of body
lacks a stratum lucidum
sweat glands, hair follicles, and sebaceous glands
What is normal skin color from?
hemoglobin, melanin, carotene
What are things that affect skin color?
hemoglobin, melanin, carotene, cyanosis, erythema, pallor, jaundice, bruise
What color does hemoglobin bring?
oxygen-binding protein in red blood cells,
bright red color upon binding oxygen
What color does melanin bring?
dark pigment produced in melanocytes
transferred to keratinocytes
amount in skin varies (heredity, UV exposure)
Albinism: Melanocytes unable to produce melanin
What color does carotene bring?
yellow-orange pigment acquired from some vegetables
What color does cyanosis bring?
blue, due to a lack of oxygen
What color does erythema bring?
red
due to fever or inflammation
What color does pallor bring?
white/pale, due to shock or anemia
What color does jaundice bring?
yellow, due to liver disorder
What color does a bruise bring?
black/blue/purple, due to hemorrhage
What are some skin markings?
nevus (moles), freckles, hemangiomas, friction ridges
What are nevus (moles)?
localized overgrowth of melanocytes
should be monitored for changes suggesting malignancy
What are freckles?
yellowish or brown spots
localized areas of increased melanocyte activity
What are hemangiomas?
skin discoloration due to benign blood vessel tumor
What are friction ridges?
large folds and valleys of dermis and epidermis, fingerprints