Chapter 7: Phospholipids
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
plasma membrane is aka
cell membrane
Where else can you find plasma membranes?
in any membrane bound organelle
ER
golgi
mitochondria, etc
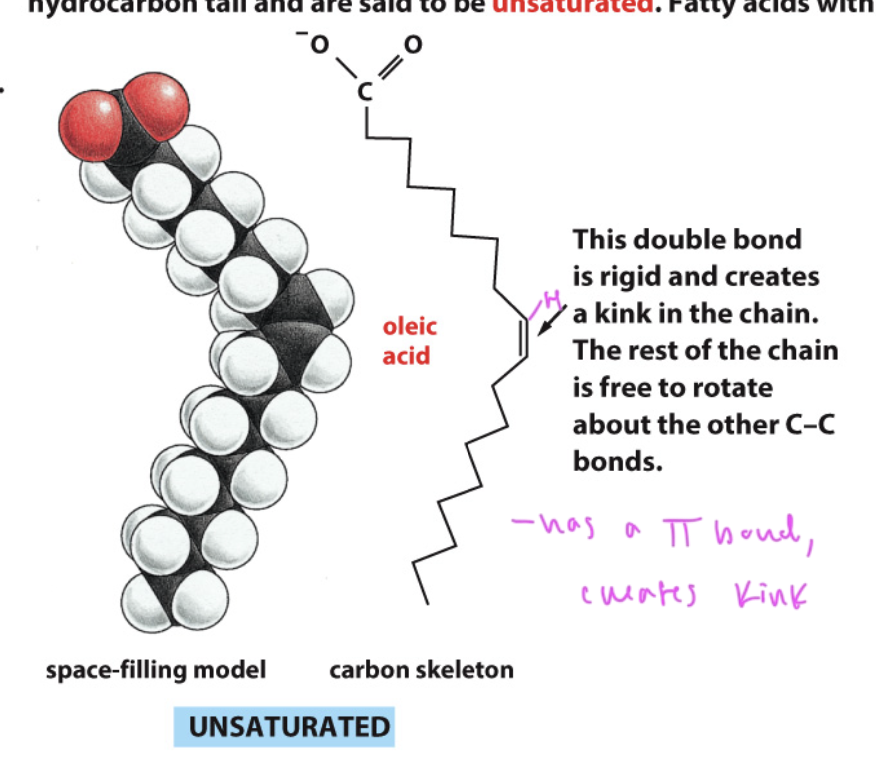
unsaturated fatty acids
have a kink from a C=C double bond
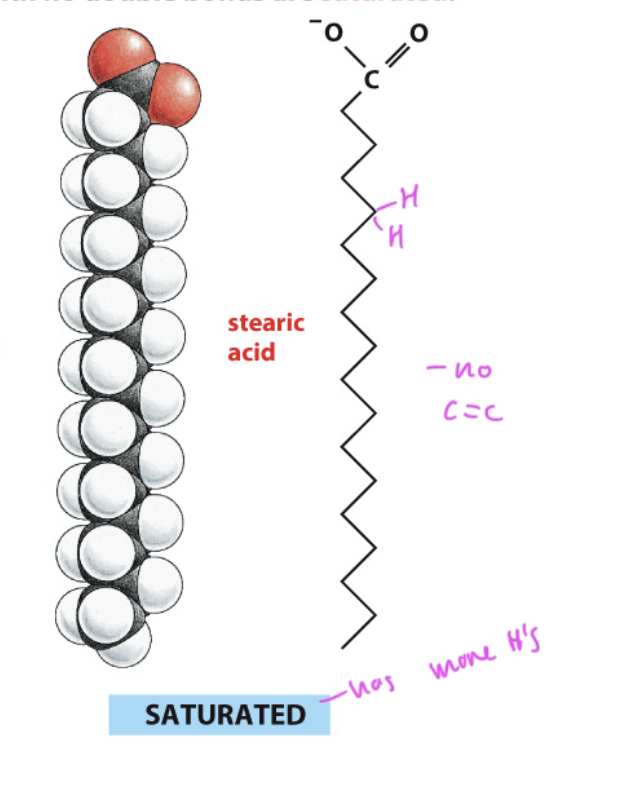
saturated fatty acid
has more hydrogens since it has no C=C double bonds
has a linear shape
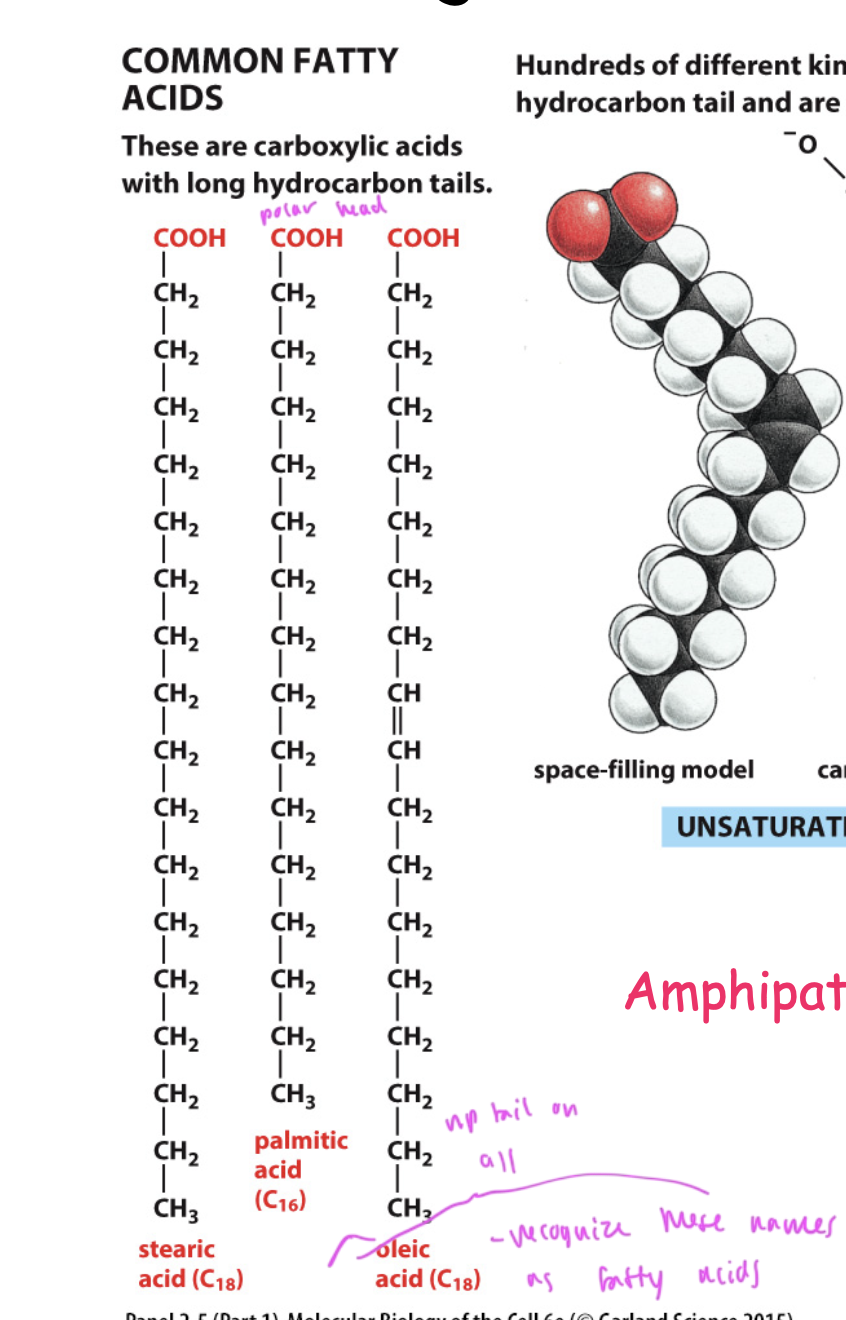
common fatty acids
stearic acid
oleic acid
palmitic acid
all have a np tail and polar head group
all are carboxylic acids with hydrocarbon tails
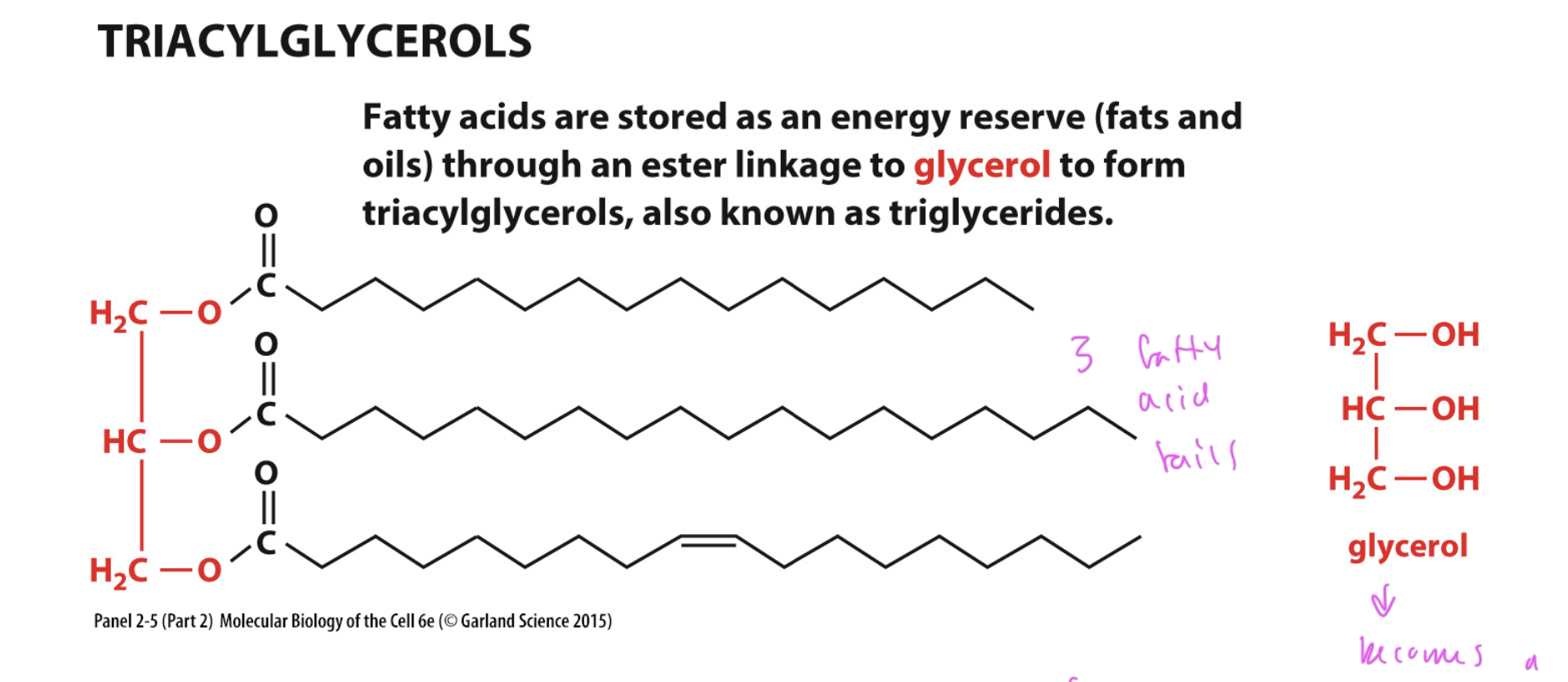
triacylglycerols
a higher order lipid
glycerol with a np hydrocarbon tail and an ester
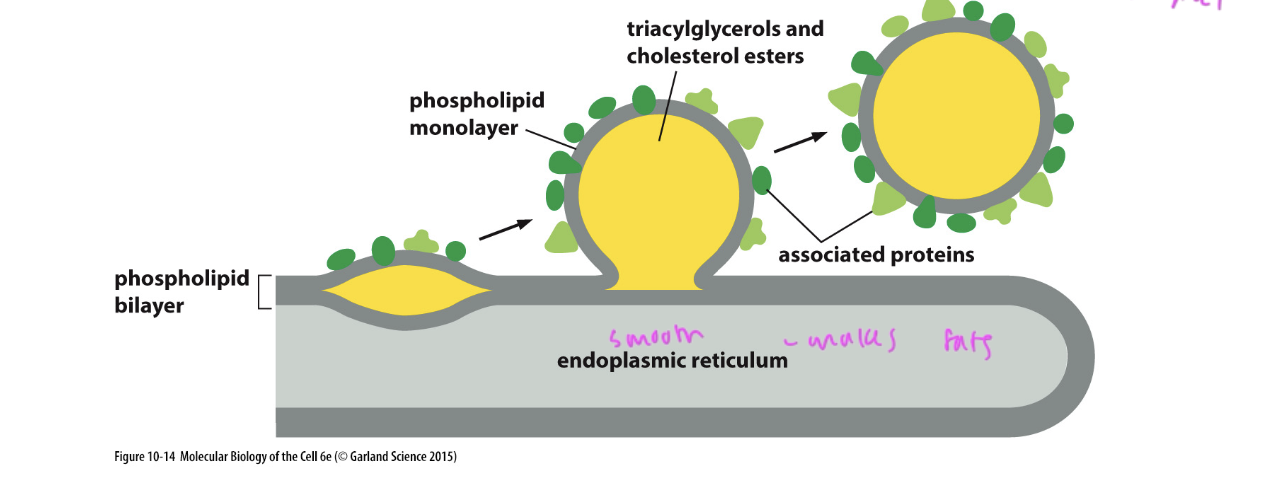
how fat droplets are formed
a droplet forms off of the phospholipid bilayer of the smooth ER
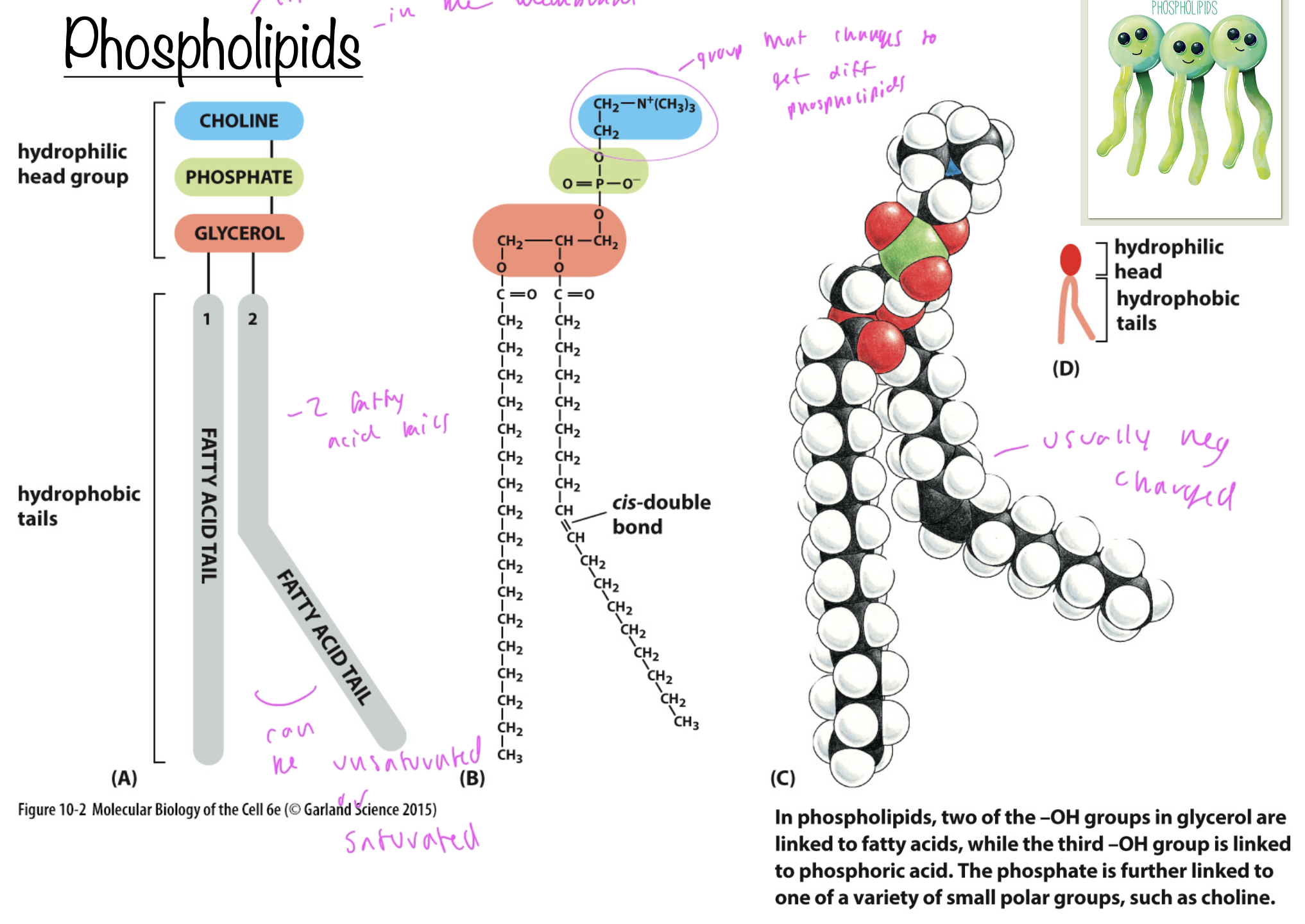
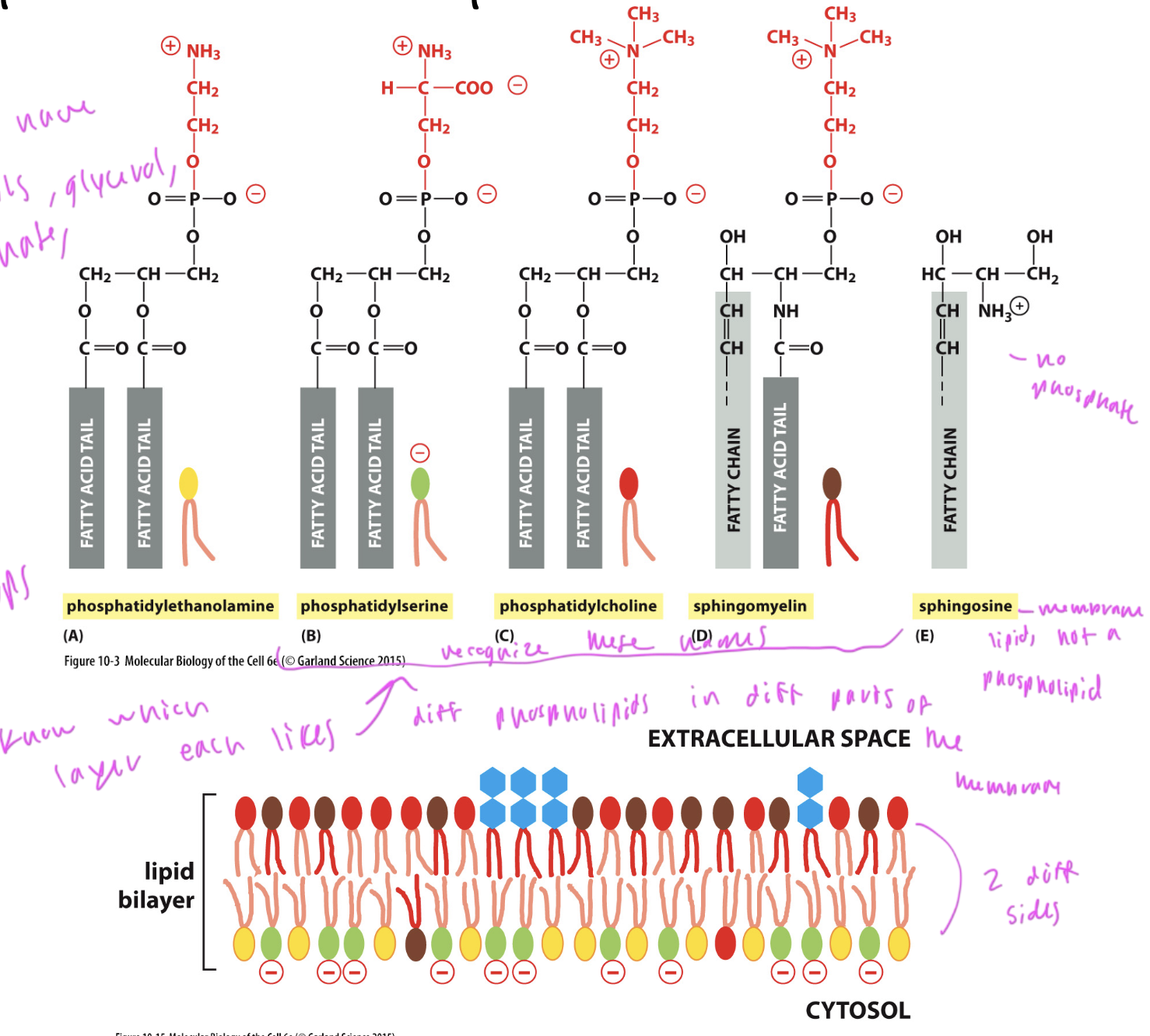
phospholipids
lipids in the membrane
all have a phosphate, fatty acids tails (unsaturated and/or saturated), a glycerol, and some group at the top
the group at the top is what differentiates different phospholipids
usually neg charged
have a hydrophillic head (polar) and hydrophobic tail (np)
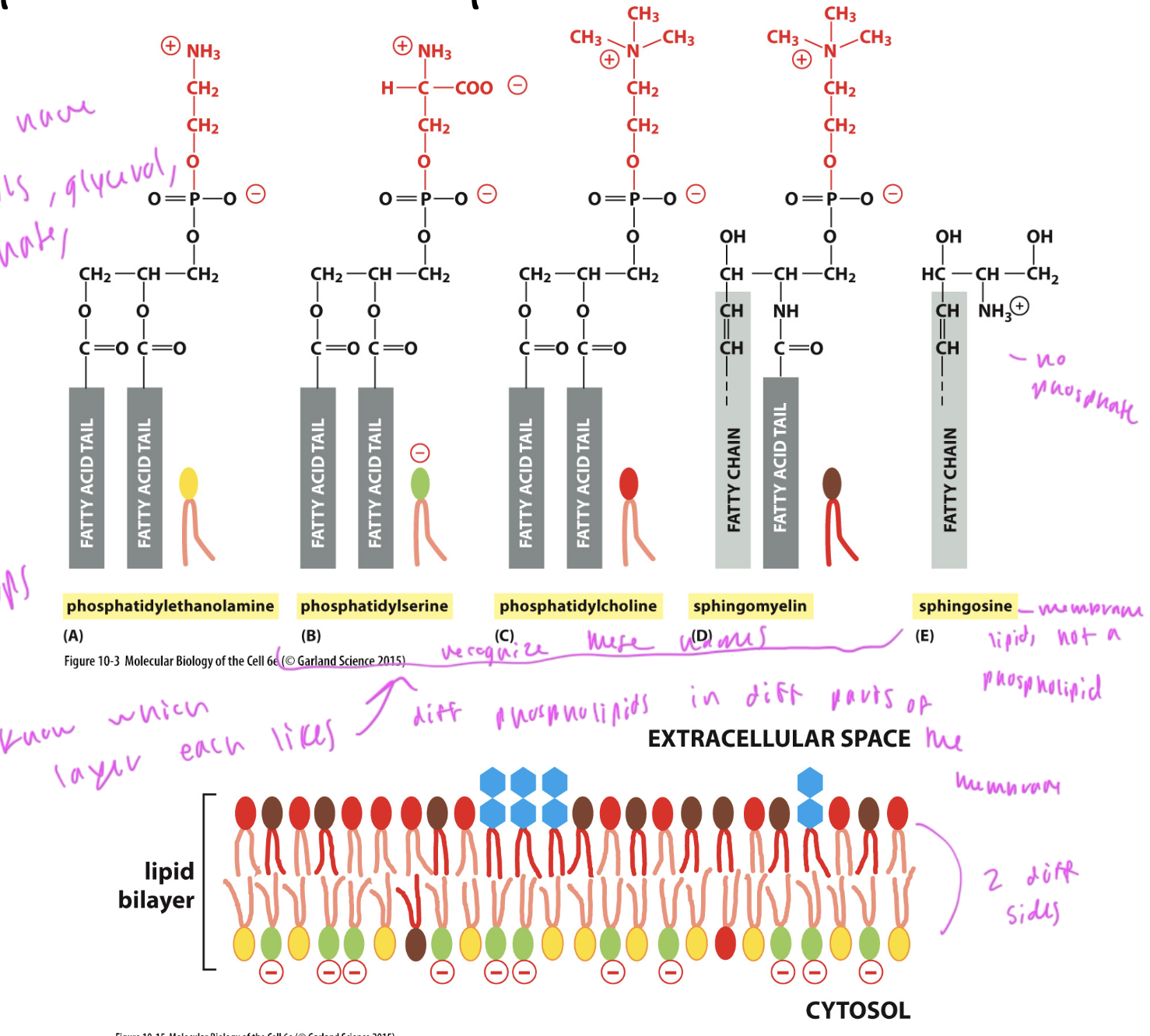
phospholipids in the plasma membrane
phosphatidylethanolamine: on the cytosol side
phosphhatidylserine: on the cytosol side
phosphatidylcholine: mostly on the ECM side (inside the cell)
sphingomyelin: mostly on the ECM side (inside the cell)
sphingosine: membrane lipid that is not a phospholipid, and only has one tail
ALL have 2 tails
membrane lipid that is not a phospholipid
sphingosine
it just lacks a phosphate
cholestrol
steroid with a polar head group (a singular O) and a np hydrocarbon tail
makes the membrane stiff by preventing nearby phospholipid tails from moving
it is rigid due to the ring structure of the steroid part

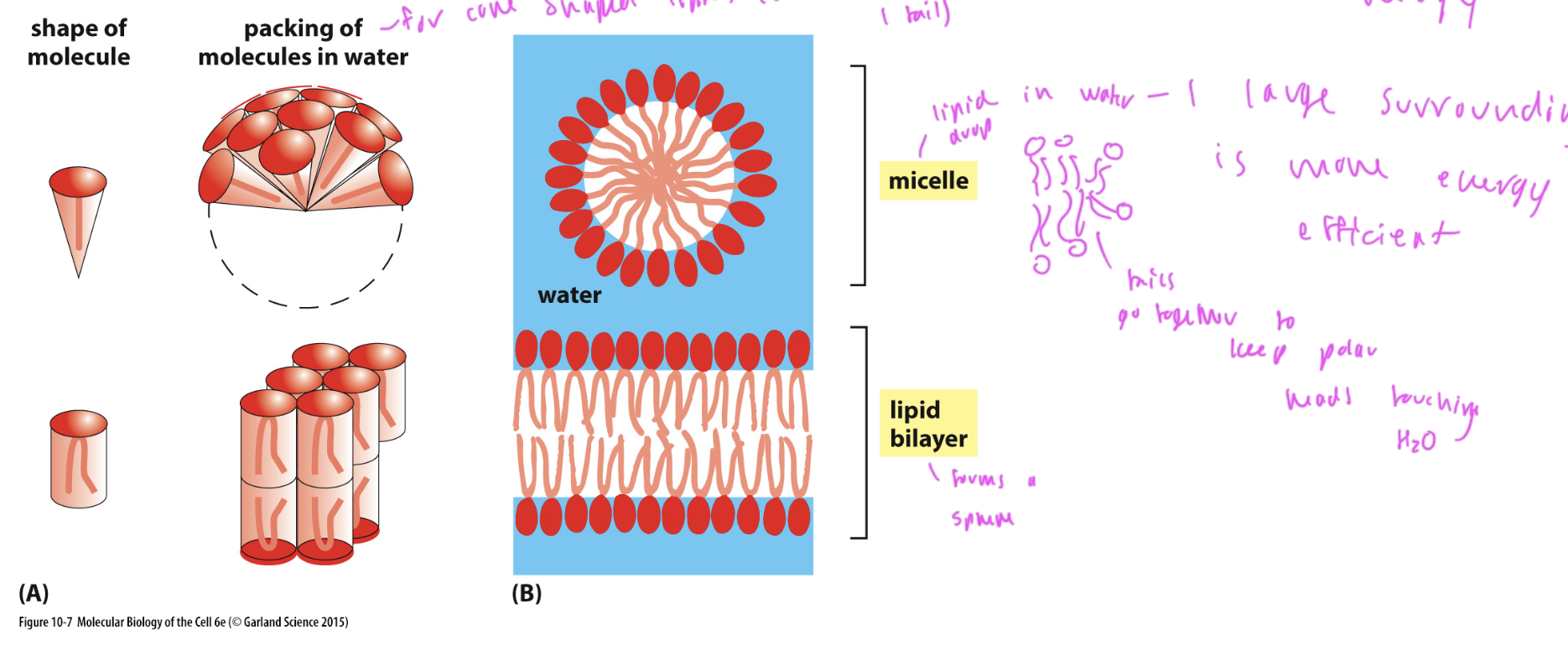
ways for lipids to form in aqueous environments
micelle: sphere shaped
forms from cone shaped lipids
lipid bilayer
forms from cylinder shaped lipids
both form to minimize hydrophobic interactions of the lipid tails with water (water wants to surround lipids since it is energetically favorable)
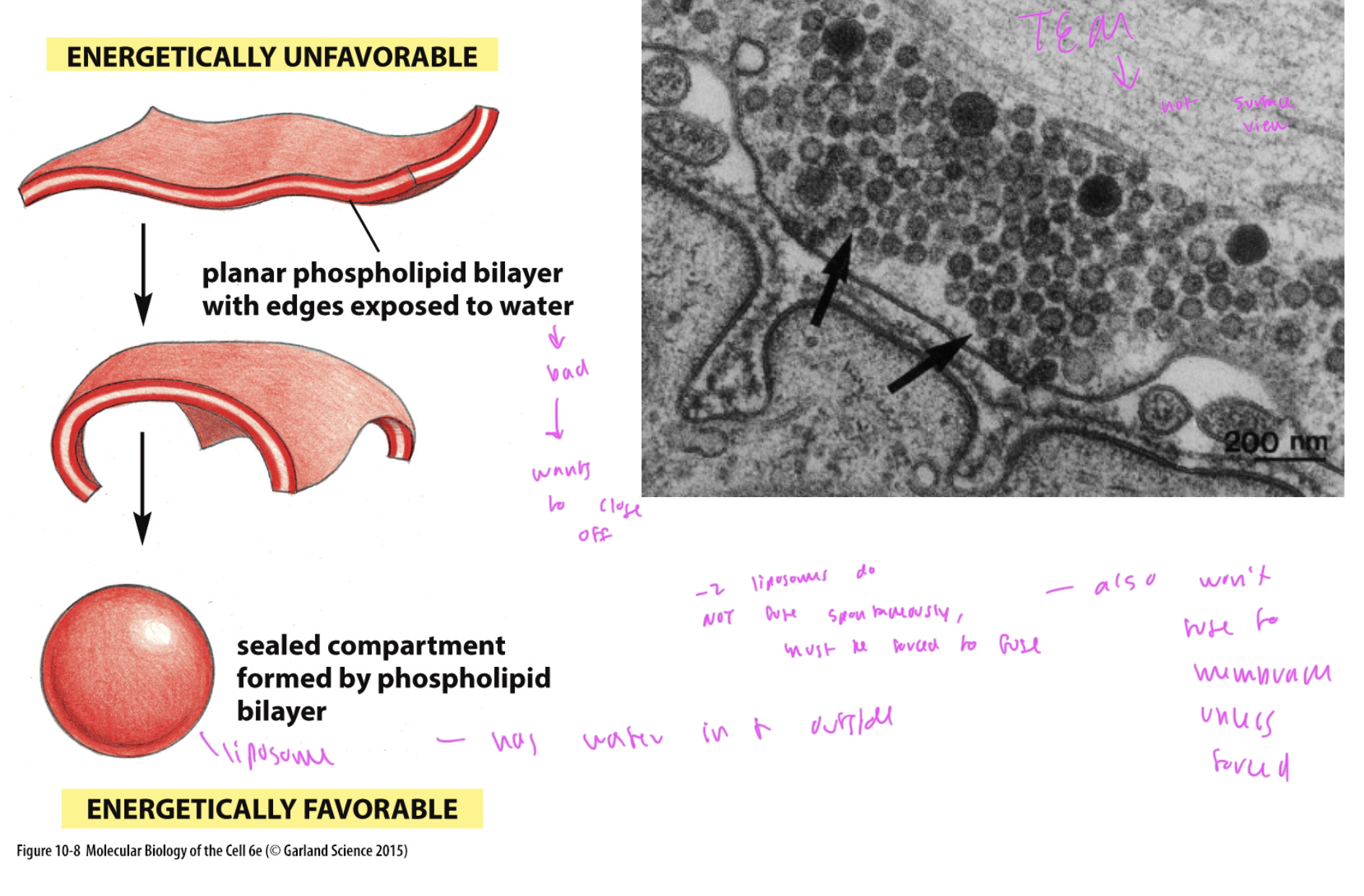
phospholipid forming a sphere/ liposome
does this when the edges of the bilayer are exposed to water, which is not favorable
forms a liposome, which has water inside and outside of it
two liposomes will not fuse together unless forced to do so
What characteristics would make a membrane more stiff?
long hydrocarbon chains (higher VDWs)
saturated fatty acids (higher VDWs)
more cholesterol (makes membrane stiff by limiting flexion and rotation of tails)
forming the membrane into a repeatable pattern shape to make a tight fit
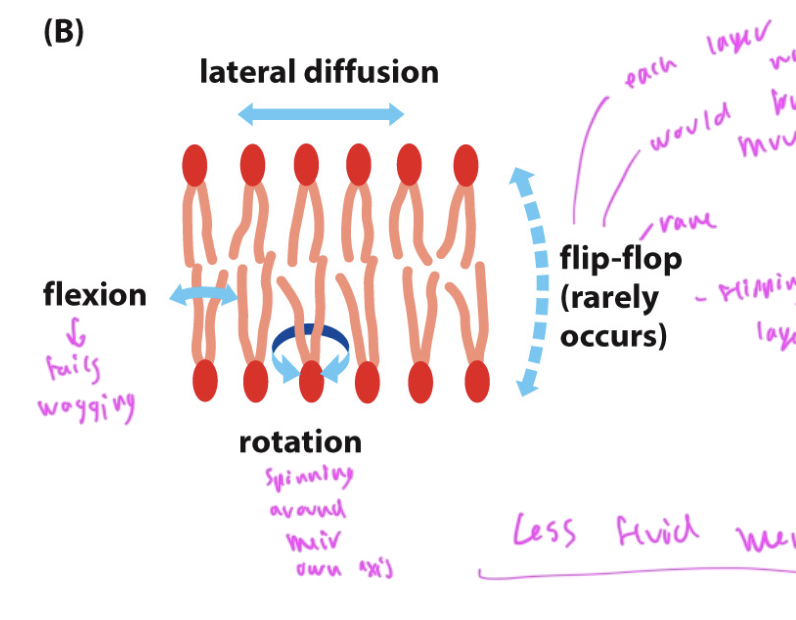
ways phospholipid tails can move
flexion: tails wagging
rotation: tails spinning around the axis of their head
lateral diffusion moving left/right
flip-flop: is very rare, occurs when the top layer flips to the bottom due to flipase
flipping is not favorable since it would require the sides to go on the opposite side, which is not energetically favorable for them, and the polar head would have to push thru the np layer below it
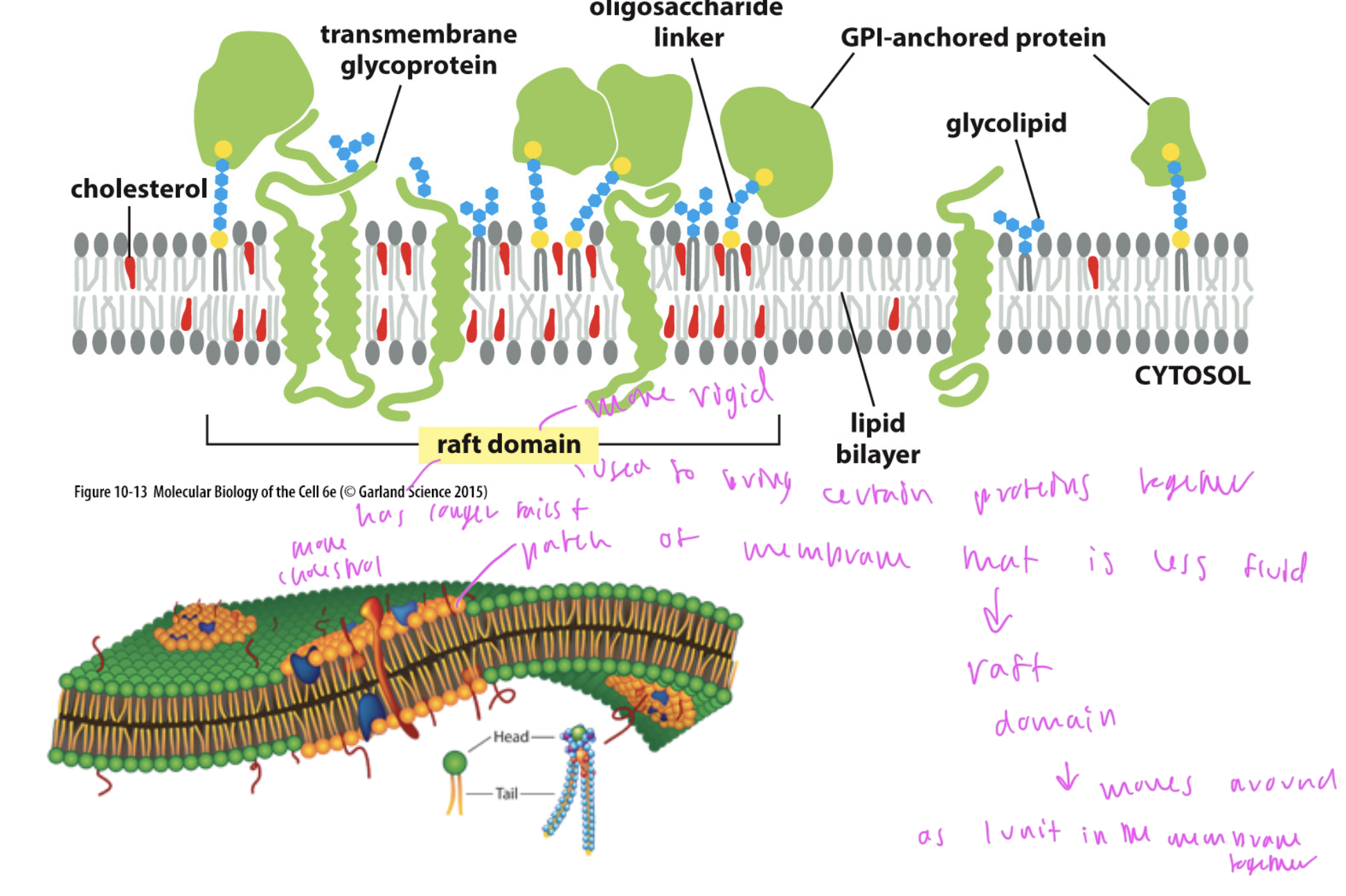
lipid rafts
rigid domains of the phospholipid bilayer formed to bring certain groups of proteins together
this region has longer hydrocarbon tails, more cholesterol, etc
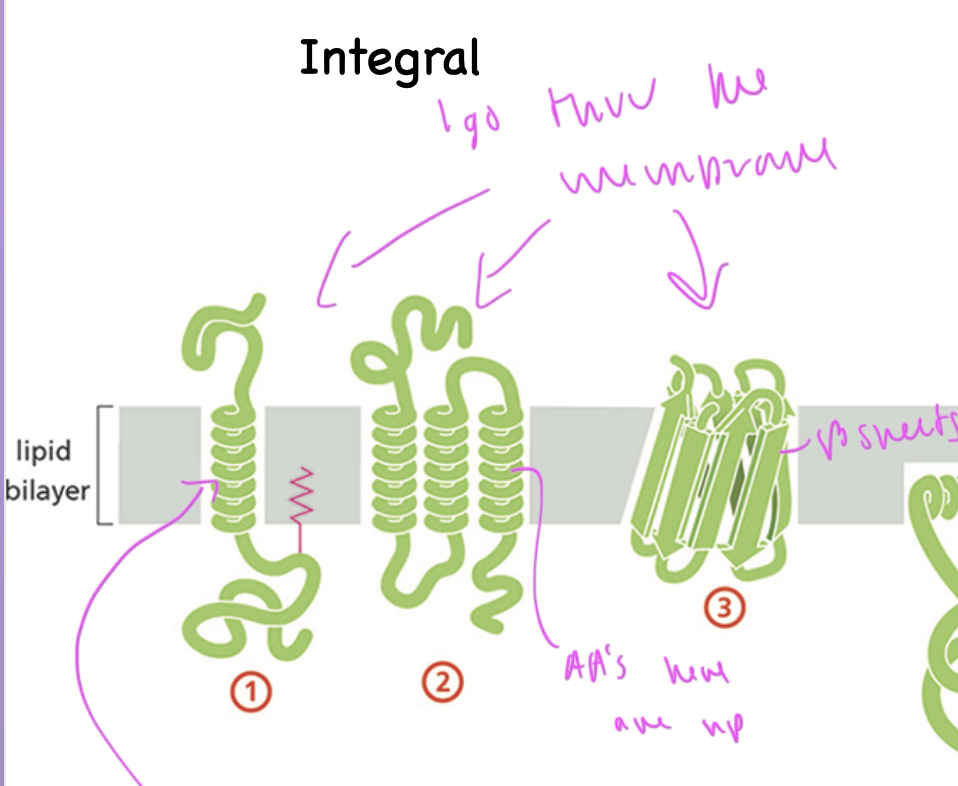
integral membrane proteins
span thru the membrane
often have an alpha helix that spans thru the membrane bilayer, made up of np AAs
can also be a beta barrel
lipid anchored proteins
have a lipid dipped into the lipid bilayer to anchor the protein at the membrane’s surface
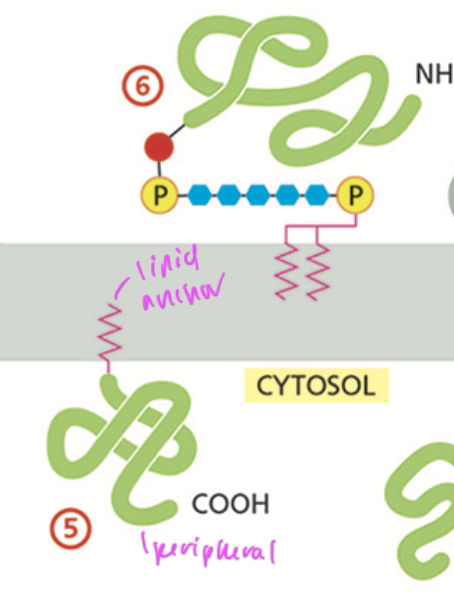
peripheral proteins
are bound to integral proteins on the interior of the plasma membrane and are on one side of the membrane
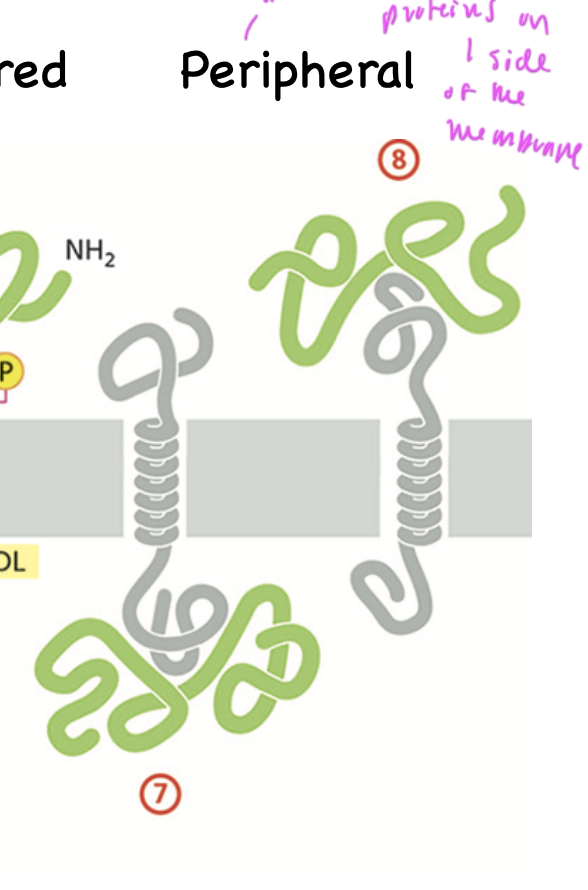
lipid anchors
helps proteins stick in the membrane and be peripheral
also lets the protein know what side of the membrane it is on
ex: myristoyl, palmitoyl, and farnesyl anchors, all which are on the cytosol side
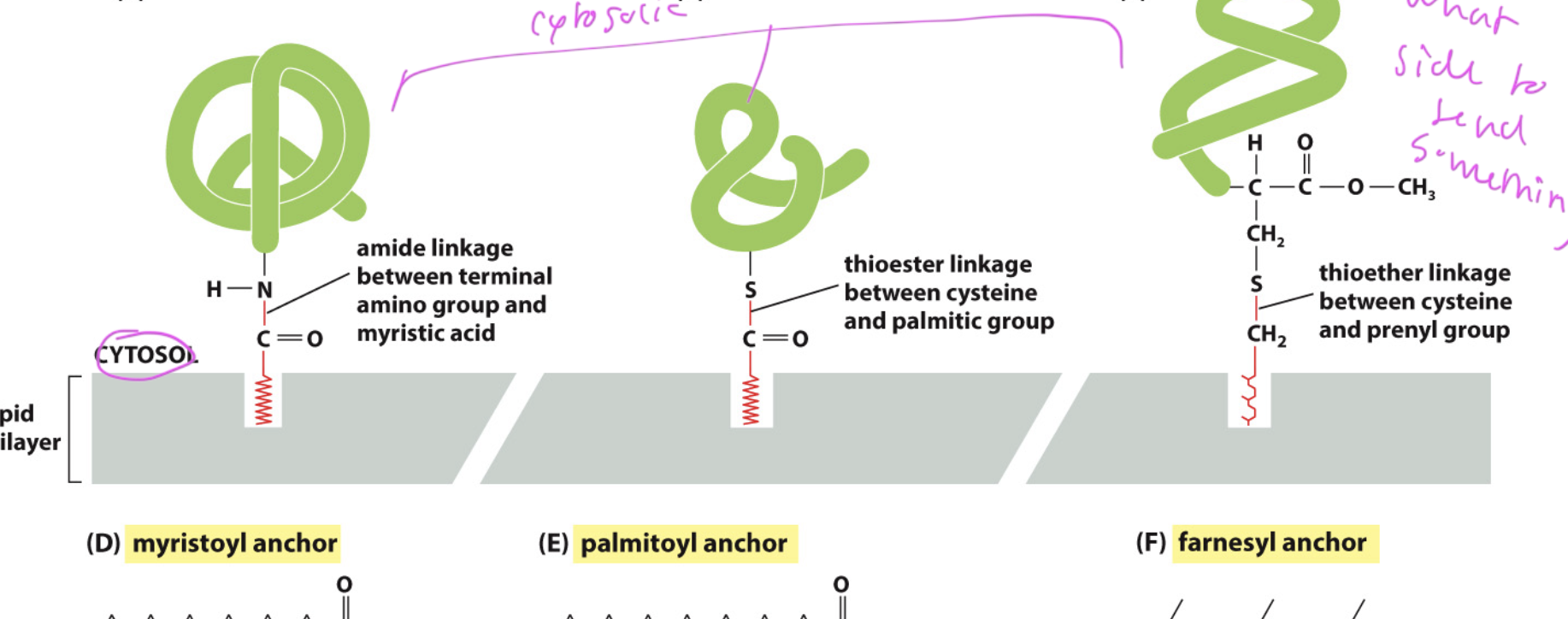
GPI (Glycosylphosphatidylinositol)
a common form of lipid anchor
allows protein to attach on the extracellular side
added in the ER and targets the exoplasmic leaflet, where the np region of the bilayer is exposed to water
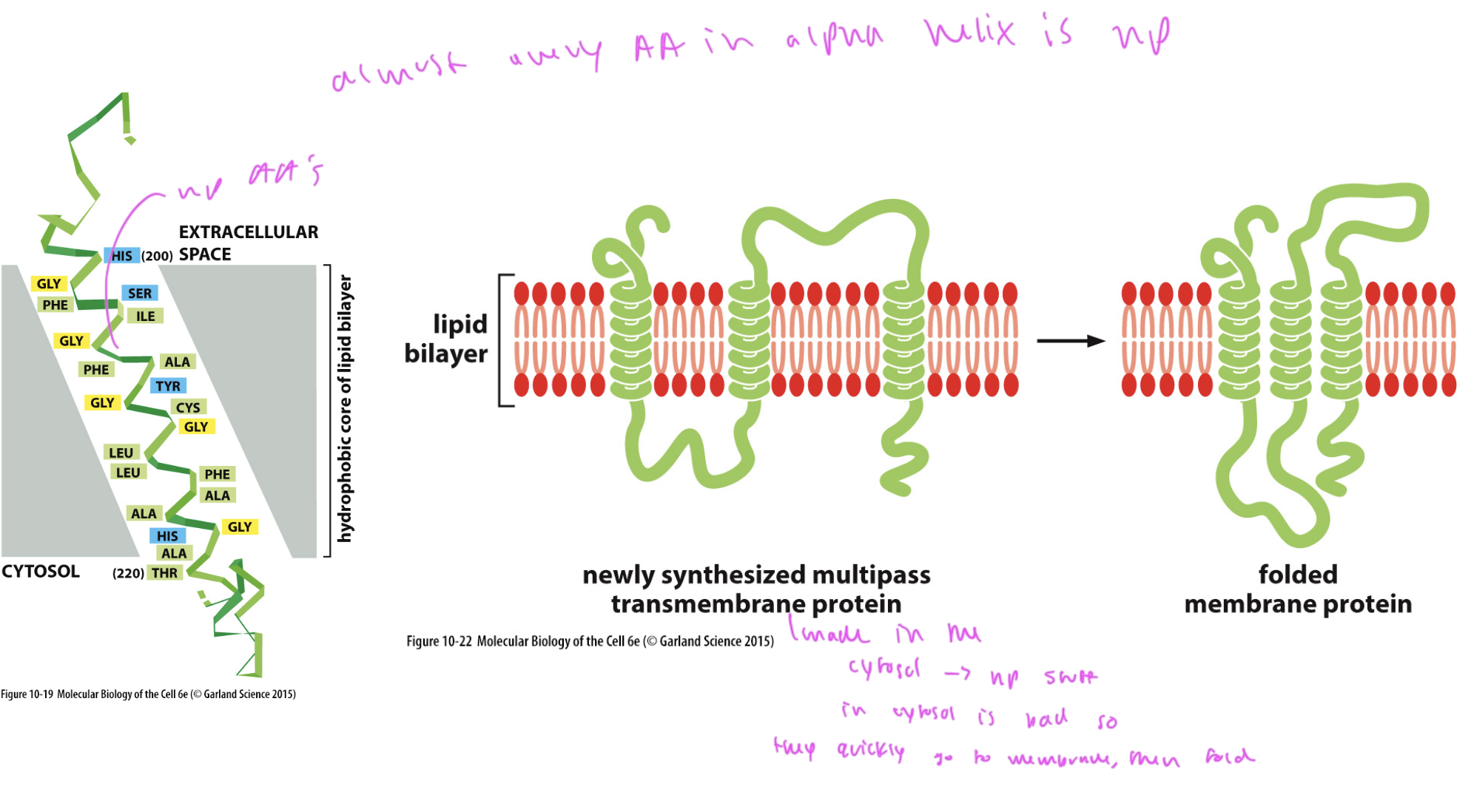
almost every AA in the alpha helix of an integral membrane protein is
np
How integral membrane proteins fold
1) they immediately go to their location in the membrane since their np regions do not like being in the aqueous environment of the cytosol
2) then they fold up
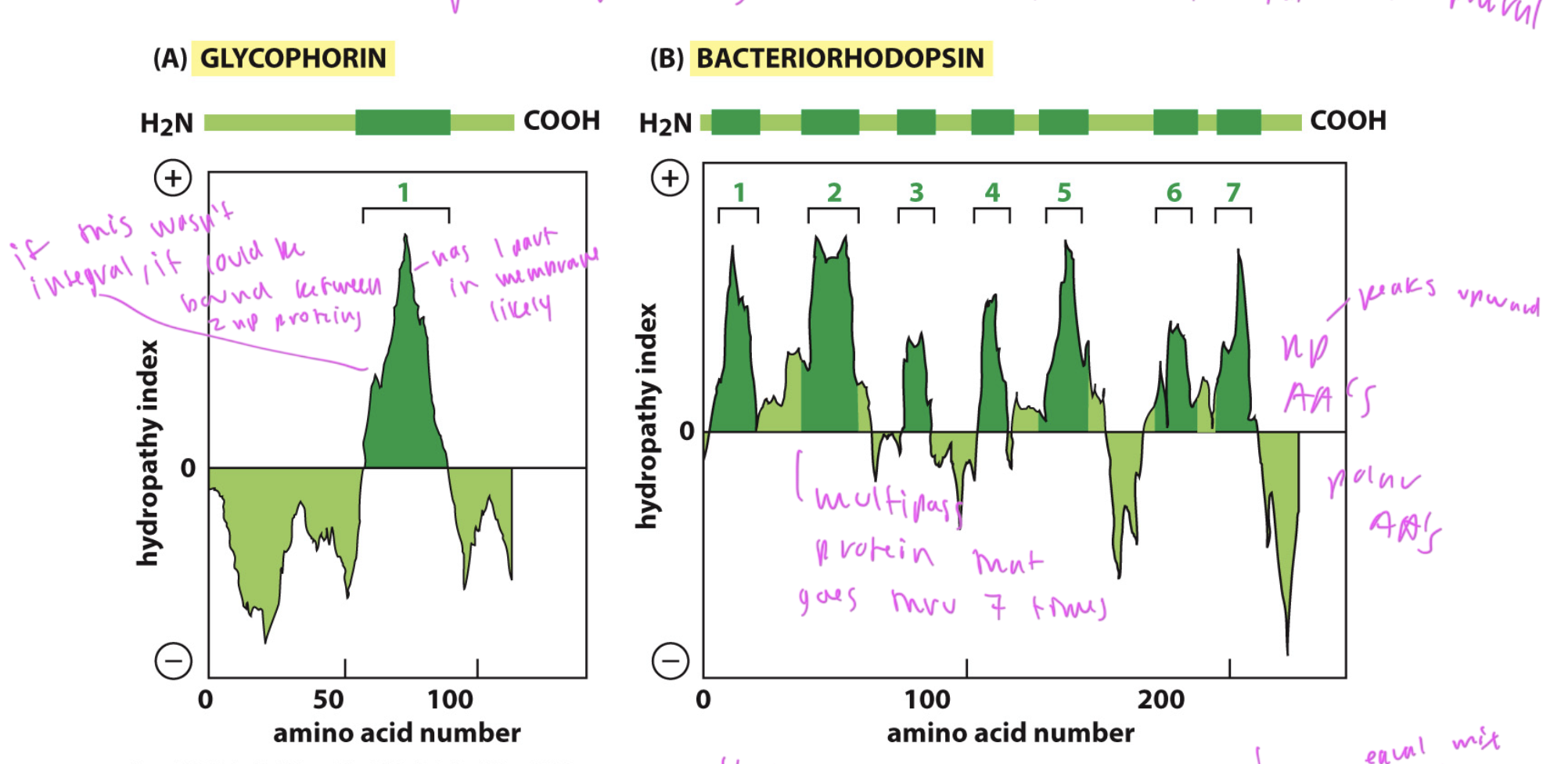
hydropathy plots
used to predict of a protein is an integral membrane protein
integral membrane proteins have large spans of np AAs in a sequence where they are in the membrane
DOES NOT predict which way it goes in the membrane, just that it is likely integral
only works for alpha helices
plot has upward peaks where np regions are and downward peaks for polar regions of the sequence
hydropathy plot showing equal amounts of np and polar AAs
so it could be a beta barrel, which has polar and np regions
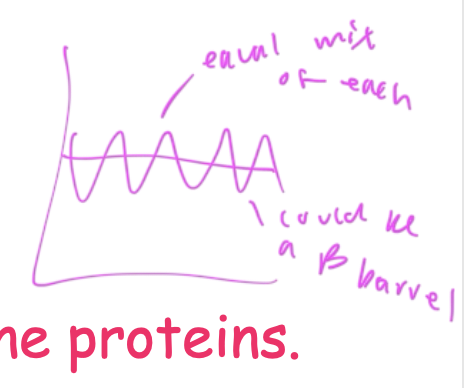
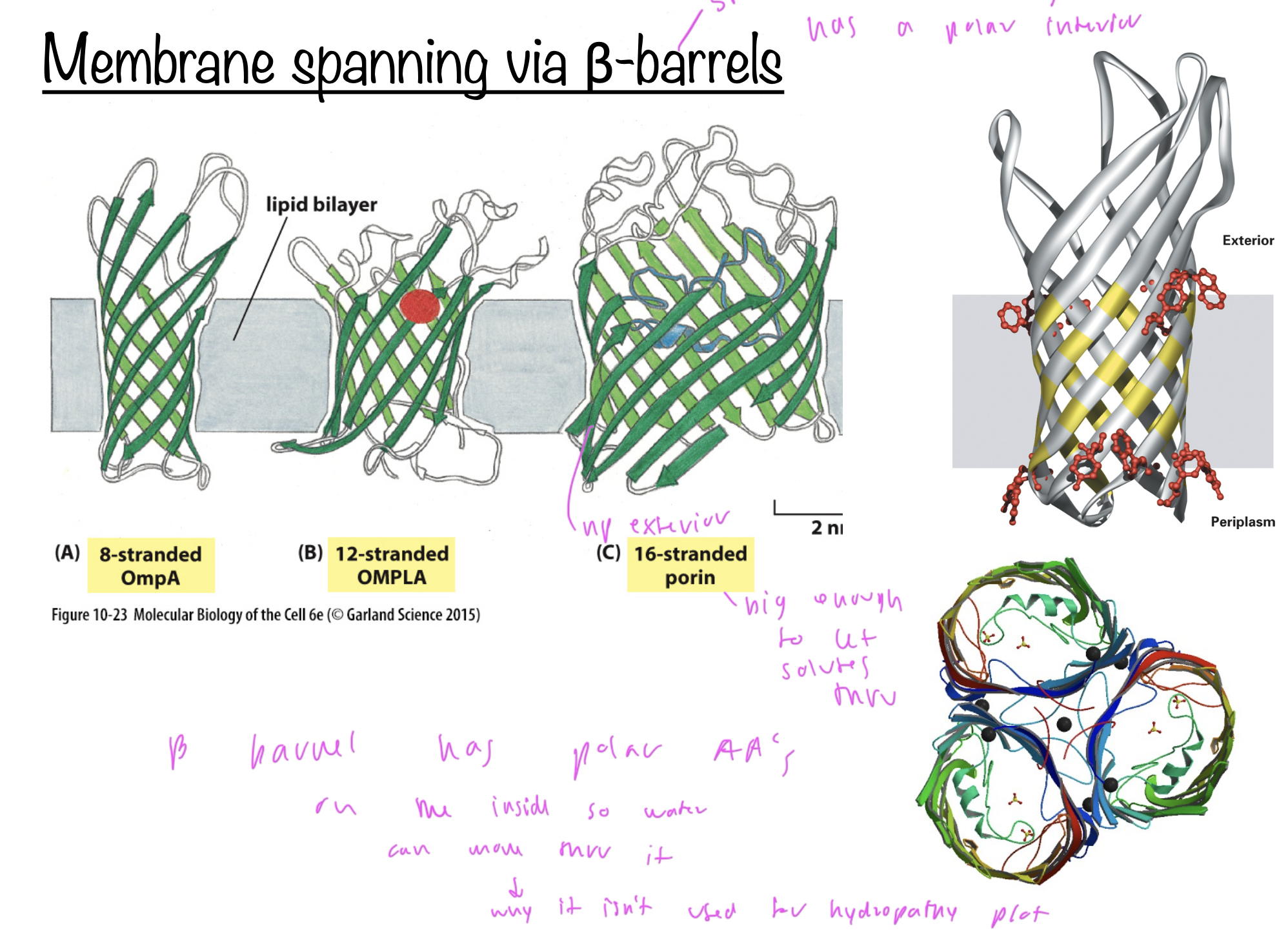
Beta barrels
integral membrane proteins that have a polar interior and np exterior where it comes into contact with the bilayer
interior is polar so aqueous solutes can pass through it
due to its np and polar aspects, it cannot be read clearly on a hydropathy plot
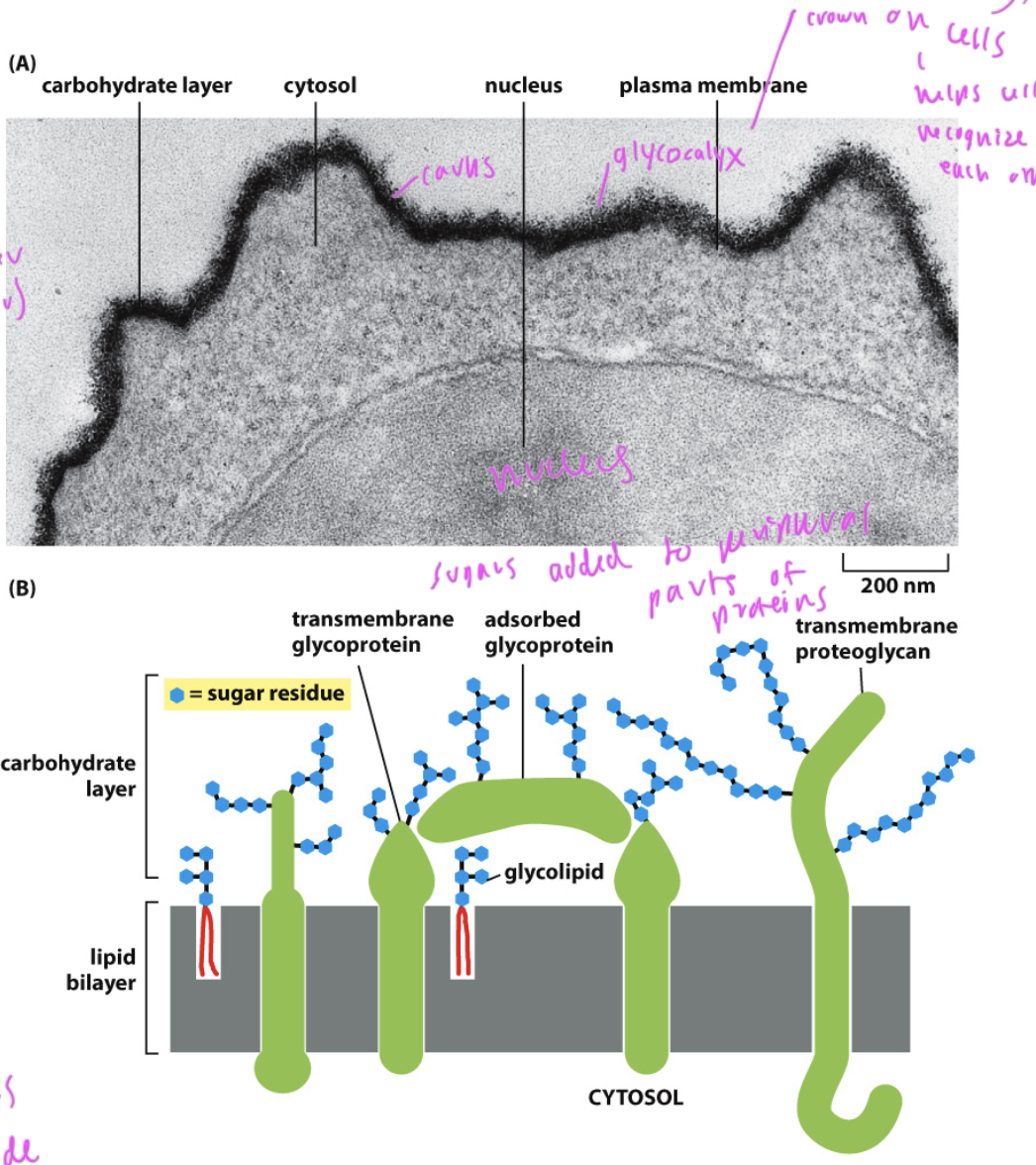
What is on the extracellular side of the bilayer?
sugars, which help cells recognize each other and help in signaling processes
if they were on the inside of the cell, they would be eaten
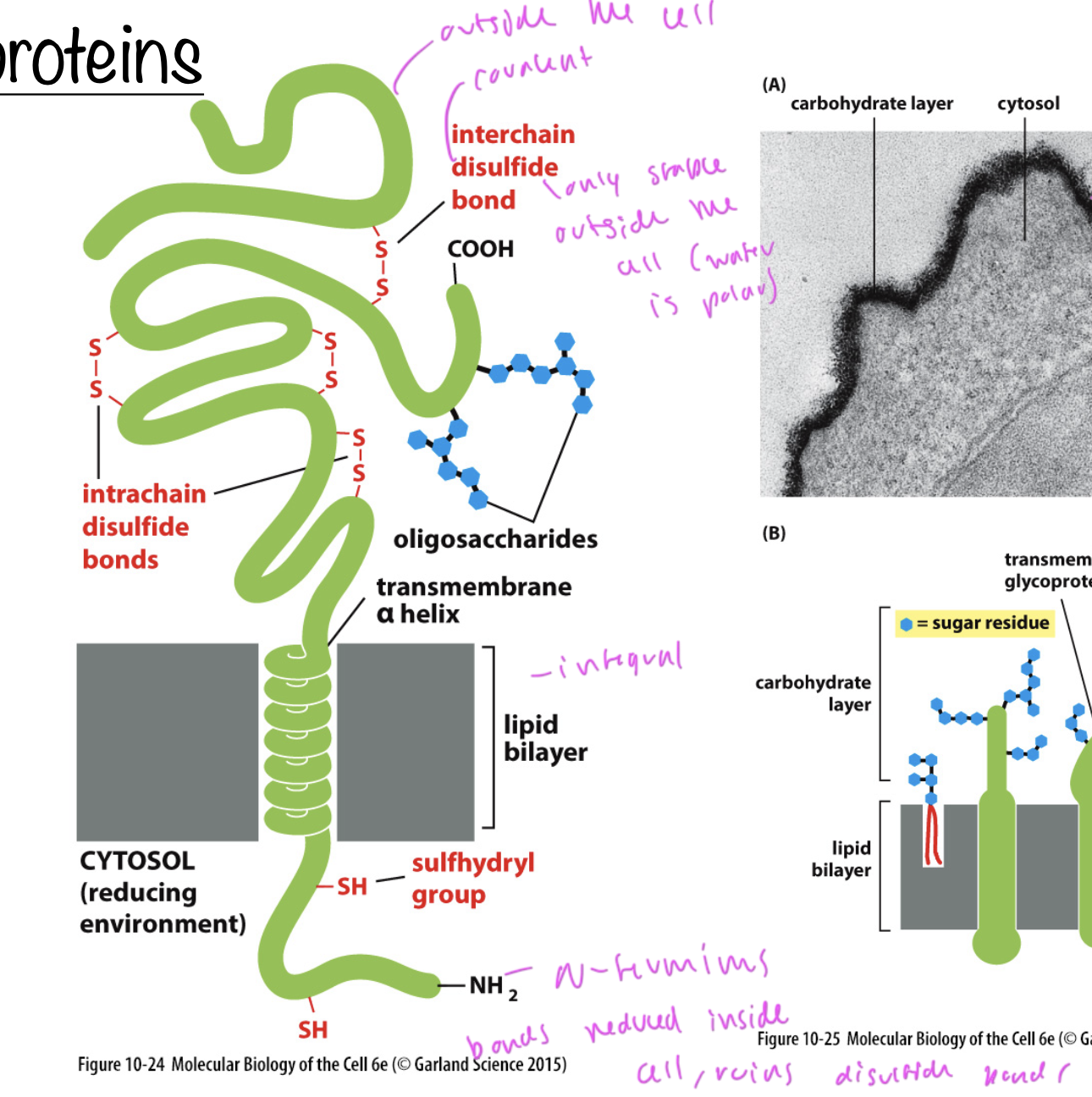
cytosolic domains of the bilayer/transmembrane
can have disulfide bonds, which are ruptured inside an organelle
bonds inside the cell are reduced (so disulfide bonds break on the cytosolic side)
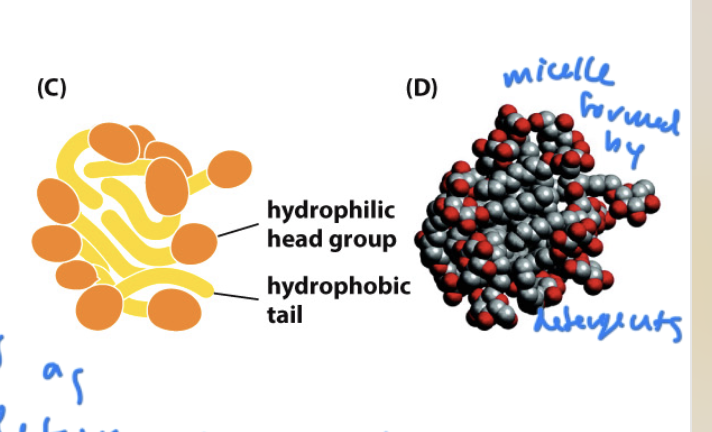
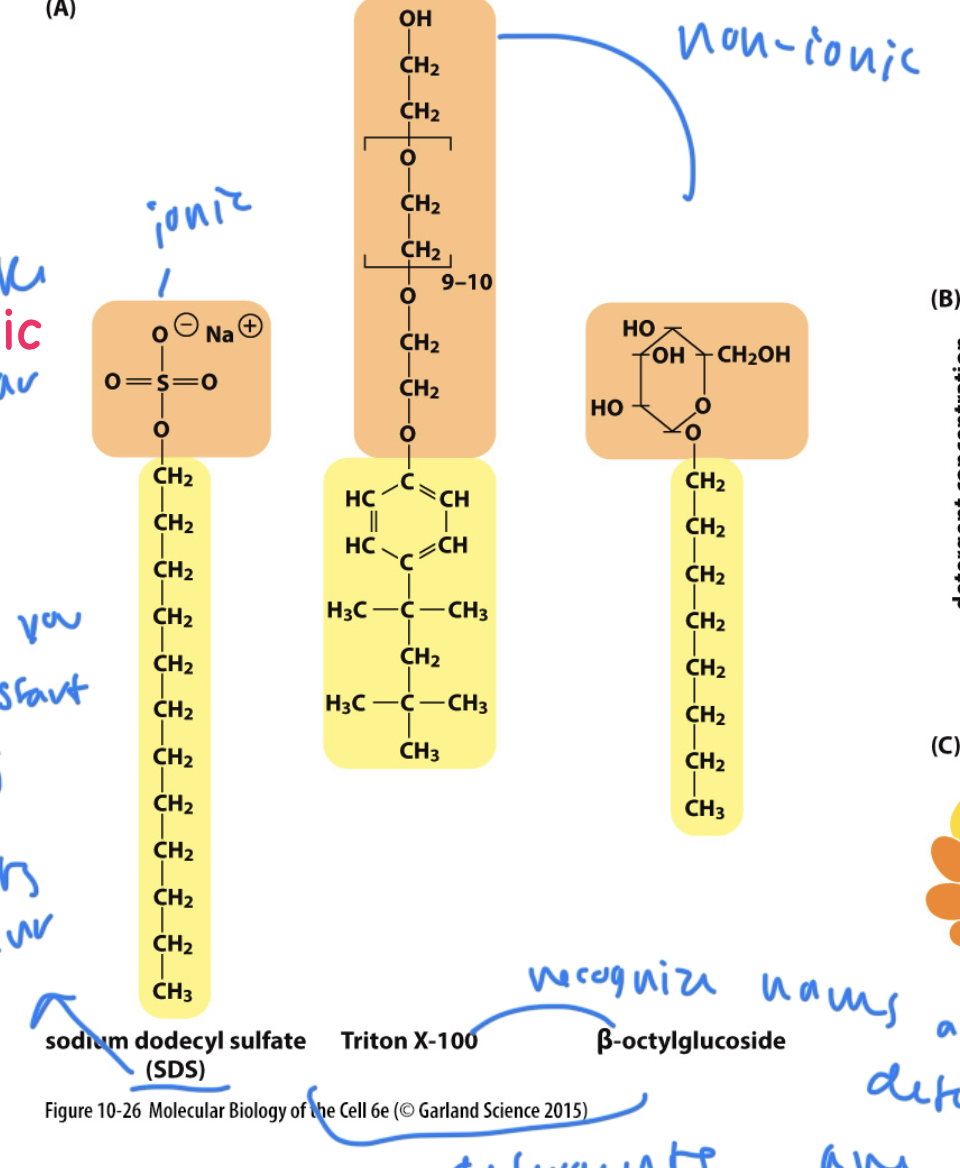
detergent
amphipathic molecules that are used to isolate lipids
can be ionic (fully charged) or non-ionic (polar)
remove phospholipids from the membrane’s bilayer
cause lipids to form micelles
types of detergents
SDS: disrupts the covalent bonds during gel electrophoresis
others: Triton X-100 and Beta-octylglucoside
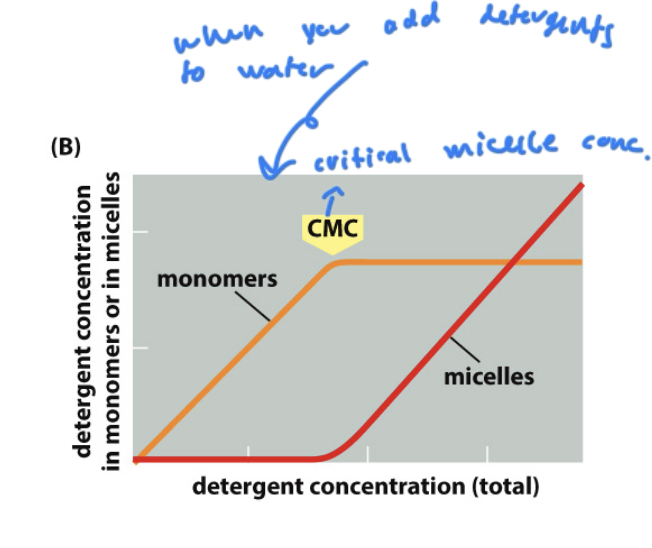
CMC
the concentration of detergent you must add to start forming micelles form lipids
critical micelle concentration
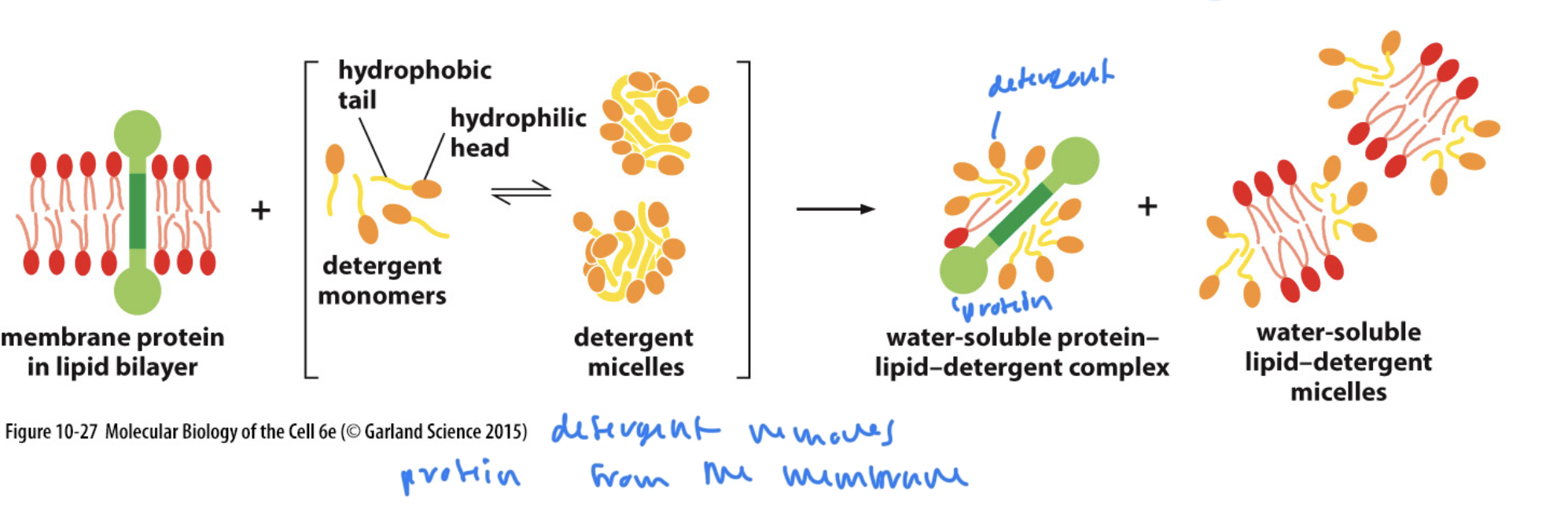
How to remove peripheral membrane and lipid-anchored proteins
with some detergent, but not much, since they are already mostly polar (which makes them more hydrophillic)
How to remove integral membrane proteins from the lipid bilayer
requires a lot of detergent since integral proteins are mostly np
requires an amount of detergent >/= the CMC
then micelles are formed
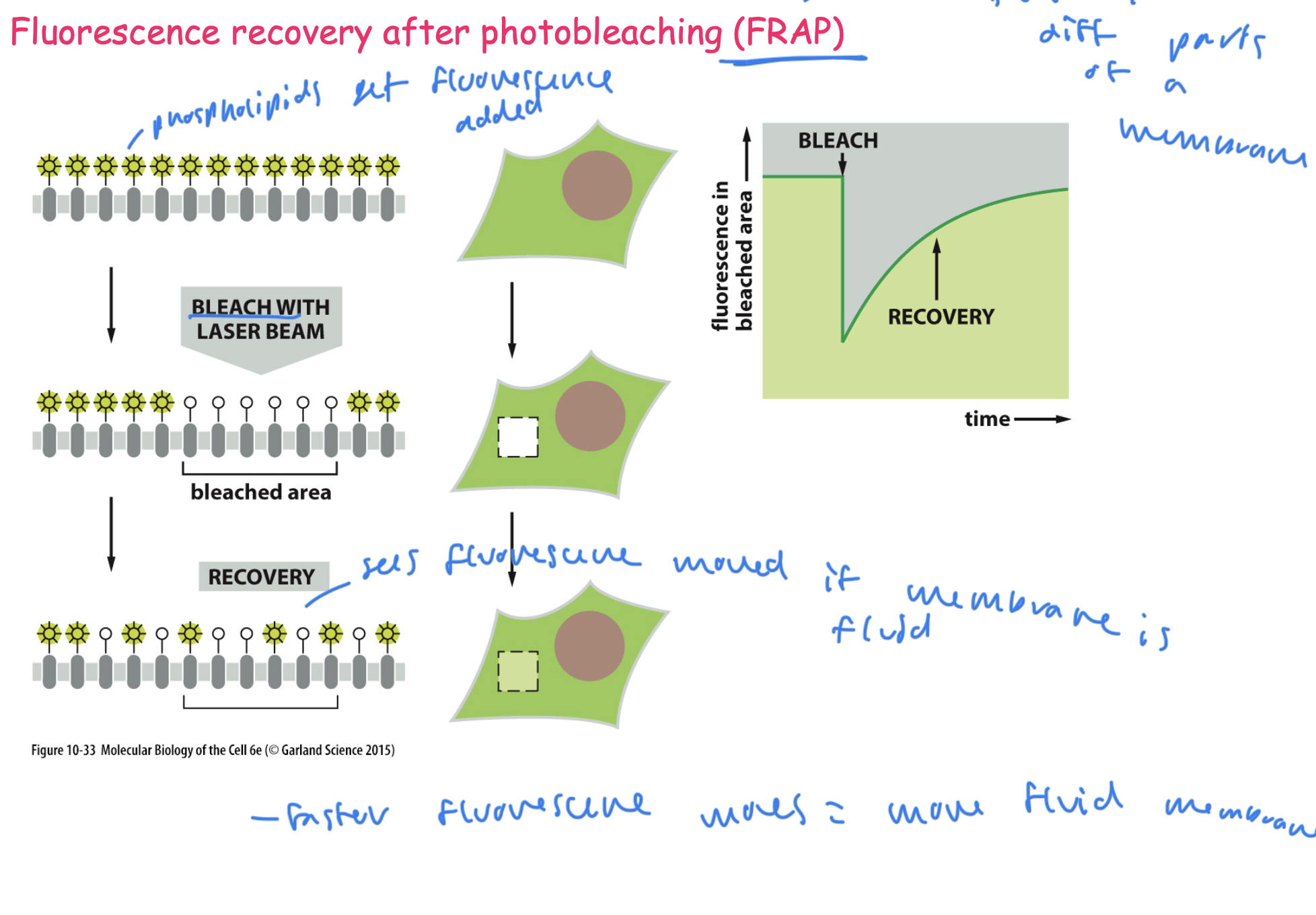
FRAP for studying the lipid bilayer
can measure the fluidity of a membrane
1) add fluorescence to phospholipids on the membrane
2) bleach a certain area of the phospholipids with a laser
3) see if fluorescence appears in the bleached area, and how quickly, to see the speed at which the membrane moves (measures membrane fluidity)
the faster the fluorescence moves= a more fluid membrane
proteins that distort the plasma membrane
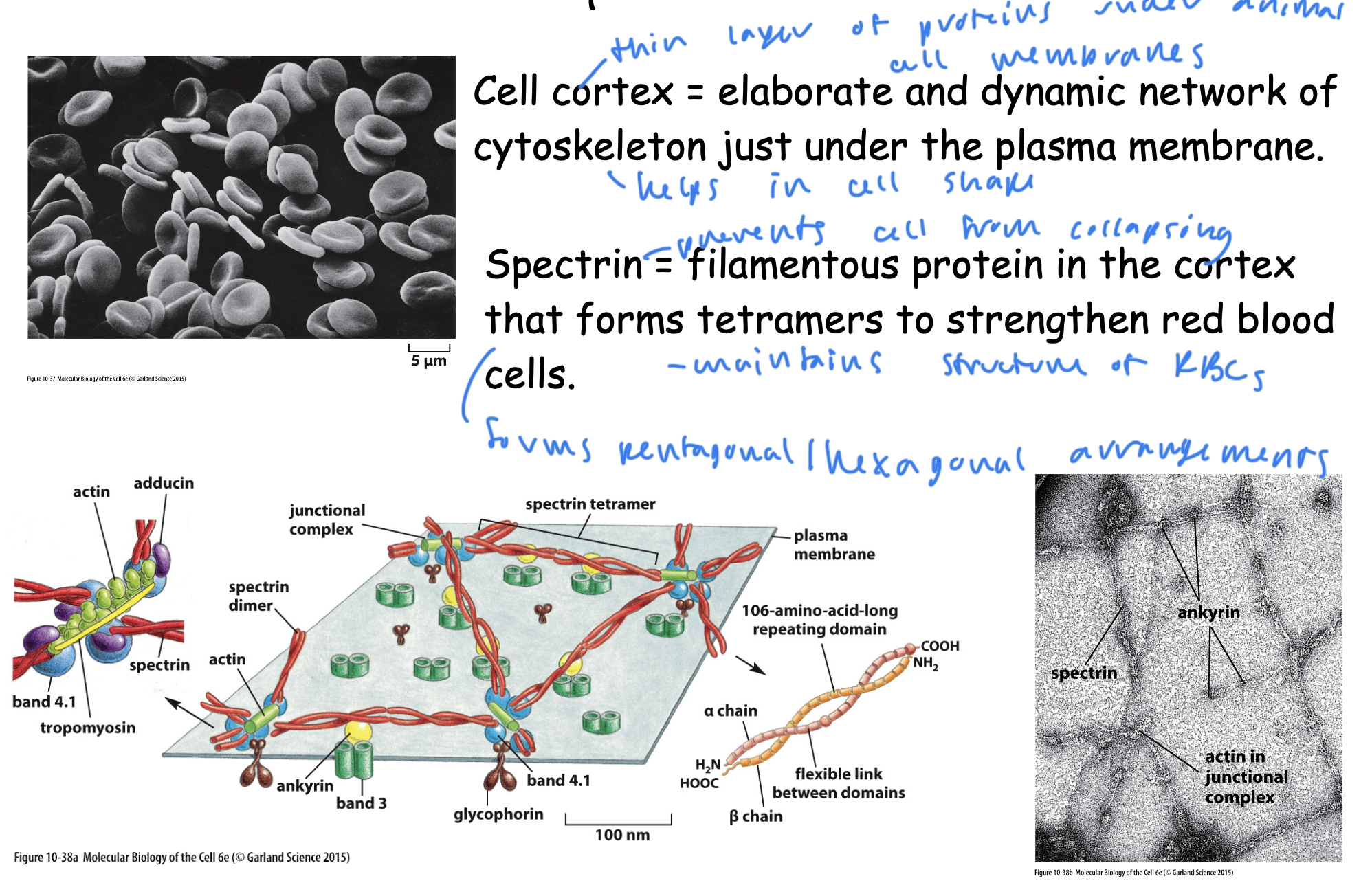
cell cortex
spectrin
cell cortex
a thin layer of proteins under animal cell membranes that helps the cell retain shape
an elaborate and dynamic network of cytoskeleton just under the plasma membrane
spectrin
protein that prevents cells, especially RBCs from collapsing and helps them retain structure
a filamentous protein in the cortex that forms tetramers to strengthen RBCs
forms pentagonal/hexagonal arrangements