Brocks Biology of Microorganisms: Chapter 14 - Metabolic Diversity of Microorganisms
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Anaerobic respiration
use of an electron acceptor other than O2 in an electron transport-based oxidation leading to a proton motive force
Anammox
anoxic ammonia oxidation
Anoxygenic photosynthesis
photosynthesis in which O2 is not produced
Antenna pigments
light-harvesting chlorophylls or bacteriochlorophylls in photocomplexes that funnel energy to the reaction center
Autotroph
an organism that uses CO2 as its sole carbon source
Bacteriochlorophyll
the chlorophyll pigment of anoxygenic phototrophs
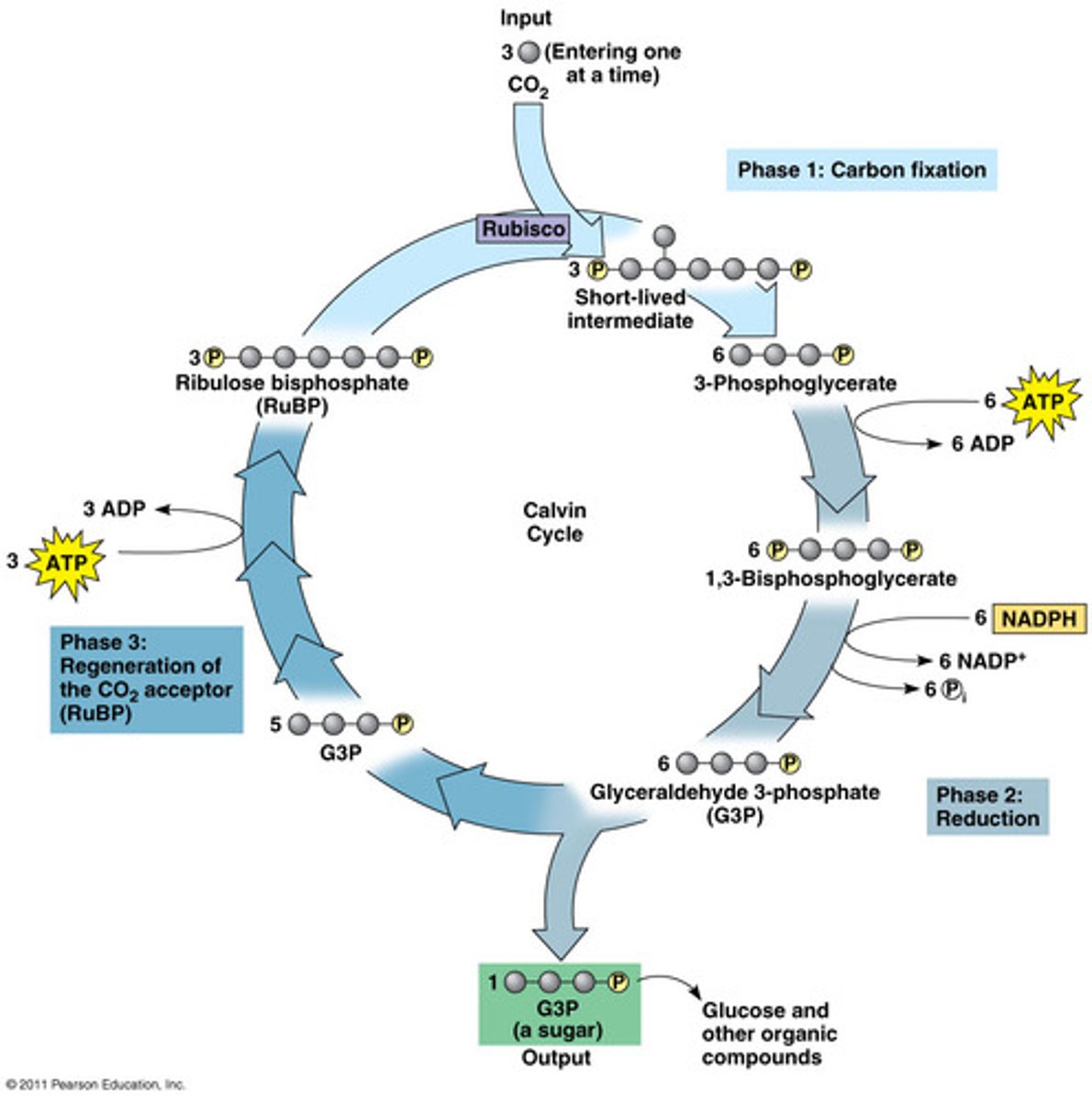
Calvin cycle
the biochemical pathway for CO2 fixation in many autotrophic organisms
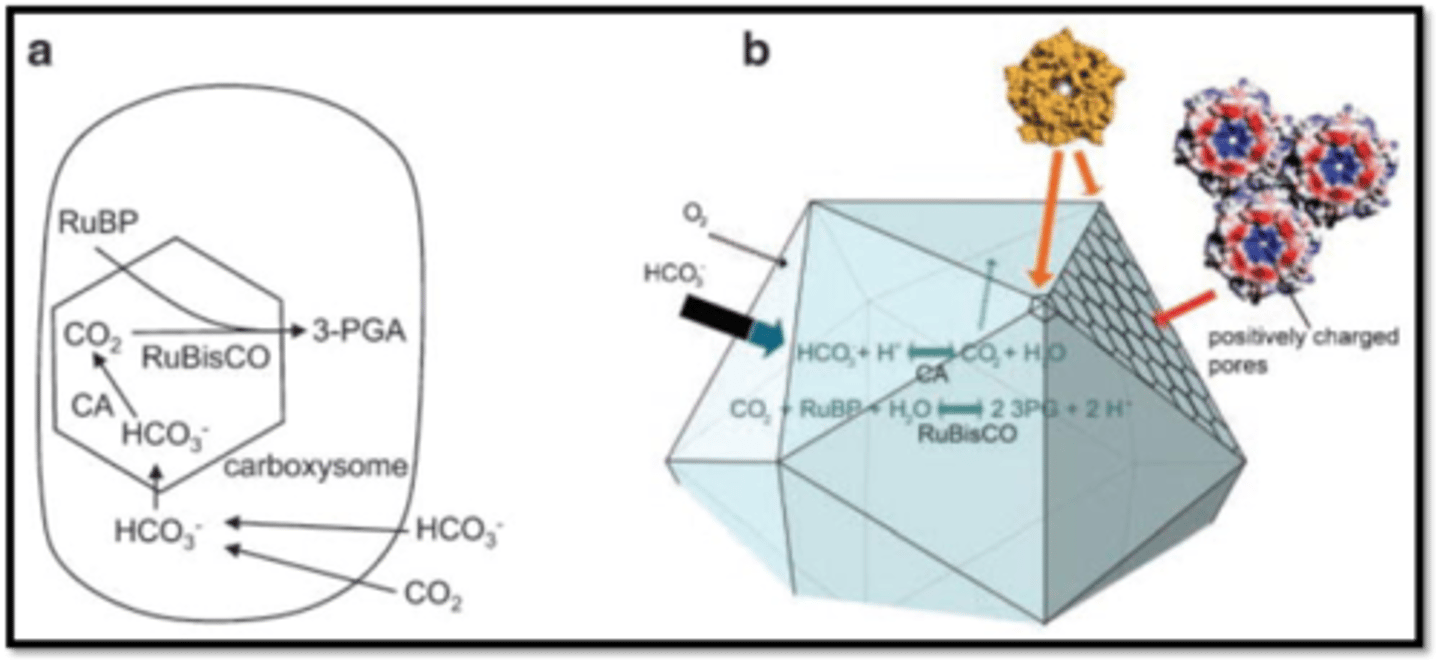
Carboxysomes
crystalline inclusions of RubisCO
Carotenoid
a hydrophobic accessory pigment present along with chlorophyll in photosynthetic membranes
Chlorophyll
a light-sensitive, Mg-containing porphyrin of phototrophic organisms that initiates the process of photophosphorylation
Chlorosome
a cigar-shaped structure present in the periphery of cells of green sulfur and green nonsulfur bacteria and containing the antenna bacteriochlorophylls (c, d, or e)
Denitrification
anaerobic respiration in which NO3 or NO2 gases, primarily N2
Dicarboxylate/4-hydroxybutyrate cycle
an autotrophic pathway found in certain Archaea
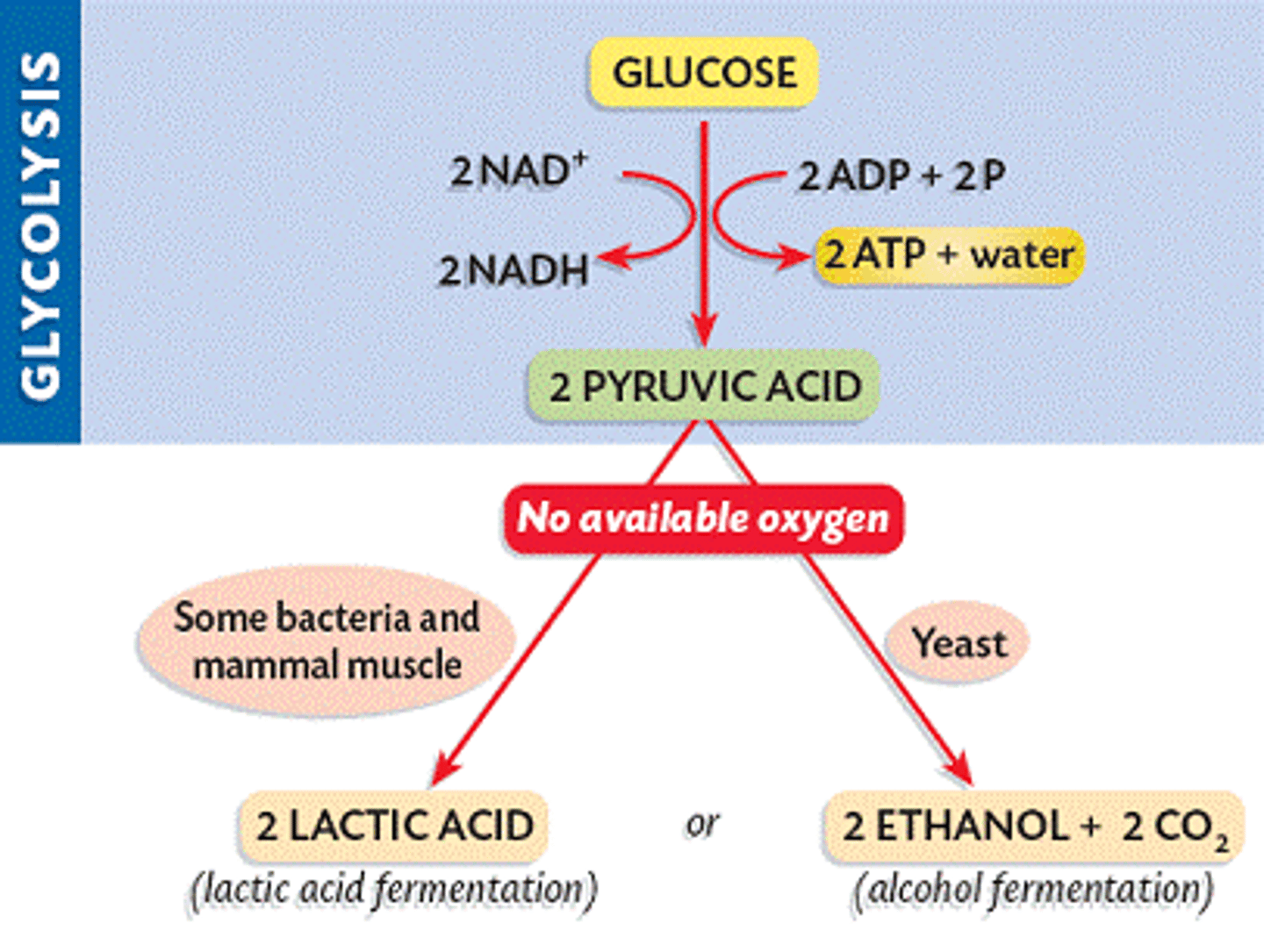
Fermentation
anaerobic catabolism of an organic compound in which the compound serves as both an electron donor and an electron acceptor and in which ATP is usually produced by substrate-level phosphorylation
Heterofermentative
producing a mixture of products, typically lactate, ethanol, and CO2, from the fermentation of glucose
Homofermentative
producing only lactic acid from the fermentation of glucose is reduced to nitrogen
Hydrogenase
an enzyme, widely distributed in anaerobic microorganisms, capable of oxidizing or evolving H2
3-Hydroxypropionate bi-cycle
an autotrophic pathway found in Chloroflexus and a few Archaea
3-Hydroxypropionate/4-hydroxybutyrate cycle
an autotrophic pathway found in certain Archaea
Methanogen
a methane-producing member of the Archaea
Methanogenesis
the biological production of CH4
Methanotroph
an organism that oxidizes CH4
Methylotroph
an organism capable of growth on compounds containing no C—C bonds; some methylotrophs are methanotrophic
Mixotroph
an organism in which an inorganic compound serves as the electron donor in energy metabolism and organic compounds serve as the carbon source
Nitrification
the microbial oxidation of ammonia to nitrate
Nitrogenase
the enzyme complex required to reduce N2 to NH3 in biological nitrogen fixation
Nitrogen fixation
the reduction of N2 to NH3 by the enzyme nitrogenase
Oxygenase
an enzyme that catalyzes the incorporation of oxygen from O2 into organic or inorganic compounds
Oxygenic photosynthesis
photosynthesis carried out by cyanobacteria and green plants in which O2 is evolved
Photophosphorylation
the production of ATP in photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
the series of reactions in which ATP is synthesized by light-driven reactions and CO2 is fixed into cell material
Phototroph
an organism that uses light as an energy source
Phycobiliprotein
the antenna pigment complex in cyanobacteria that contains phycocyanin and allophycocyanin or phycoerythrin coupled to proteins
Phycobilisome
an aggregate of phycobiliproteins
Reaction center
a photosynthetic complex containing chlorophyll or bacteriochlorophyll and several other components; the initial electron transfer reactions of photosynthetic electron flow occur here
Reductive acetyl-coenzyme A (acetylCoA) pathway
a pathway used for acetogenesis, autotrophic CO2 fixation, and acetate oxidation (when run in the reverse direction) widespread in obligate anaerobes including methanogens, acetogens, and sulfate-reducing bacteria
Reductive dechlorination
an anaerobic respiration in which a chlorinated organic compound is used as an electron acceptor, usually with the release of Cl
Reverse citric acid cycle
a mechanism for autotrophy in green sulfur bacteria and a few other autotrophic Bacteria, and also in some Archaea
Reverse electron transport
the energydependent movement of electrons against the thermodynamic gradient to form a strong reductant from a weaker electron donor
Ribulose monophosphate pathway
a reaction series in certain methylotrophs in which formaldehyde is assimilated into cell material using ribulose monophosphate as the C1 acceptor molecule
RubisCO
the acronym for ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase, a key enzyme of the Calvin cycle
Secondary fermentation
a fermentation in which the substrates are the fermentation products of other organisms
Serine pathway
a reaction series in certain methylotrophs in which CH2O plus CO2 are assimilated into cell material by way of the amino acid serine
Stickland reaction
the fermentation of an amino acid pair
Syntrophy
a process whereby two or more microorganisms cooperate to degrade a substance neither can degrade alone
Thylakoids membrane
stacks in cyanobacteria or in the chloroplast of eukaryotic phototrophs