Transport in plants.
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
support.
root hair cell adaptations
the root hairs have a large surface area
increases the rate of absorption:
water by osmosis
mineral ions by active transport
transpiration factor
Factor Transpiration Rate Explanation | ||
Temperature | Increases | Rate of transpiration increases. The water molecules have more kinetic energy and move faster. More water evaporates from the surface of spongy mesophyll cells into the air spaces and diffuses out of the leaves through the stomata. Increased rate of evaporation and diffusion. Stomatal pores becomes wider and more stomata open. |
Wind Speed | Increases | Rate of transpiration increases. Wind removes/blows way water vapour surrounding the leaf. Increased concentration gradient for diffusion and evaporation/transpiration. More water evaporates from the surface of spongy mesophyll cells into the air spaces and diffuses out of the leaves through the stomata. |
Humidity | Decreases | Rate of transpiration decreases. If there is more water vapour in the air surrounding the leaf, there will be a less steep/weaker concentration gradient for diffusion and evaporation/transpiration. Less water evaporates from the surface of spongy mesophyll cells into the air spaces and diffuses out of the leaves through the stomata. |
how does water evaporate through a leaf
Water evaporates from the surfaces of the mesophyll cells into the air spaces and diffuses out of the leaves through the stomata
explain how water vapour loss is related to: the large internal surface area provided by the interconnecting air spaces between mesophyll cells and the size and number of stomata.
- Evaporation takes place from the surfaces of spongy mesophyll cells.
- The many interconnecting air spaces between these cells and the stomata creates a large surface area.
- This means evaporation can happen rapidly when stomata are open.
Stomatal density increases
More transpiration
Greater opportunity for water vapour loss through stomata by evaporation from surfaces of spongy mesophyll cells into the air spaces
transpiration pull
Transpiration pull draws up a column of water.
Held together by forces of attraction between water molecules called cohesion. Xylem forms a long continuous empty tube.
Loss of water from leaf reduces water potential/hydrostatic pressure.
There is adhesion of water to the walls of the xylem.
wilting
water in a plant keeps it turgid and helps support it
water in cells not being replaced as quickly (as it is being lost)
lack of turgor pressure
no longer a push against cell wall
wilting occurs
plant becomes soft and droops for the cell walls become flaccid and are unable to support that plant
xylem structure
Cells joined end to end with no cross walls to form a long continuous tube
Made of dead cells, without cell contents. This means water passes easily, with low resistance to flow. Allows efficient flow.
Waterproof to prevent water loss. Lignin is waterproof.
large cross-sectional area to allow the transport of a large volume of water
Outer walls are thickened with a substance called lignin, strengthening the tubes, which helps support the plant
how does increased light intensity increase rate of transpiration
Rate of transpiration increases. Stomatal pores becomes wider and more stomata open for gas exchange for photosynthesis, so oxygen can diffuse out and carbon dioxide can diffuse in. Energy from light increases the kinetic energy of water molecules. More water evaporates from the surface of spongy mesophyll cells into the air spaces and diffuses out of the leaves through the stomata.
translocation
the movement of sucrose and amino acids in phloem from sources to sinks
sources
parts of plants that release sucrose or amino acids
sinksus
sinks - the parts of plants that use or store sucrose or amino acid
when might stuff become source or sink?
During growing season and when the plant is photosynthesising.
Leaves are source. Substances are transported down to the roots. (sink)
And transported up to the growing points, flowers, seeds and fruits. (sink)
During the time of year when there is no photosynthesis and when food is not made.
Substances are transported upwards to leaves and seeds (sink) from roots and other storage organs. (source)
Substances are transported from source to sink.
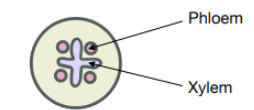
cross-section of a stem
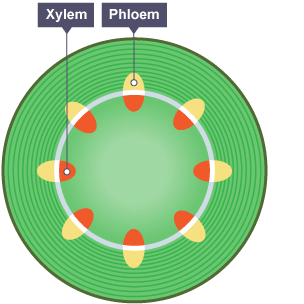
cross-section of a root