Bone basics
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Bones
Bones are the hardest structure in the body, made up by 10% cells and 90% matrix
Growth Plates
These are usually at the end of long bones, where cartilage (hyaline) is found, and osteoblasts (converts) and chondroblasts (deposits) help build bone.
Fontanels
These are creases found in the skulls of newborns to allow for the growth of the brain
Ossification
This is the process of bone formation (6th to 7th week of embryonic development)
Functions of Skeletal Systems
Structural support
Movement + muscle
Protection
Mineral storage of calcium and phosphate to form hydroxyapatite for bone density
Blood cell formation (marrow)
Ligaments
Dense fibrous connective tissue (type 1 collagen)
bone to bone
provides strength and support for joints to enable movement
Tendon
Connects muscle to bone
Cartilage
fibres of collagen (type 2) and elastin in a gel matrix (proteoglycans that are high in h20 to provide fluid distribution)
Cushions the vertebrae (spine bones)
Reduces friction on joints
Hyaline
Located in:
Embryonic structures (cartilage is the building block for bones)
Protects the end of long bones (ie. humerus)
Elastic cartilage
The most flexible
Located in:
Outer ear
tip of the nose
Fibrocartilage
Toughest form of cartilage
Located in:
Intervertebral disks (vertebrae)
Menisci (knee)
Pubic region
Perichondrium
Surrounds cartilage, making it a resilient "tissue" (springs back)
Extracellular matrix in bones
Calcium and phosphate (hydroxyapatite to make bones strong)
Collagen
Proteins
Water
This matrix is hard, unlike the ECM in cells, which is gelatinous
Osteoblasts
These are the builders. They produce the ECM in the form of osteoids, which later turns into the bones.
Osteogenic cells
These are the stem cells for bones, which later becomes osteoblasts
Osteocytes
These are the maintainers who help support and maintain the bone matrix. They stem from osteoblasts
Osteoclasts
These are the destroyers; they break down bone, usually during maintenance, fractures, or when calcium levels are low
Compact bone
Made up of osteons (haversian system)
Forms the shaft (diaphysis) and ends
Yellow bone marrow
Found in the shaft, it contains fat for readily usable ATP and decreases the weight of the bone
Spongey Bone
These are weaker and are generally in a trabecular form lattice structure to decrease the weight of the bone and allow it to store blood.
Trabeculae contain lamellae, lacunae, and osteocytes, but are randomly places in these branches as they are too small to contain osteons
Haversian System
Found only in compact bones
Lamellae: The exterior of the bone contains collagen to allow the bone to “give” a little
Lacunae: Contains the osteocytes, canaliculi (branches that give nutrients to the osteocytes)
Central canal: Contains the vessels and nerves
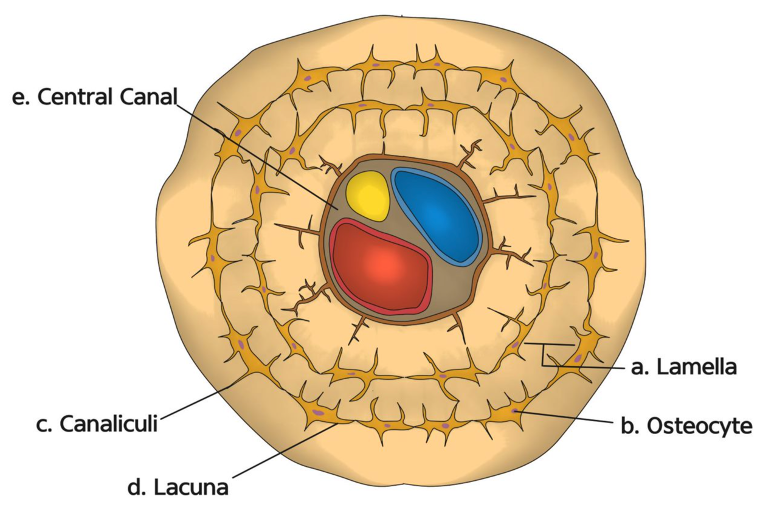
These osteons compile together to form the compact bone
Data on bone remodeling
500 mg of calcium leaves/enters the adult skeleton
Spongey tissue is replaced 3 to 4 years
Compact tissue is replaced every 10 years
Bone Remodeling
Osteoclasts come and break down the bone area (Ca in blood goes up)
Osteoblasts repair the bone (Ca in blood goes down)
Osteocytes maintain the bone
This will occur only in the periosteal and endosteal surfaces
Stresses on the body that affect how the bone grows and is shaped.
Ie, compressions, tension. bending, shear, torsion, or breakage.
Intramembranous Ossification
This occurs only in flat bones, originating from the bases of mesenchyme (a type of tissue that does not need to differentiate into cartilage).
1) Cells cluster together to form a center. Here, they’ll differentiate into osteoblasts
2) Osteoblasts secrete osteoid, which is calcified into bone
3) Spongy tissue forms and the periosteum (outer vessel for bones)
4) Trabeculae and periosteum thicken to become compact
Endochondral Ossification
This occurs for all other bones except flat ones from the hayline cartilage
Epiphysis
Rounded ends of bones
Diaphysis
Longer ends of bones
Epiphyseal plates
These are also known as growth plates. Cartilage cells are found here and push the epiphysis away from the diaphysis.
Chondroblasts divide and mature into chondrocytes, which then calcifies into bone
Organization of Cartilage
Rest Zone
Proliferation (mitosis)
Hypertrophic (older cartilage enlarges)
Calcification (hardens)
Ossification (bone formation)
Postnatal growth
Bones lengthen (interstitial) and widen (appositional)
Plates thin
Diaphysis and the epiphysis fuse
Hormone regulation
hGH: Stimulates the growth plates
Thyroid hormone: ensures that the bones are at the proper size
Sex hormones (produced by the adrenal glands and reproductive organs): Promotes bone growth and induces the closure of growth plates
Sesamoid bone
There is only one, your knee cap (patella)
Endosteum
Interior part of the bone (wrap around internally)
Periosteum
External wrap around the bone
Medullary Cavity
Contains yellow marrow (fat)
Short, Irrgeular, and Flat bones
These contain bone marrow but no cavity as it is found in the trabeculae cavities
Simple fracture
Bone is broken but skin is not torn
Compound Fractures
Bones are broken and skin is torn
Type of Fractures
Compression
Compound
Transverse
Comminuted (breakage everywhere 3+)
Spiral (breakage is in the shape of an S or oblique)
Greenstick (only one side has broken while the rest is bent)
Epiphyseal (epiphysis separates from diaphysis)
Depressed
Healing a Fracture
1) blood pools in (hematoma)
2) fibrocartilaginous callus (temporary fibrous tissue and cartilage) forms
3) Bony callus forms from osteoblasts
4) Bone heals, usually there is a bump around the site as the body overdoes the healing
Bone Growth = Age
Young, bone formation is more than reabsorption
In adults, bone formation is equal to reabsorption
Elderly (35+), bone formation is less than reabsorption (chondrocytes decrease)
Osteoporosis
Due to age, bones become more porous, making them more brittle. This disease is much more prevalent in women because of menopause (50+ = 6.5%)
Risk Factors:
Diet (low vitamin d and calcium)
Low exercise
Hormonal imbalance
Osteomalacia
Adults - bones are poorly mineralized
Rickets
Children - bones are poorly mineralized
Paget’s disease
Excessive bone deposition
Osteosarcoma
Bone cancer as sarcoma, means tissue cancer.