ACYFARP10: Borrowing Cost & Intangible Assets
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
For purposes of capitalization of borrowing cost, which of the following is not a qualifying asset?
a. Manufacturing plant
b. Power generation facility
c. Investment property
d. Asset that is ready for the intended use or sale
D
If the qualifying asset is financed by specific borrowing, the capitalizable borrowing cost is equal to
a. Actual borrowing cost incurred
b. Actual borrowing cost incurred up to completion of asset
c. Actual borrowing cost incurred up to completion of asset minus any investment income from the temporary investment of the borrowing
d. Zero
C
If the qualifying asset is financed by general borrowing, the capitalizable borrowing cost is equal to
a. Actual borrowing cost incurred
b. Total expenditures on the asset multiplied by the capitalization rate
c. Average expenditures on the asset multiplied by the capitalization rate or actual borrowing cost incurred, whichever is lower
d. Average expenditures on the asset multiplied by the capitalization rate or actual borrowing cost incurred, whichever is higher
C
During 2025, BSA Company constructed a new building at a cost of P30,000,000. The expenditures for the building which was finished late in 2025 were incurred evenly during the year. The entity had the following loans outstanding on December 31, 2025:
10% note to finance specifically the construction, dated January 1, 2025, P10,000,000. The note is unpaid on December 31, 2025. Investments were made on the proceeds from the loan and income of P100,000 was realized in 2025.
12% 10-year bonds issued at face amount on April 30, 2024, P30,000,000.
8% 5-year note payable, dated March 31, 2024, P10,000,000.
What is the capitalizable borrowing cost?
a. P1,550,000
b. P1,450,000
c. P1,400,000
d. P1,500,000
B

During 2025, BSA Company constructed a new building at a cost of P30,000,000. The expenditures for the building which was finished late in 2025 were incurred evenly during the year. The entity had the following loans outstanding on December 31, 2025:
● 10% note to finance specifically the construction, dated January 1, 2025, P10,000,000. The note is unpaid on December 31, 2025. Investments were made on the proceeds from the loan and income of P100,000 was realized in 2025.
● 12% 10-year bonds issued at face amount on April 30, 2024, P30,000,000.
● 8% 5-year note payable, dated March 31, 2024, P10,000,000.
What is the interest expense for 2025?
a. P4,400,000
b. P2,850,000
c. P3,850,000
d. P2,950,000
C
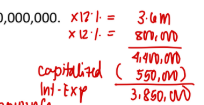
An intangible asset is defined as
a. An identifiable asset without physical substance
b. A nonmonetary asset without physical substance
c. An identifiable nonmonetary asset without physical substance
d. An identifiable monetary and nonmonetary asset without physical substance
c. An identifiable nonmonetary asset without physical substance
Which of the following statements is true concerning separate acquisition of intangible asset?
a. If an intangible asset is acquired separately, the cost of the intangible asset can usually be measured reliably
b. If payment for an intangible asset is deferred beyond normal credit terms, the cost is equal to the cash price equivalent
c. The cost of a separately acquired intangible asset comprises the purchase price and any directly attributable cost of preparing the asset for its intended use
d. All of these statements are true
d. All of these statements are true
Which of the following statements is true concerning amortization and impairment of intangible assets?
a. Intangible assets with finite useful life are amortized over the useful life
b. Intangible assets with finite useful life are tested for impairment at the end of reporting period when there is an indication of impairment
c. Intangible assets with indefinite useful life are not amortized but are tested for impairment at least annually
d. All of these statements are true
d. All of these statements are true
An entity was granted a patent on January 1, 2022 and appropriately capitalized P450,000 of related costs. The entity was amortizing the patent over the useful life of 15 years.
During 2025, the entity paid P150,000 in legal costs in successfully defending an attempted infringement of the patent. After the legal action was completed, the entity sold the patent to the plaintiff for P750,000. The policy is to take no amortization in the year of disposal.
What amount should be reported as gain from sale of patent in 2025?
a. P150,000
b. P240,000
c. P270,000
d. P390,000
d. P390,000


Pinnacle Company developed a trademark to distinguish its products from those of the competitors. Through advertising and other means, the entity is seeking to establish significant product identification to increase future
sales.
The similarity between the trademark costs and other intangible and operating costs has caused some confusion over proper accounting. The following items are being treated as part of the cost of the trademark:
What is the initial cost of the trademark?
a. P1,700,000
b. P1,900,000
c. P2,300,000
d. P2,100,000
a. P1,700,000

At the beginning of current year, Mr. Accounting Company signed an agreement to operate as a franchise for an initial franchise fee of P6,000,000. On the same date, the entity paid P2,000,000 and agreed to pay the balance in four equal annual payments of P1,000,000 at every year-end.
The down payment is not refundable and no future services are required of the franchisor. The entity can borrow at 14% for a loan of this type.
Present value of 1 at 14% for 4 periods 0.59
Future amount of 1 at 14% for 4 periods 1.69
Present value of an ordinary annuity of 1 at 14% for 4 periods 2.91
What is the initial measurement of the franchise?
a. P6,760,000
b. P6,000,000
c. P4,910,000
d. P4,360,000
c. P4,910,000
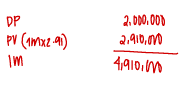
An entity provides engineering and operational support services to aircraft manufacturers. The entity received a confirmed order from an aircraft manufacturer to develop a new design for ducting the air conditioning of an aircraft.
The entity incurred the following expenditures in the current year in pursuance of a project for the air conditioner
duct:
Salaries of engineers, consultants and technicians 400,000
Cost of developing the duct and producing the test model 500,000
Additional cost for revising the ducting process
to ensure that product could be introduced in the market 600,000
Cost of developing the first model or prototype and testing
it with air conditioners to ensure comparability 100,000
Cost of conference for the introduction of this new project 150,000
What amount should be reported as research and development expense for the current year?
a. P1,600,000
b. P1,750,000
c. P1,500,000
d. P1,200,000
a. P1,600,000