Microbiology Chapter 7
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
What composed DNA?
made of nucleotides
What composed a mononucleotide?
phosphate group, a pentose sugar, and nitrogenous base
How many strands are there in a DNA molecule?
two strands
What is meant by antiparallel?
the two strands run in opposite directions
Describe the structure of a DNA molecule
double helix
sides are made of pentose and phosphate group
middle is made up of pairs of nitrogenous bases
Adenine pairs with Thymine
Guanine pairs with Cytosine
Compare number of chromosomes of bacteria with the human cell
Bacteria are haploid (single copy) and humans are diploid (23 chromosomes from each parent)
What types of nucleic acid make up the genome of bacteria?
circular or linear DNA
Where can DNA be found in bacteria?
in the nucleoid
Where can DNA be found in plant and animal cells?
in the nucleus
What is the shape of bacterial chromosomes?
circular
how are bacterial chromosomes packaged inside the cell?
in loops back and forth
what is a nucleoid
bundled DNA
What composed the plasmid?
DNA molecules
What is the shape of plasmids?
circular
What is the size of plasmids in relation to the bacterial cell?
0.1 - 10% the size of a chromosome
What are the functions of plasmids?
can replicate independently of chromosome
carry genes for selective advantage: antimicrobial resistance and heavy metal resistance
What are the 4 steps in DNA replication in bacteria?
begins at origin of replication
unwinding of the DNA
RNA primer formation
elongation of the leading and lagging strand
What are the enzymes involved in DNA replication?
Helicase
RNA primase
DNA Polymerase I
DNA Polymerase III
DNA ligaments
What is the function of helicase?
unwinds the two strands of DNA
What is the function of RNA primase?
synthesizes RNA primer
What is the function of DNA polymerase I?
removes RNA primers and replaces them with DNA; adds nucleotides
What is the function of DNA polymerase III?
adds nucleotides and proof reads
What is the function of DNA ligaments?
joins short segments of DNA
How many origin of replication is there?
only 1
How many replication forks are formed when a molecule of DNA replicates?
two
What is semi-conservative method of DNA replication?
an old strand of DNA and a new strand of DNA
Where does DNA replication begin at?
origin of replication
The two strands of DNA separate forming ____________ and ____________
Replication bubble; replication fork
What is the replication fork?
the Y-shaped regions of replicating DNA molecules where new strands are growing.
What enzyme catalyzes the formation of RNA primer?
RNA primase
Elongation of the leading strand is:
continuous
What is the direction of the process of the leading strand?
towards the replication fork
How many primers are needed for the leading strand?
one
Name the enzymes that catalyze the elongation of new DNA at a replication fork
DNA polymerase I and III
What end does DNA polymerase III add nucleotides to?
3 OH
in the leading strand, how is DNA synthesized?
as a single polymer
How many primers are needed for the lagging strand?
depends of the size of DNA
What is the direction of the process of the lagging strand?
away from the replication fork
What are Okazaki fragments?
short DNA fragments produced in the lagging strand
What are the enzymes that remove RNA primers and replace them with DNA?
DNA polymerase I and DNA ligase
What is gene expression?
process by which DNA directs protein synthesis
what are the two processes involved in gene expression?
translation and transcription
what is transcription?
synthesis of RNA from DNA
what is translation?
synthesis of proteins from mRNA
where does transcription take place in prokaryotes?
cytoplasm
where does transcription take place in eukaryotes?
nucleus
where does translation take place in prokaryotes?
ribosome in the cytoplasm
where does translation take place in eukaryotes?
cytoplasm
What are the different RNAs produced by the cell?
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
what does the template strand of DNA do in transcription?
provides a template for ordering the sequence of complementary nucleotides in an RNA transcript
What is the function of mRNA?
carries genetic information from DNA in nucleus to cytoplasm where proteins are to be synthesized
What is the function of tRNA?
carries amino acids from amino acid pool to mRNA
What is the function of rRNA?
structural component of ribosomes
What is the saying for nitrogenous bases pairing?
Apples in the Tree, Cars in the Garage
What is genetic code?
set of rules by which the sequence of nucleotides in DNA or RNA determines the sequence of amino acids in proteins
How many total codons are there?
64 codons
How many codons code for amino acids?
61 codons
What is a codon?
sequence of 3 nucleotides in DNA or RNA that codes for a specific amino acid
What is an anticodon?
sequence of 3 nucleotides on a tRNA molecule that is complementary to a codon on mRNA
What is the start codon?
AUG
What are the stop codons?
UAA
UAG
UGA
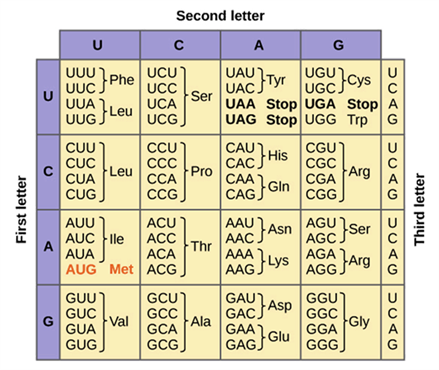
What amino acids are coded by AUA codon?
Ile
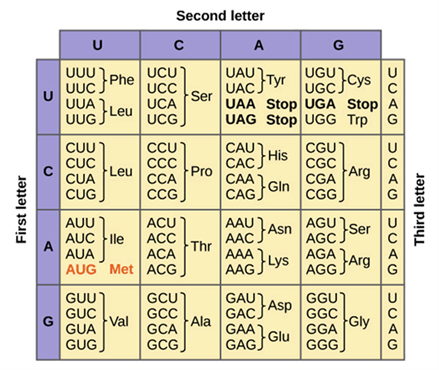
What amino acids are coded by CAC codon?
His
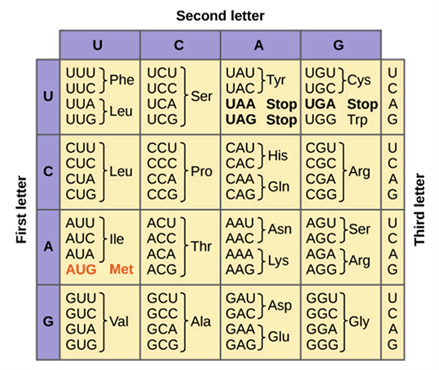
What amino acids are coded by AUU codon?
Ile
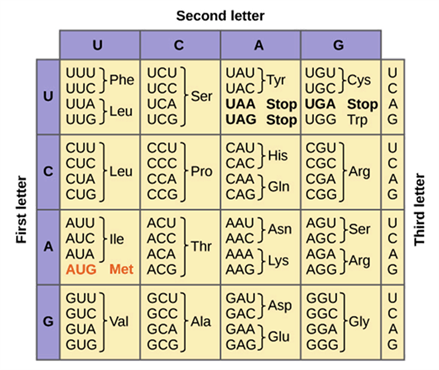
What amino acids are coded by GCG codon?
Ala
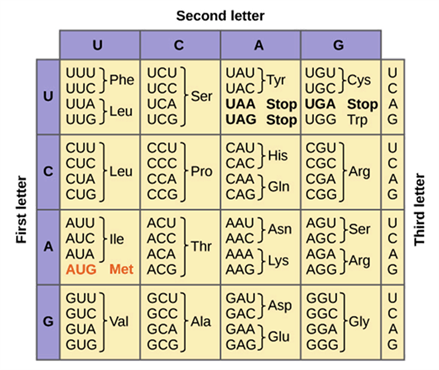
What amino acids are coded by AAC codon?
Asn
During translation, what does each codon specify to be placed at each corresponding position along a polypeptide?
amino acids
What is gene transfer?
mechanisms for uptake of DNA to create variability
What are the two types of gene transfer?
Vertical transfer
Horizontal transfer
What are the three processes of horizontal gene transfer in bacteria?
transformation
transduction
conjugation
What is transformation?
uptake of “naked” DNA from environment
What is transduction?
via bacteriophage aka “phage”
What is conjugation?
Direct cell to cell; sex pilus
What are required in bacterial transformation?
competent cells, DNA to introduce, and a method to help DNA enter the cells
What is a competent cell?
a cell that is able to integrate the gene for capsule formation and synthesis
describe the process of bacterial tranformation
uptake of ‘naked’ DNA from environment (lysed bacterial cells)
dead bacterium DNA from a donor binds to protein in a living, competent recipient and the donor DNA gets taken up and changes the recipient
What is vertical transfer?
from mother to daughter; think triangle
What is horizontal transfer?
from cell to cell of the same generation; think straight line
Describe the experiment of Griffith
injected mic with different forms of pneumonia bacteria
living smooth strain resulting in mouse dying
dead smooth strain resulting in mouse living
living rough strain resulting in mouse living
When the living rough strain and dead smooth strain were mixed and injected, the mouse died
a culture of streptococcus pneumoniae from the dead mouse was taken and living smooth strain was present
concluded that living rough strain transformed into living smooth strain by taking up DNA from dead smooth strain
What is transduction?
the transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another with the use of a bacteriophage
What are the two primary types of bacteriophages?
lytic bacteriophages
temperate bacteriophages
How does lytic bacteriophage replicate?
by lytic life cycle
How does temperate bacteriophage replicate?
by lysogenic life cycle
Describe lytic life cycle
Describe lysogenic life cycle
Describe generalized transduction
What is a prophage?
Wha tis required in transduction?
What is a transducing phage?
What is bacterial conjugation?
Discuss the process of plasmid transfer or F+ conjugation
After F plasmid transfer, what happens to the donor cell (F+ or F-)?
After F plasmid transfer, what happens to the recipient cell (F+ or F-)?
Discuss R plasmid conjugation
Discuss the process of chromosomal transfer conjugation or Hfr conjugation?
What is an Hfr?
How is an Hfr formed?
After chromosomal transfer, what happens to the donor cell (F+ or F-)?
After chromosomal transfer, what happens to the recipient cell (F+ or F-)?
What are the requirements for transformation, transduction, and conjugation?