The National Grid: Electricity: Physics: GCSE (9:1)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
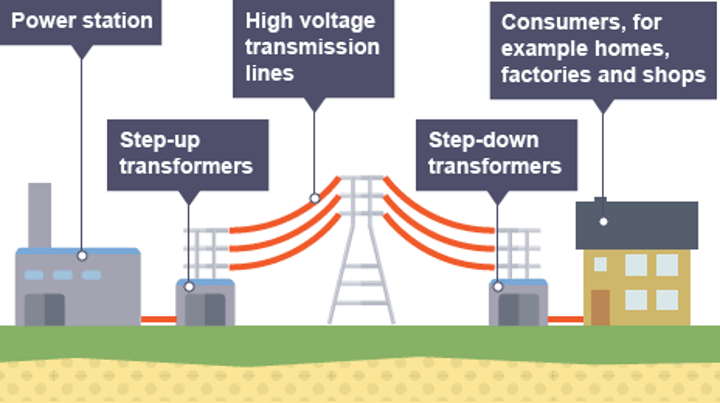
National Grid
A system of cables and transformers linking power stations to consumers
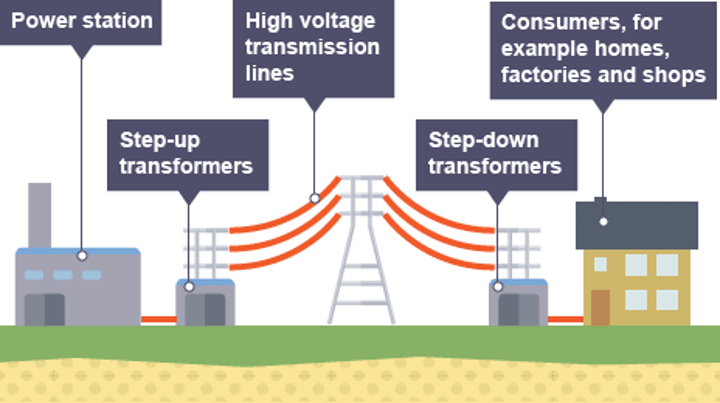
What the National Grid does
Connects power stations to homes, workplaces and public buildings all around the country
Transformer
An electrical device that changes the potential difference of an alternating current
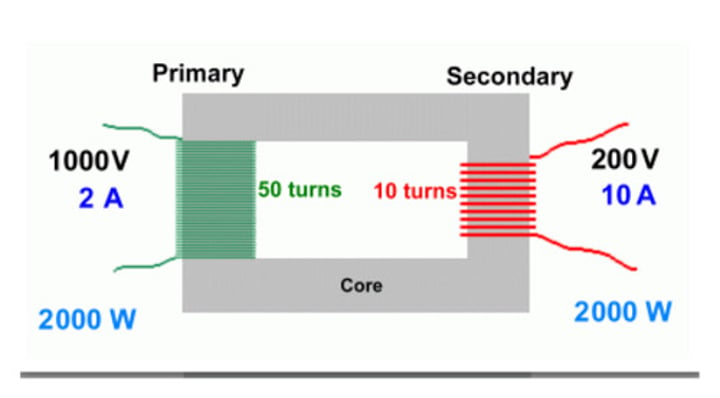
Structure of a transformer
Two coils of wire wrapped around a magnetic core
Step-up transformer
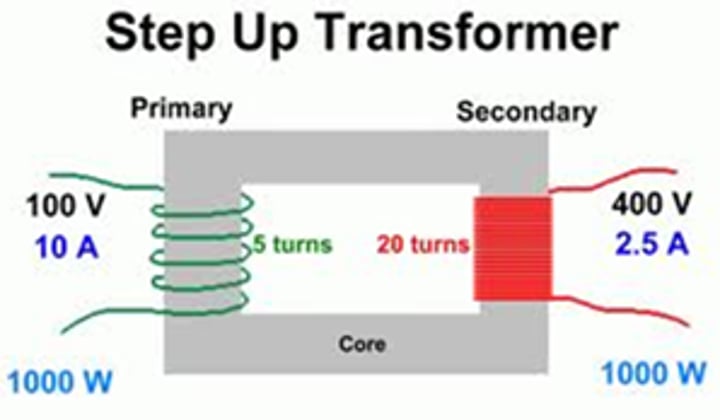
A transformer used to increase the potential difference from the power station to the transmission cables
Step-down transformer
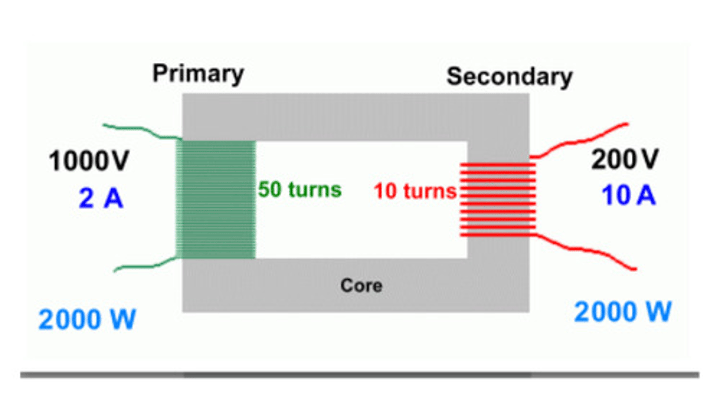
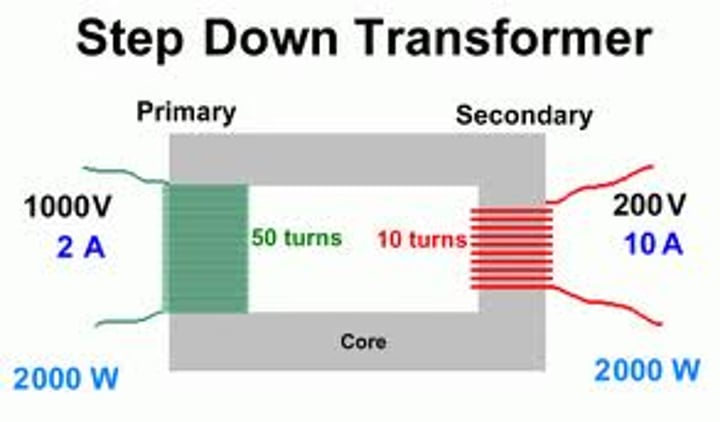
A transformer used to decrease the potential difference to a much lower value for domestic use
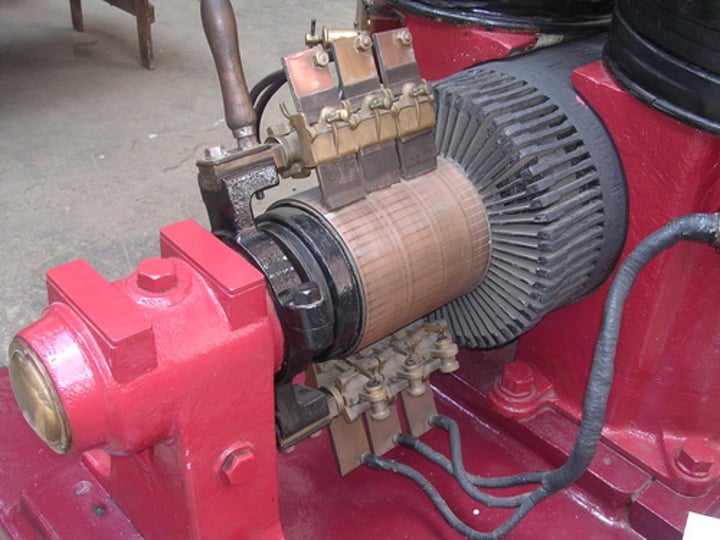
Generator
A device found in power stations that transfers kinetic energy to electrical energy

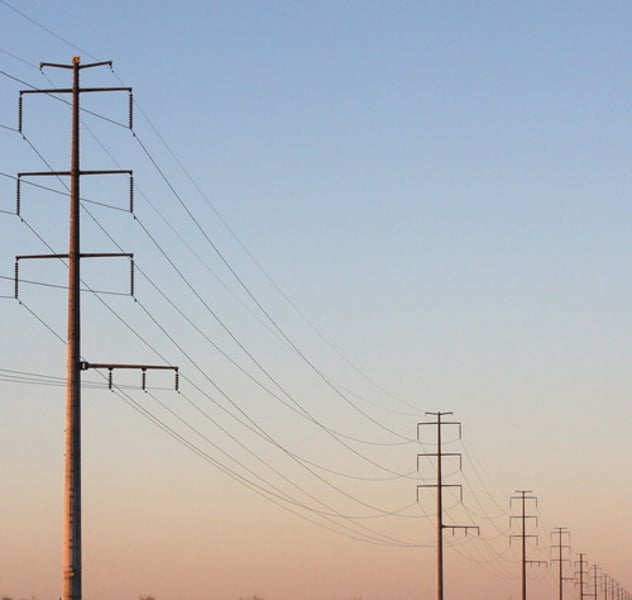
Transmission lines
Cables used to carry electricity long distances via the National Grid

Energy dissipated by transmission lines
wasted energy transferred to the surroundings due to an electric current flowing through the cables and causing them to get hotter

P = I²R
The equation linking power (dissipated), current and resistance
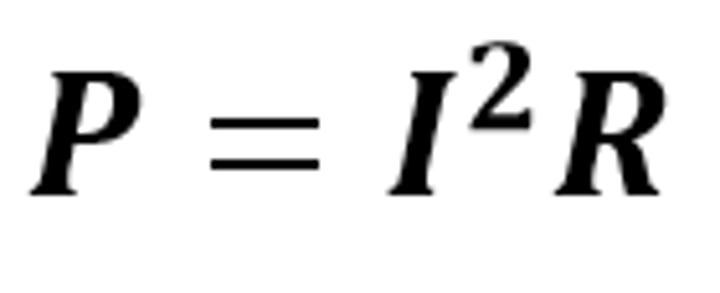
How to reduce the energy dissipated from transmission lines
1) thick cables which have a low resistance
2) high potential difference to reduce the current passing through them
25,000 V
The potential difference of the electricity produced in power stations
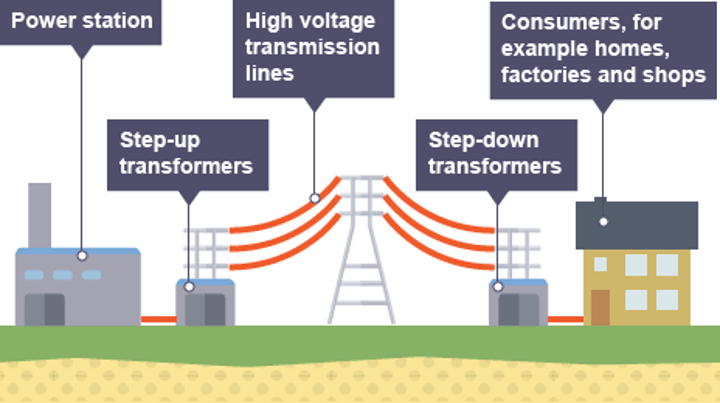
400,000 V
The potential difference that electricity is stepped to before it is transmitted across the country
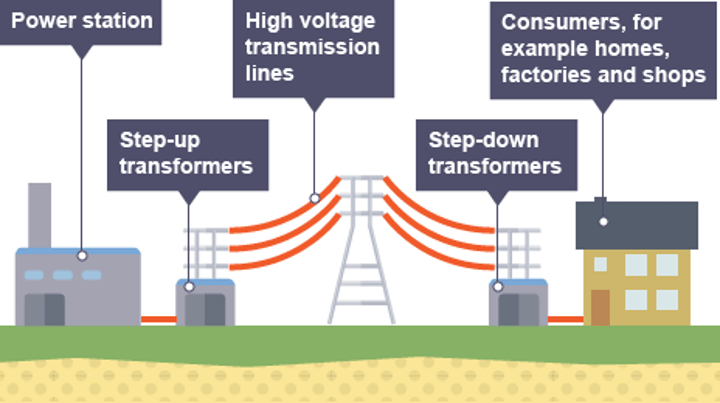
230 V
The potential difference that electricity is stepped down to before it is delivered to houses