chapter 2 (mcgraw hill)
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
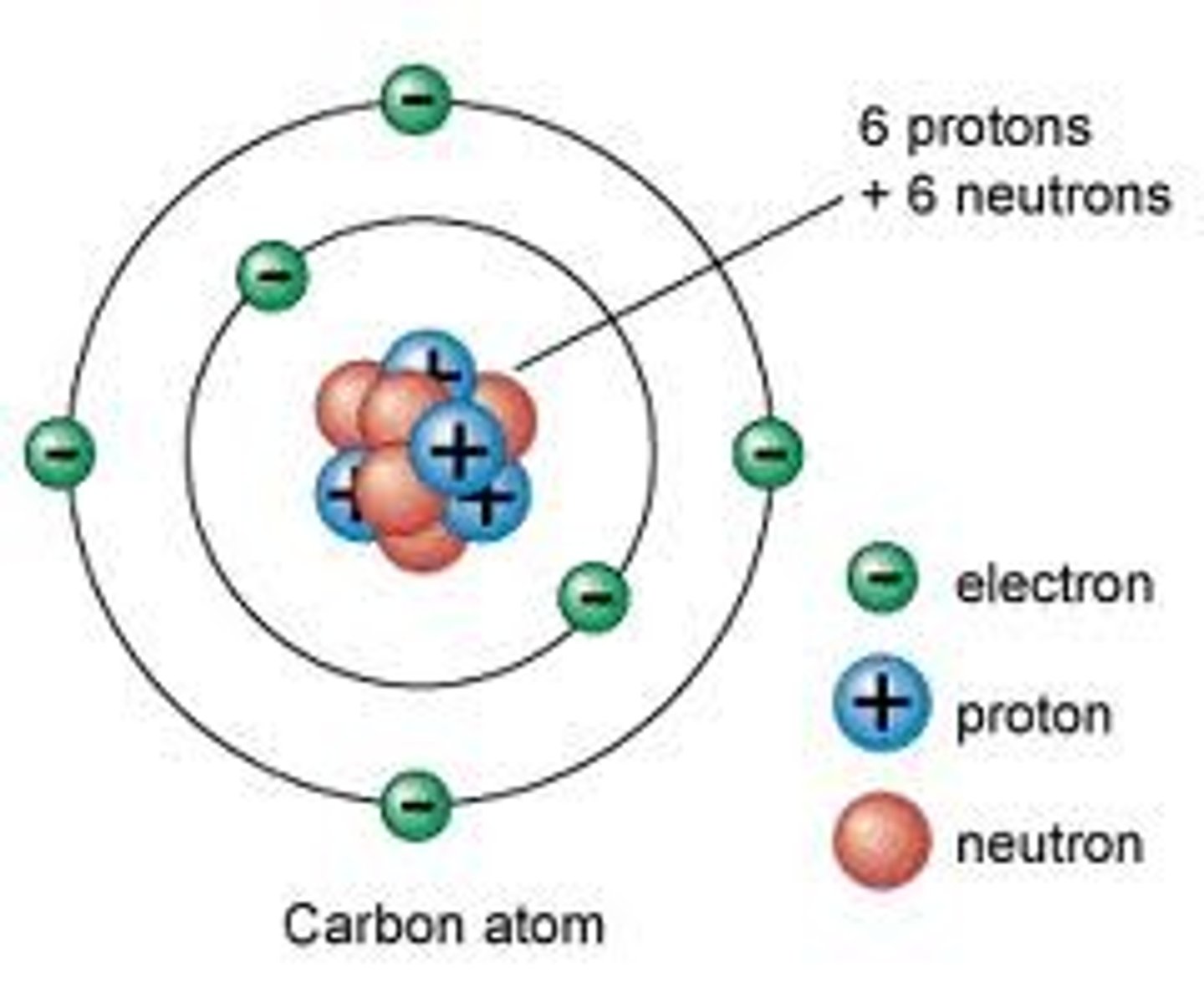
-found in nucleus, positive charge
-the same as the atomic #
protons (basics)
-neutral charge, found in the nucleus
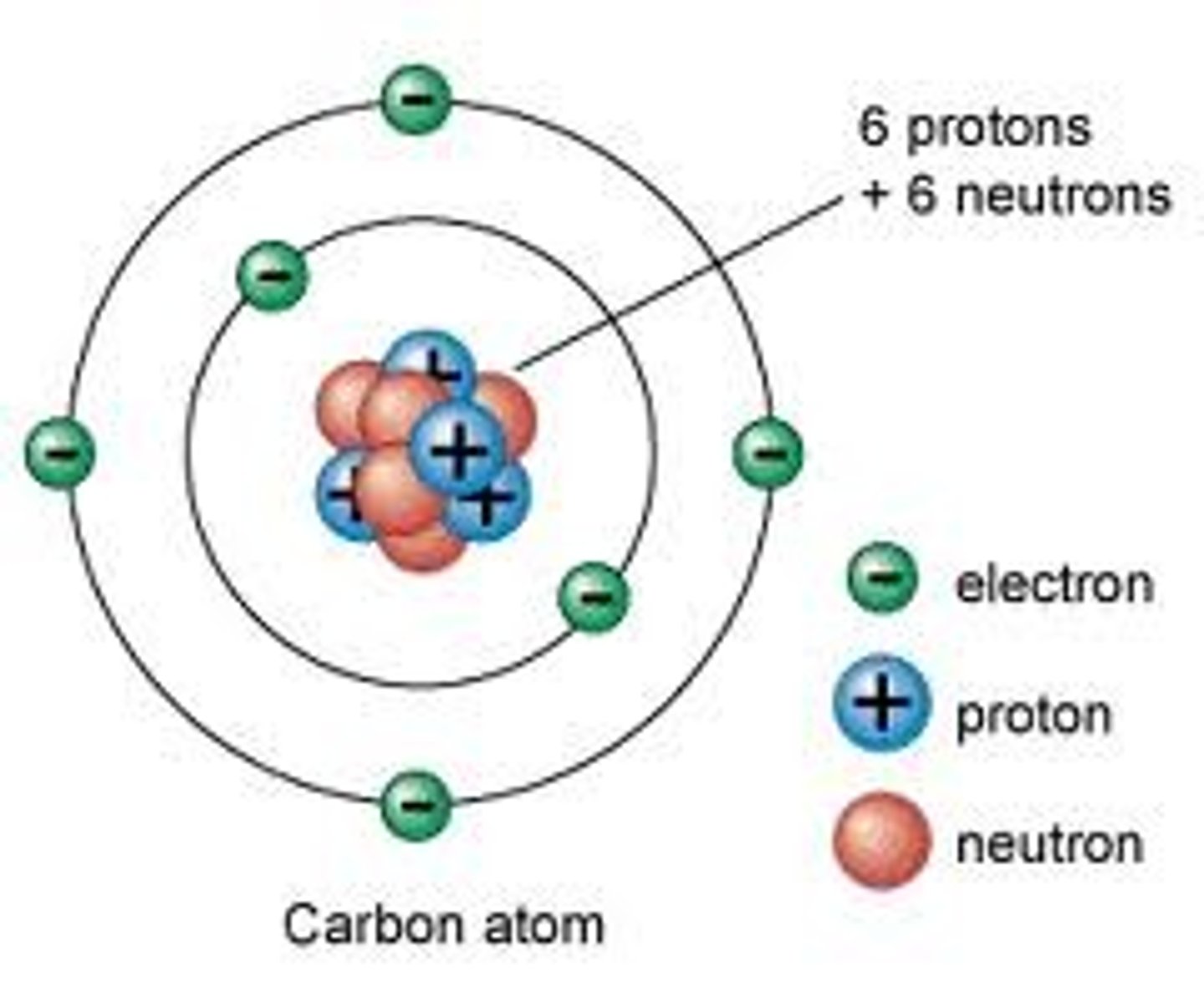
- subtract atomic mass from atomic #
neutrons (basics)
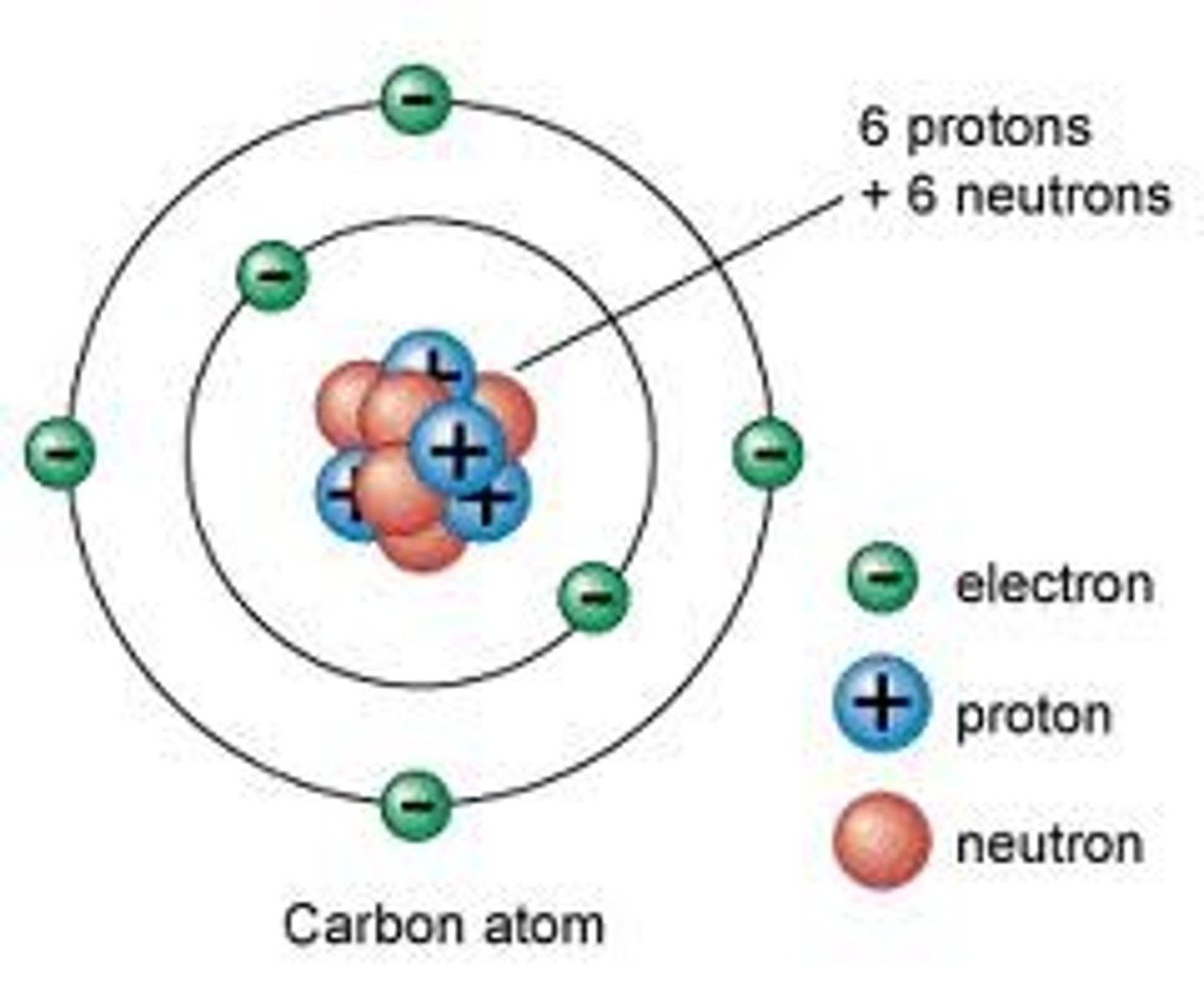
-negative charge, found in orbitals surrounding the nucleus
- the same as the atomic #
electrons (basics)
the same, neutrons
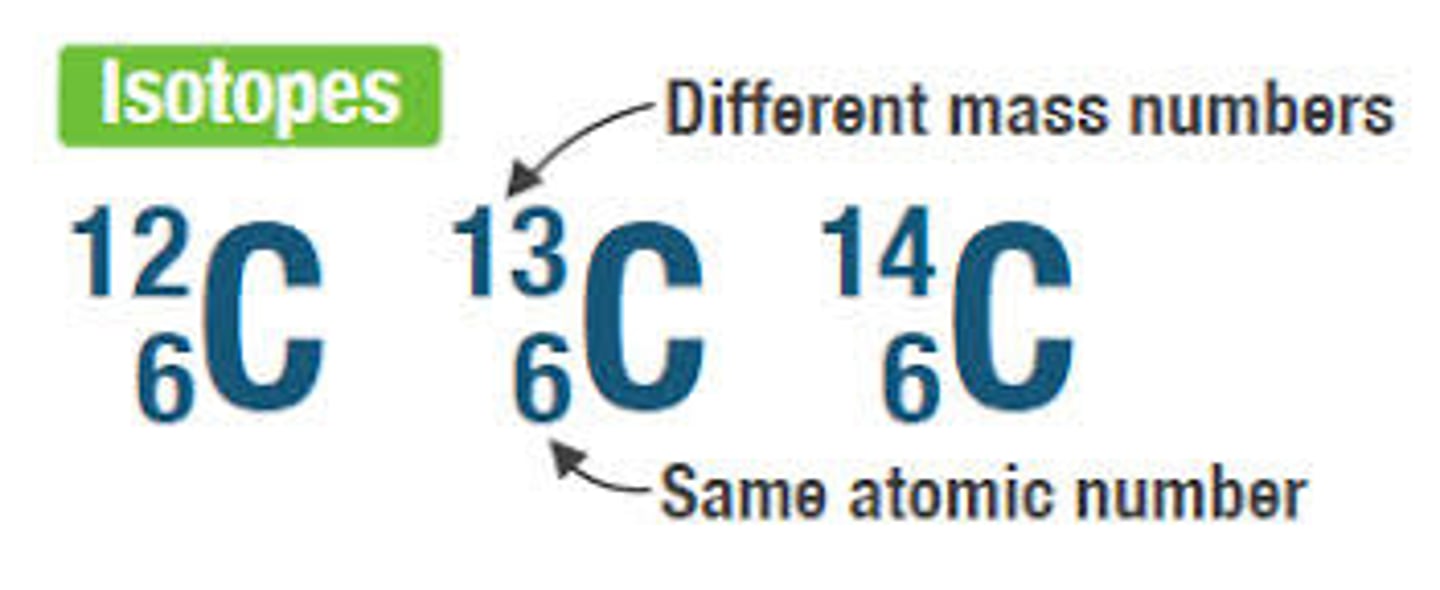
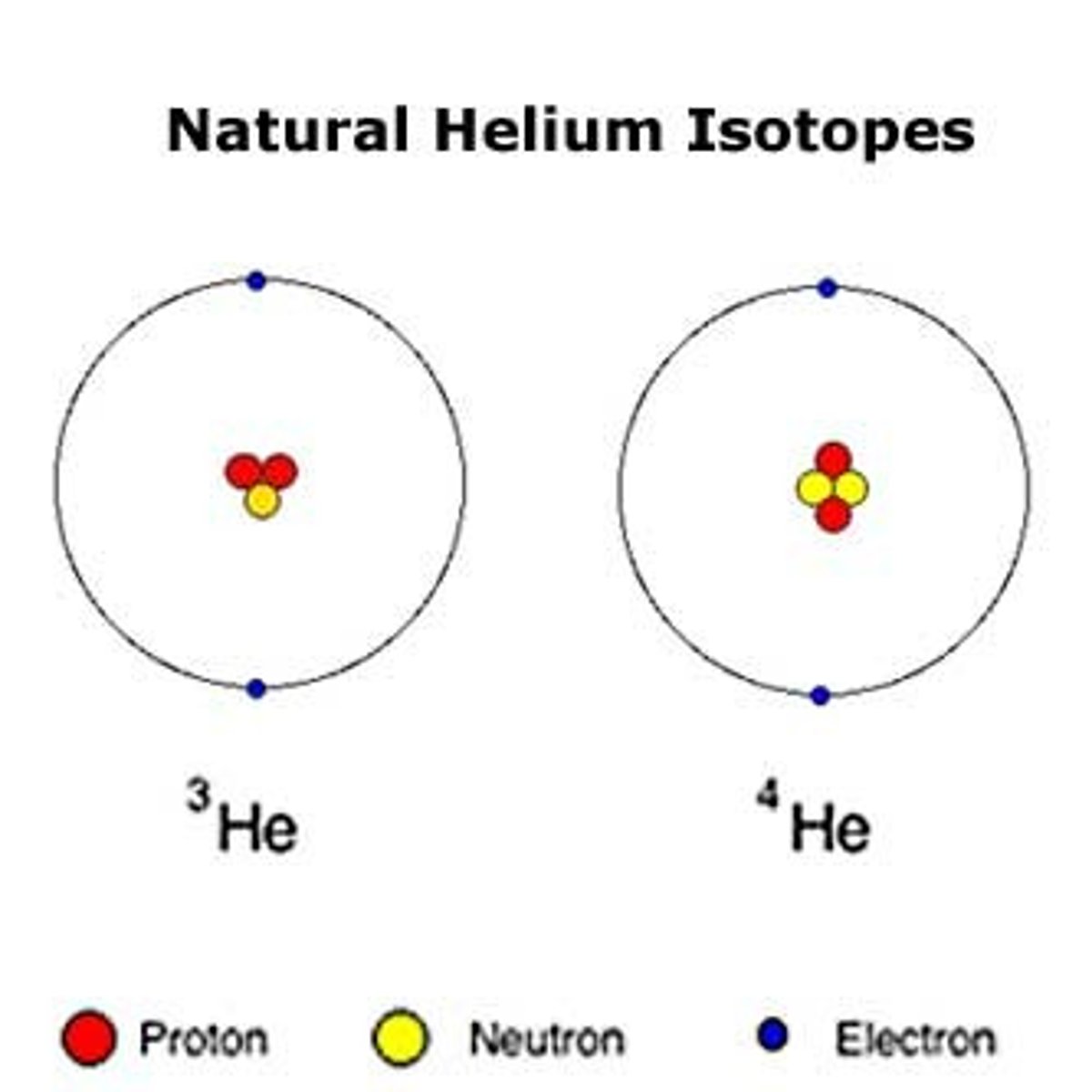
isotopes are atoms of _____ element(s) that differ in their number of ____
carbon
the element ____ has 3 isotopes: one with the atomic mass of 12, one with an atomic mass of 13, and one with an atomic mass of 14.
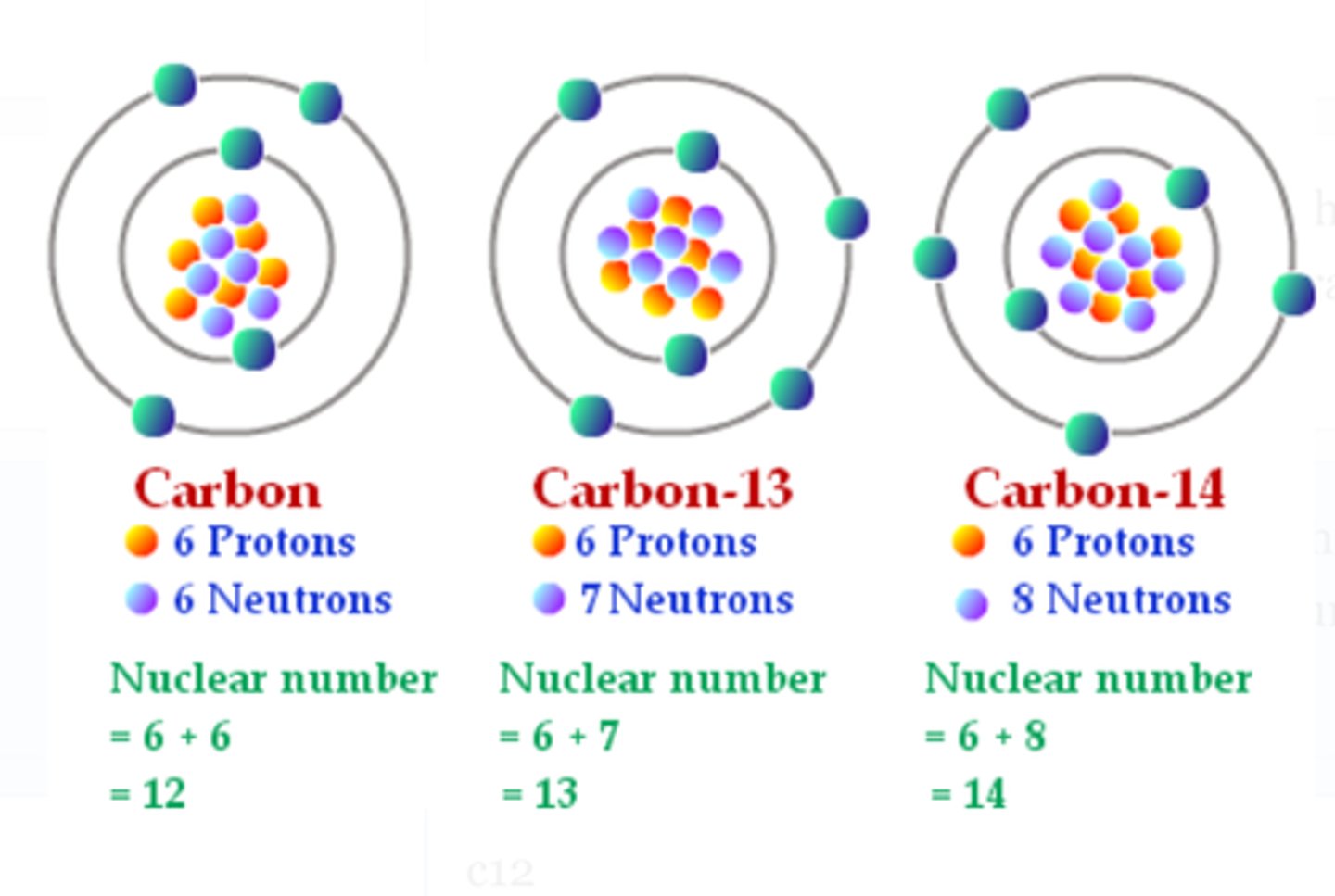
6, protons
(carbon) the atomic # of all of these isotopes is____ because all 3 have the same # of ____ in the nucleus
stable, unstable, 14
some isotopes of an atom are ____, while others are ____, or radioactive. Carbon ____ is an example of un unstable isotope of Carbon.
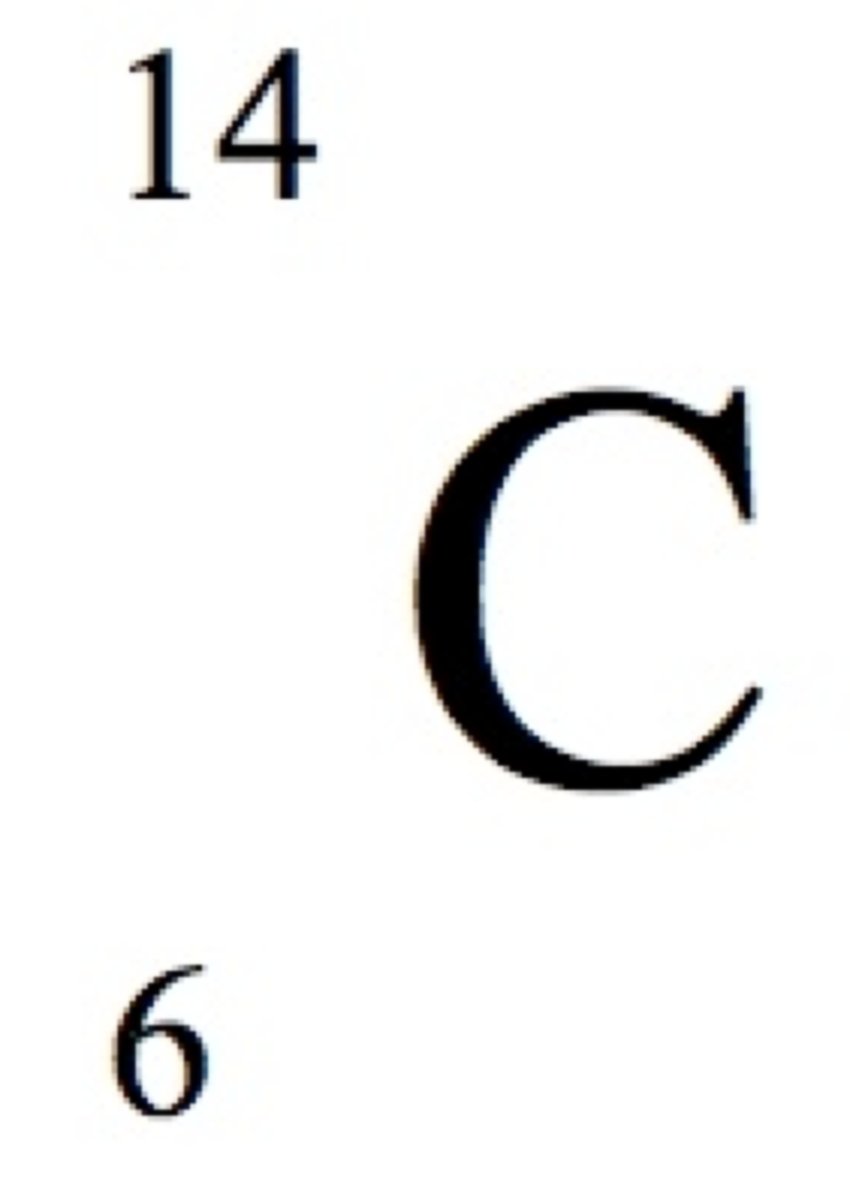
atomic mass, beta particles
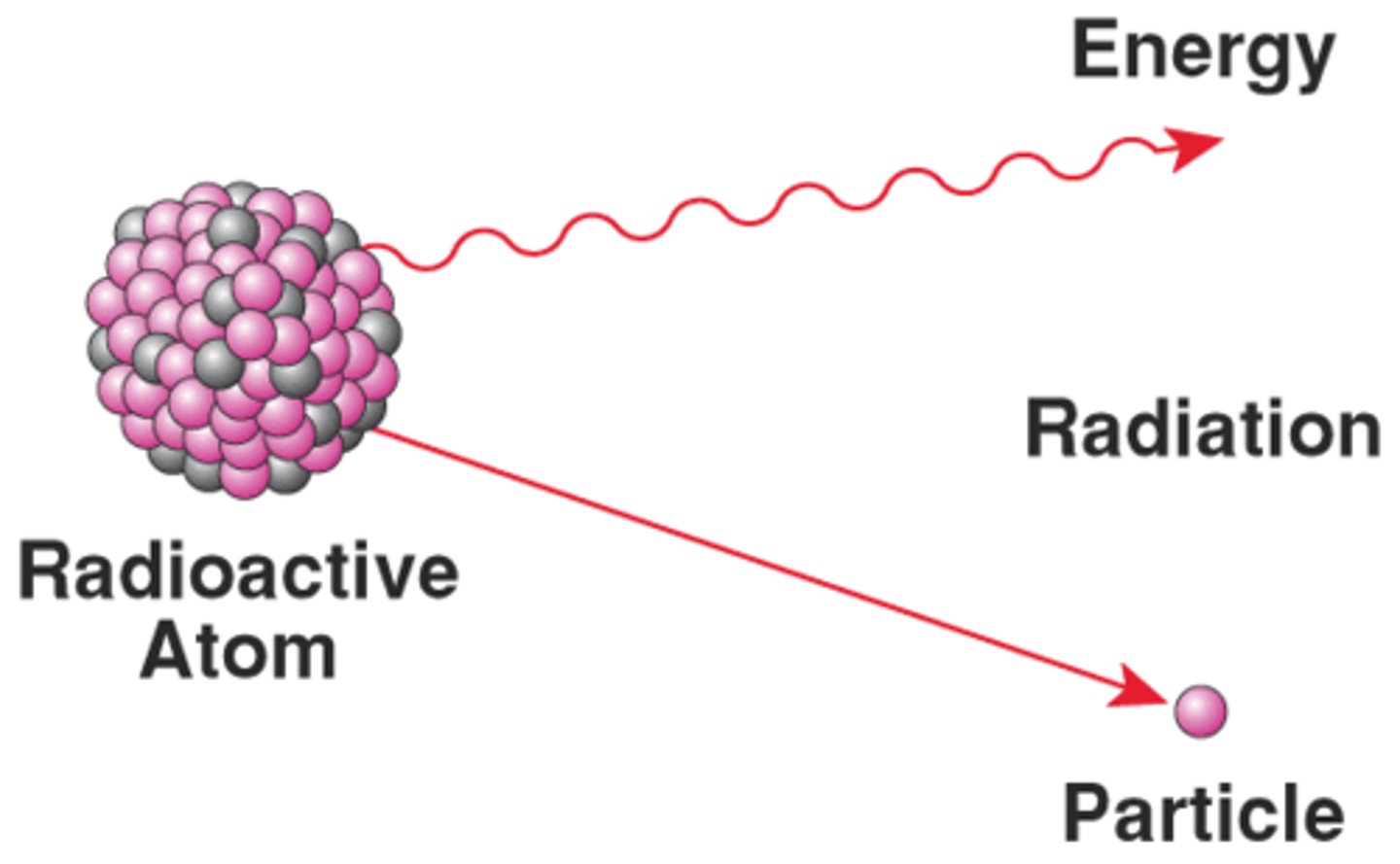
The main difference between a stable and unstable isotope is the ____ and wether or not it is radioactive. Radioactive, or unstable isotopes release energy as they decay. This energy may be relatively harmless, or harmful, as is the case with ____ and gamma radiation
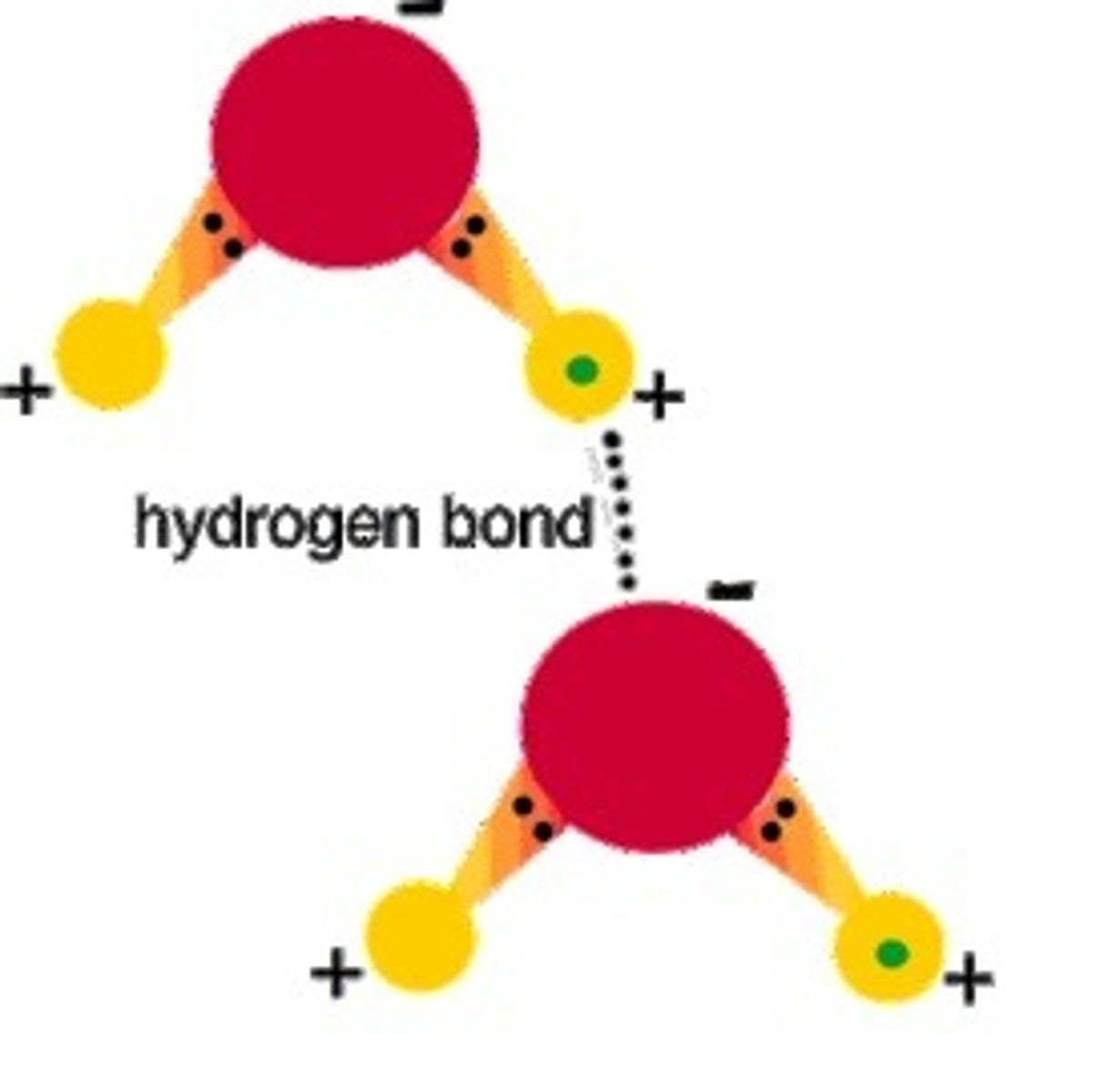
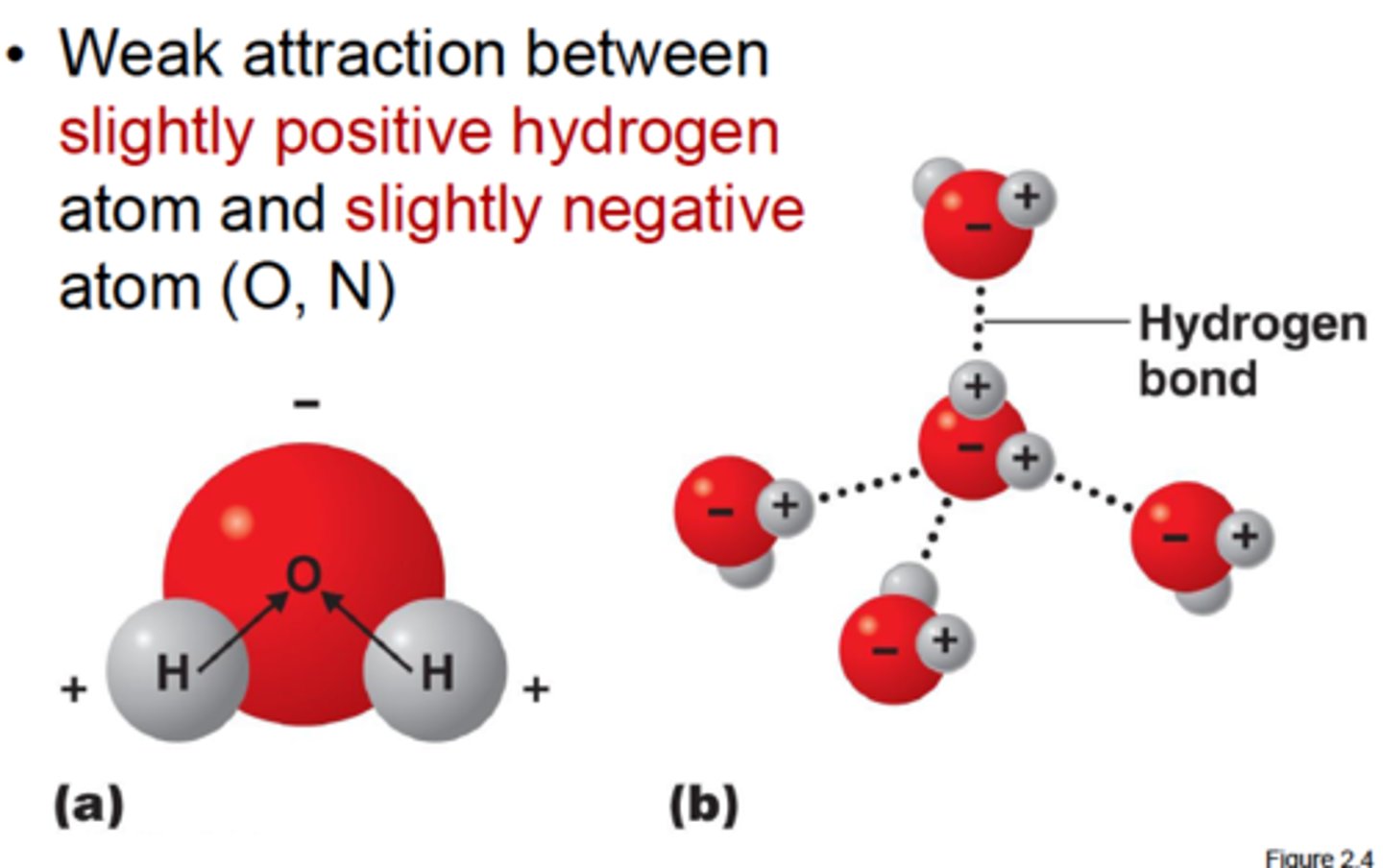
hydrogen bond
2 water molecules, 2 strands of DNA are what kind of bond?
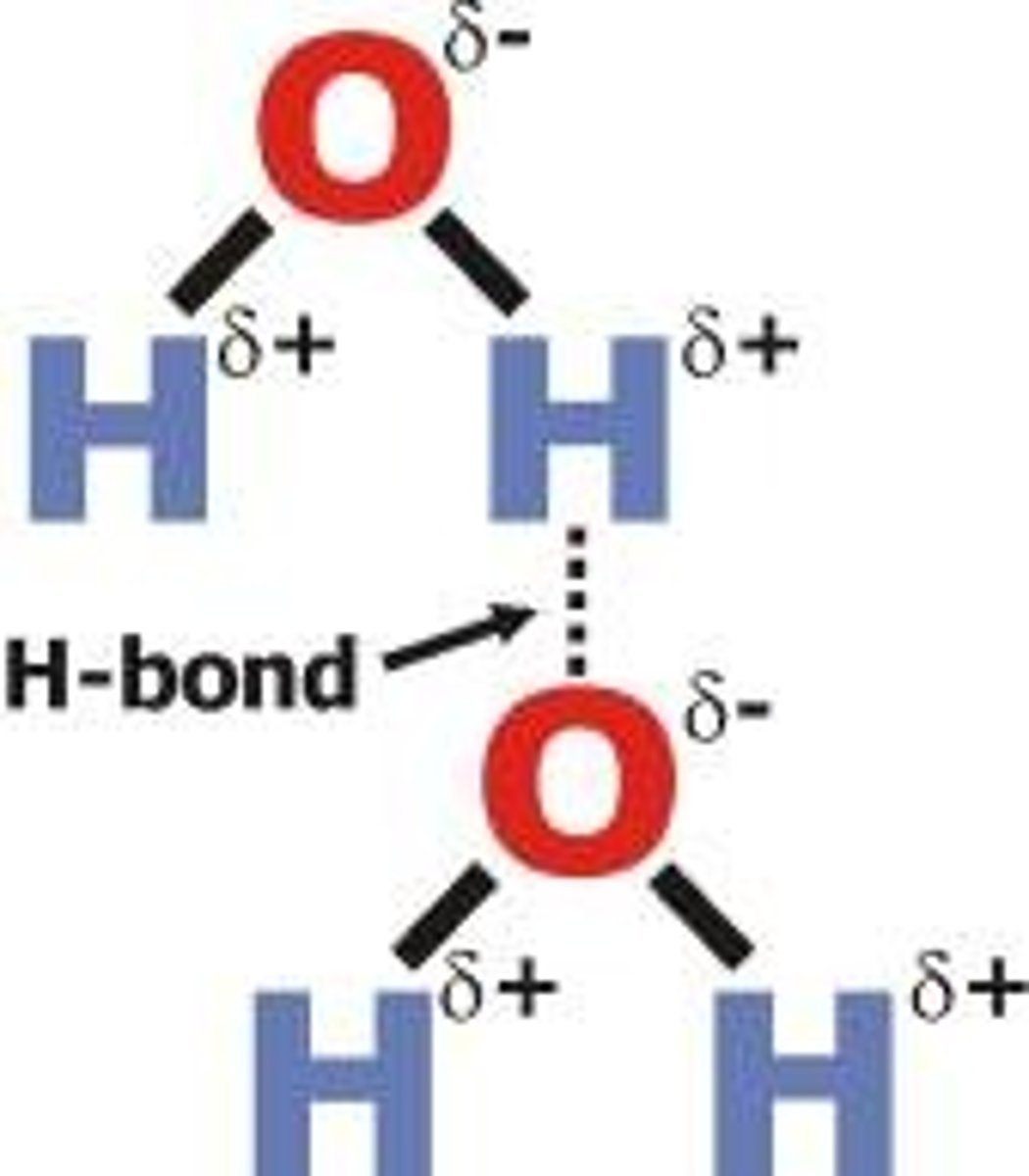
polar covalent bond
H20 is what kind of bond?
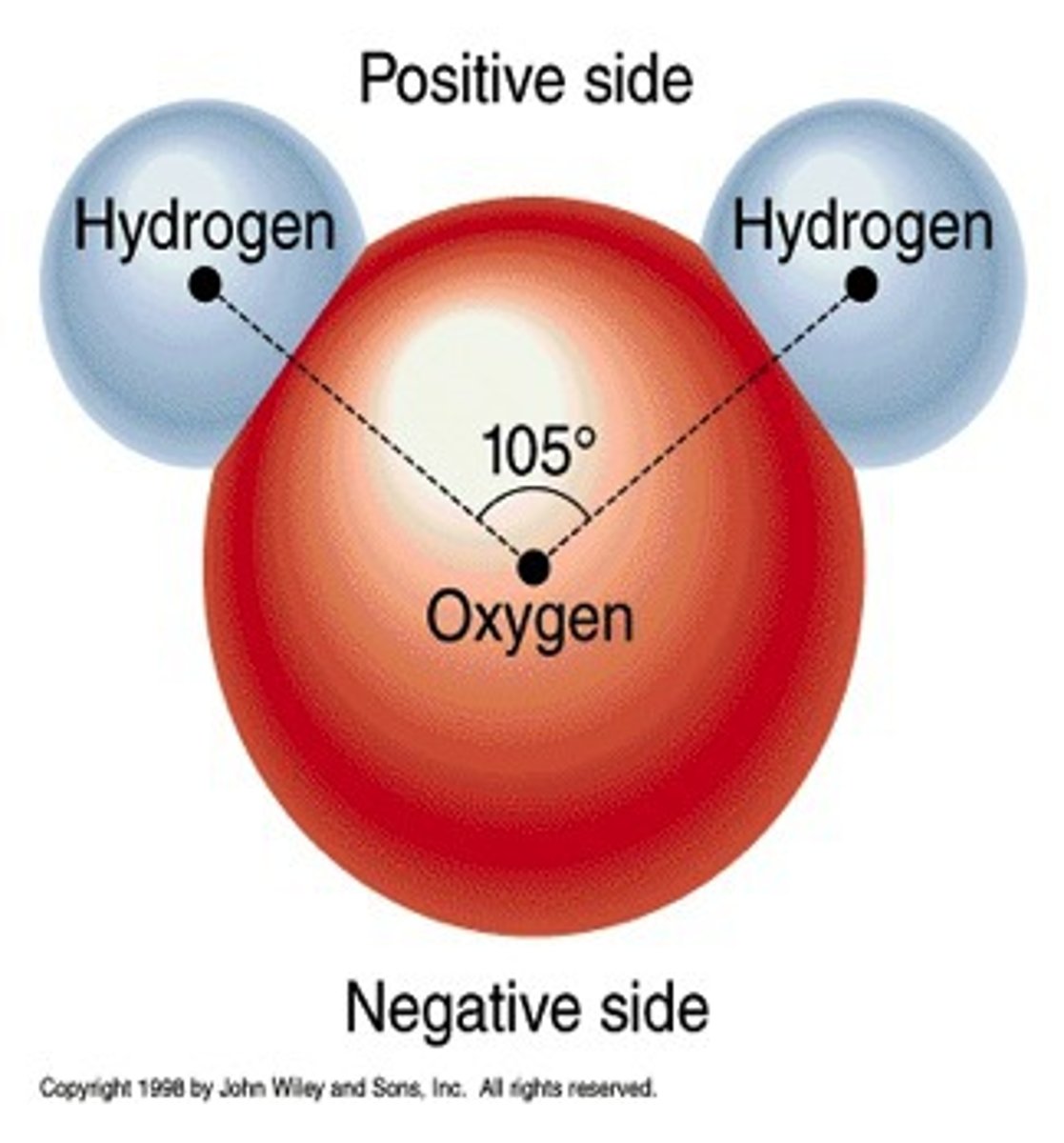
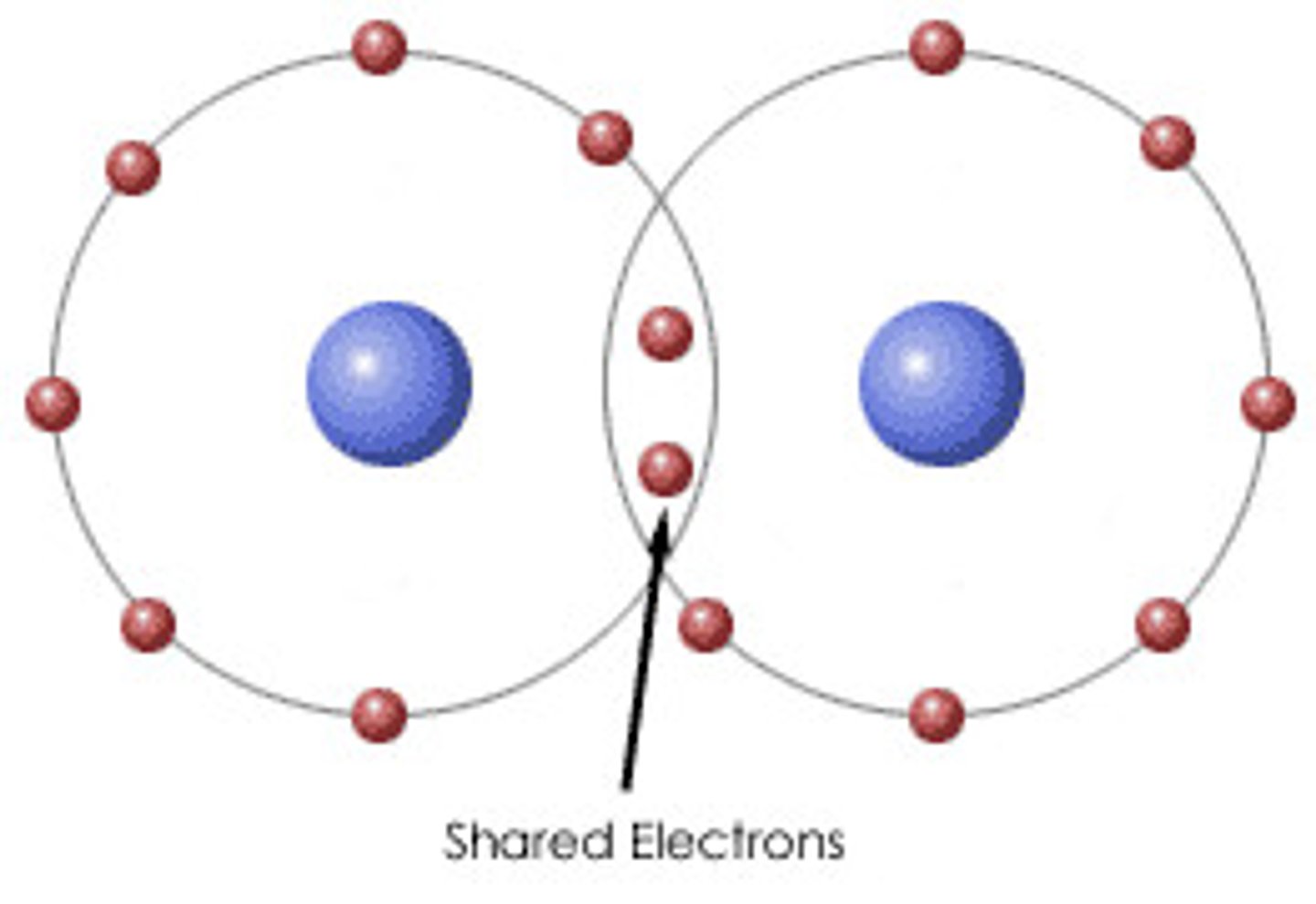
non-polar covalent bonds
H2, CH4 are what kind of bond?
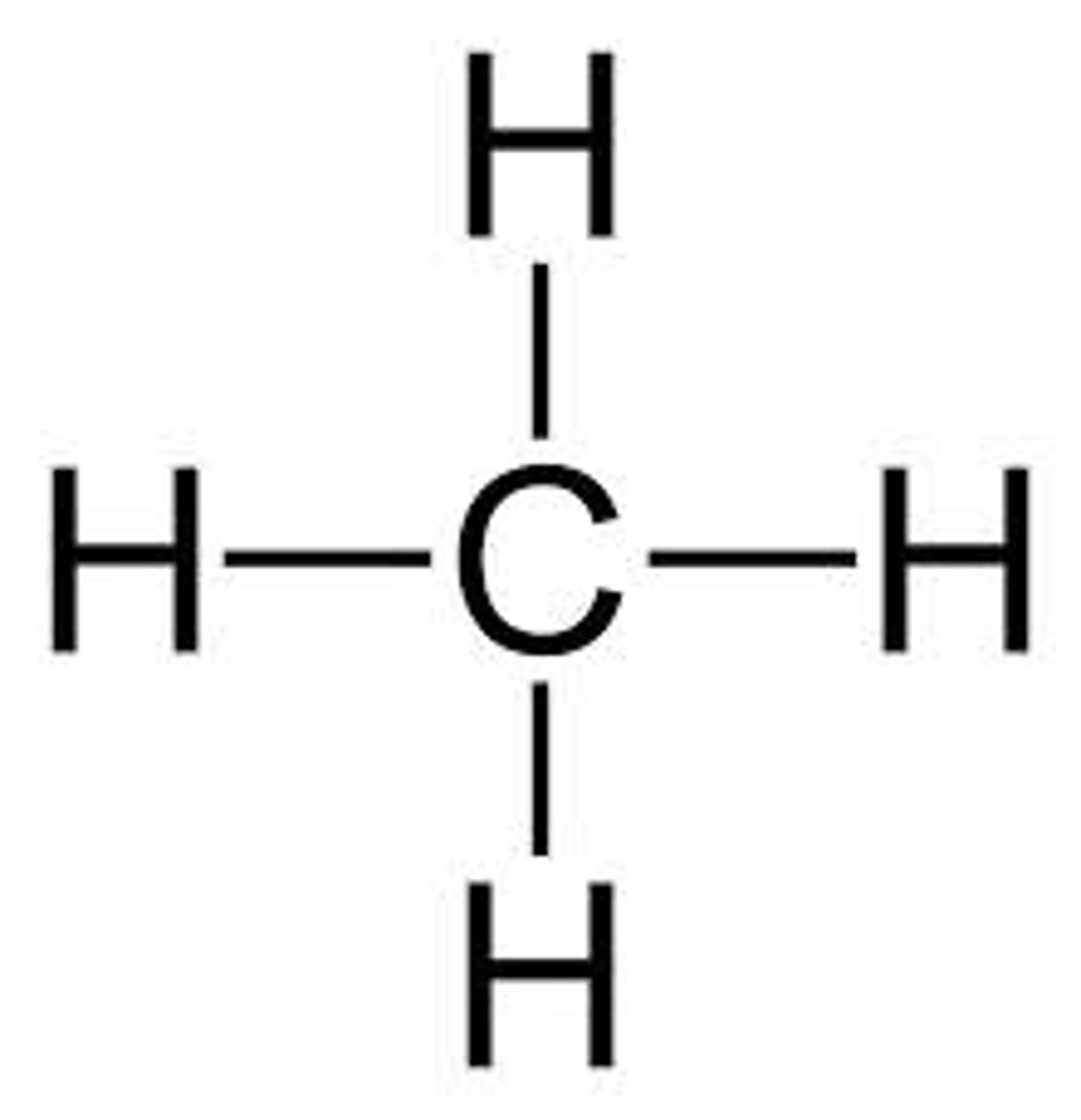
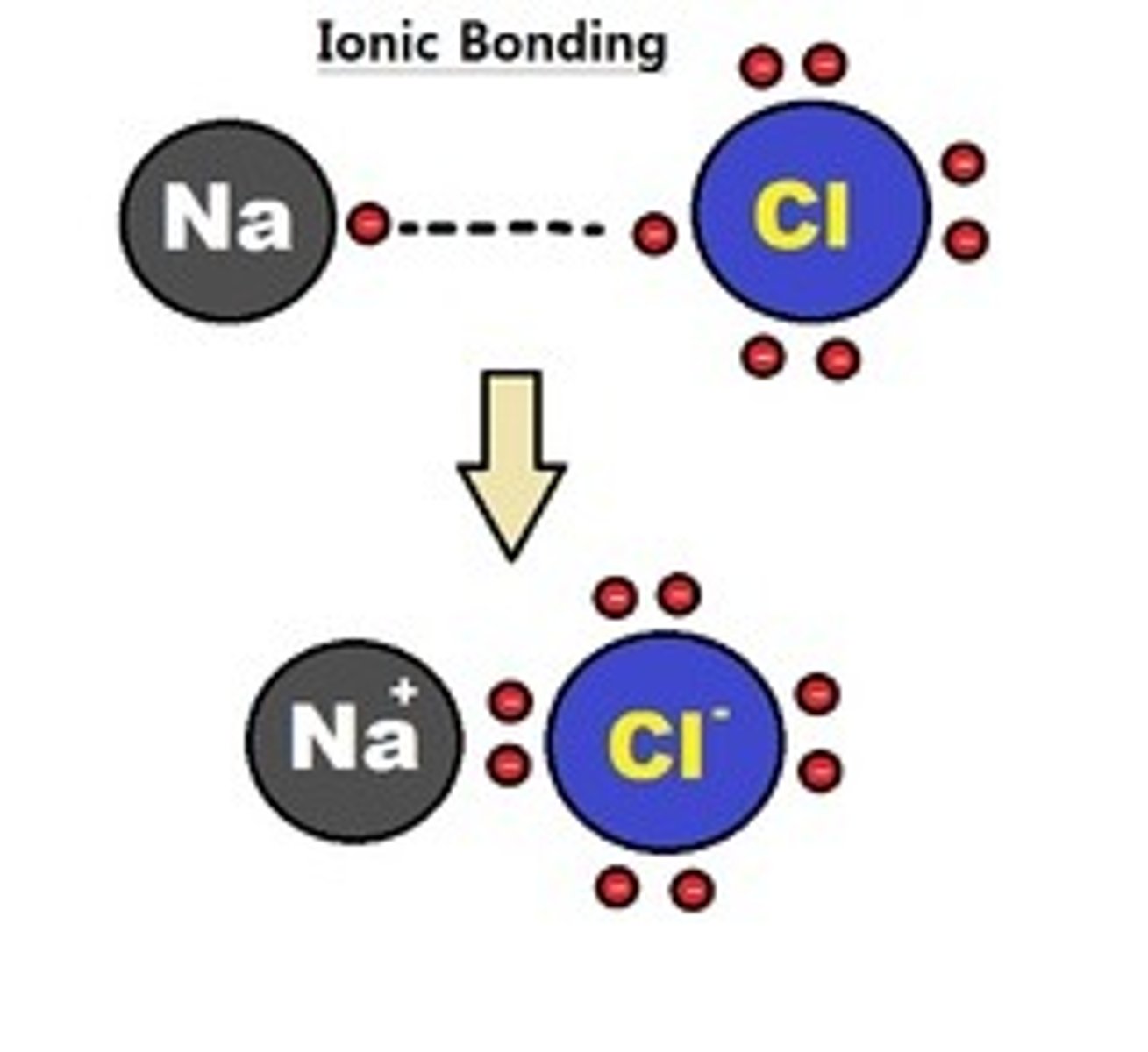
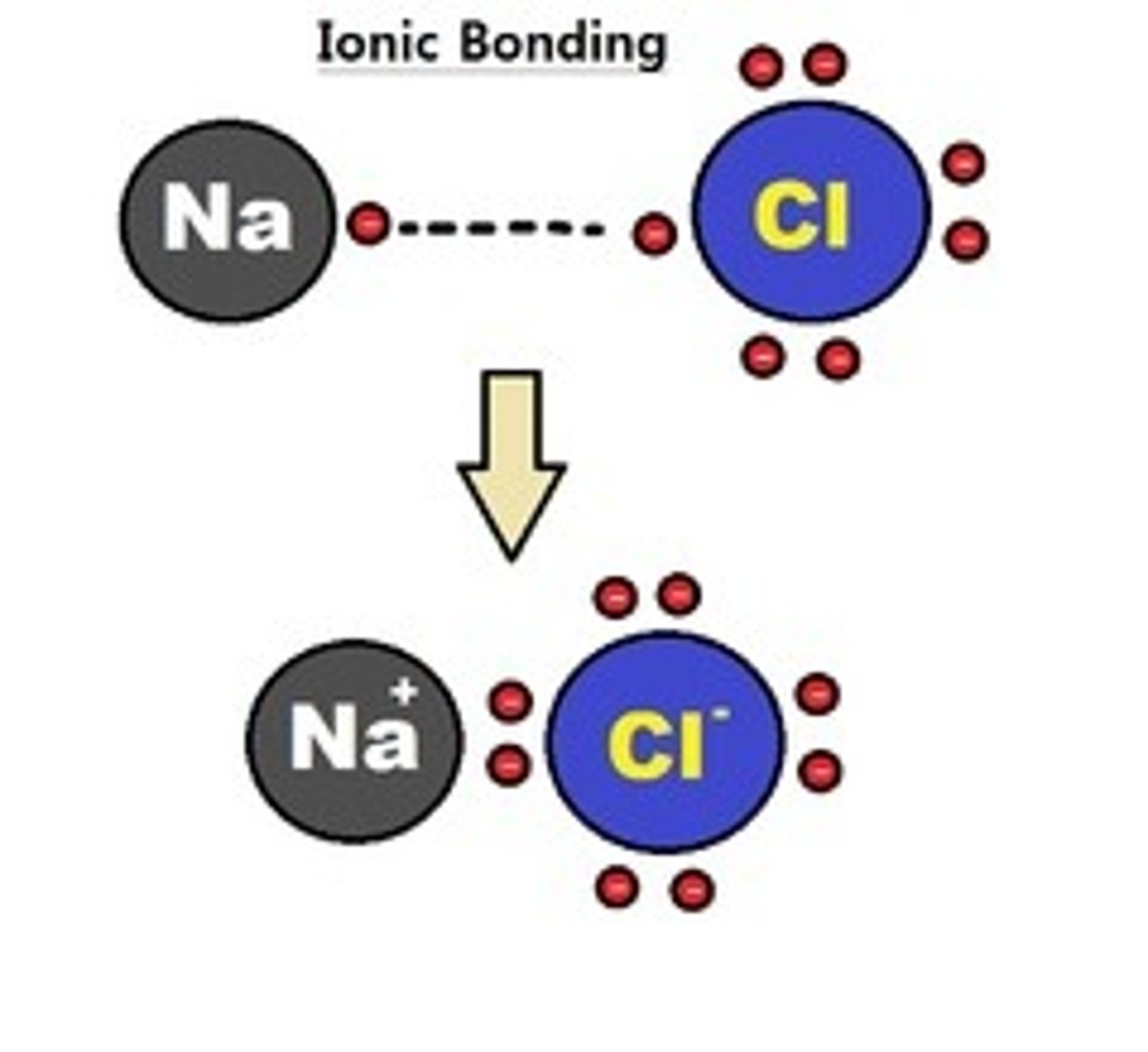
ionic bonds
NaCl, MgCl2 are what kind of bond?
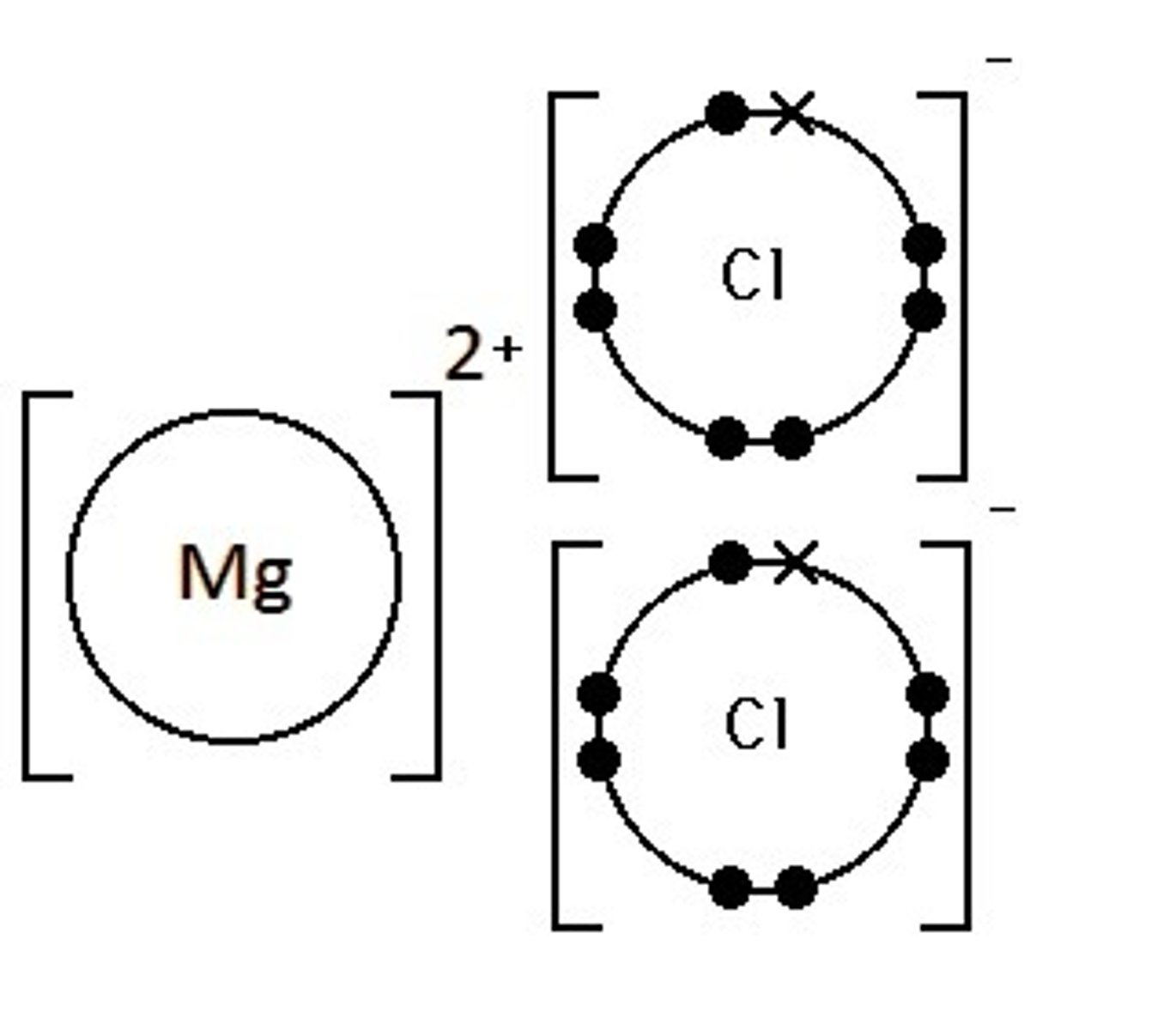
hydrogen bonds, hydrogen atoms, attraction between 2 molecules of water
____ occur when partially positive ____ attract partially negative atoms nearby. Examples include____
ionic bonds, ions, NaCl and MgCl2
____ occur when atoms are held together by an attraction between negatively and positively charged ____. Examples include ____
single covalent bond, electrons, bond between 2 hydrogen atoms
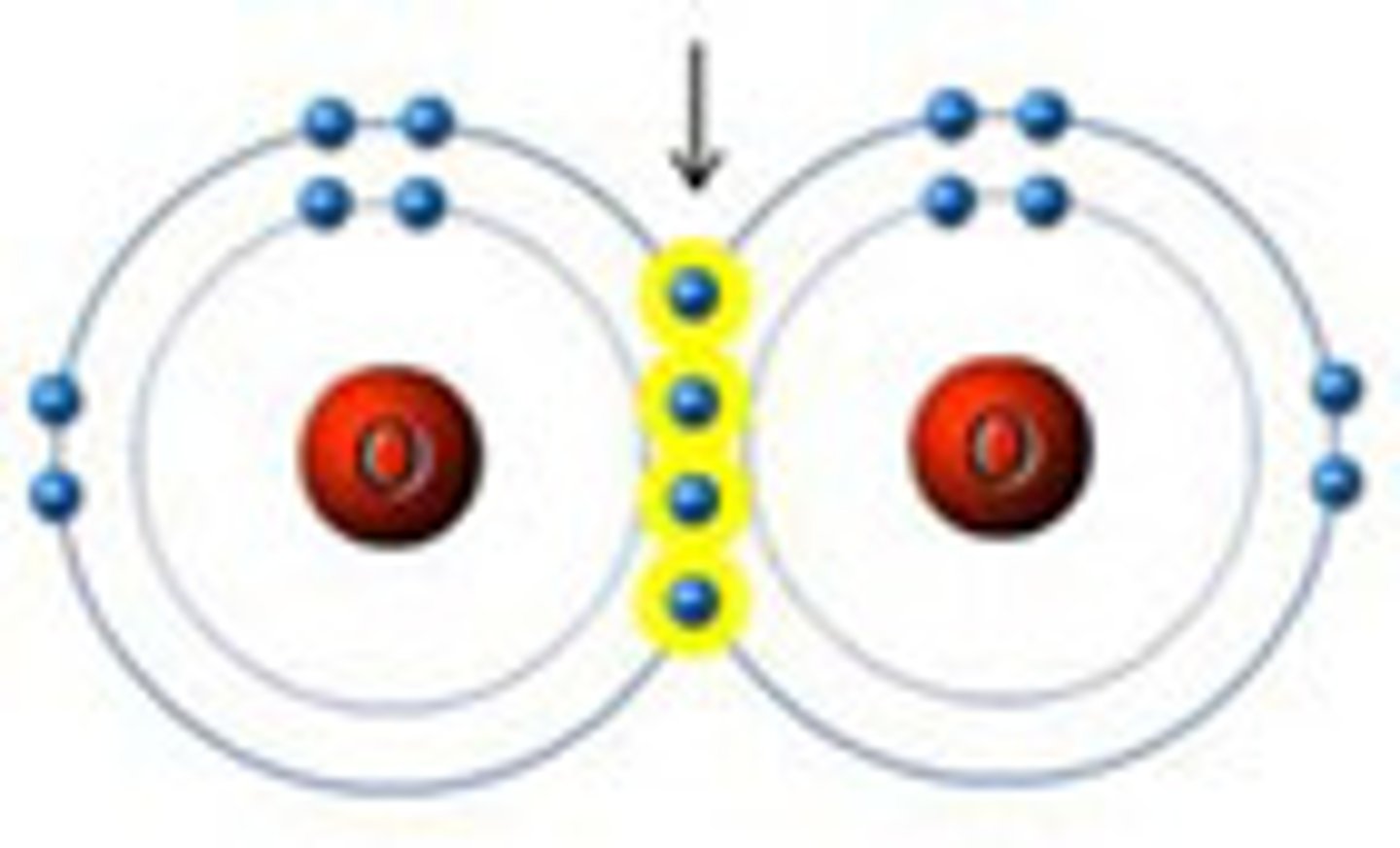
____ occur when one pair of ____ is shared between the outer shells of 2 atoms. Examples include ____
double covalent bond, electrons, bond between 2 oxygen atoms
____ occur when 2 pairs of ____ are shared between the outer shells of 2 atoms. Examples include____
electrons, bond between 2 nitrogen atoms
Triple covalent bond occurs when 3 pairs of ____ are shared between the outer shells of 2 atoms. Examples include____
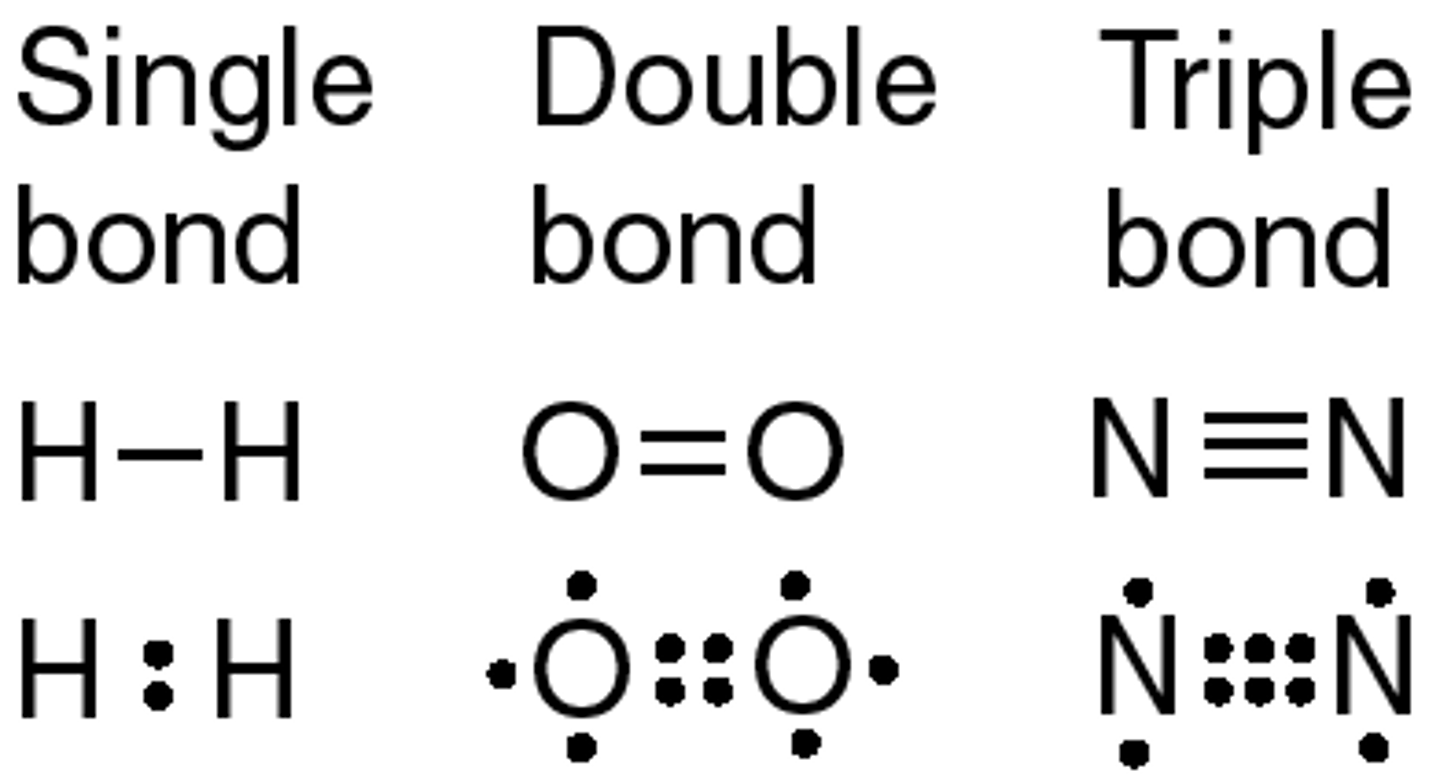
unequal
The attraction of electrons in the covalent bond between hydrogen and oxygen atoms in a water molecule is ____
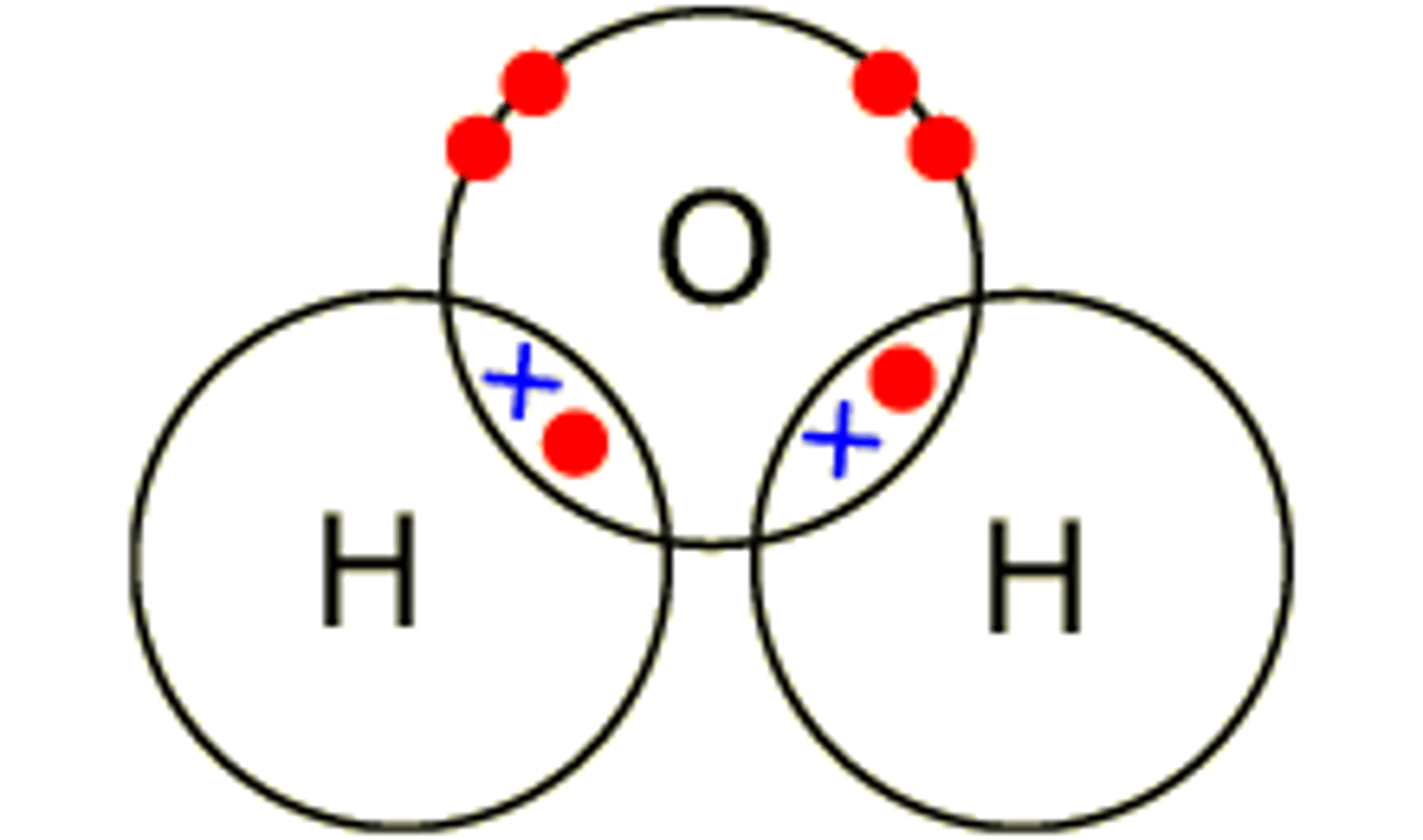
electronegative
The larger oxygen atom, with more protons, is more ____ than the hydrogen atom and attracts the electron pair closer
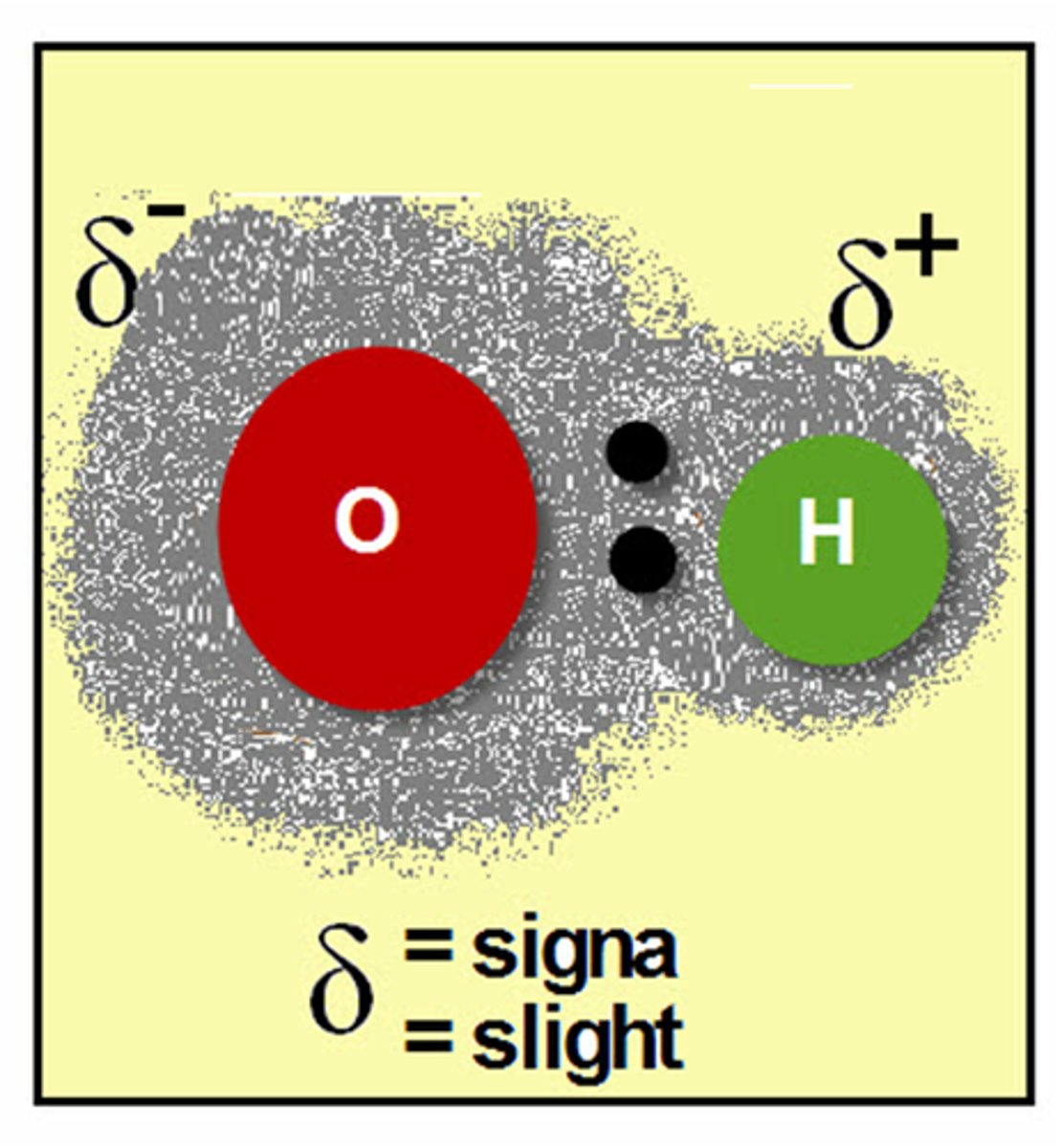
polar covalent
the unequal sharing of electrons in a covalent bond created a ____ bond.
Hydrogen atoms
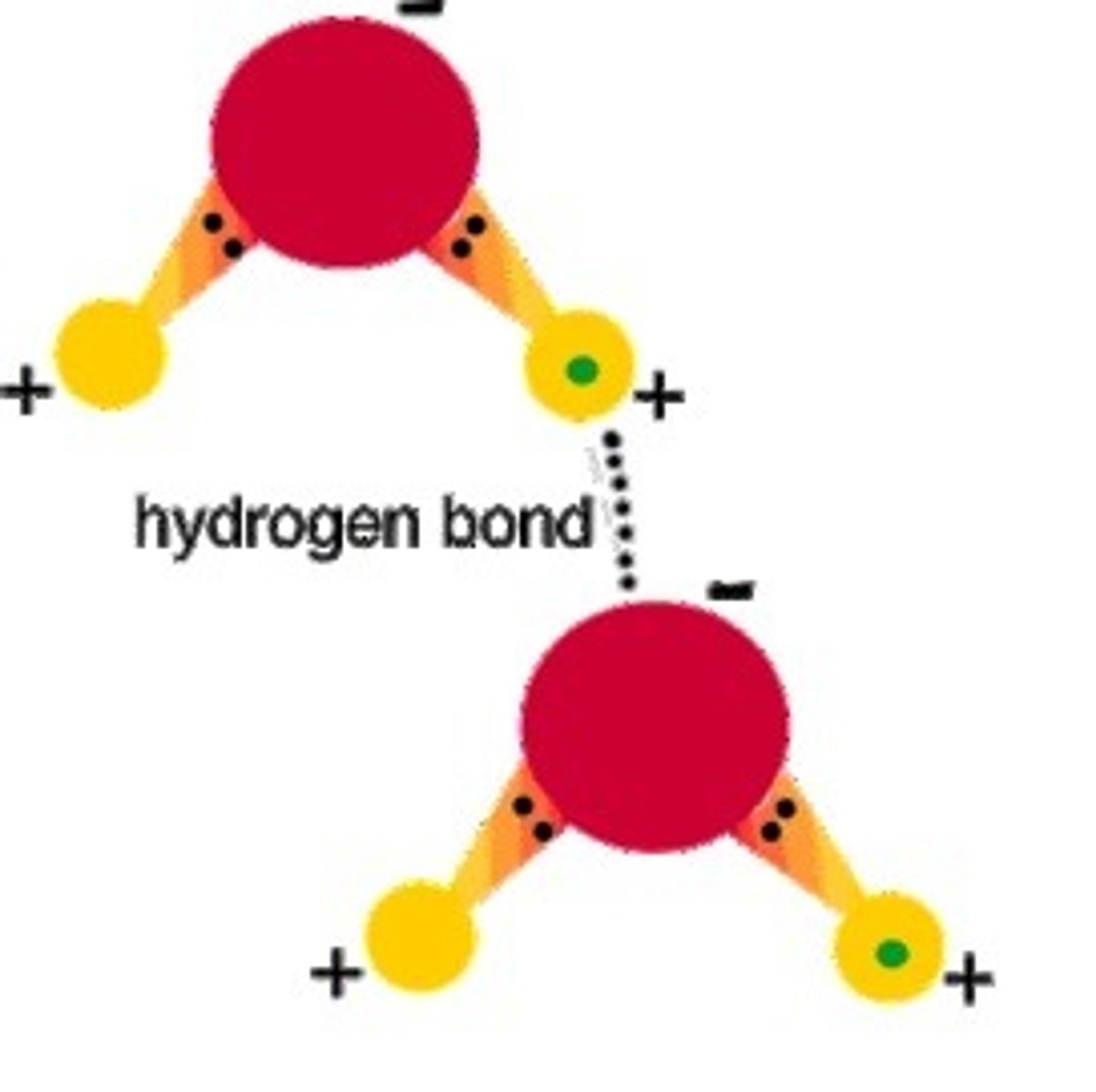
Due to the partial charges on atoms in water molecules, ____ in water molecules are attracted to oxygen atoms in other water molecules
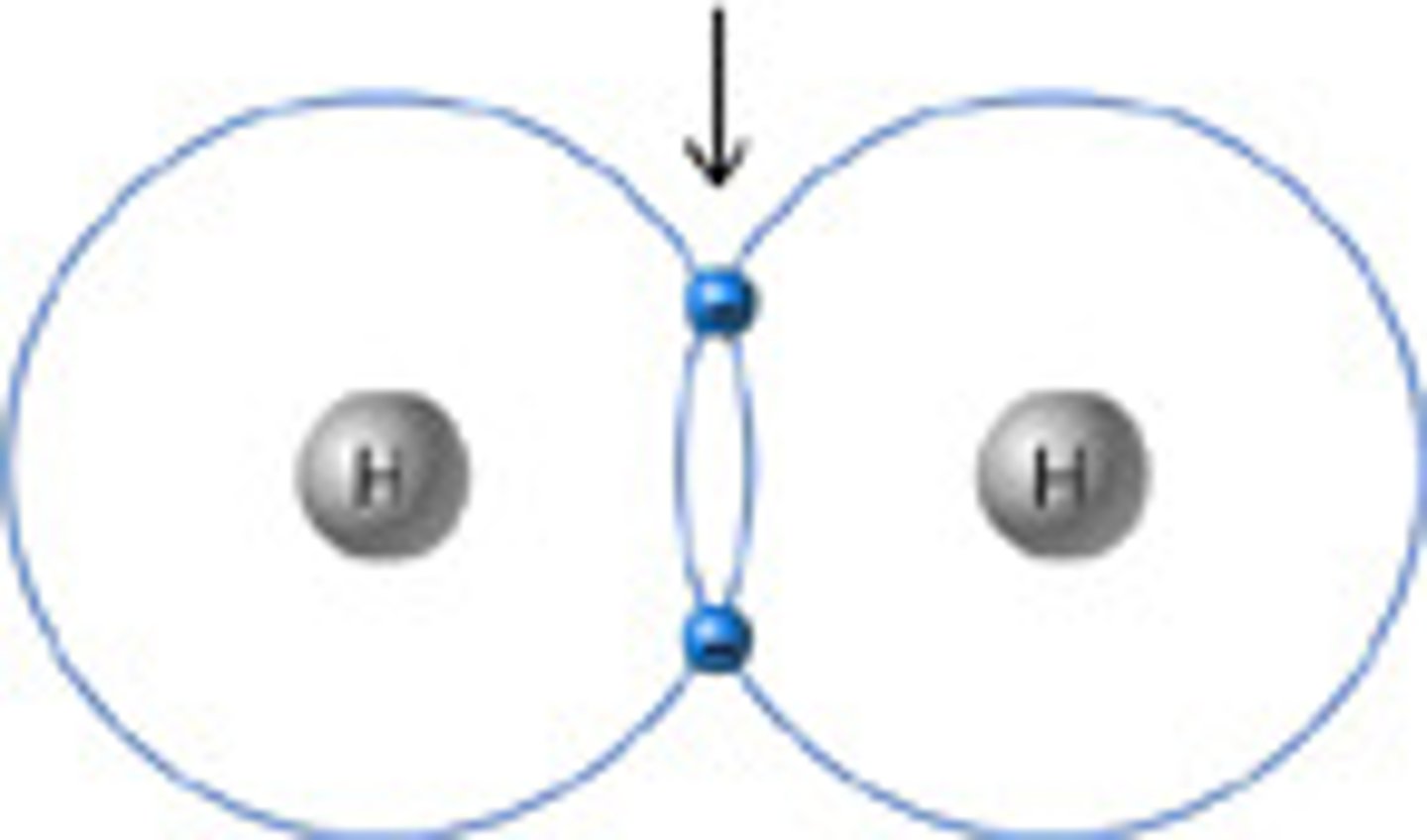
hydrogen
The weak bond formed between the hydrogen atoms of 1 water molecule and the oxygen atom of another water is called a ____ bond
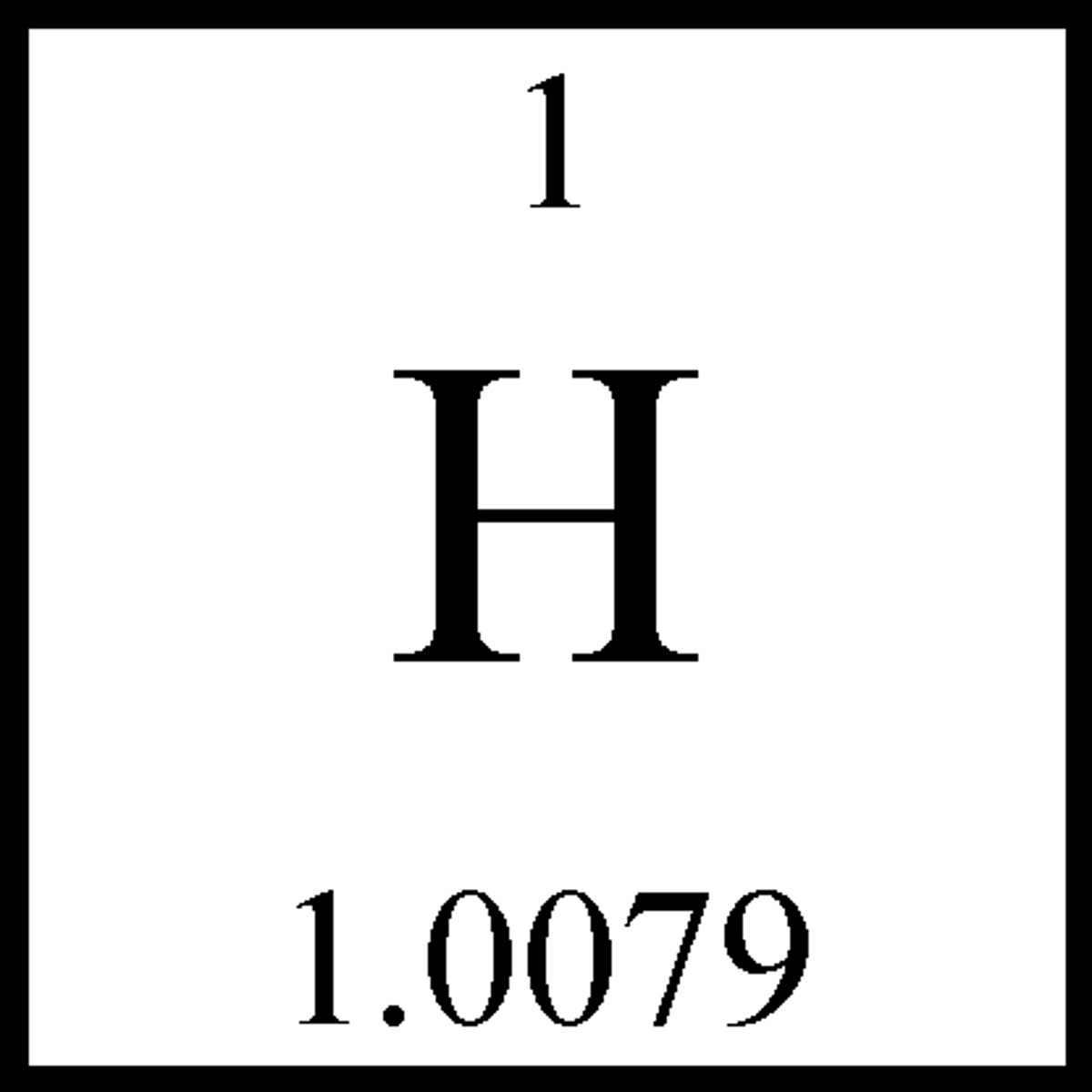
polarity
Due to waters ____ it is capable of dissolving a great number of substances
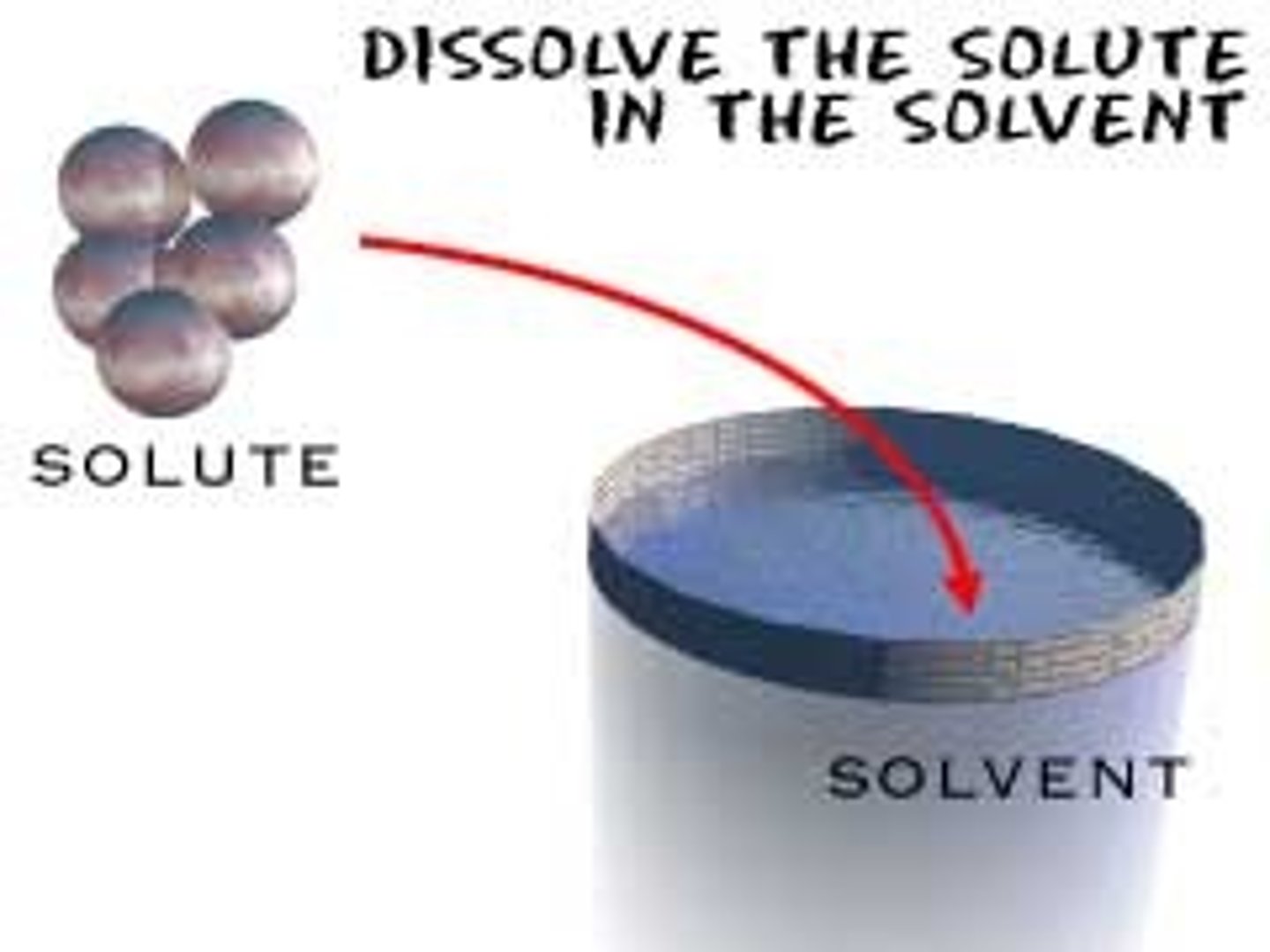
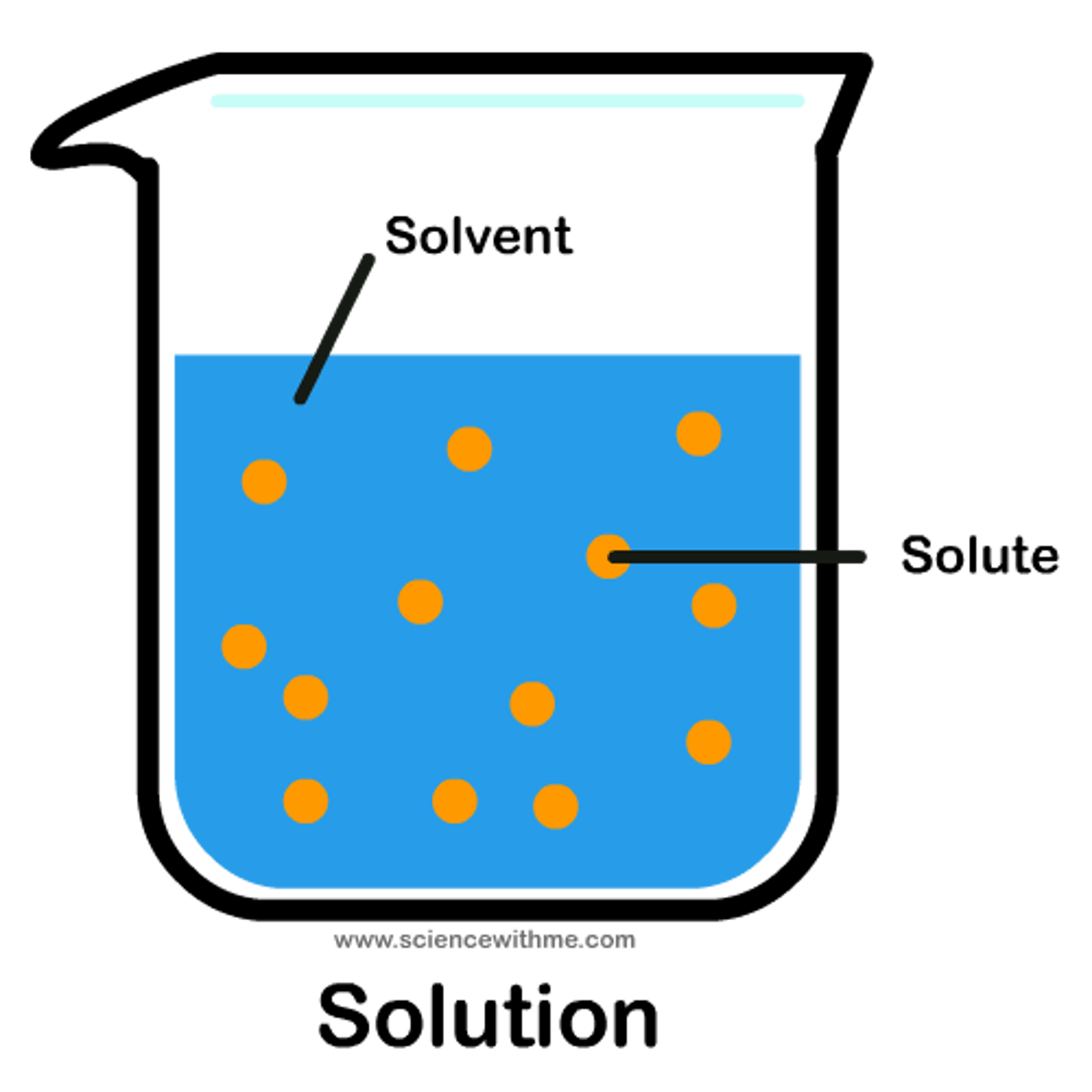
solution, solute
a ____ contains a dissolved substance called a ____

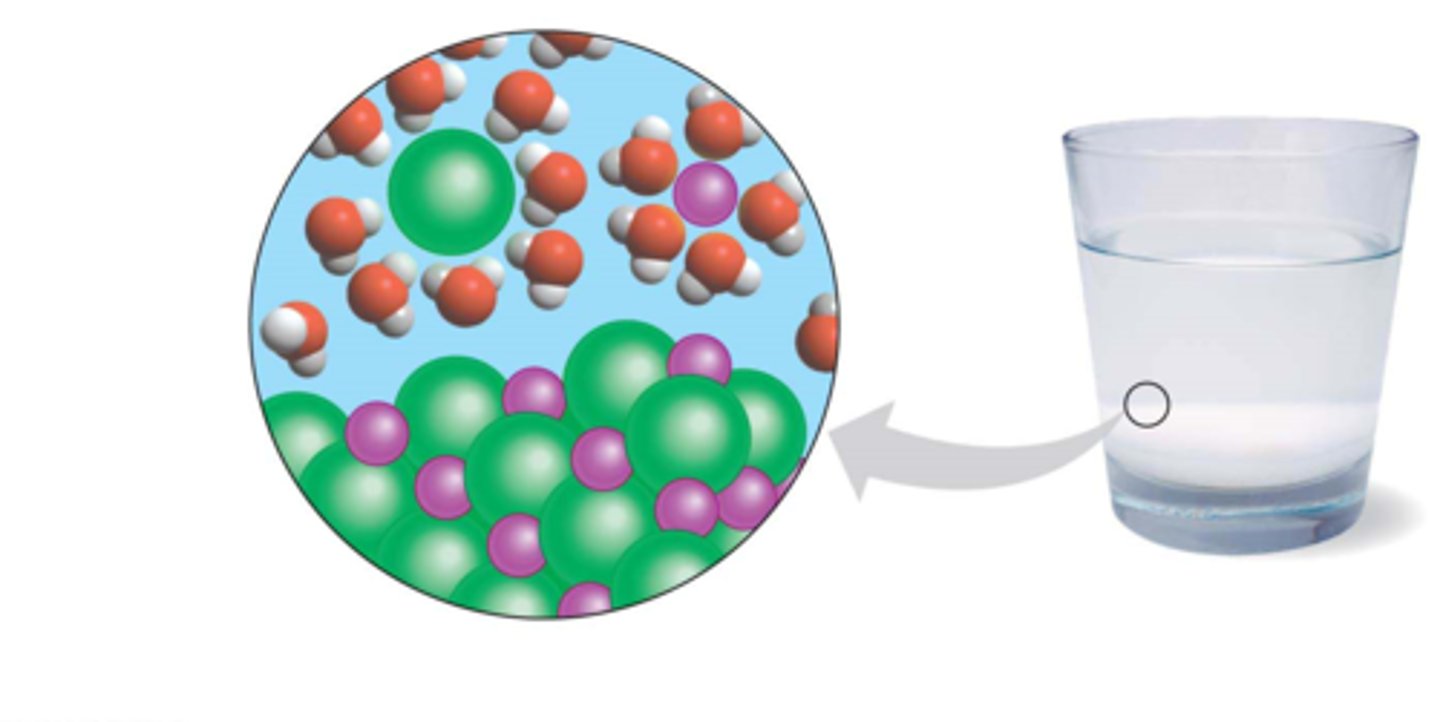
salt, water, salt water
In a mixture of salt water, ____ is the solute, ____ is the solvent and ____ is the solution
negative, positive, positive, negative
when salt is added to water, the ____ poles of the water molecules are attracted to the ____ sodium ions and the ____ poles of the water molecule are attracted to the ____ chloride ions
dissociate
The result is that the sodium and chloride ions ____ in water
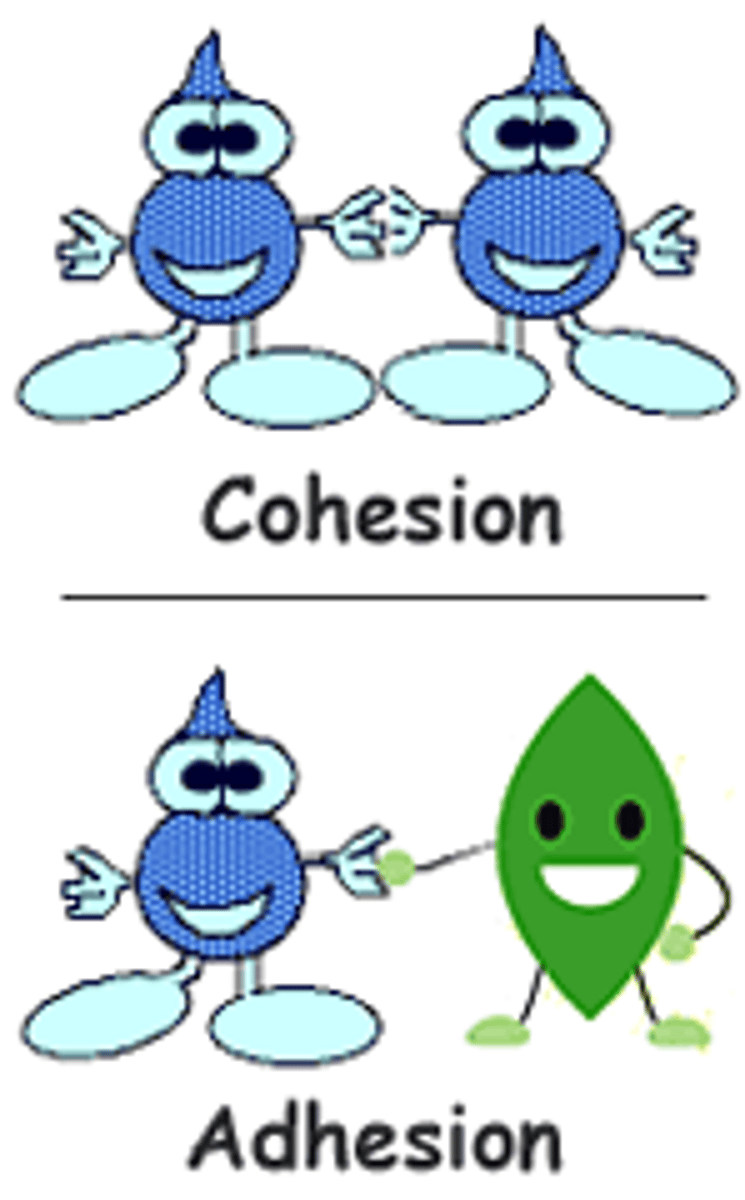
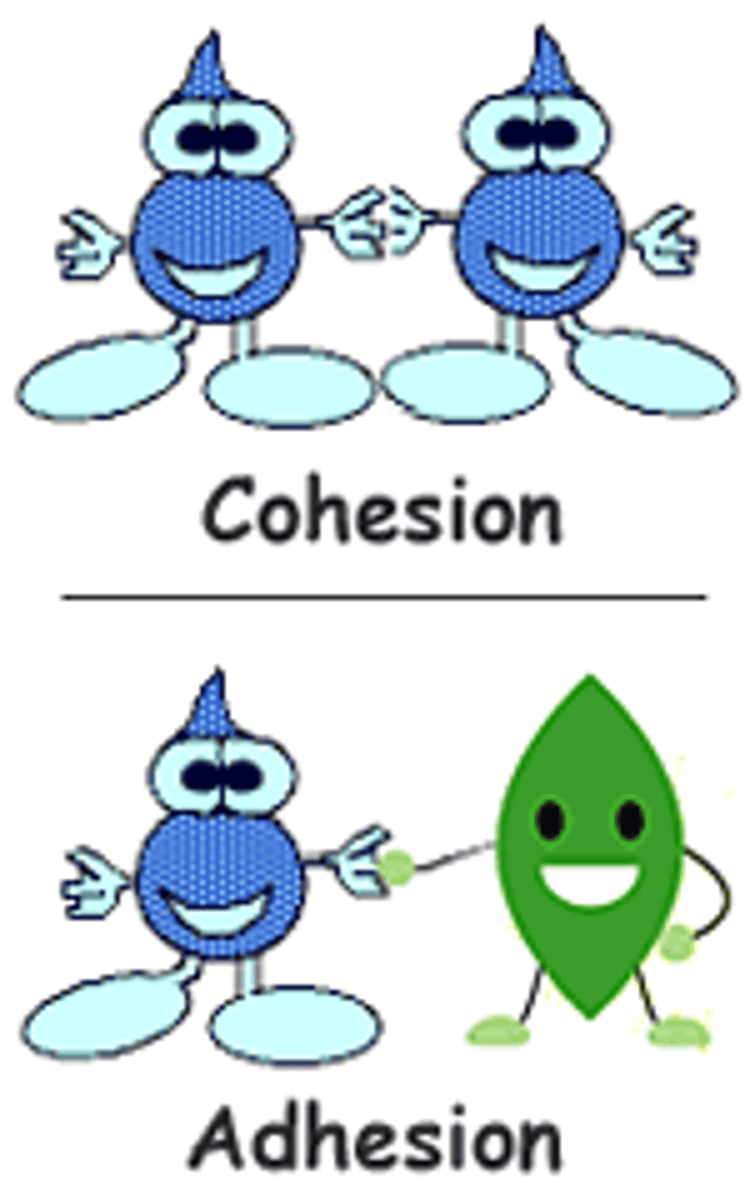
cohesion
the ability of water molecules to cling to each other is referred to as ____
hydrogen
The clinging ability is due to the fact that water molecules are held together by ____ bonds
transport
most organisms contain vessels that utilize the function of water in order to ____ nutrients and waste
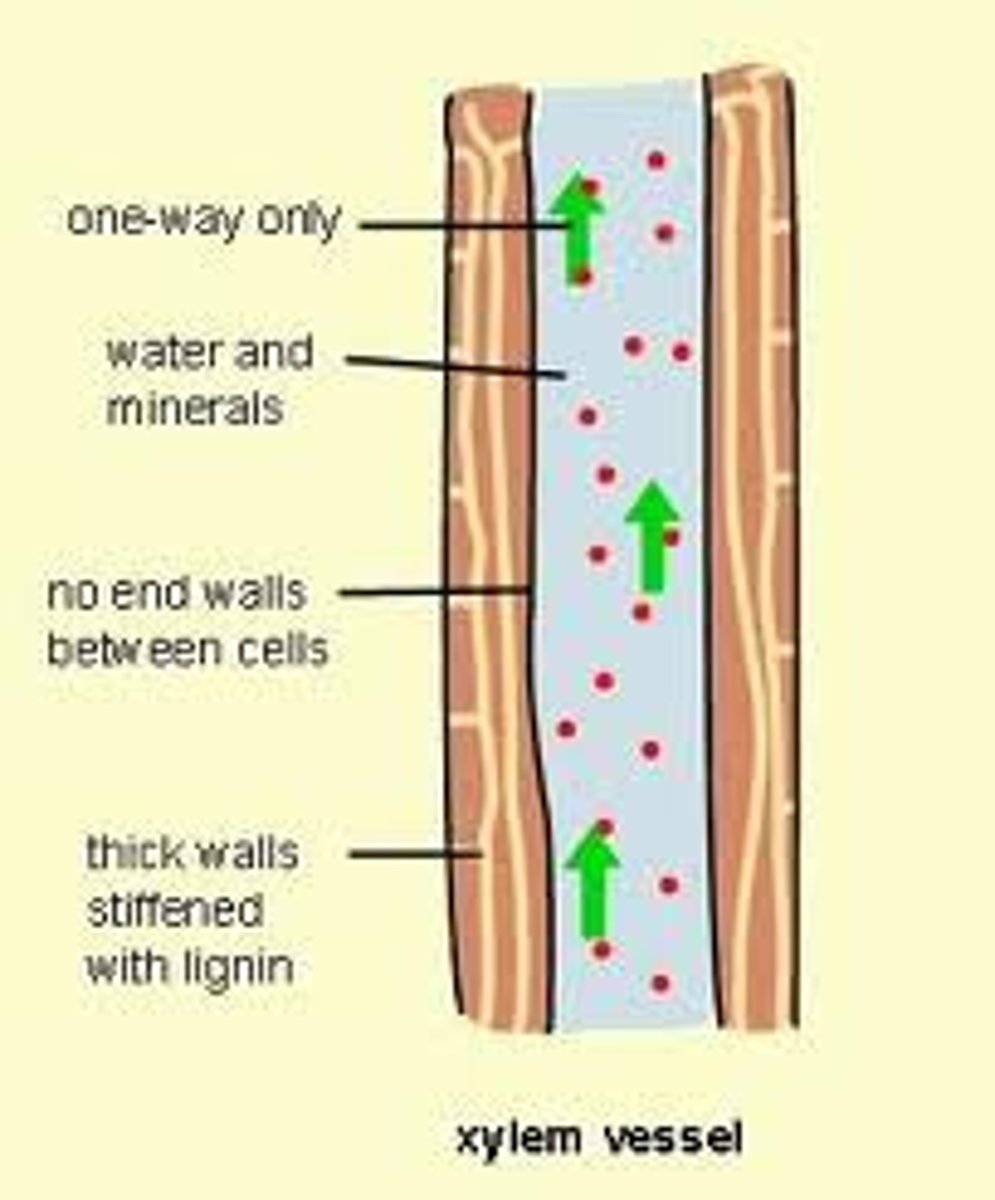
plants
in ____ vessels are used to help move the water through the roots to the leaves
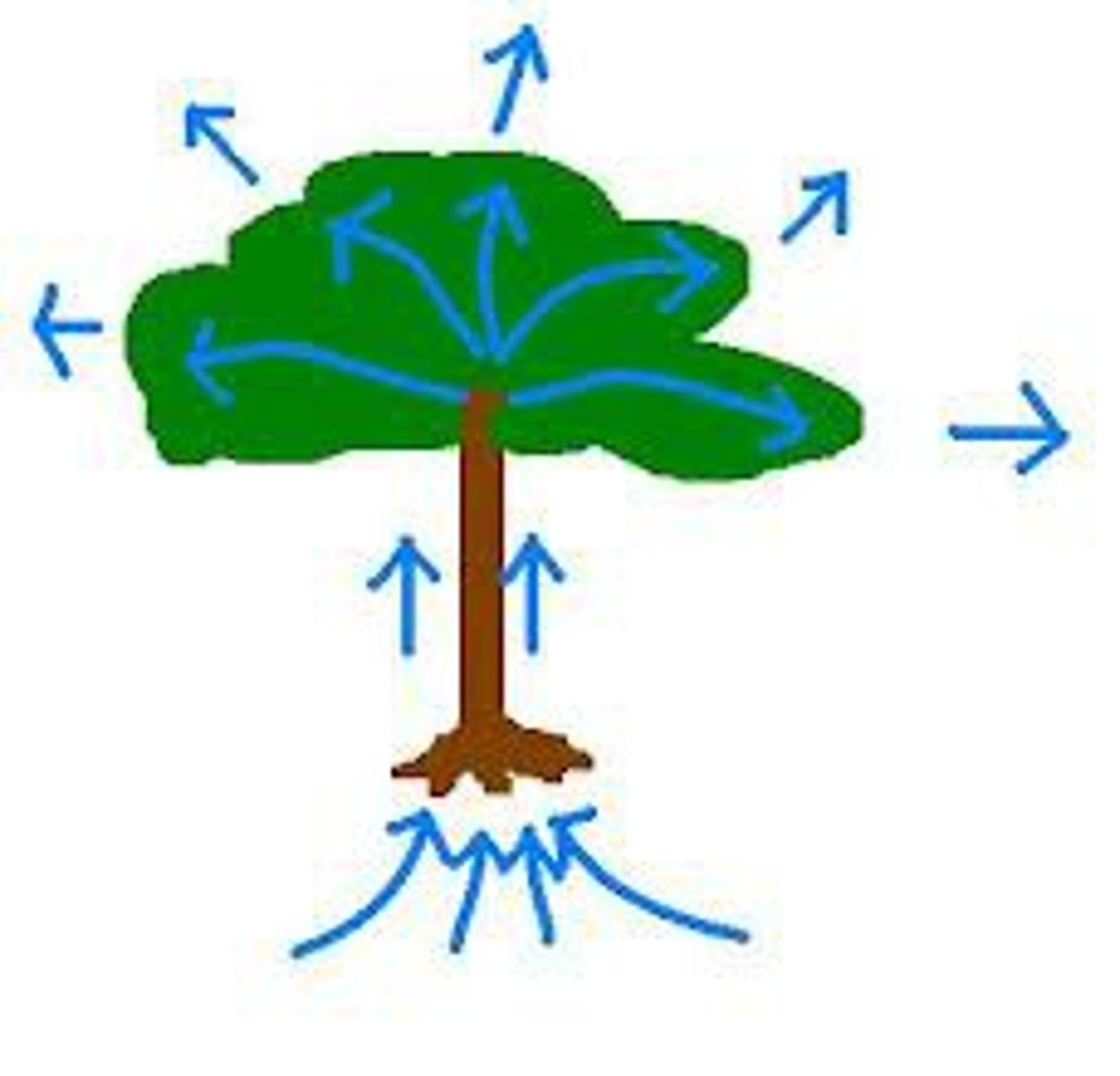
adhesion
when moving through the vessels in plants, ____ also keeps the water attached to the vessels for movement
water molecules are cohesive and adhesive (examples)
- plants absorb water from roots and transport it to the rest of the plant
- blood fills the narrow tubular vessels within the cardiovascular system
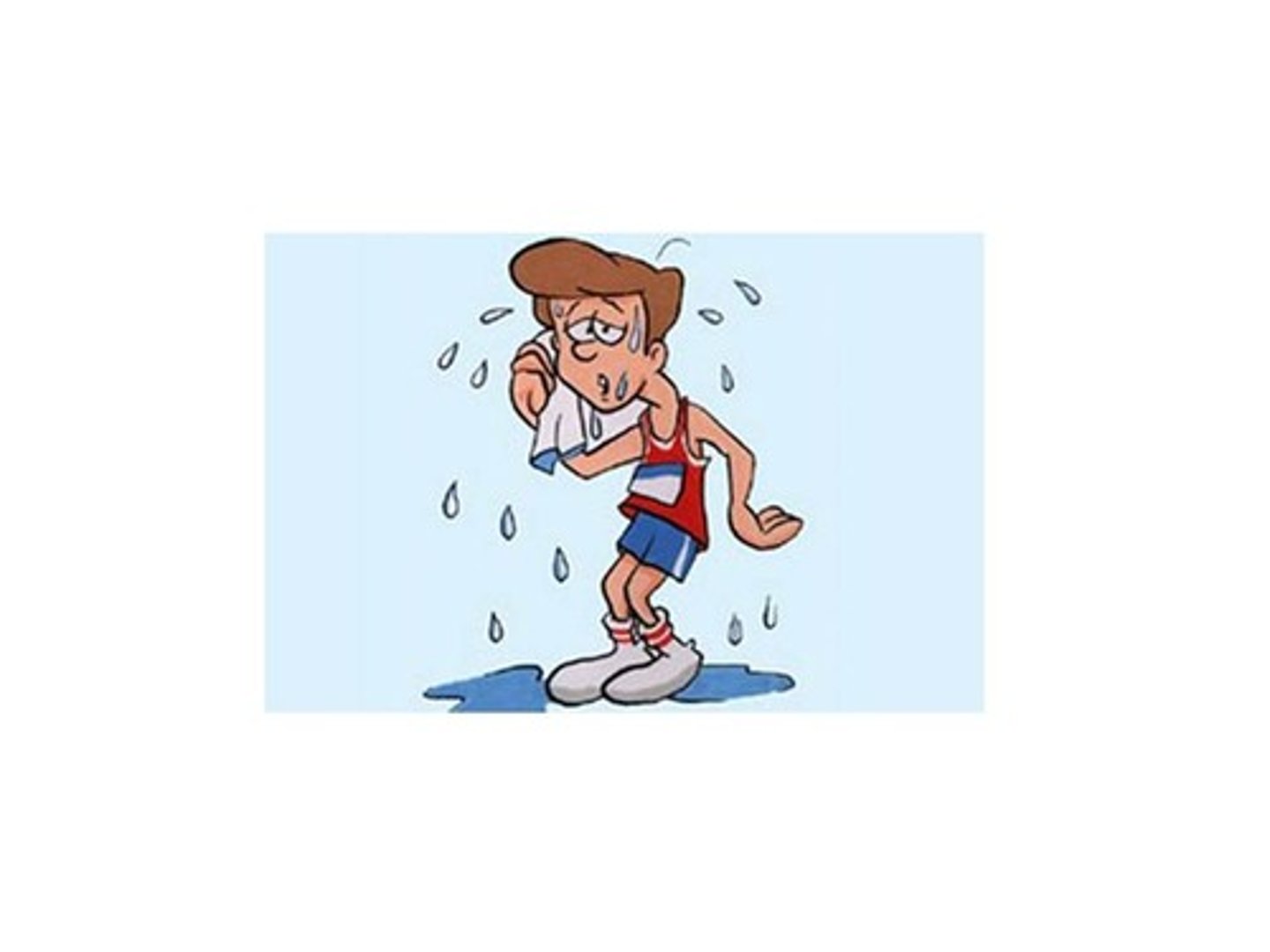
water has a high heat of evaporation (examples)
- when we sweat, it cools our bodies

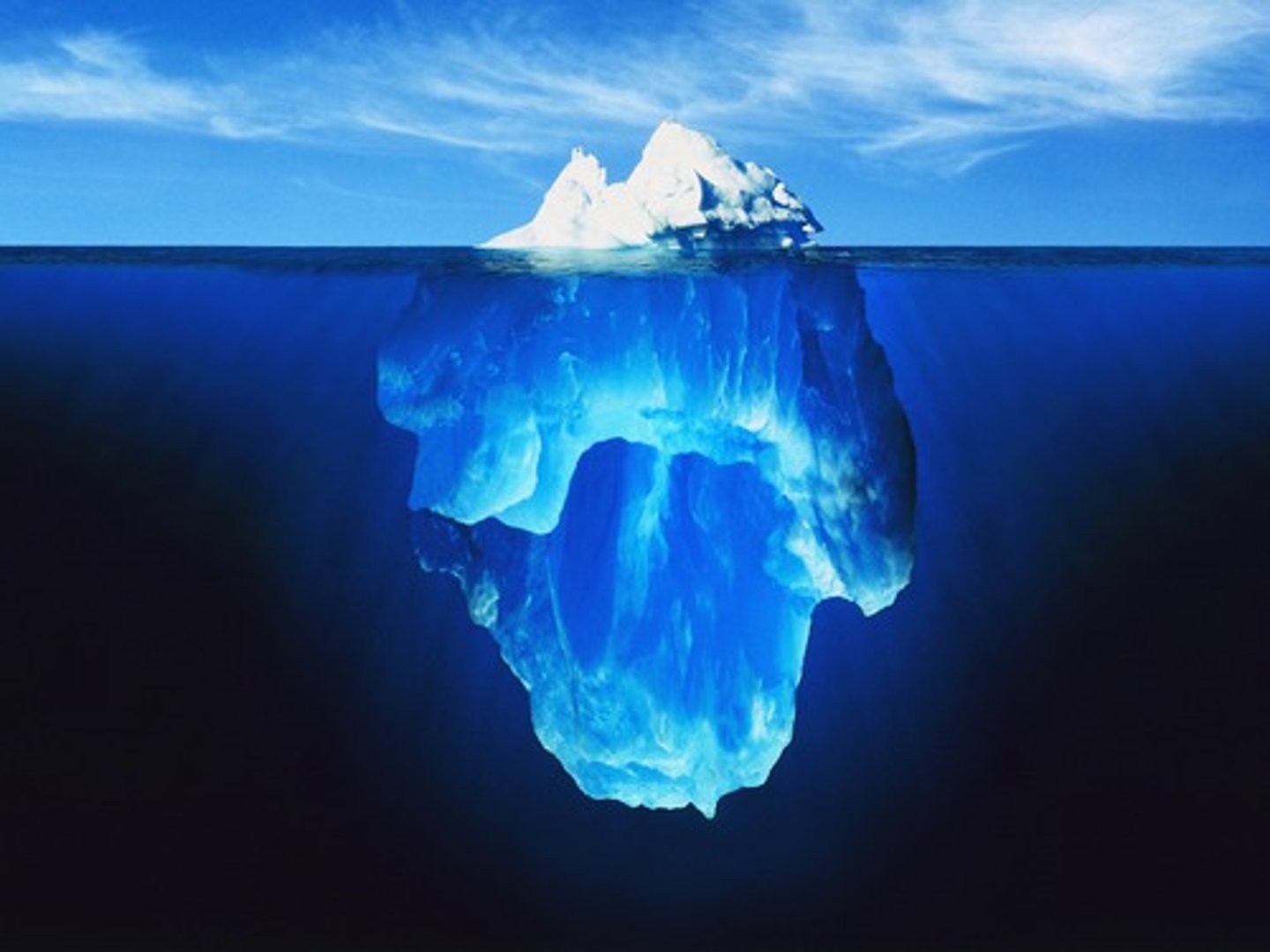
frozen water is less dense than liquid water (examples)
- aquatic organisms are insulated by upper layers of ice during cold winters
- the ocean doesn't freeze solid in the winter because the ice layers act to insulate the water below

water has a high heat capacity (examples)
- most organisms, especially those that are warm-blooded are able to maintain a constant body temp. even in colder weather
- a body of water tends to hold onto its heat such that waters temp. drops slowly
water is a good solvent (exmaple)
-the liquid portion of our blood is 90% water and transports vital dissolved substances
expands
most substances contract when they solidify but water ____

hydrogen bonds
this is because ____ in ice are permanent, holding the molecules further apart compared to liquid water
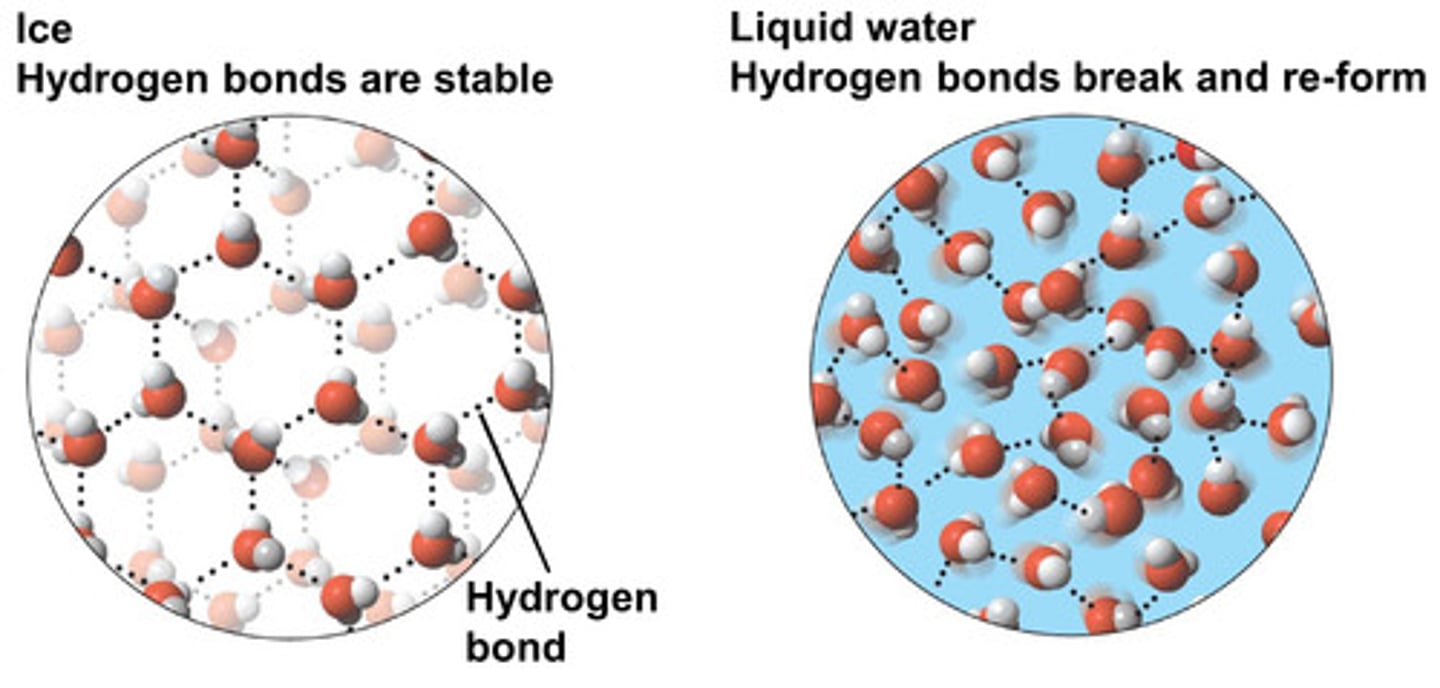
less
this makes ice ____ dense than water
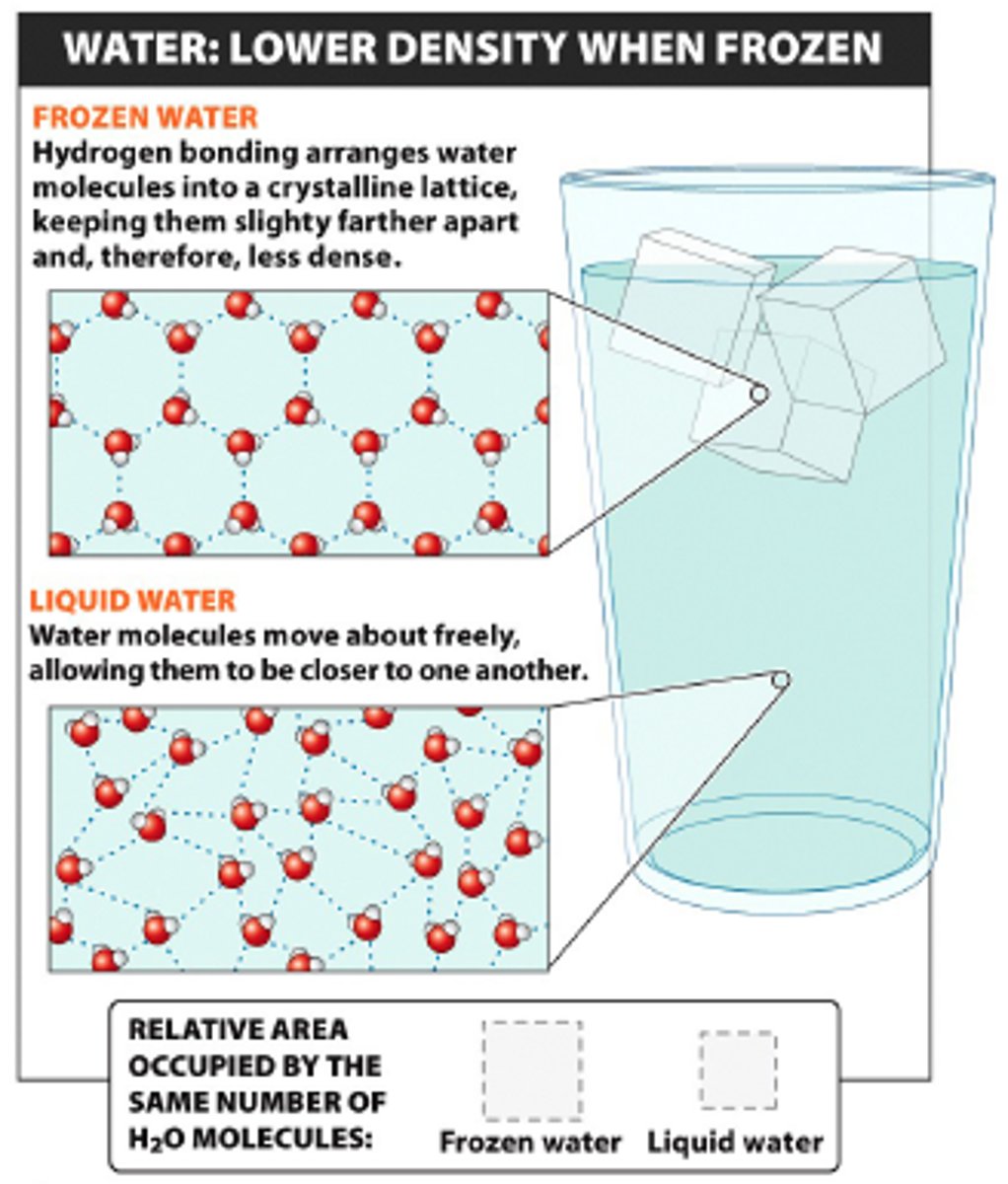
floats
its density is the reason that ice ____ in water
insulator
frozen ice at the surface of a body of water acts as an ____

liquid
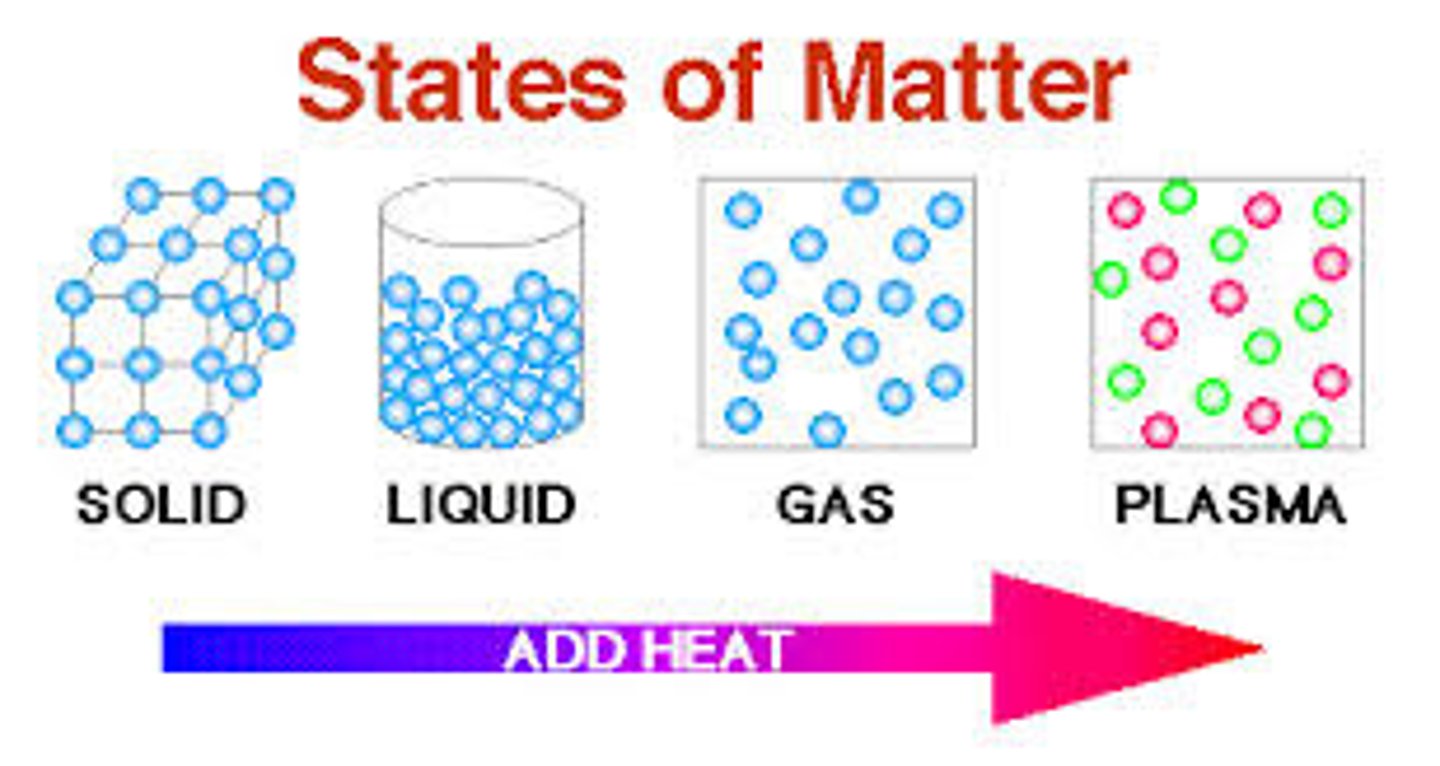
water can be a solid, liquid or gas at naturally occurring environmental temps. At room temp. water is a ____

solid, releases, higher
When water freezes it becomes a ____ (ice), it ____ heat, helping keep the environmental temps. ____ than expected

evaporates, absorbs, lowers
When water ____ to become a gas, it ____ large amounts of heat and ____ surrounding temps.

sweating
this explains why the process of ____ cools of the body

moderate
this is also why coastal areas experience ____ temps. in the winter and summer

acids
- increase H+
- HCl is an example of a "strong one"
- found in foods like lemon juice, vinegar and coffee
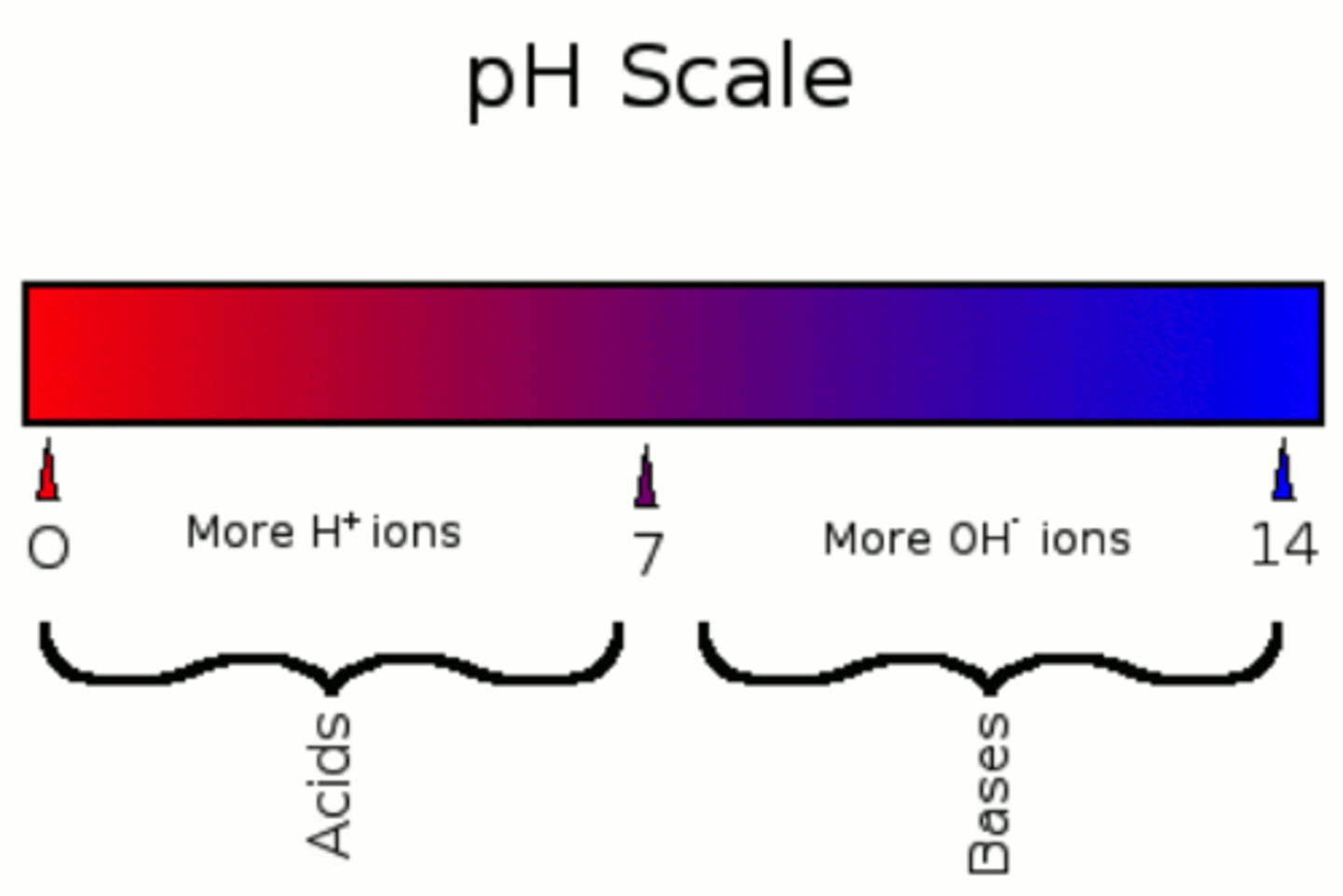
both (acid and base)
-strength can be measured by the pH scale
-disassociate in water
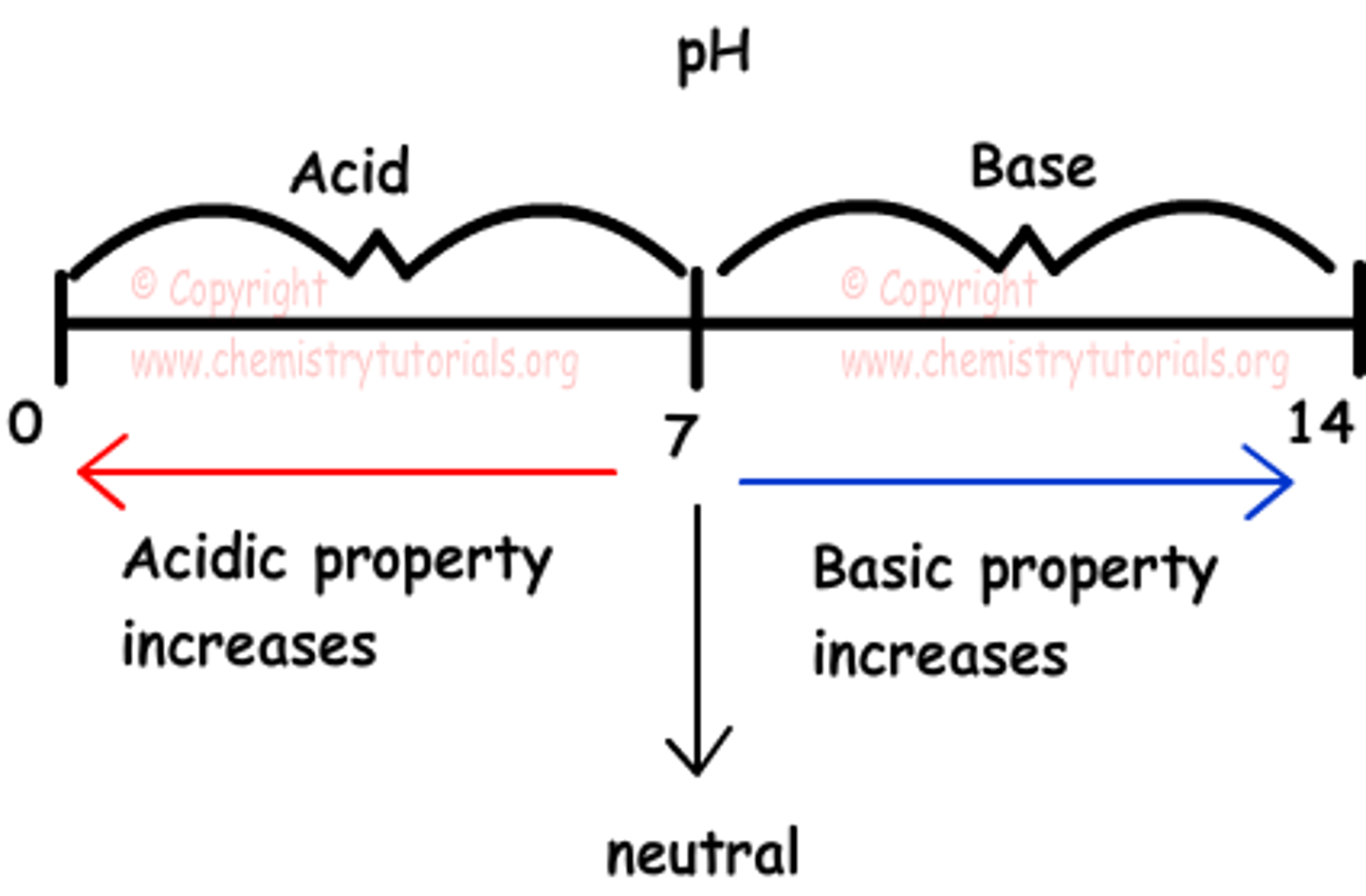
base
- increase OH-
-take up H+
-NaOH is an example of a "strong one"
-commonly associated with milk of magnesia or bicarbonate soda, which decrease stomach acid.
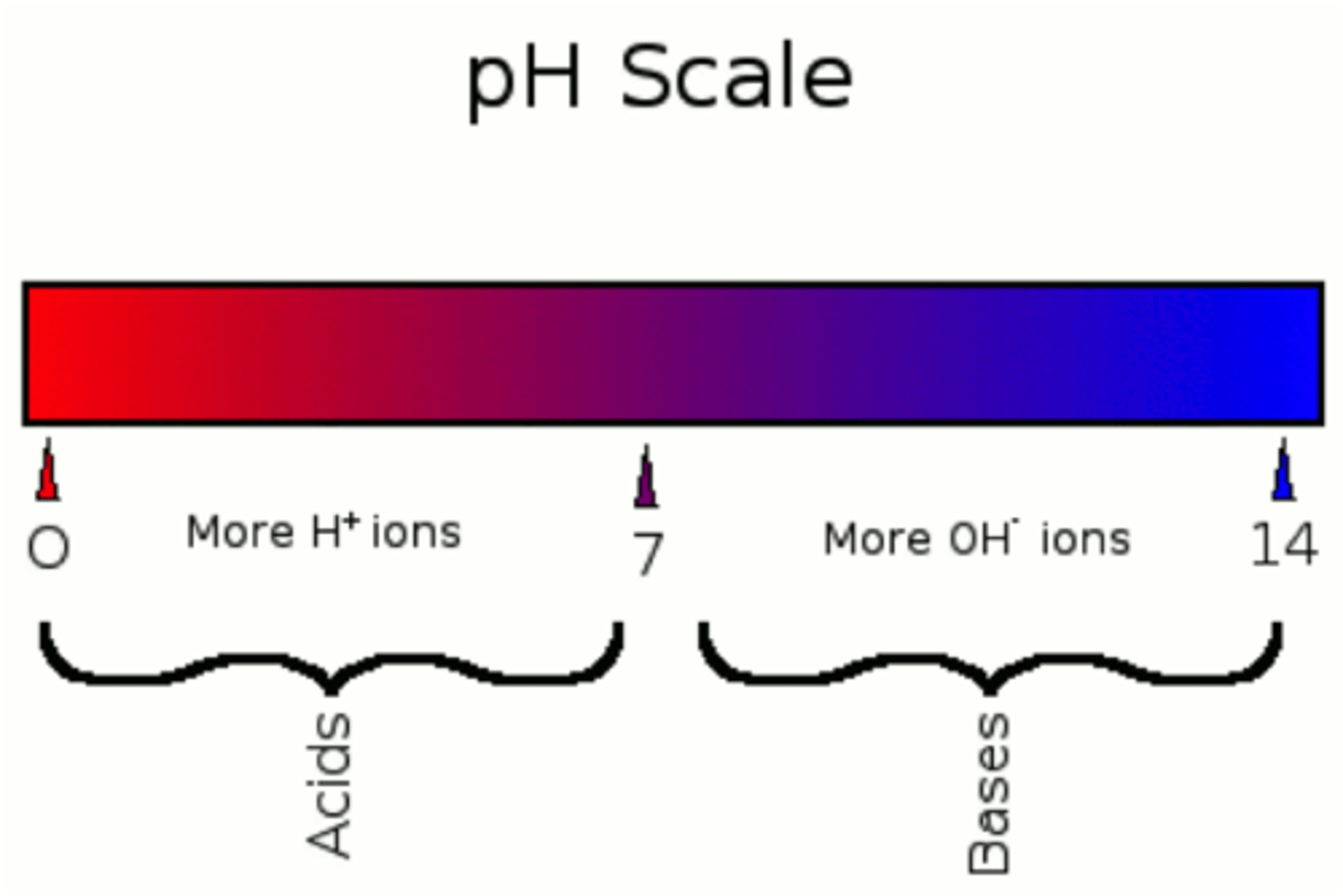
acid (def)
A substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution.

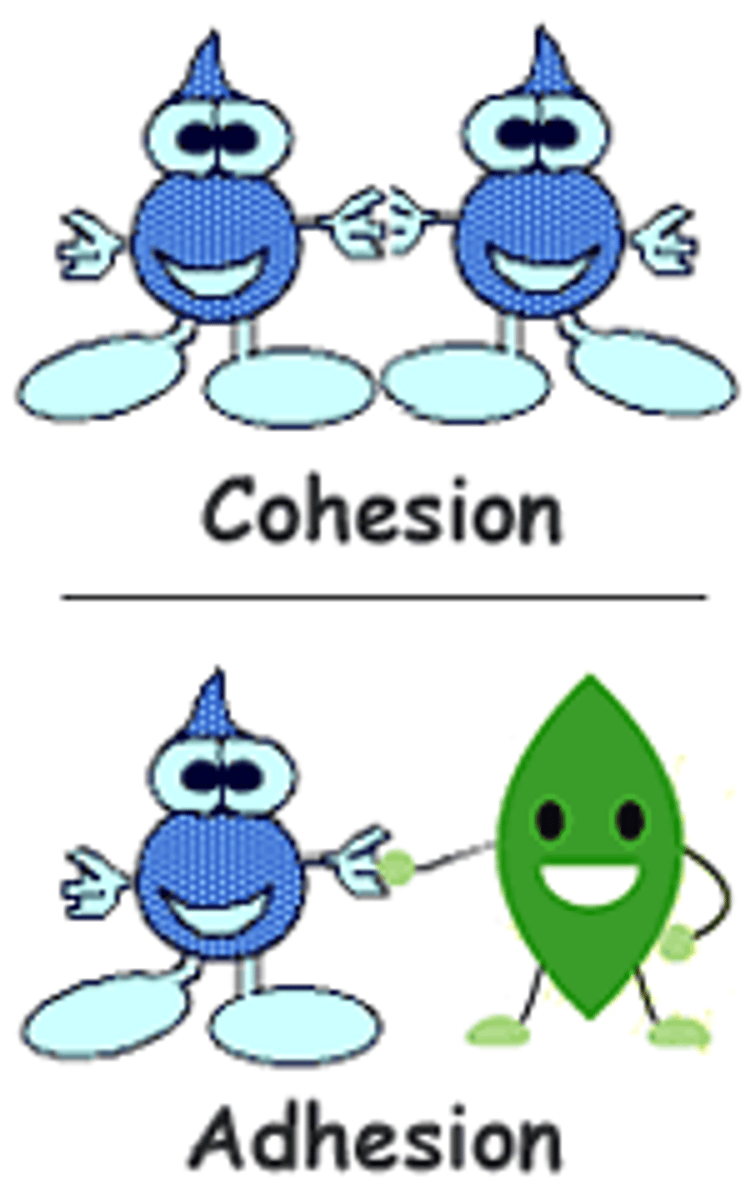
adhesion (def)
the attraction between different kinds of molecules
aqueous solution
a solution in which water is the solvent

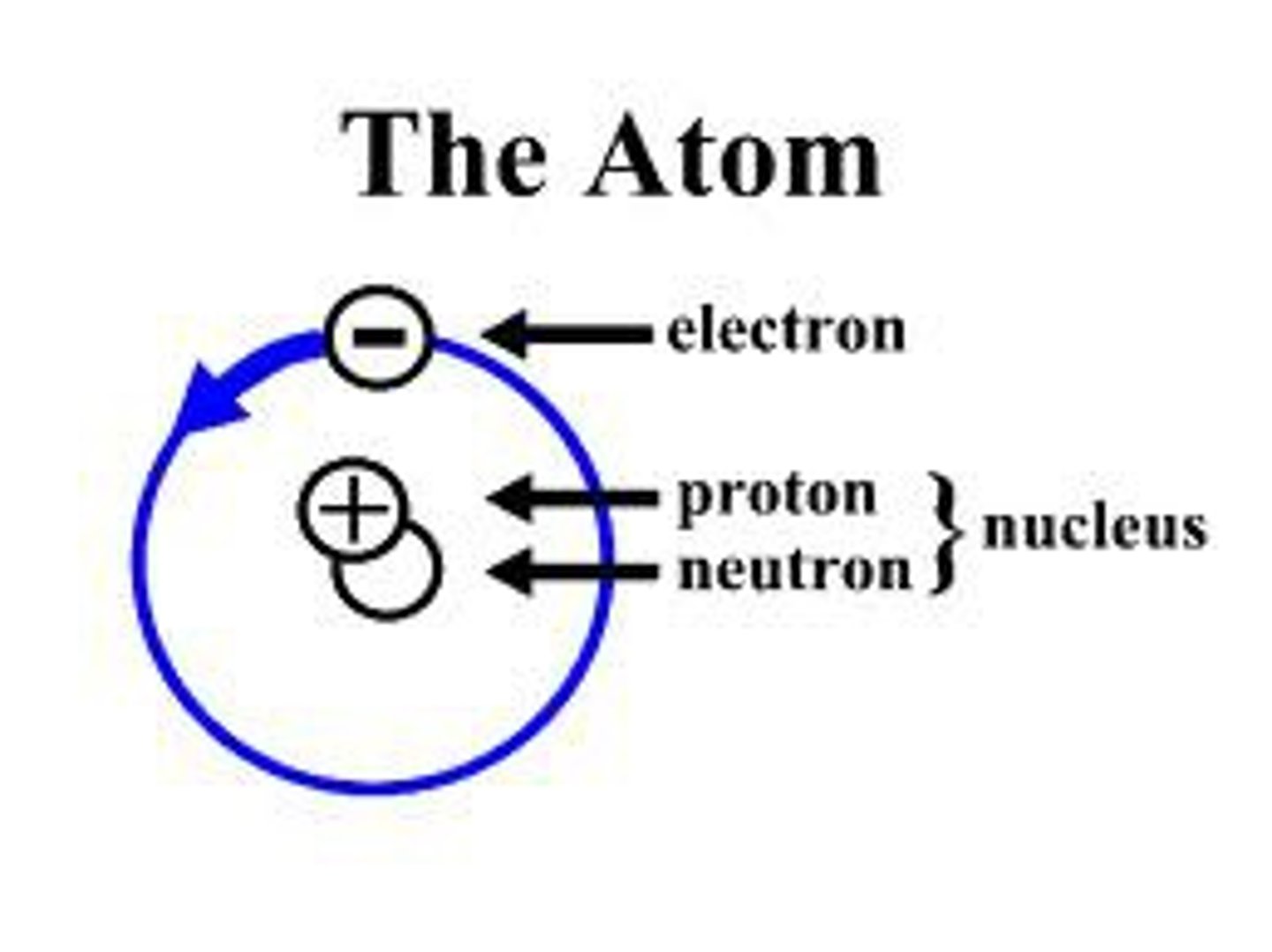
atom
the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element
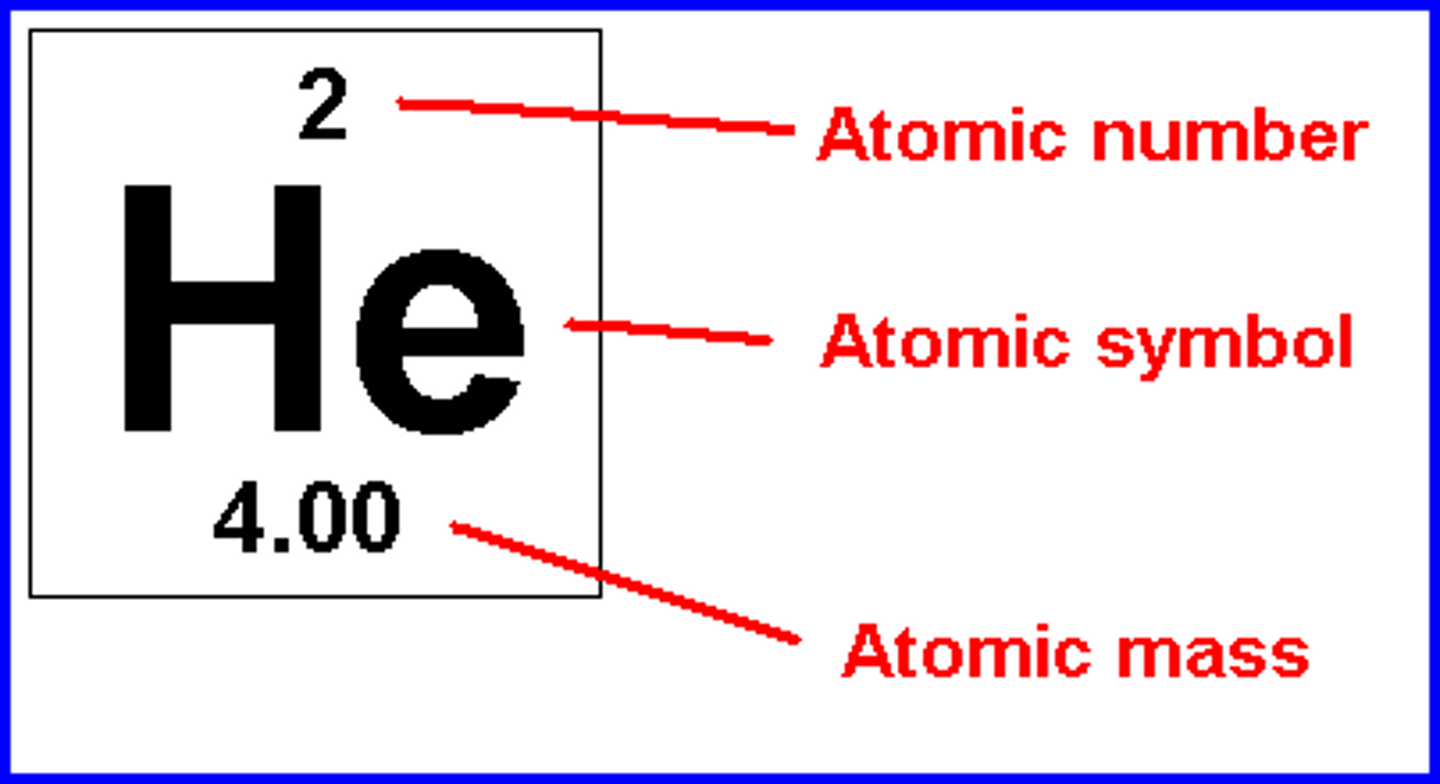
atomic mass
the total mass of an atom, also called atomic weight. Given as a whole number, the atomic mass approx. equals the mass number
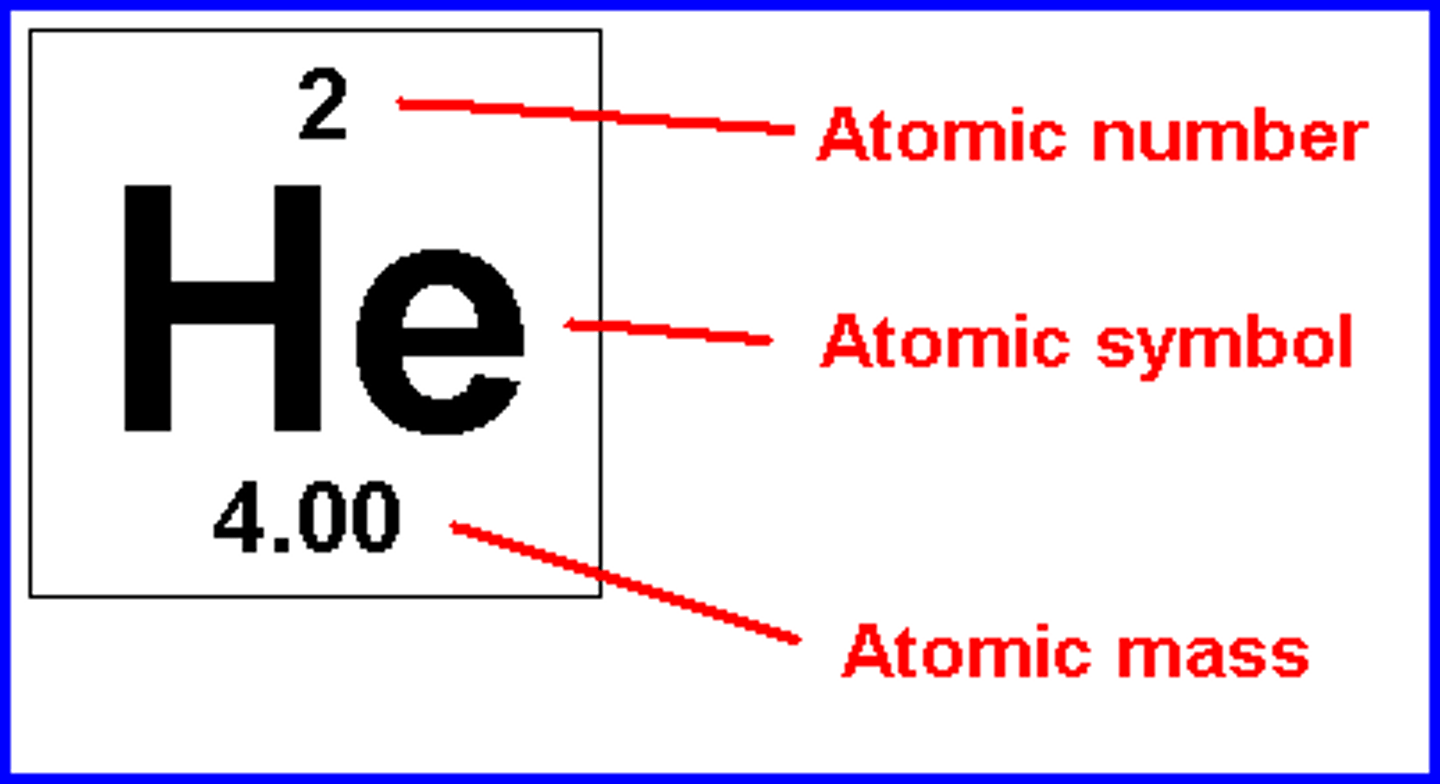
atomic number
the number of protons in each atom of a particular element
base (def)
A substance that decreases the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution.

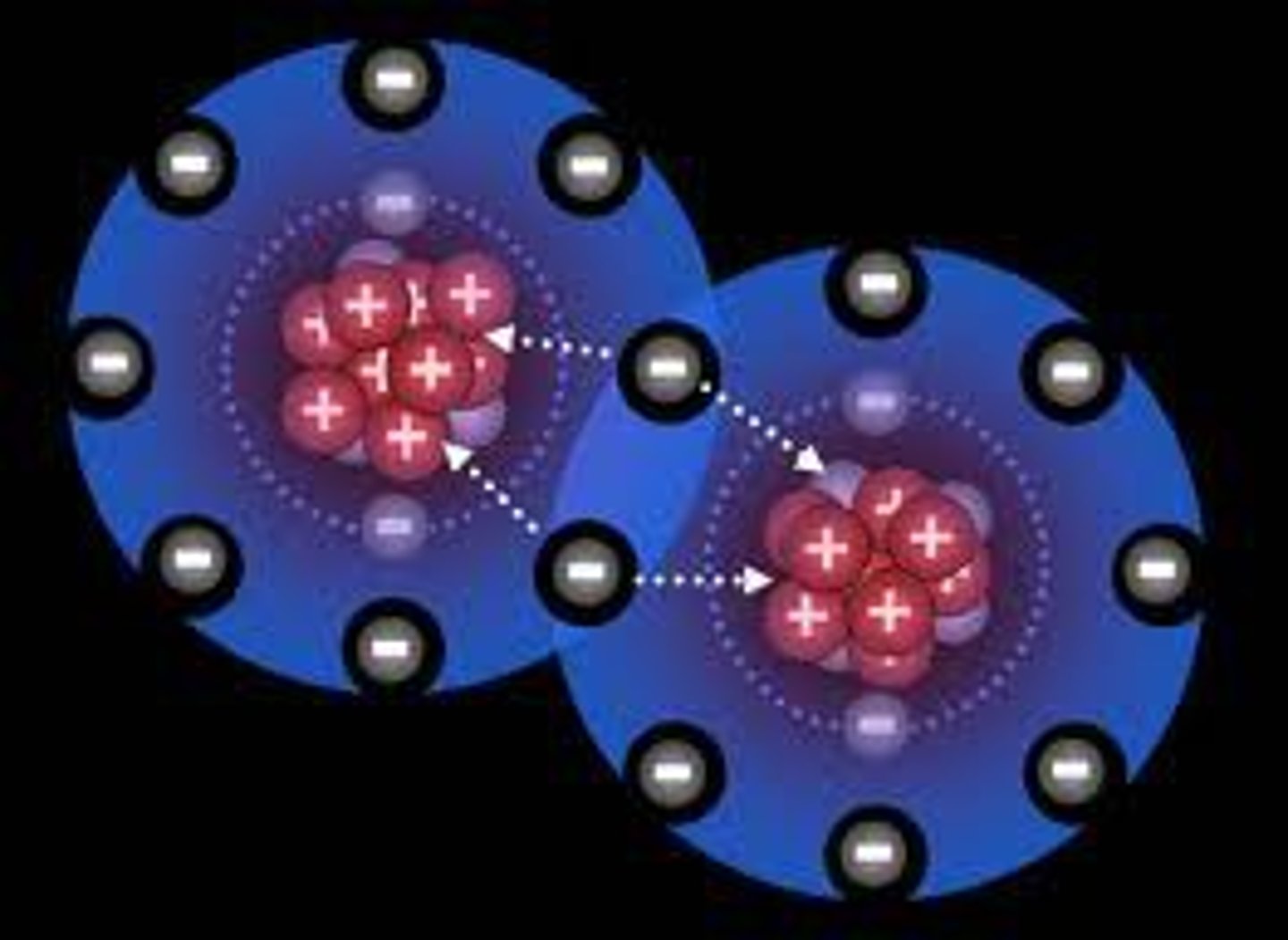
chemical bond
An attraction between two atoms resulting from a sharing of outer-shell electrons or the presence of opposite charges on the atoms. The bonded atoms gain complete outer electron shells.
chemical reaction
the making and breaking of chemical bonds, leading to changes in the composition of matter
cohesion
the sticking together of molecules of the same kind, often by hydrogen bonds
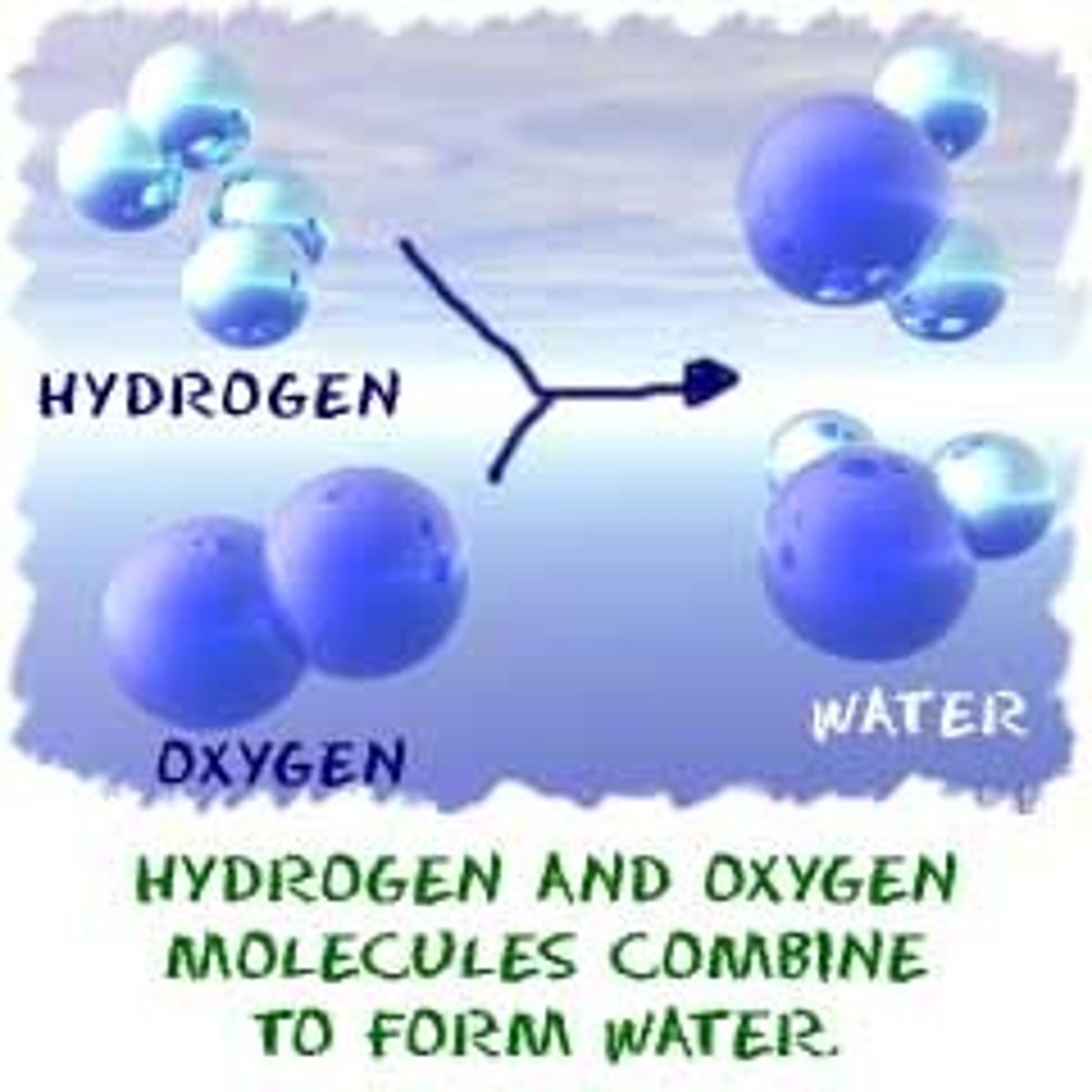
compound
a substance containing 2 or more elements in a fixed ration. Examples- table salt (NaCl) consists of one atom of the element (Na) for every atom of chlorine (Cl)
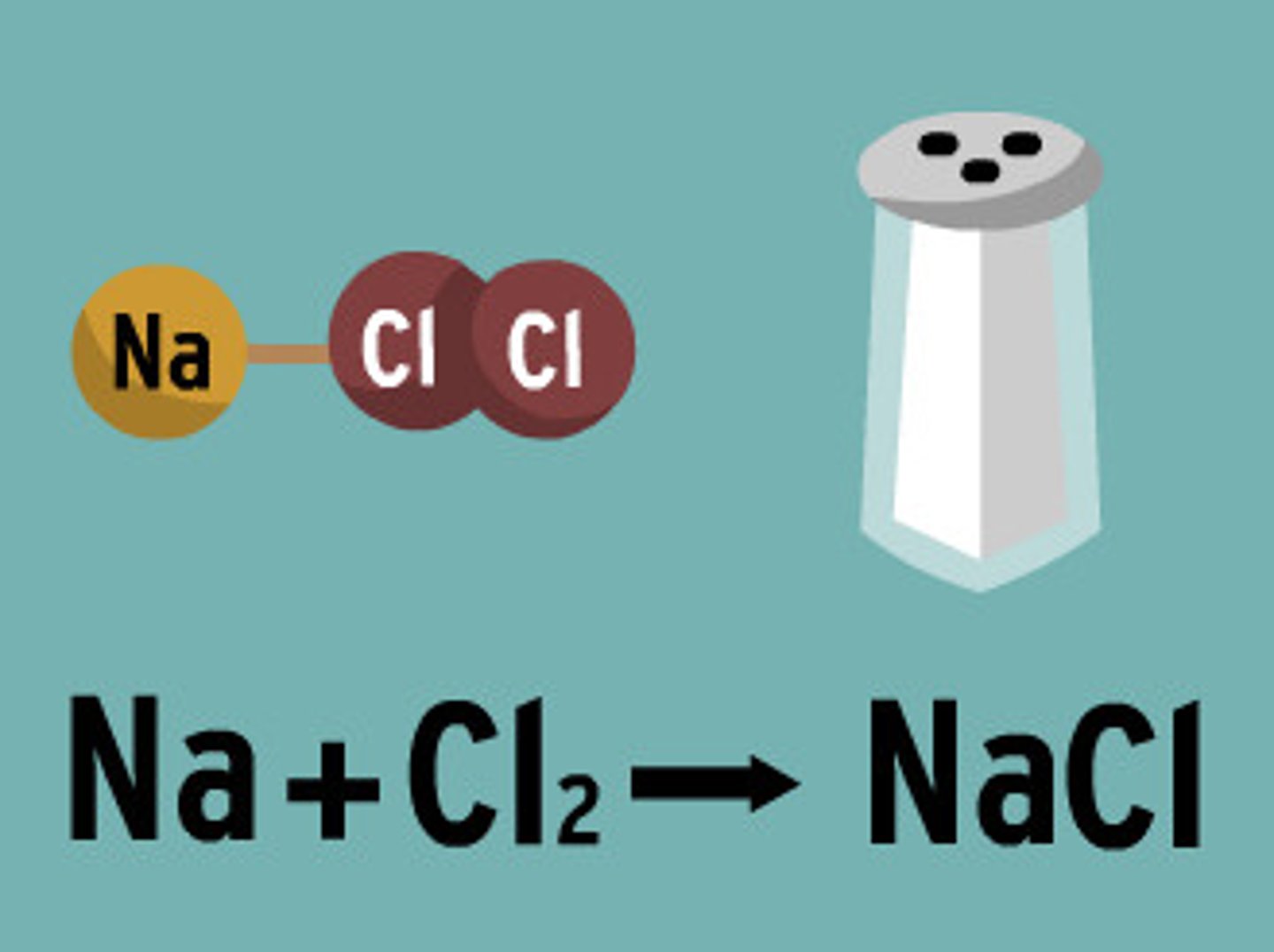
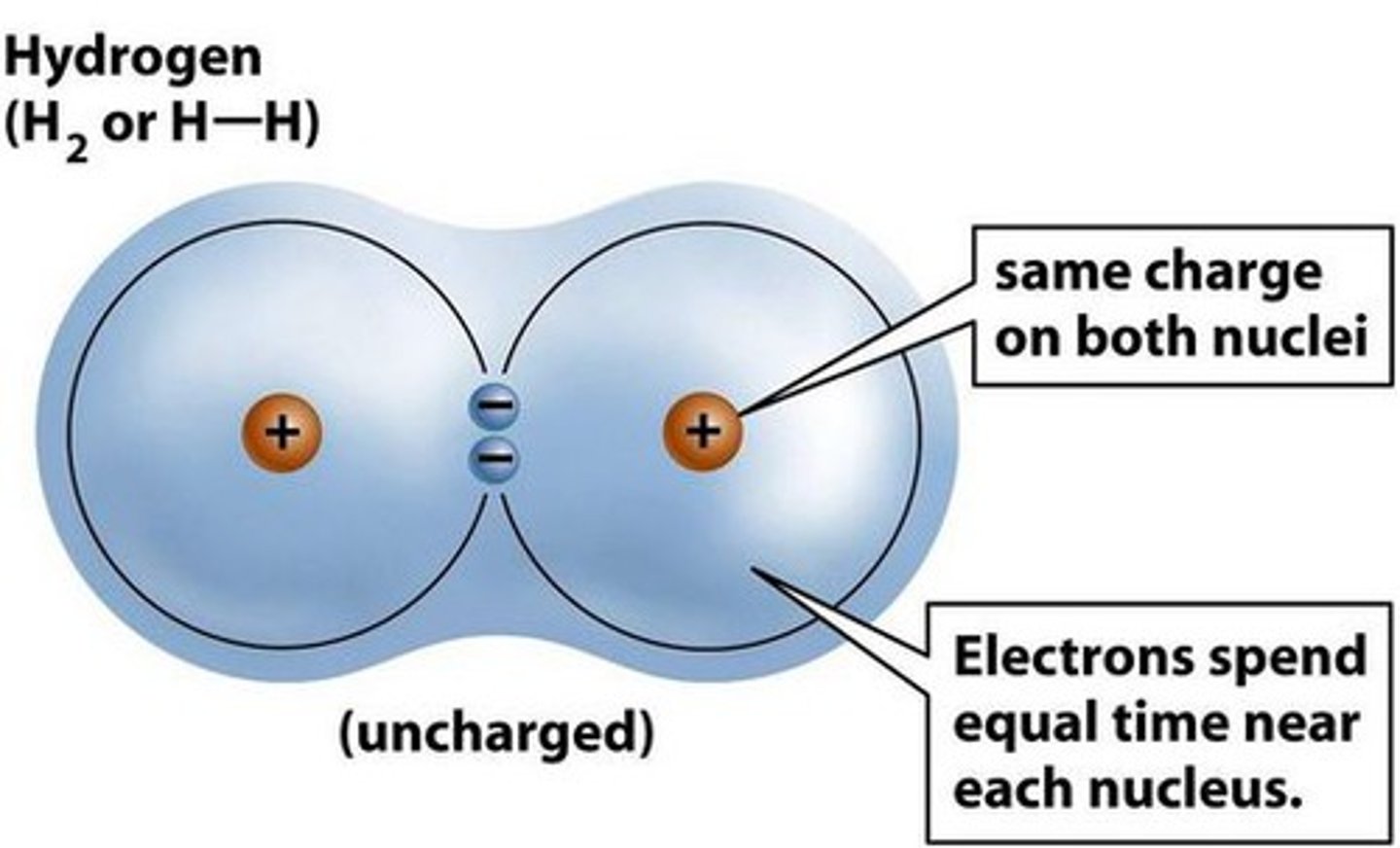
covalent bond
A type of strong chemical bond in which two atoms share one or more pairs of valence electrons.
electron (def)
a subatomic particle with a single negative electrical charge. One or more electrons move around the nucleus of an atom
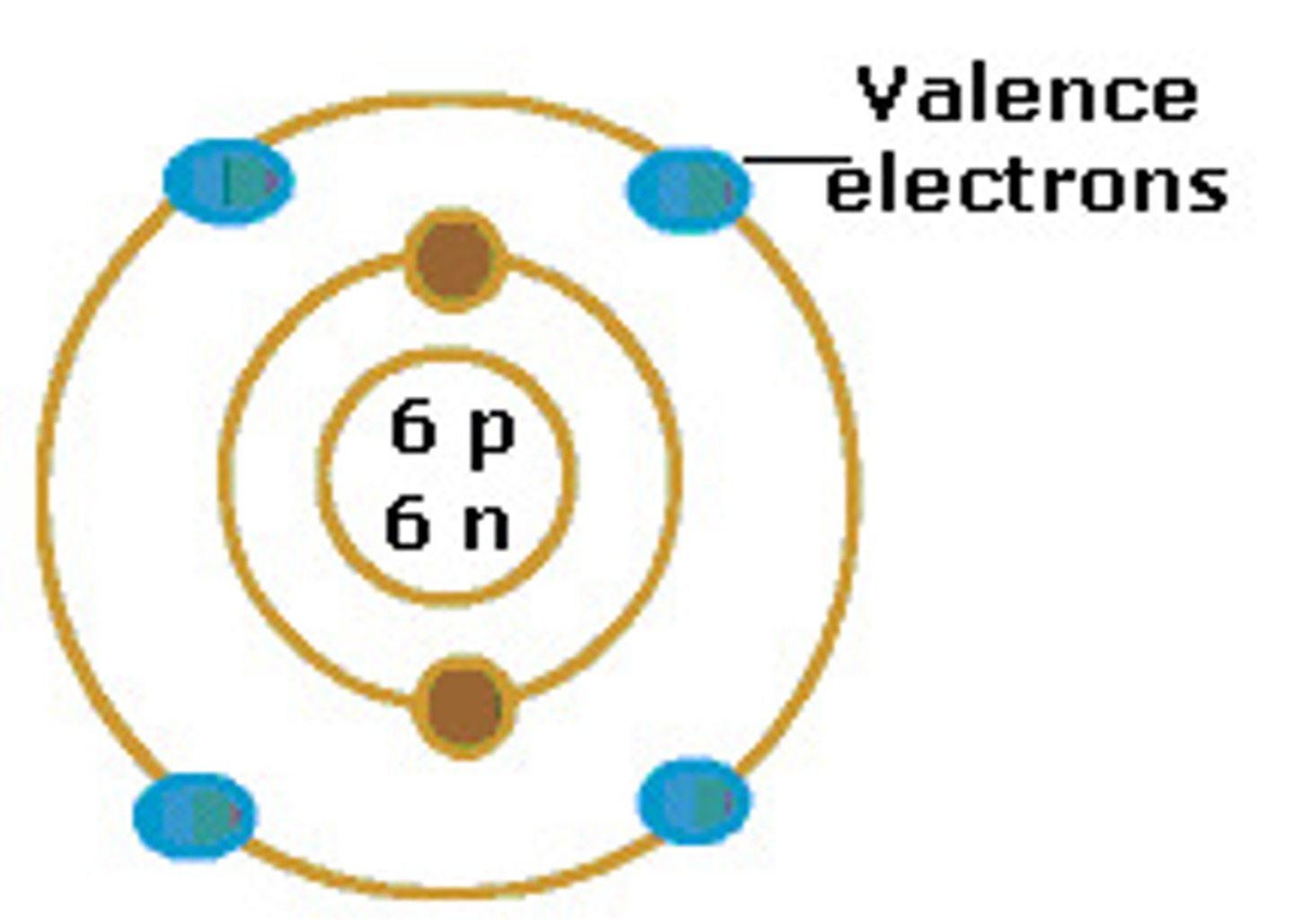
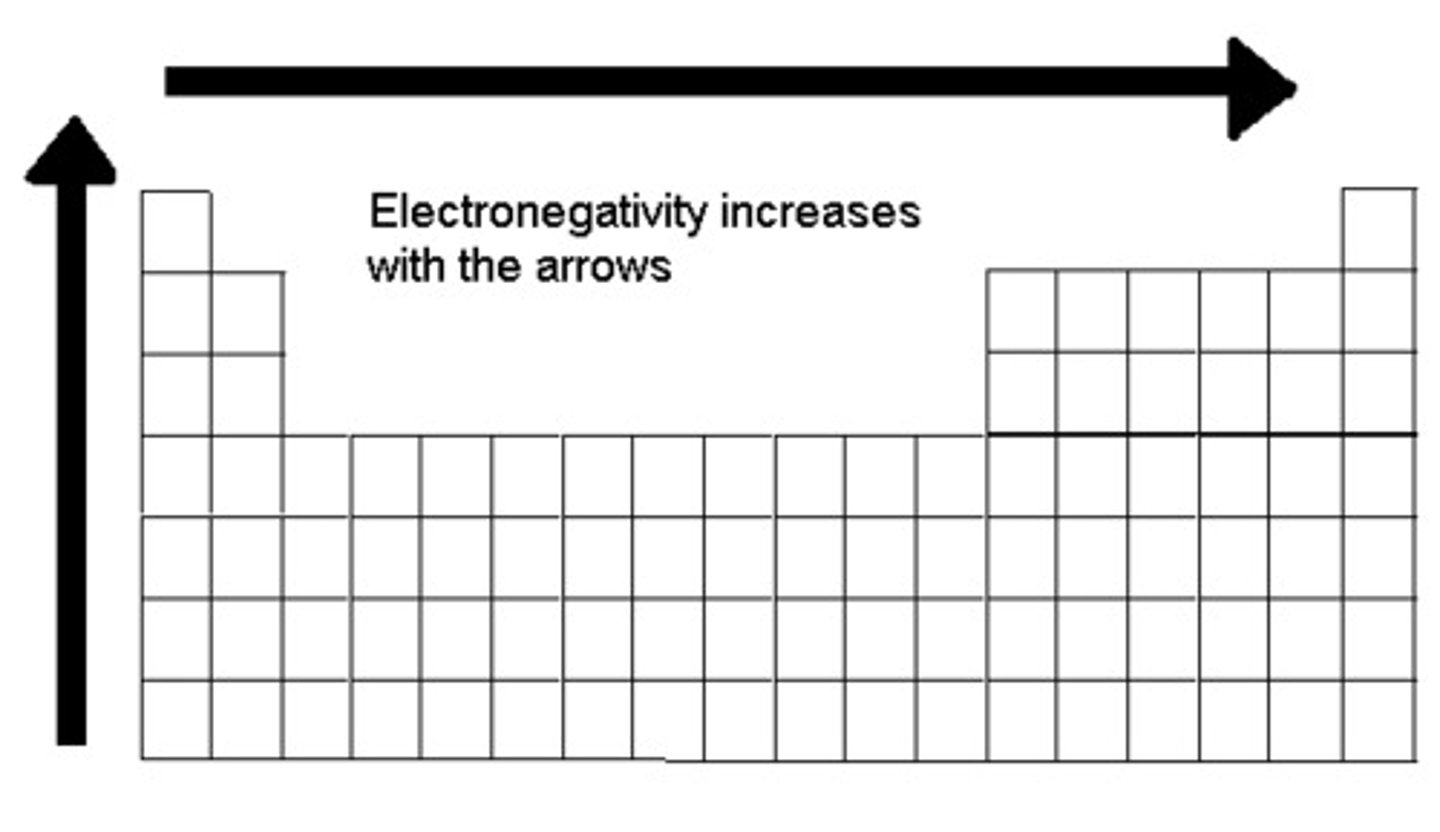
electronegativity
The attraction of a given atom for the electrons of a covalent bond.
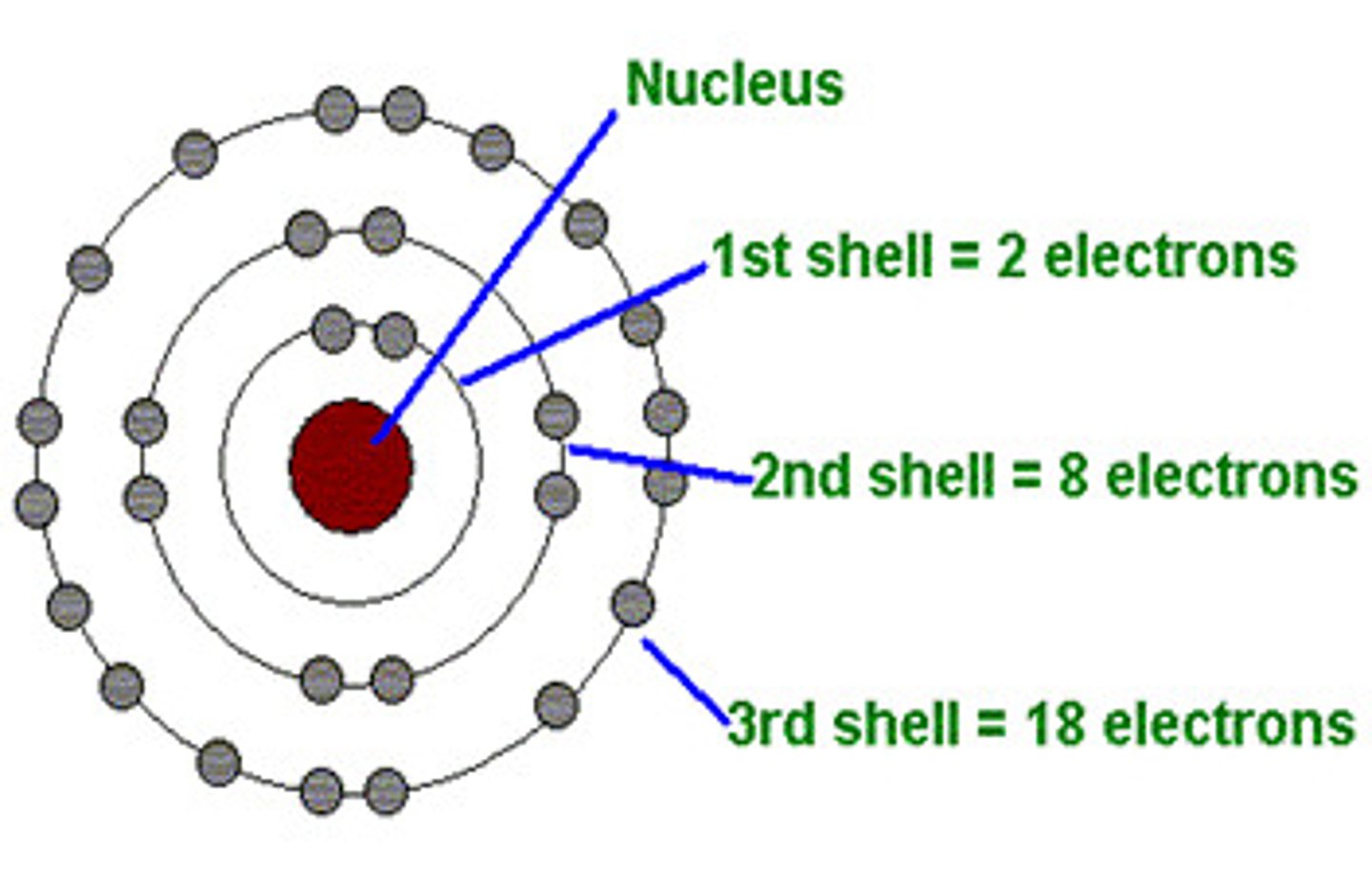
electron shell
a level of electrons at a characteristic average distance from the nucleus of an atom
element
a substance that cannot be separated or broken down into simpler substances by chemical means
evaporative cooling
The process in which the surface of an object becomes cooler during evaporation, a result of the molecules with the greatest kinetic energy changing from the liquid to the gaseous state.

heat
thermal energy in transfer from one body of matter to another

hydrogen bond
A type of weak chemical bond formed when the slightly positive hydrogen atom of a polar covalent bond in one molecule is attracted to the slightly negative atom of a polar covalent bond in another molecule.
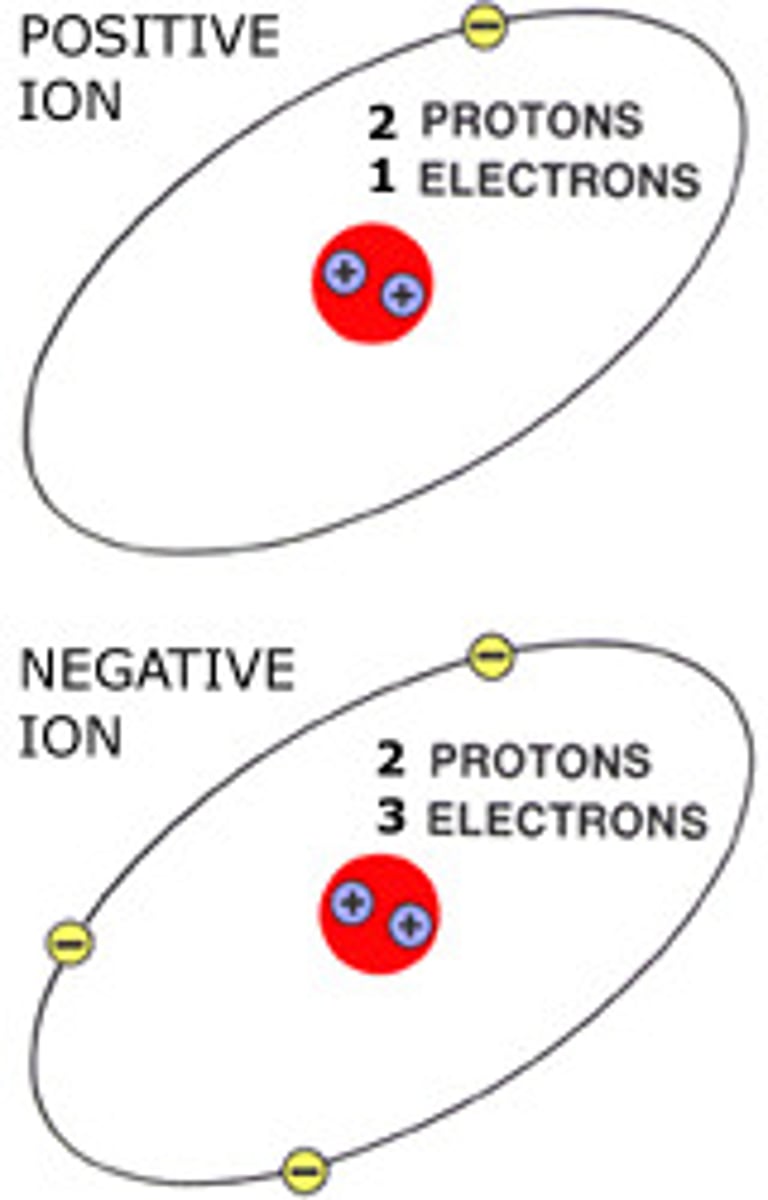
ion
An atom or group of atoms that has gained or lost one or more electrons, thus acquiring a charge.
ionic bond
A chemical bond resulting from the attraction between oppositely charged ions.
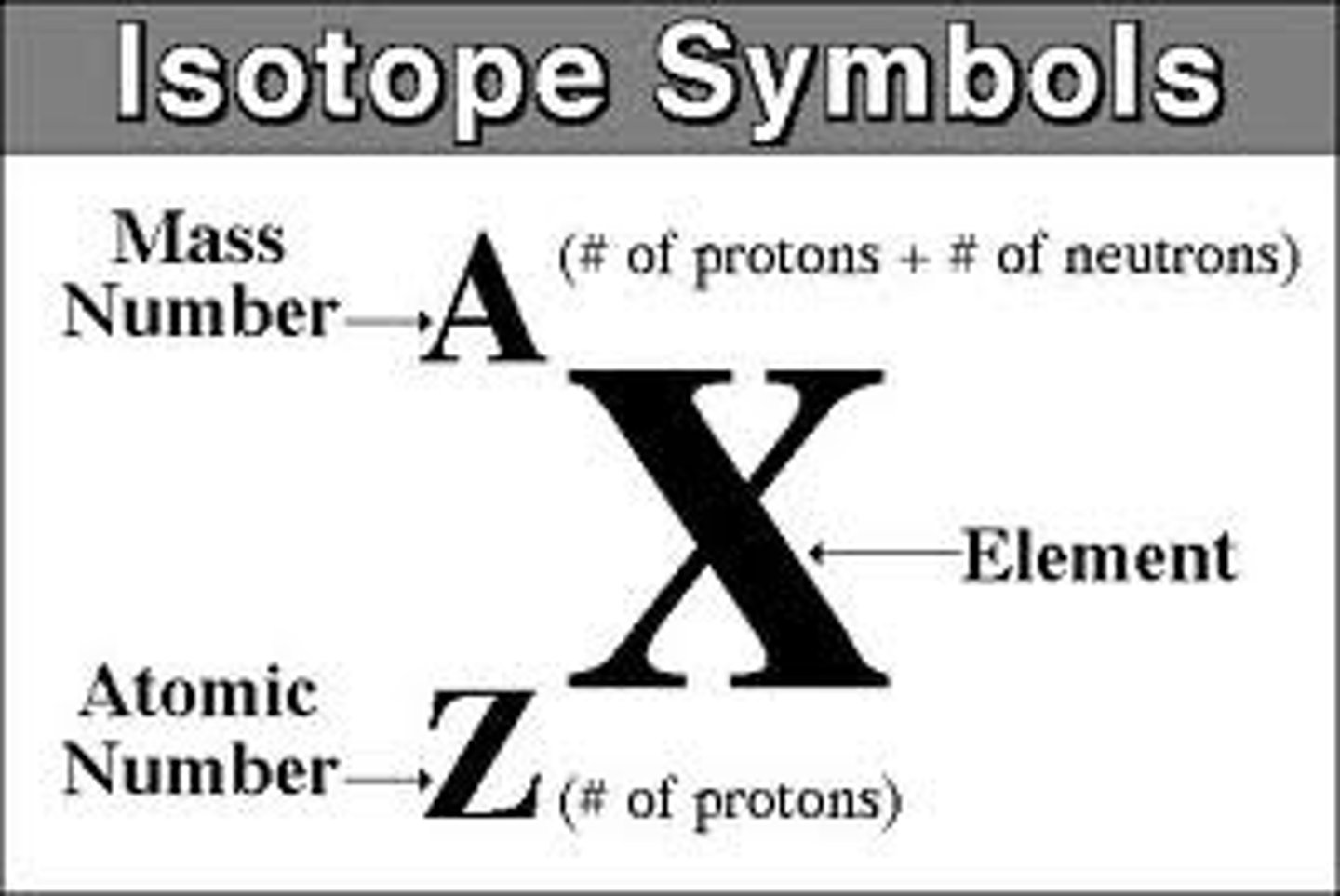
isotope
One of several atomic forms of an element, each with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons
mass number
the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom

matter
anything that occupies space and has mass
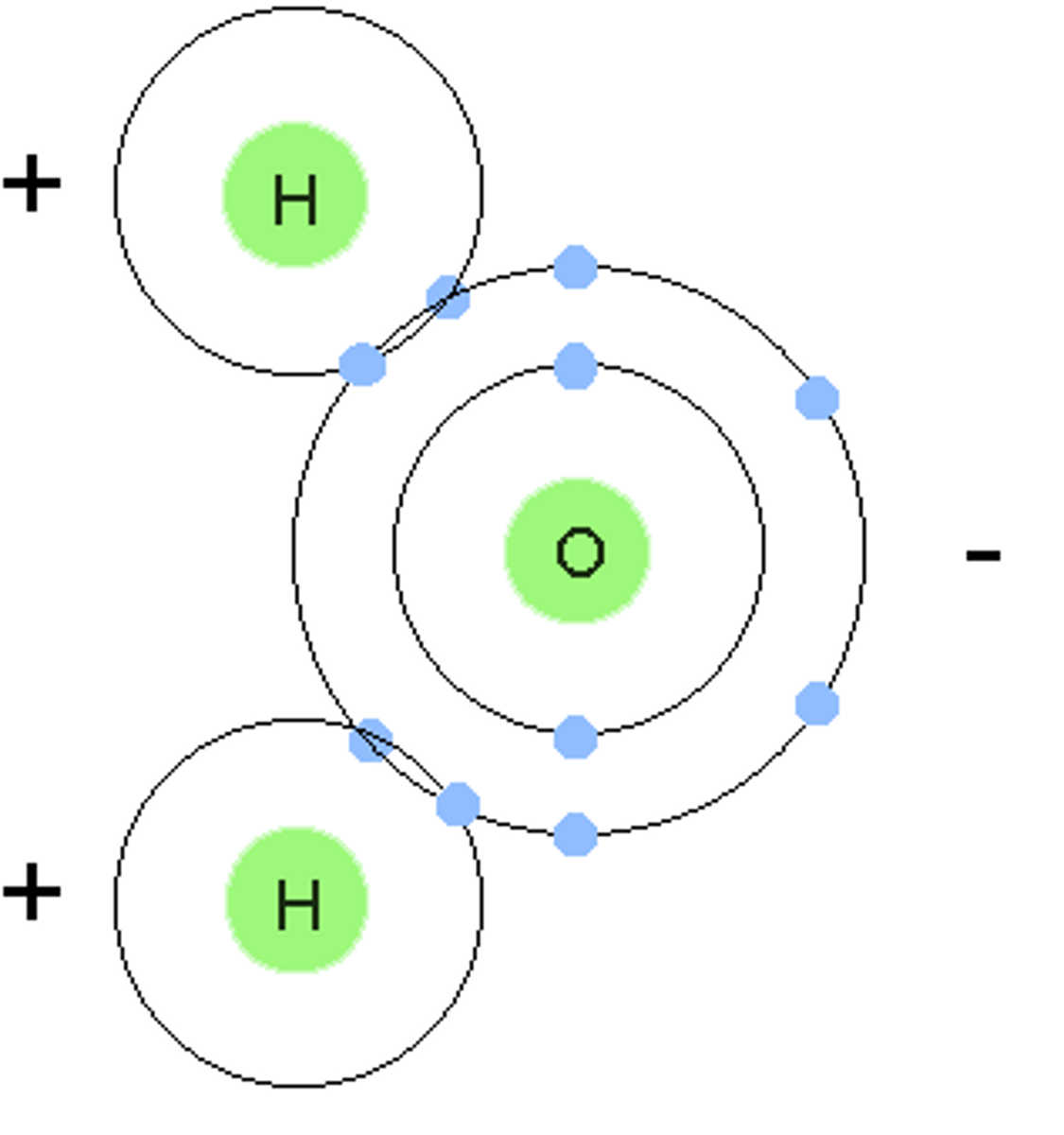
molecule
2 or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
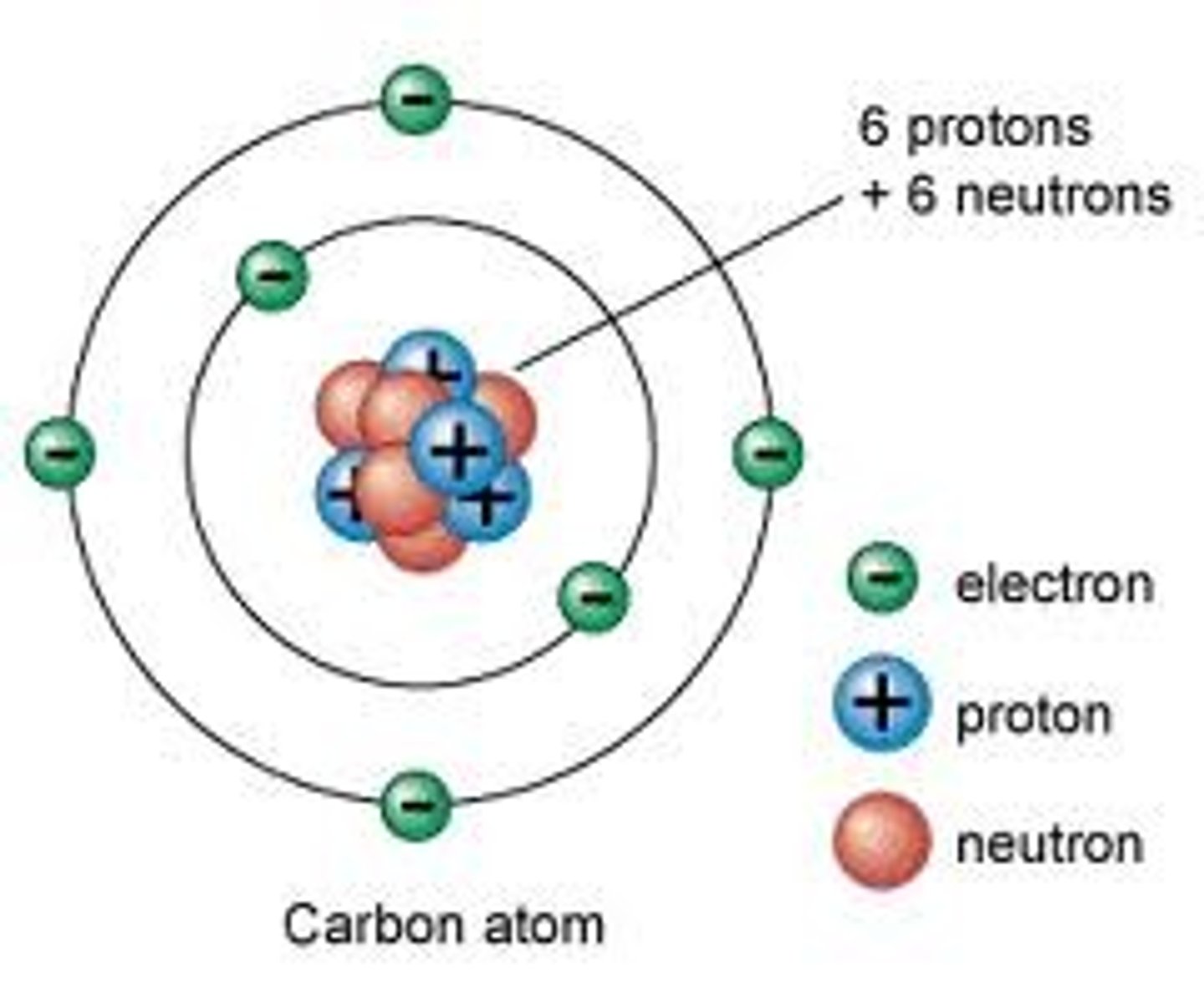
neutron (def)
A subatomic particle that has no charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
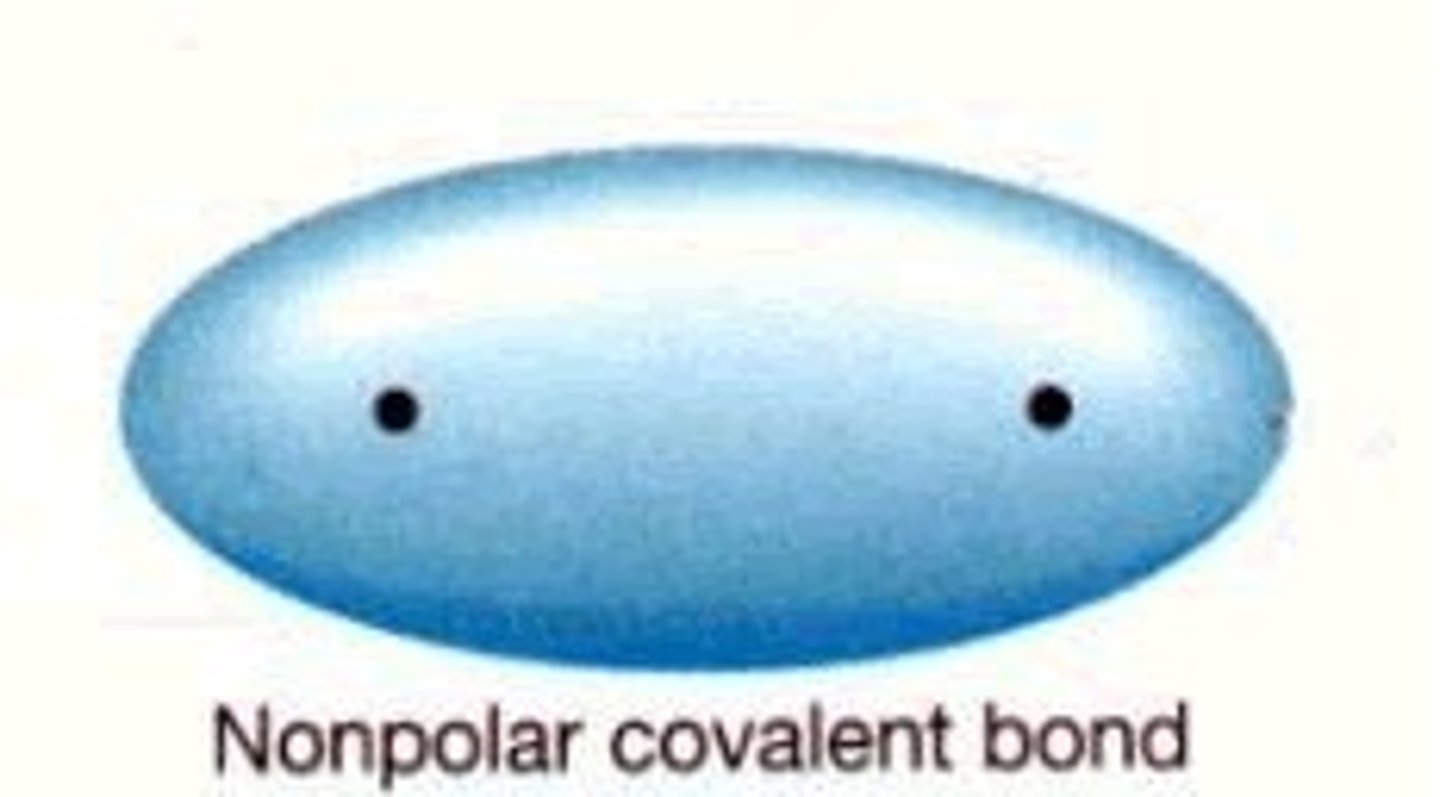
nonpolar covalent bond
A type of covalent bond in which electrons are shared equally between two atoms of similar electronegativity.
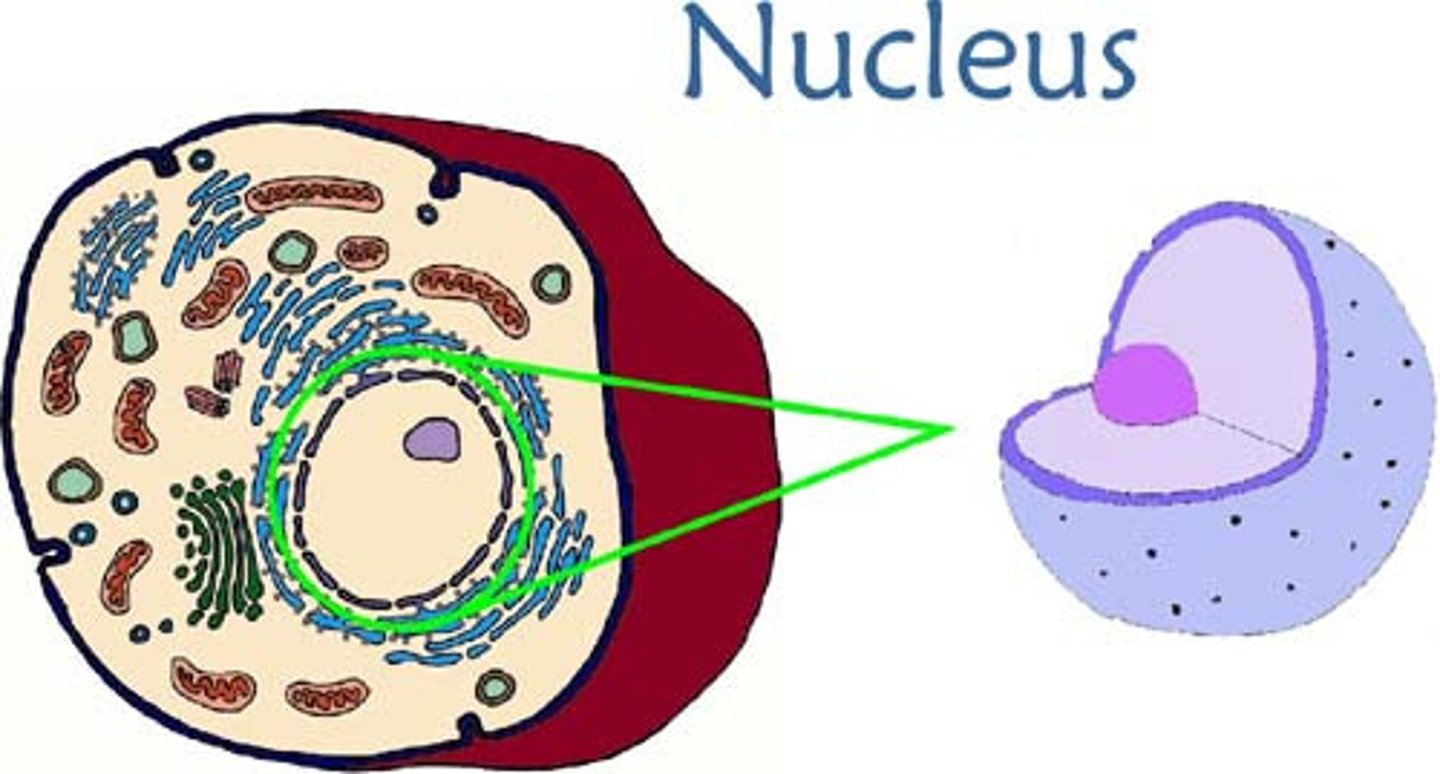
nucleus
1) an atoms central core, containing protons and neutrons. 2) the organelle of a eukaryotic cell that contains the genetic material in the form of chromosomes, made of chromatin
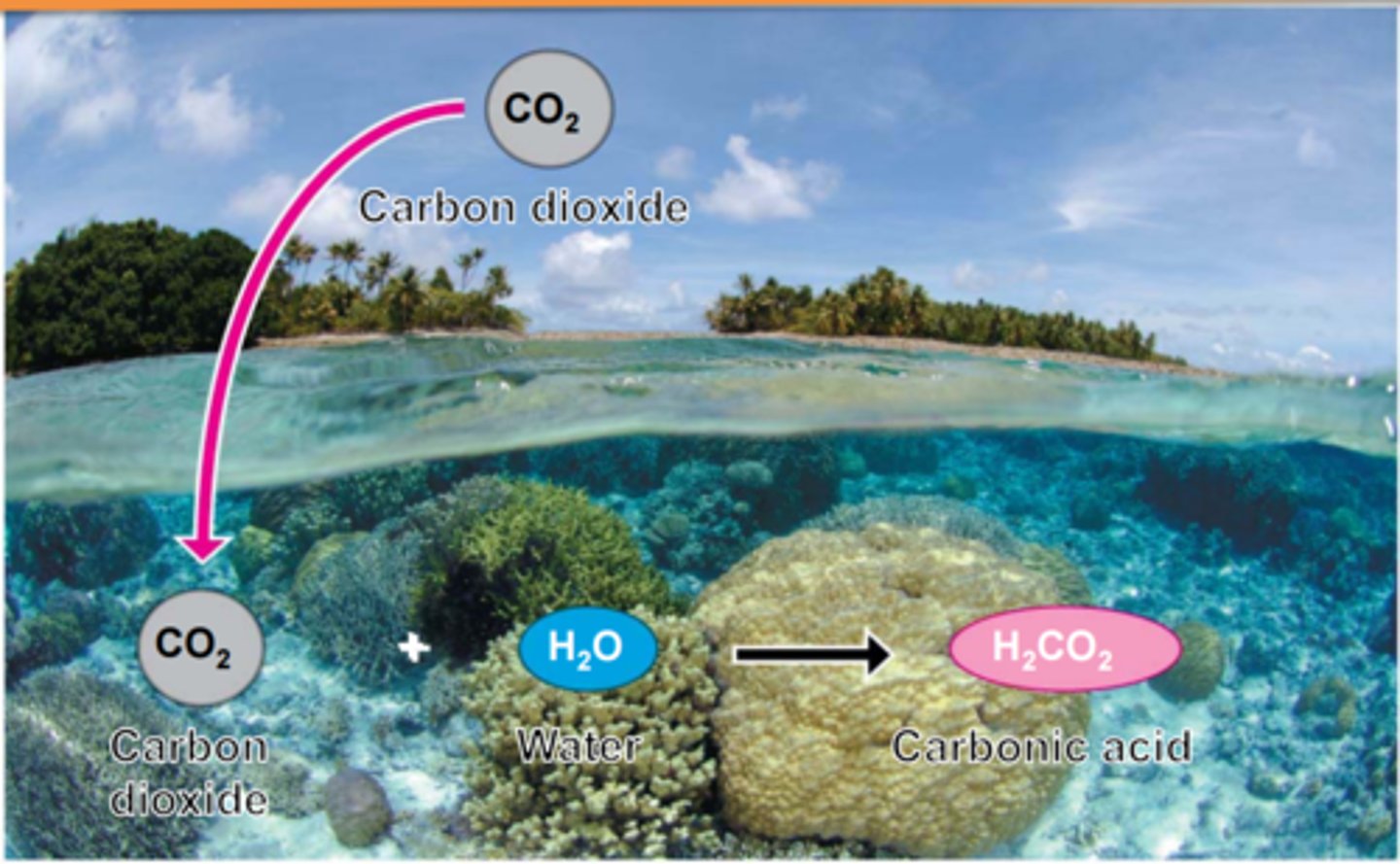
ocean acidification
The process by which the pH of the ocean is lowered (made more acidic) when excess CO2 dissolves in seawater
pH scale
a measure of the acidity of a solution, ranging in value from 0 (most acidic) to 14 (most basic). The letters pH stand for potential hydrogen and refer to the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+)

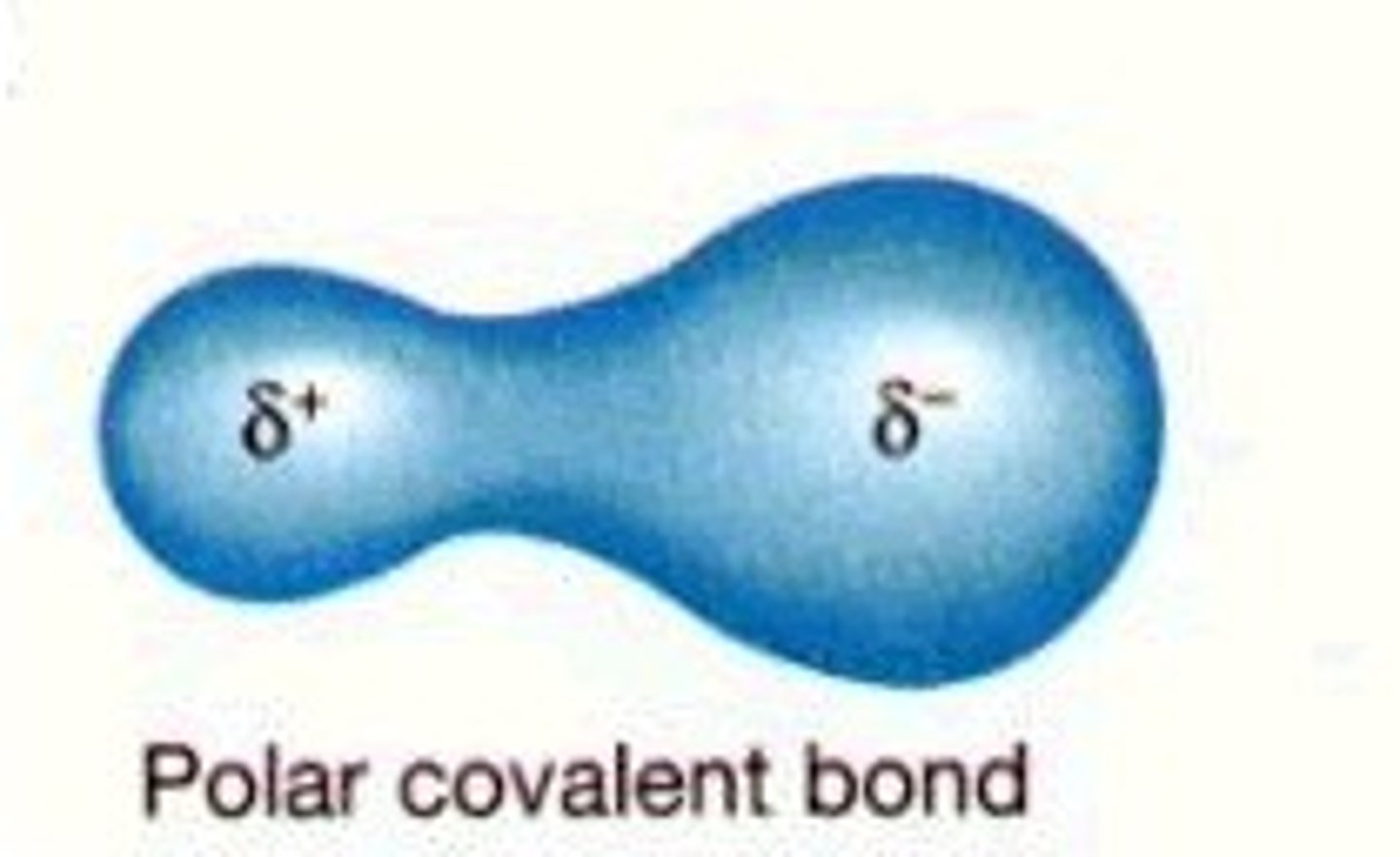
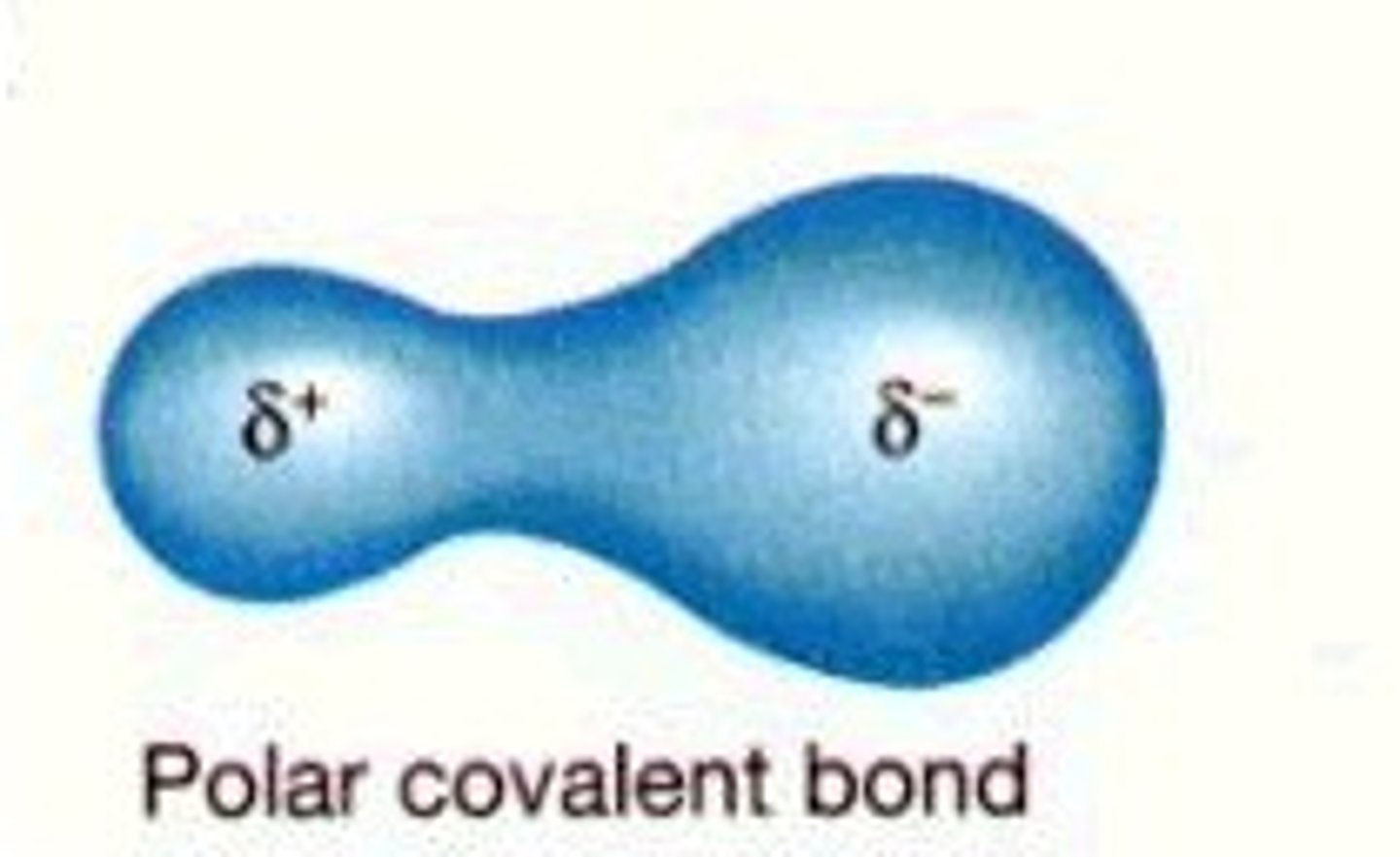
polar covalent bond
A covalent bond between atoms that differ in electronegativity. The shared electrons are pulled closer to the more electronegative atom, making it slightly negative and the other atom slightly positive.
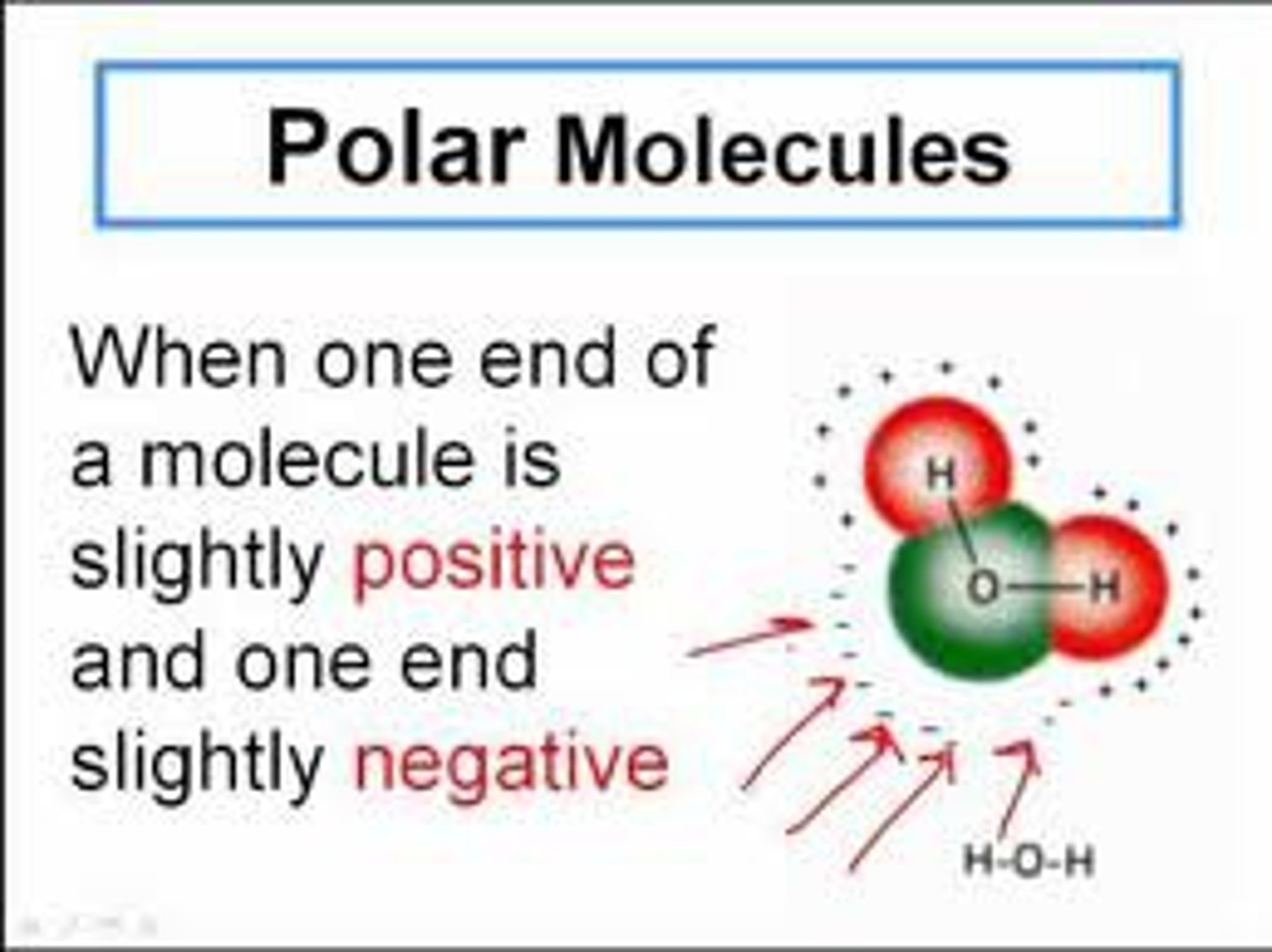
polar molecule
A molecule containing polar covalent bonds and having an unequal distribution of charges in different regions of the molecule.
product
an ending material in a chemical reaction
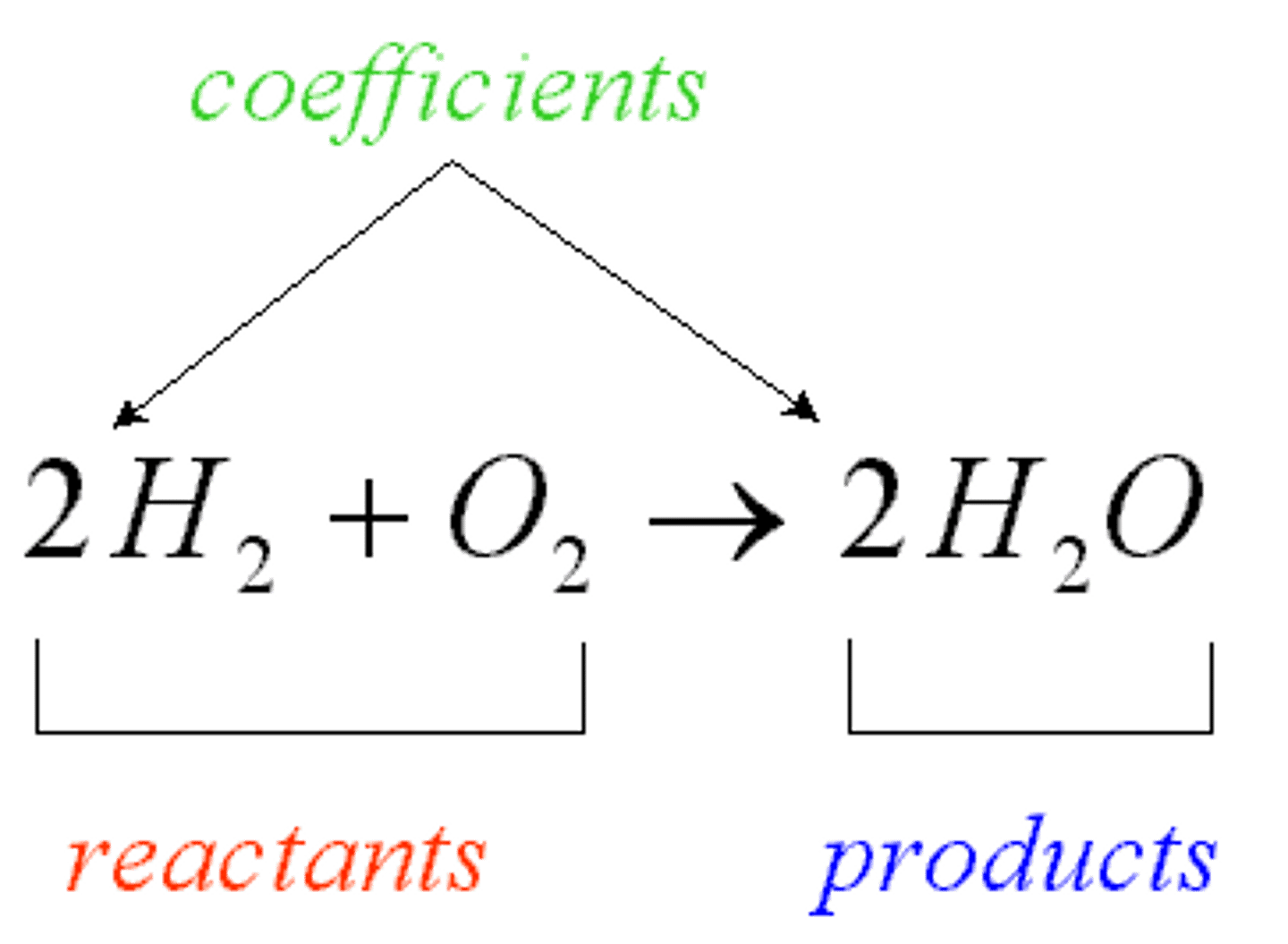
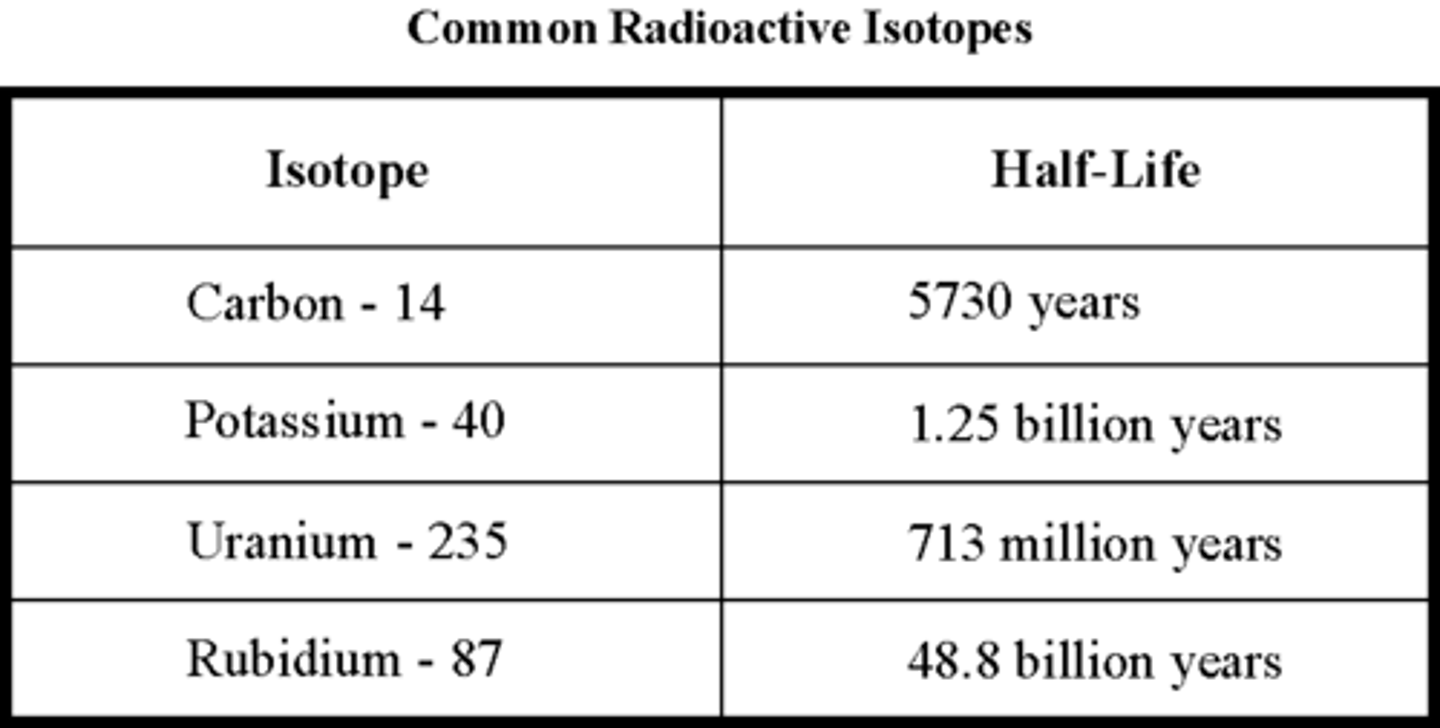
radioactive isotope
An isotope whose nucleus decays spontaneously, giving off particles and energy.
reactant
A starting material in a chemical reaction
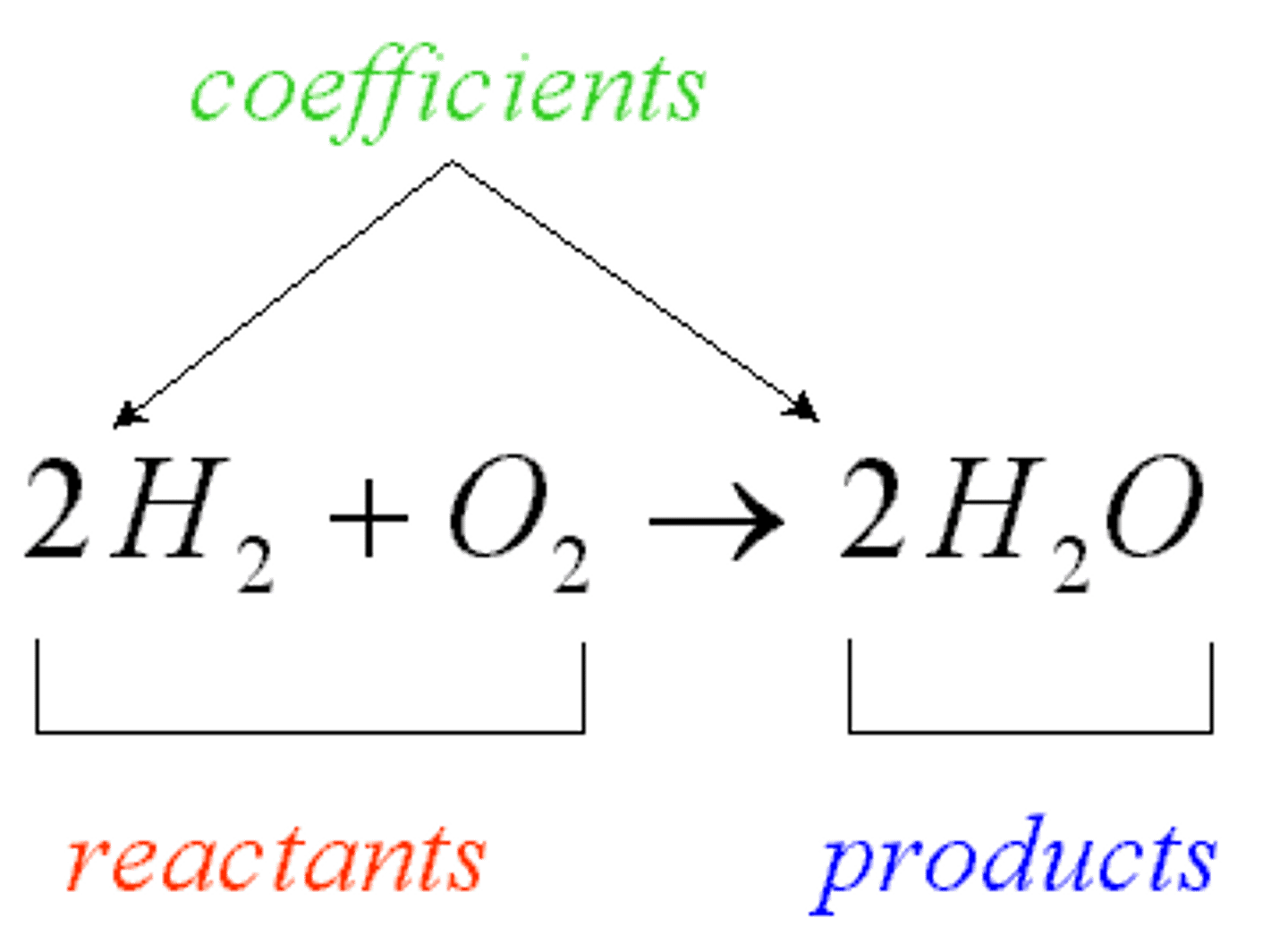
salt
A compound resulting from the formation of an ionic bond

solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
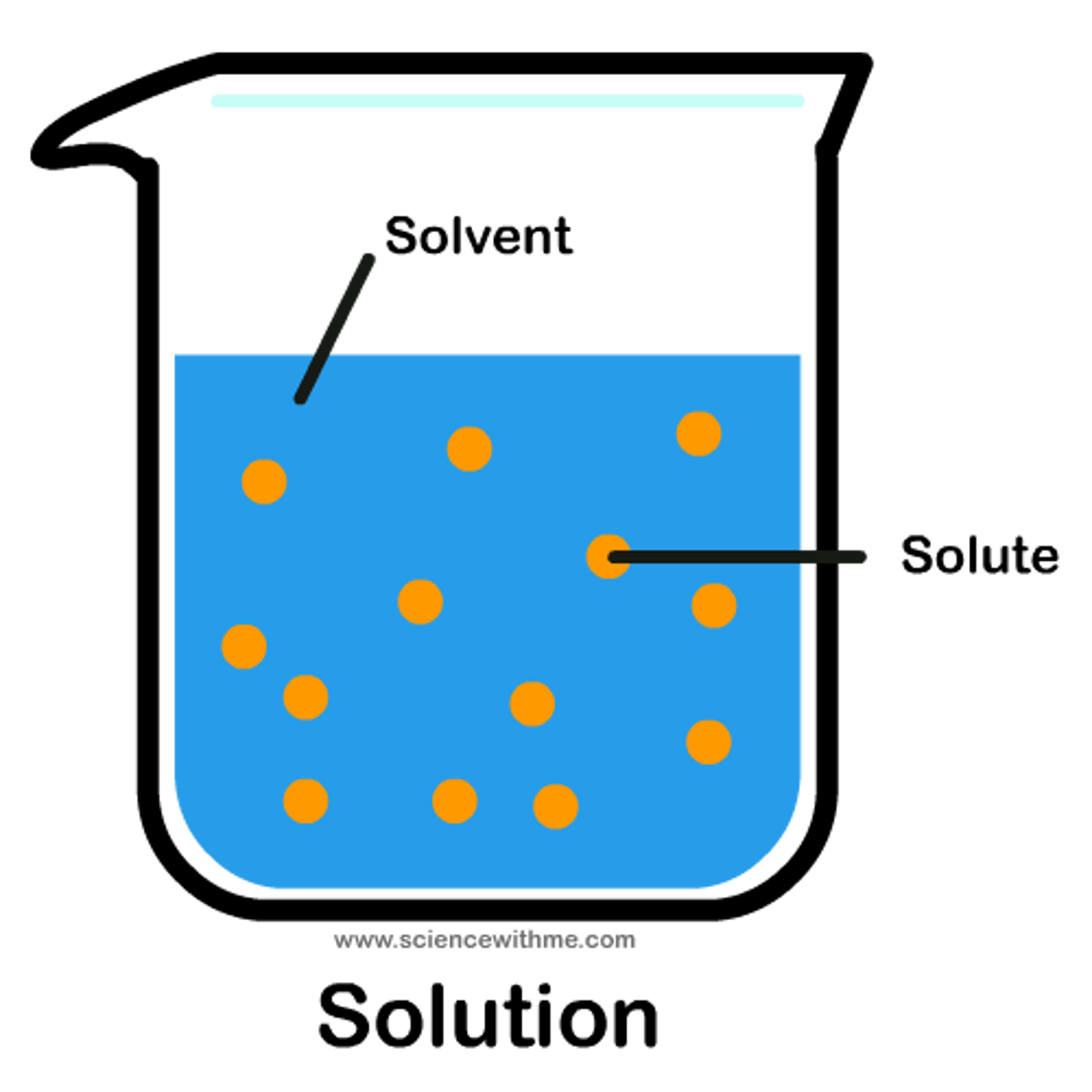
solution
A homogeneous mixture of two or more substances
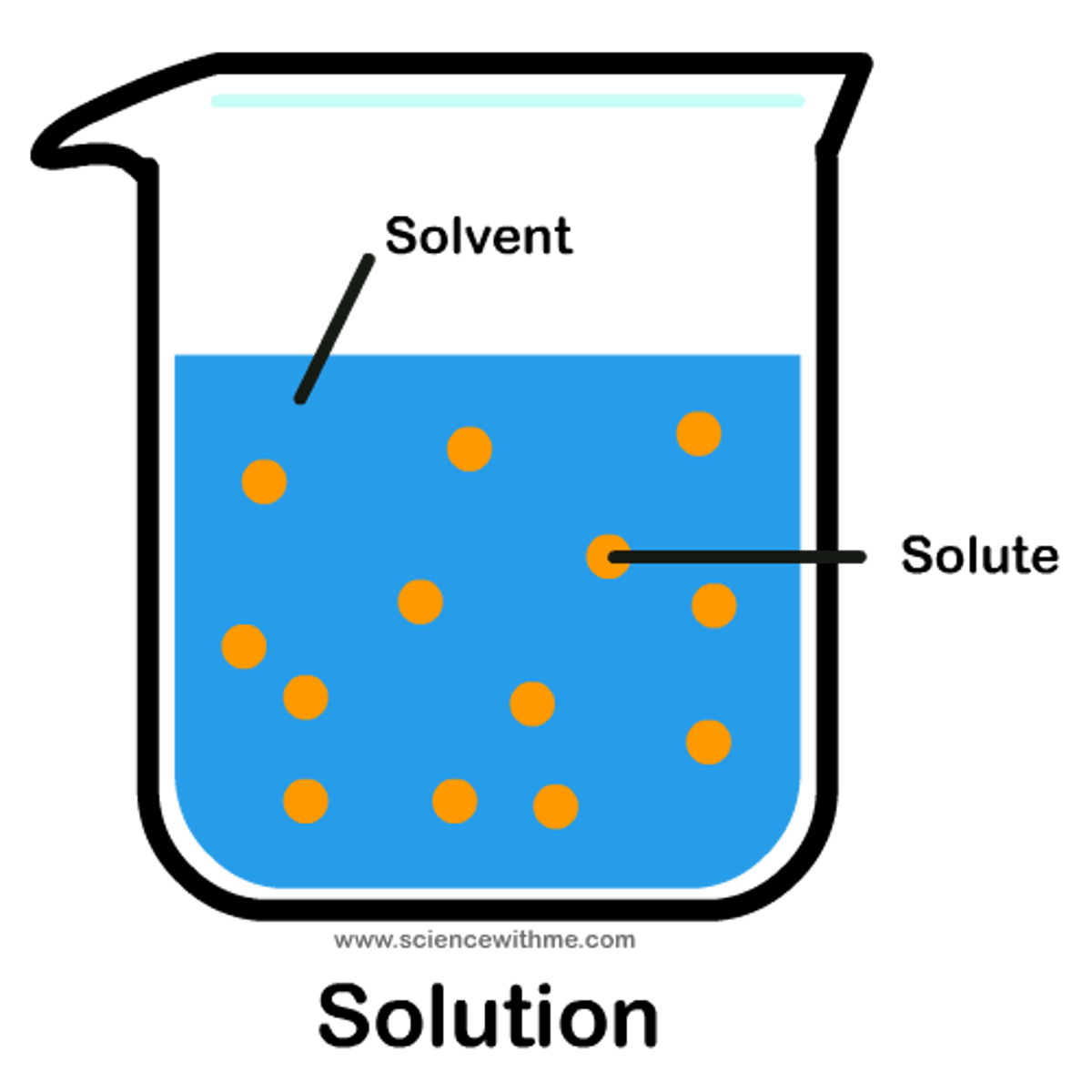
solvent
The dissolving agent of a solution. Water is the most versatile solvent known.
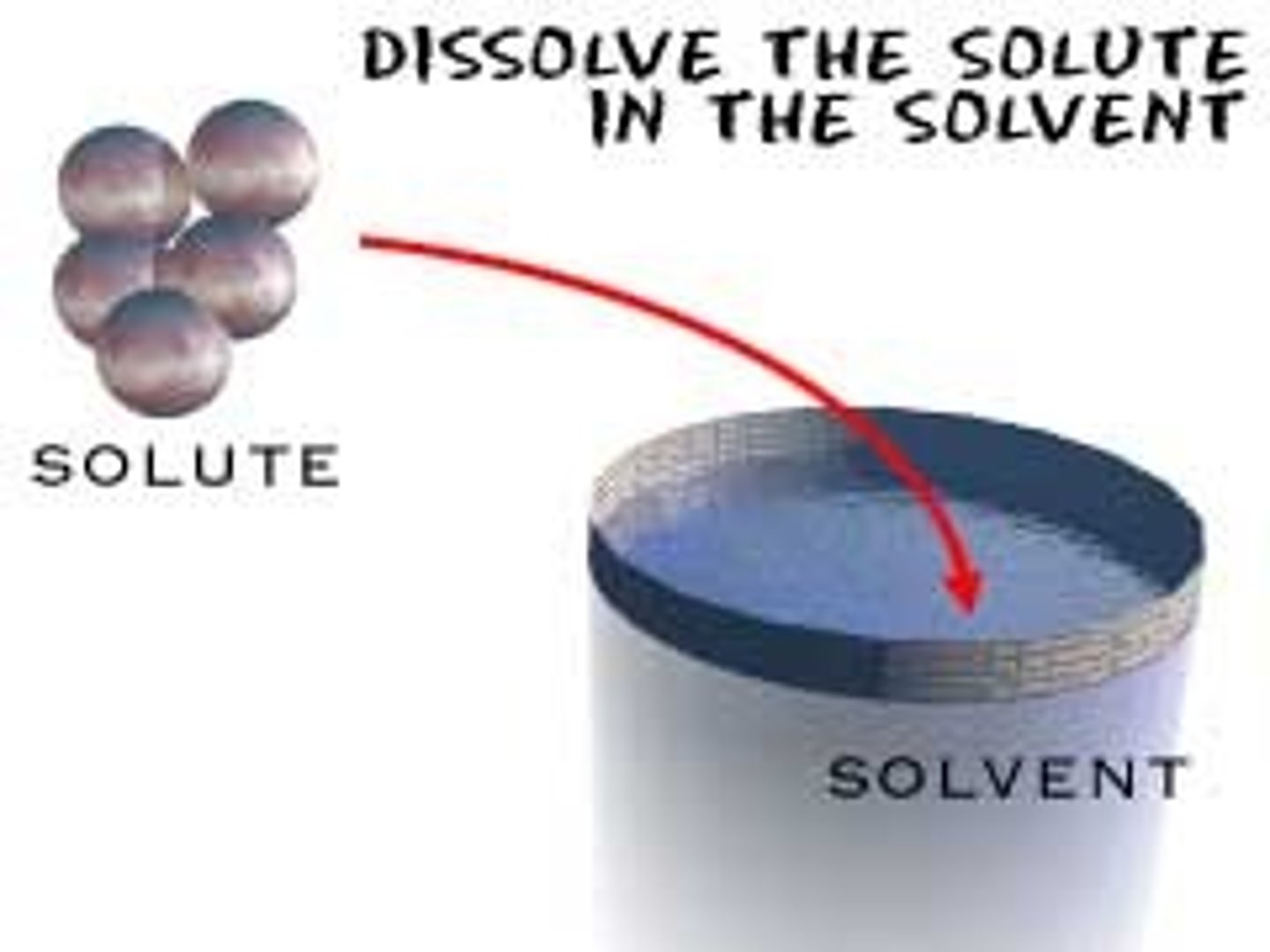
surface tension
A measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid. Water has a high surface tension because of the hydrogen bonding of surface molecules

temperature
a measure in degrees of the average thermal energy of the atoms and molecules in a body of matter
thermal energy
kinetic energy associated with the random movement of atoms or molecules, energy in its most random form
trace element
an element that is essential for life but required in extremely minute amounts
