Archimedes' Principle
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Vfl/Vobj = (mfl/ρfl)/(mobj/ρobj)
Equation of the fraction submerged
Fraction submerged = ρobj/ρfl
Final simplified form of the fraction submerged that gets used to calculate the average density,
lower-density, higher-density
Numerous _____________ objects or substances float in ____________ fluids
Earth’s mantle
The thick layer of solid rock between Earth’s crust and core. Though solid, it behaves like a very slow-flowing fluid over millions of years due to high heat and pressure.
Isostasy
The scientific theory that Earth’s lighter crust “floats” on the denser, flexible mantle beneath it, like icebergs float on water. Mountain ranges have deep roots below the surface to stay balanced.
The crust is solid, but the mantle beneath can flow slowly like a fluid under pressure and heat. Over long times, this allows the solid crust to “float” and adjust its height, making isostasy valid.
Why is isostasy valid if the crust is solid?
Silica
A chemical compound of silicon and oxygen (SiO₂), the main component of many rocks and minerals.
Quartz
The crystalline form of silica, common in granitic rocks; appears as clear or colored crystals.
Magma
Hot, molten rock beneath Earth’s surface that contains liquid rock, crystals, and dissolved gases. When it erupts, it becomes lava.
Igneous rock
Rock formed when molten magma or lava cools and solidifies, e.g., granite (granitic) and basalt (basaltic).
Granitic rock
Light-colored, coarse-grained igneous rock rich in silica and quartz; makes up most of the continental crust. Less dense than basaltic rock.
Basaltic rock
Dark-colored, fine-grained igneous rock rich in iron and magnesium; makes up most of the oceanic crust. Denser than granitic rock.
T
(1)
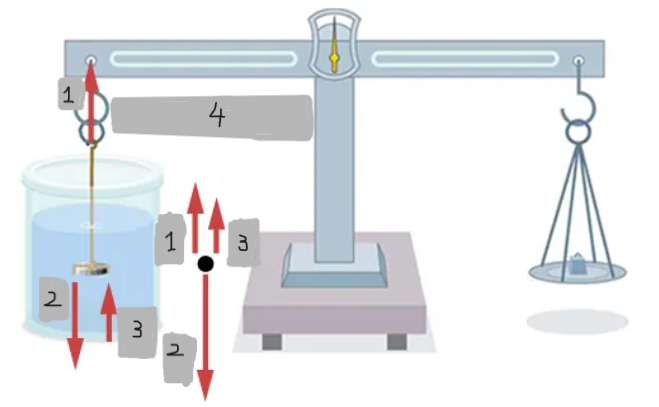
w
(2)
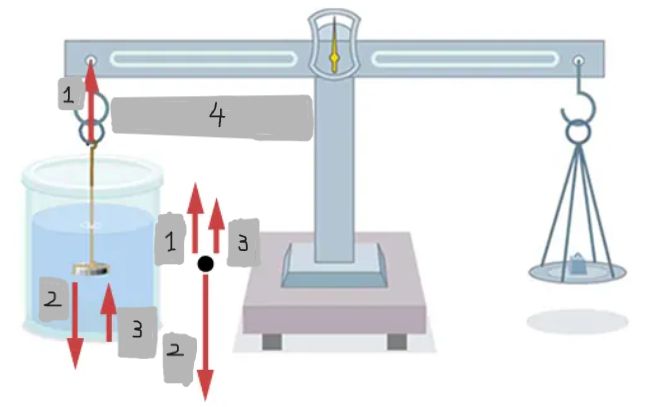
Fb
(3)
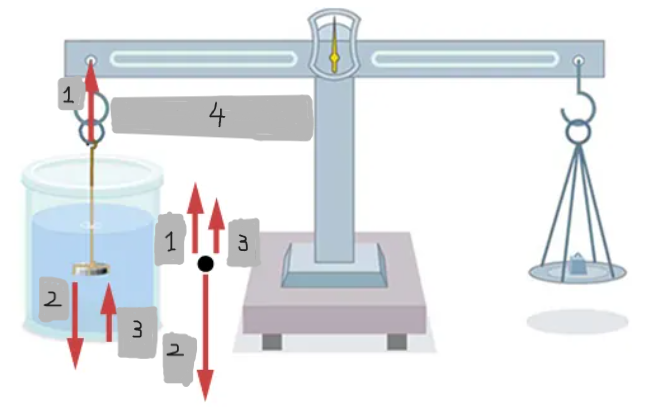
T = w - Fb = wapp
(4)
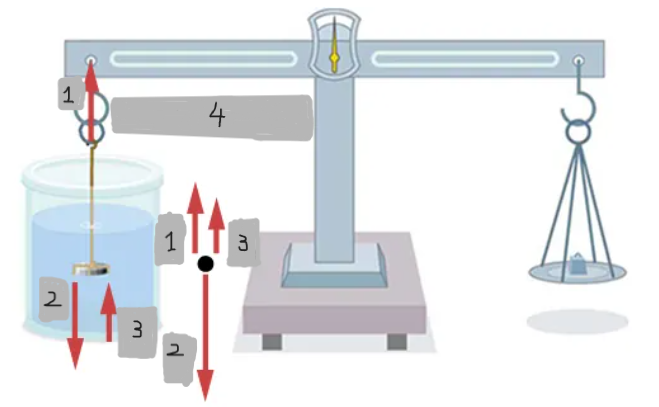
Weighing in air vs. liquid
An object weighs less when submerged in a fluid because it experiences an upward buoyant force.
Density determination by weighing
If the fluid density is known, the object’s density can be calculated; if the object’s density is known, the fluid’s density can be determined.
Archimedes’ principle
Buoyant force equals the weight of the displaced fluid.
Apparent weight
The reduced weight an object seems to have when submerged in a fluid due to buoyant force.
Apparent weight loss
Equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.
Apparent mass loss
On balances that measure mass, the loss is equal to the mass of the fluid displaced.