Cell Wall/Membrane Acting Agents
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
1
New cards
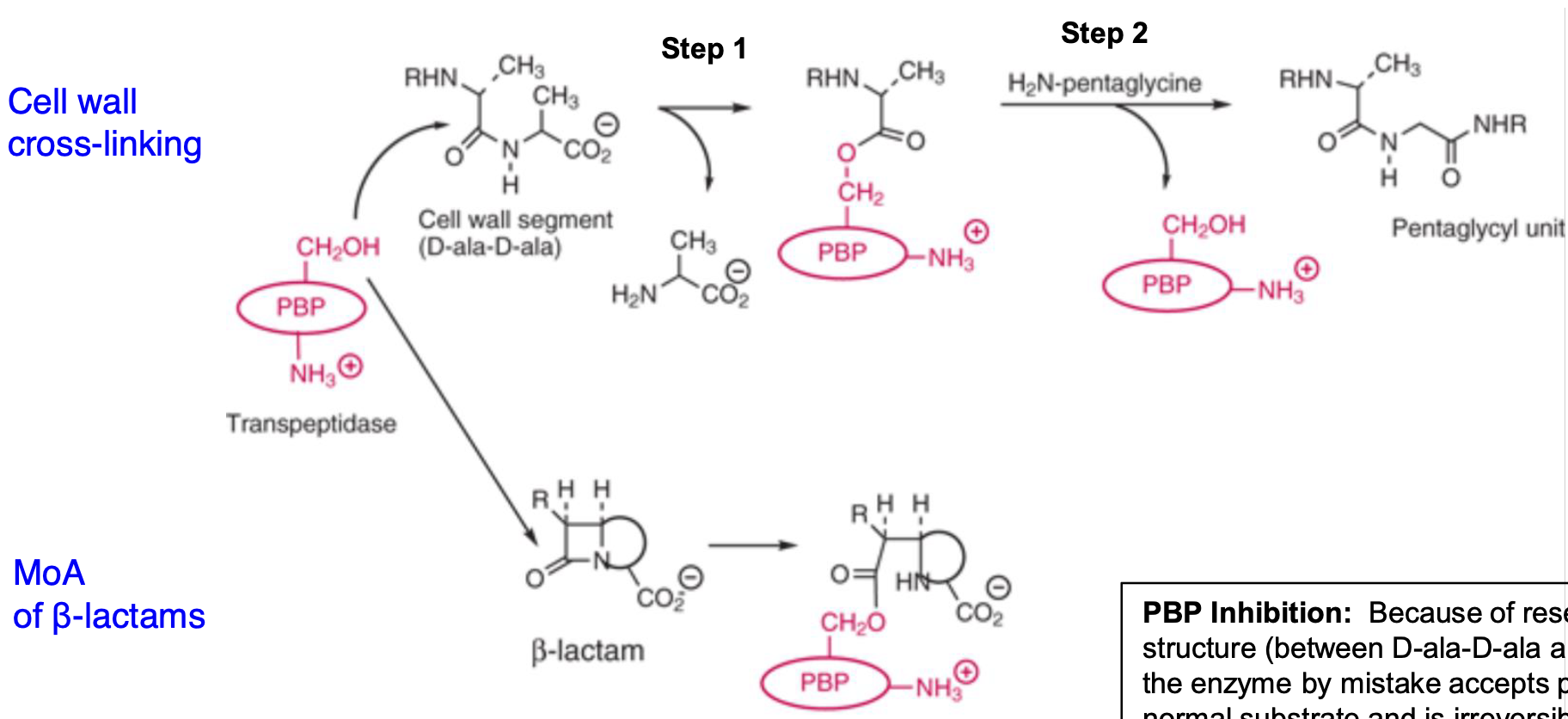
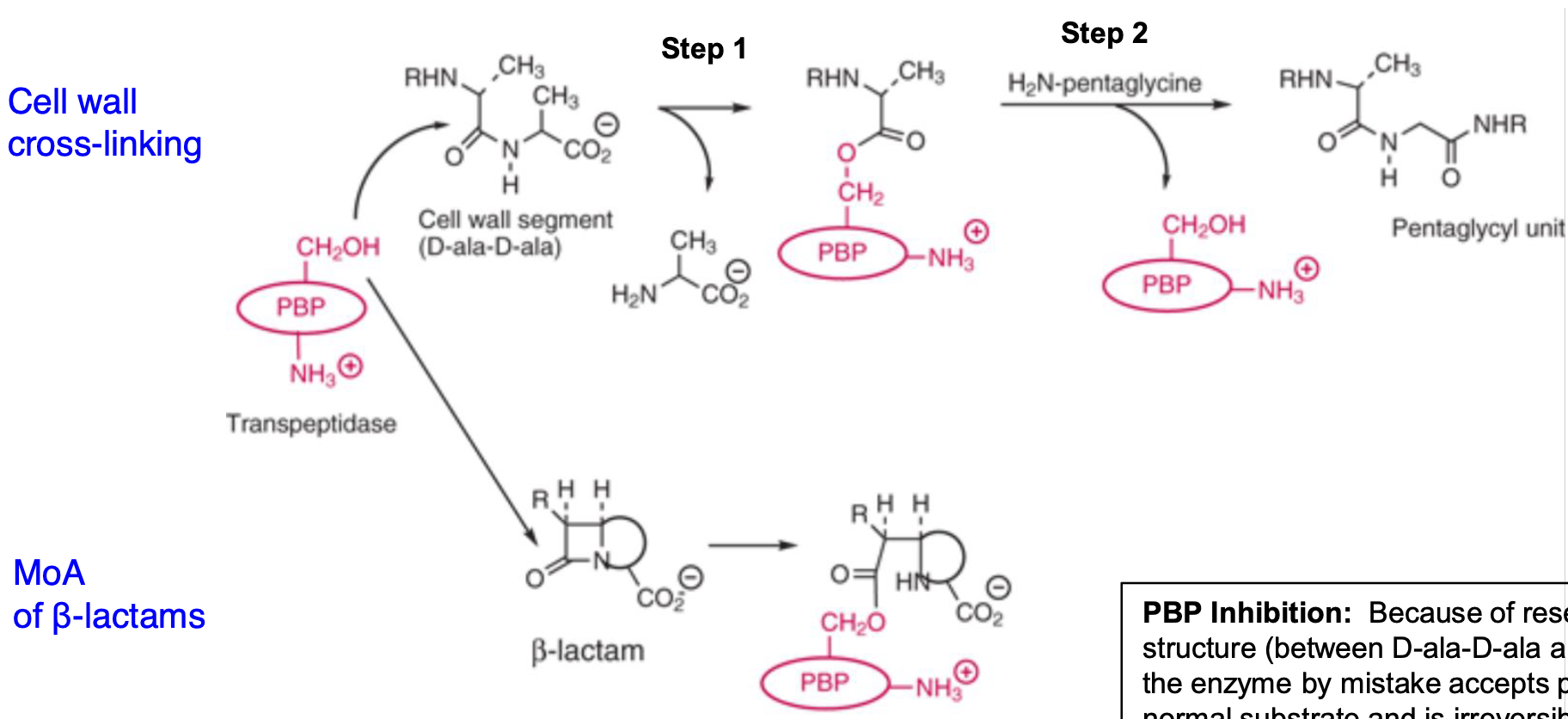
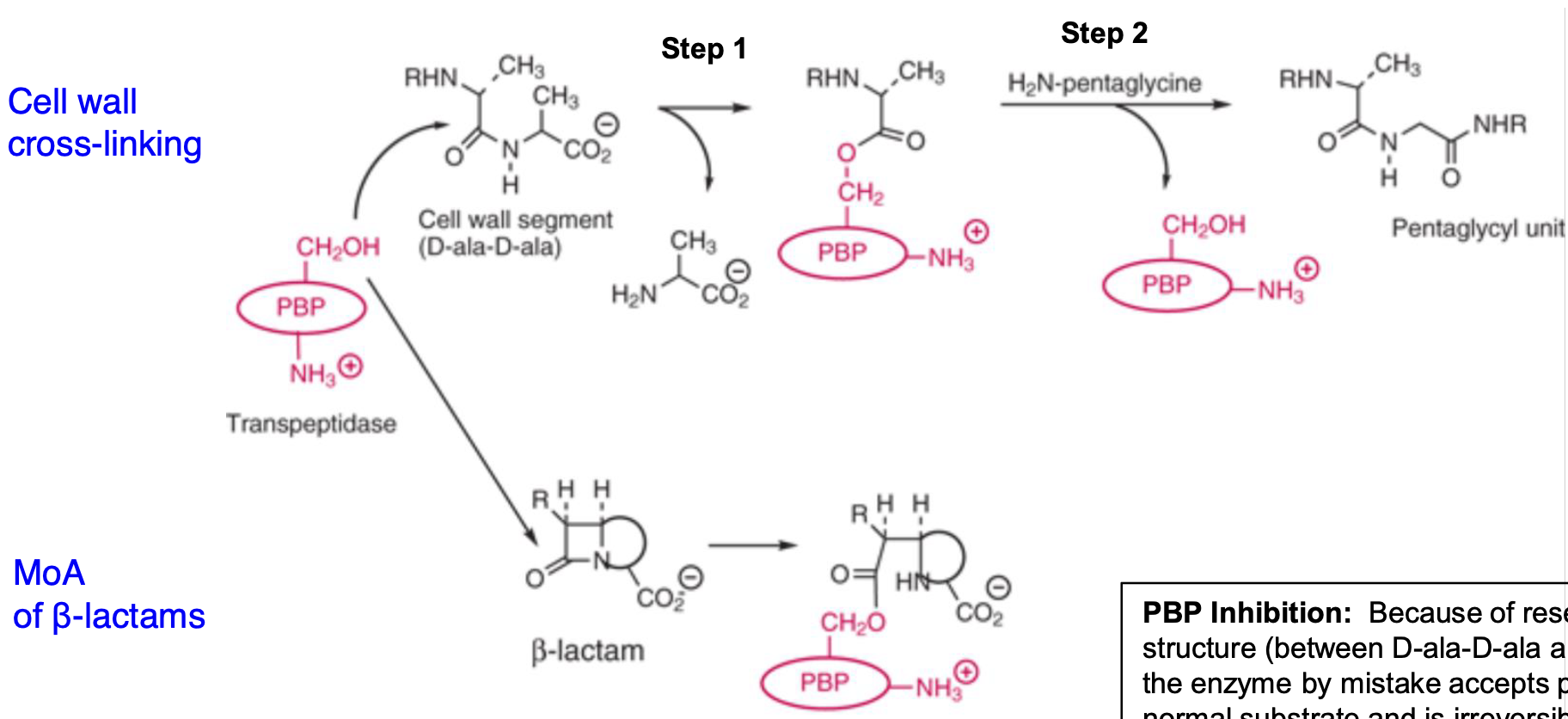
What is the primary target of β-lactam antibiotics?
β-lactam antibiotics target penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), specifically transpeptidases involved in peptidoglycan synthesis.
2
New cards
How do β-lactam antibiotics inhibit PBPs?
β-lactam antibiotics mimic the D-ala-D-ala structure of peptidoglycan and irreversibly bind to PBPs, inhibiting their enzymatic activity.
3
New cards
What is the result of β-lactam inhibition of PBPs?
Inhibition prevents cross-linking of peptidoglycan chains, leading to weakened bacterial cell walls and cell lysis.
4
New cards
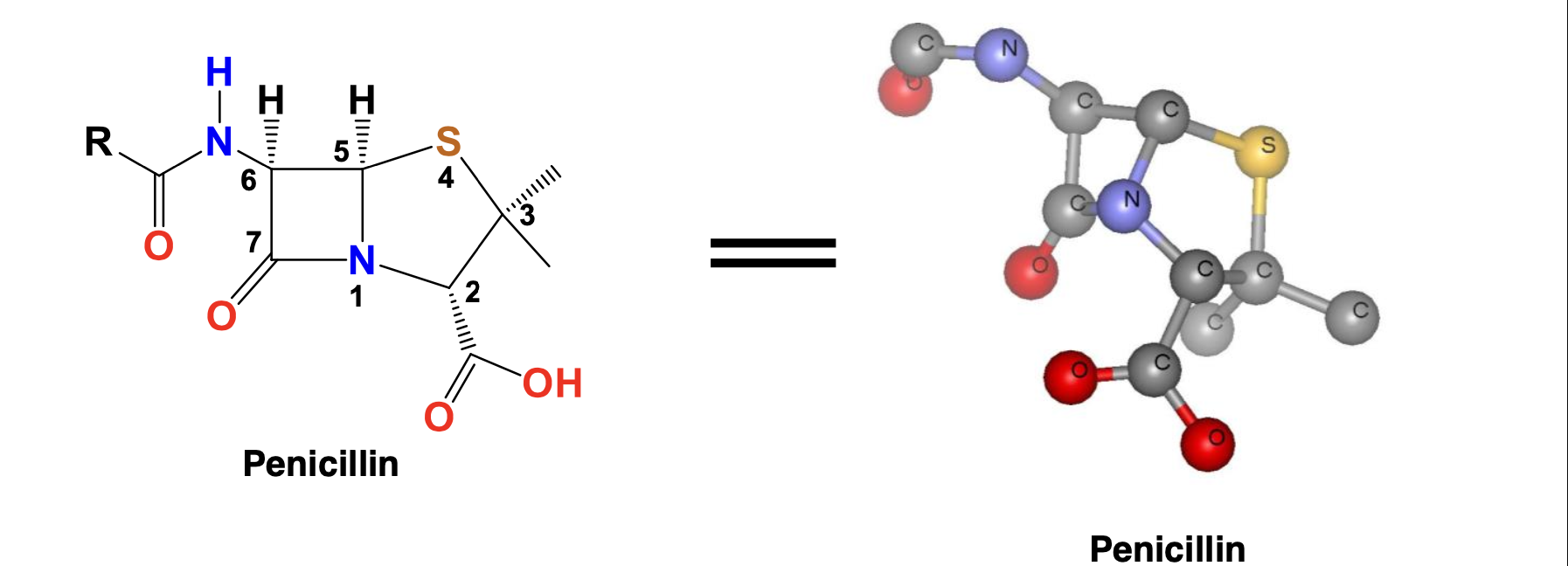
Why are β-lactam antibiotics highly reactive?
The reactivity is due to the ring strain in the β-lactam ring and the lack of resonance stabilization in the amide bond.
5
New cards
What happens to the terminal D-alanine during transpeptidase inhibition by β-lactam antibiotics?
The terminal D-alanine is released during the formation of a covalent bond between the β-lactam antibiotic and the PBP.
6
New cards
What is target alteration as a mechanism of resistance to β-lactam antibiotics?
Bacteria acquire PBPs with reduced affinity for β-lactam antibiotics, such as PBP2a in MRSA.
7
New cards
How does reduced permeability contribute to β-lactam resistance in Gram-negative bacteria?
The outer membrane limits antibiotic entry, and variations in porin channels reduce drug uptake.
8
New cards
What role do efflux pumps play in β-lactam resistance?
Efflux pumps actively remove β-lactam antibiotics from bacterial cells before they can act.
9
New cards
How do β-lactamases confer resistance to β-lactam antibiotics?
β-lactamases hydrolyze the β-lactam ring, inactivating the antibiotic.
10
New cards
What are extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs)?
ESBLs are enzymes that can hydrolyze extended-spectrum β-lactams, including penicillins, cephalosporins, and monobactams.
11
New cards
What is the primary mechanism of β-lactamase inhibitors?
β-lactamase inhibitors irreversibly bind to the active site of β-lactamase enzymes, preventing them from hydrolyzing β-lactam antibiotics.
12
New cards
How do β-lactamase inhibitors mimic substrates?
They structurally resemble β-lactam antibiotics, allowing them to acylate the β-lactamase enzyme and inactivate it.
13
New cards
What is an example of a β-lactamase inhibitor's role in combination therapy?
Clavulanic acid is combined with amoxicillin to protect it from enzymatic degradation by β-lactamases.
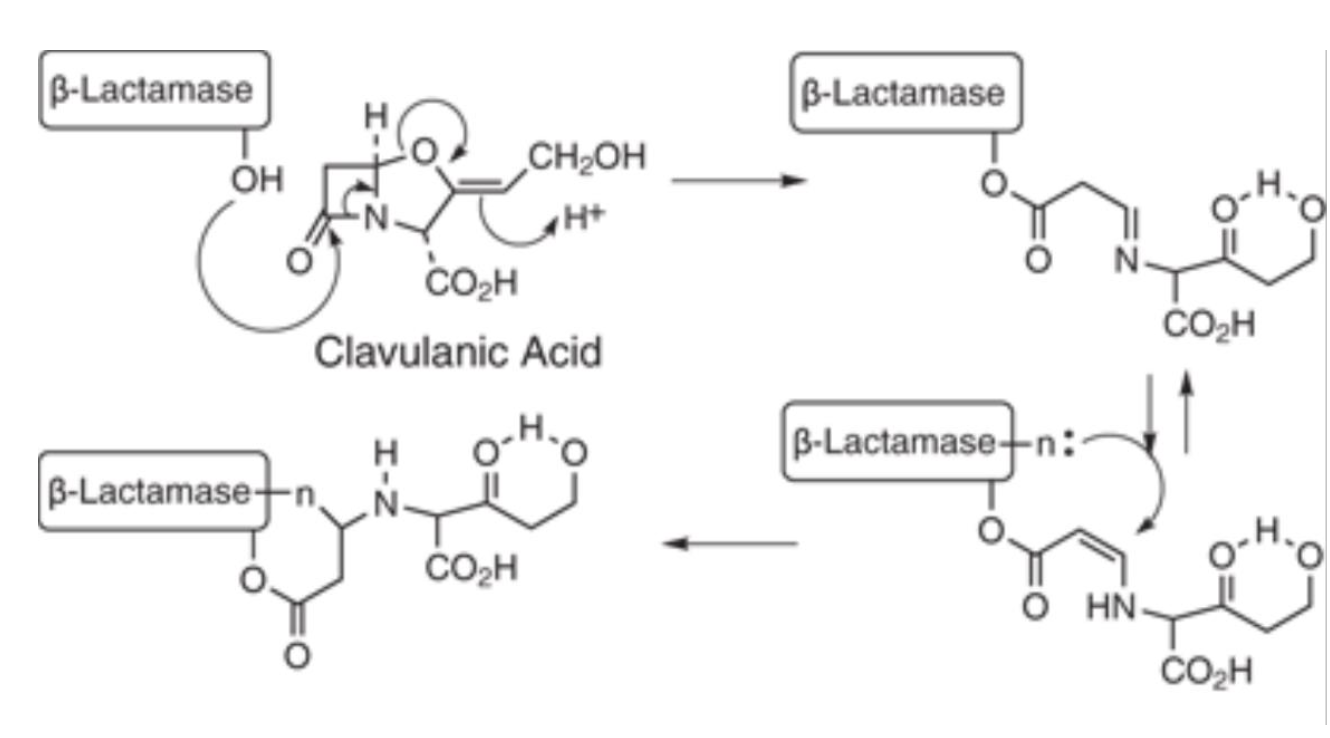
14
New cards
Why are β-lactamase inhibitors not effective on their own?
They do not possess significant antibacterial activity and rely on the β-lactam antibiotic for bacterial cell wall inhibition.
15
New cards
What types of β-lactamases are inhibited by clavulanic acid?
Clavulanic acid inhibits most serine β-lactamases, including those in classes A, C, and D.
16
New cards
What types of hypersensitivity reactions can penicillin cause?
Penicillin can cause immediate IgE-mediated reactions (Type I), antibody-mediated cytotoxic reactions (Type II), immune complex-mediated reactions (Type III), and delayed T-cell-mediated reactions.
17
New cards
What is a common severe reaction associated with penicillin allergy?
Severe T-cell-mediated reactions, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), can occur in some patients.
18
New cards
How can penicillin allergy impact antibiotic selection?
Reported penicillin allergy can lead to the use of broader-spectrum antibiotics, increasing risks of antimicrobial resistance and Clostridium difficile infection.
19
New cards
What diagnostic steps can confirm a penicillin allergy?
Penicillin skin testing and direct amoxicillin challenges are used to confirm or rule out penicillin allergy in patients with a history of allergic reactions.
20
New cards
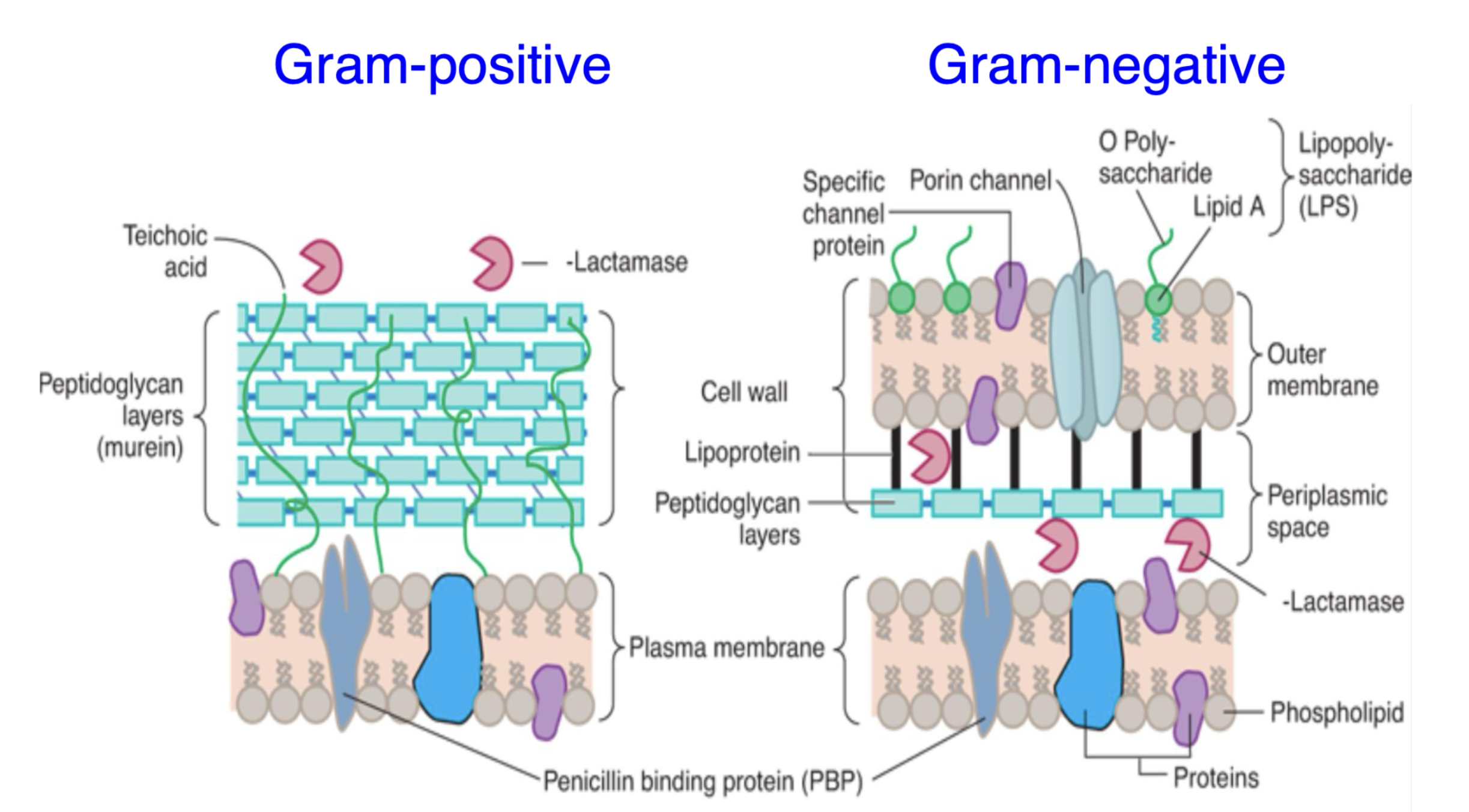
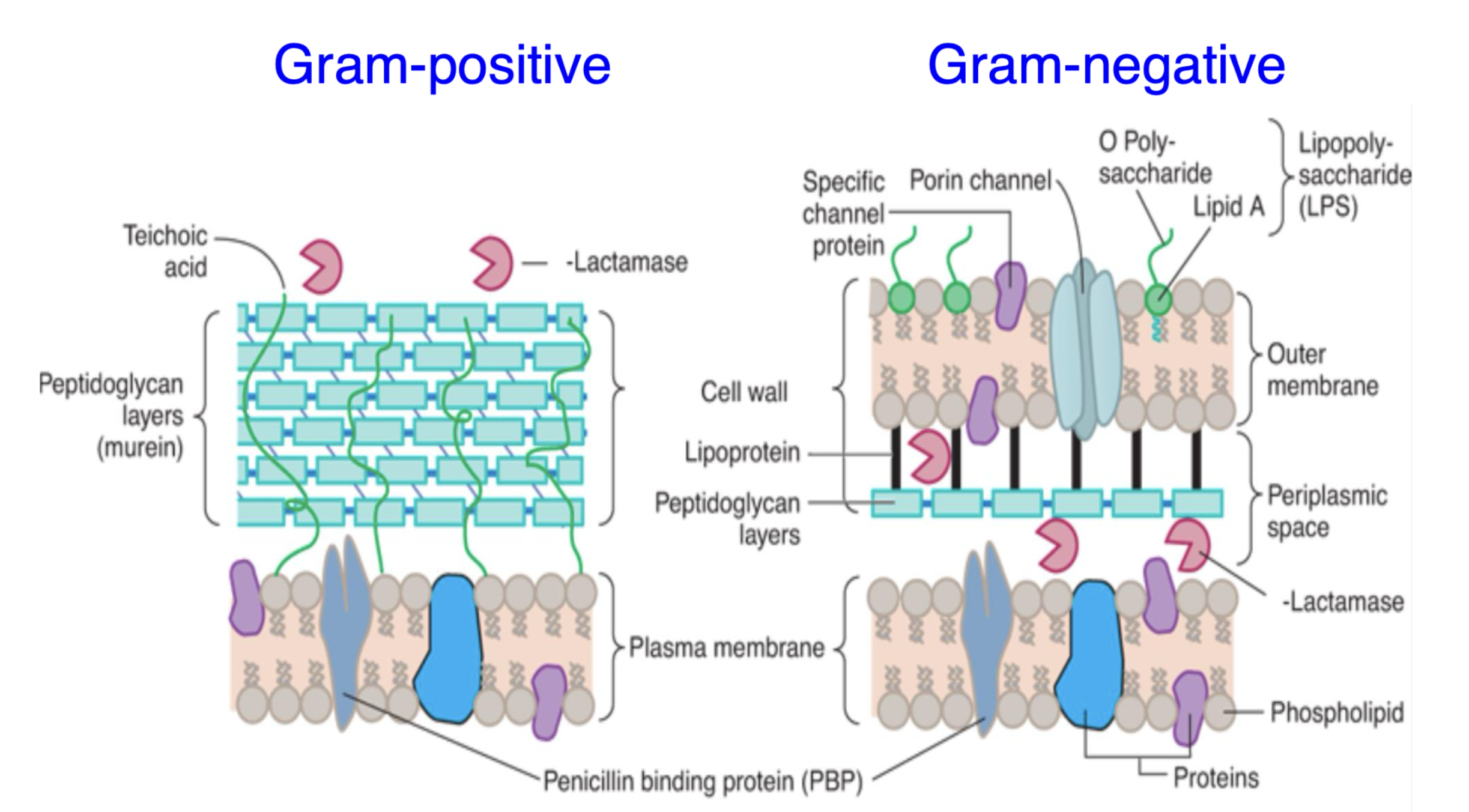
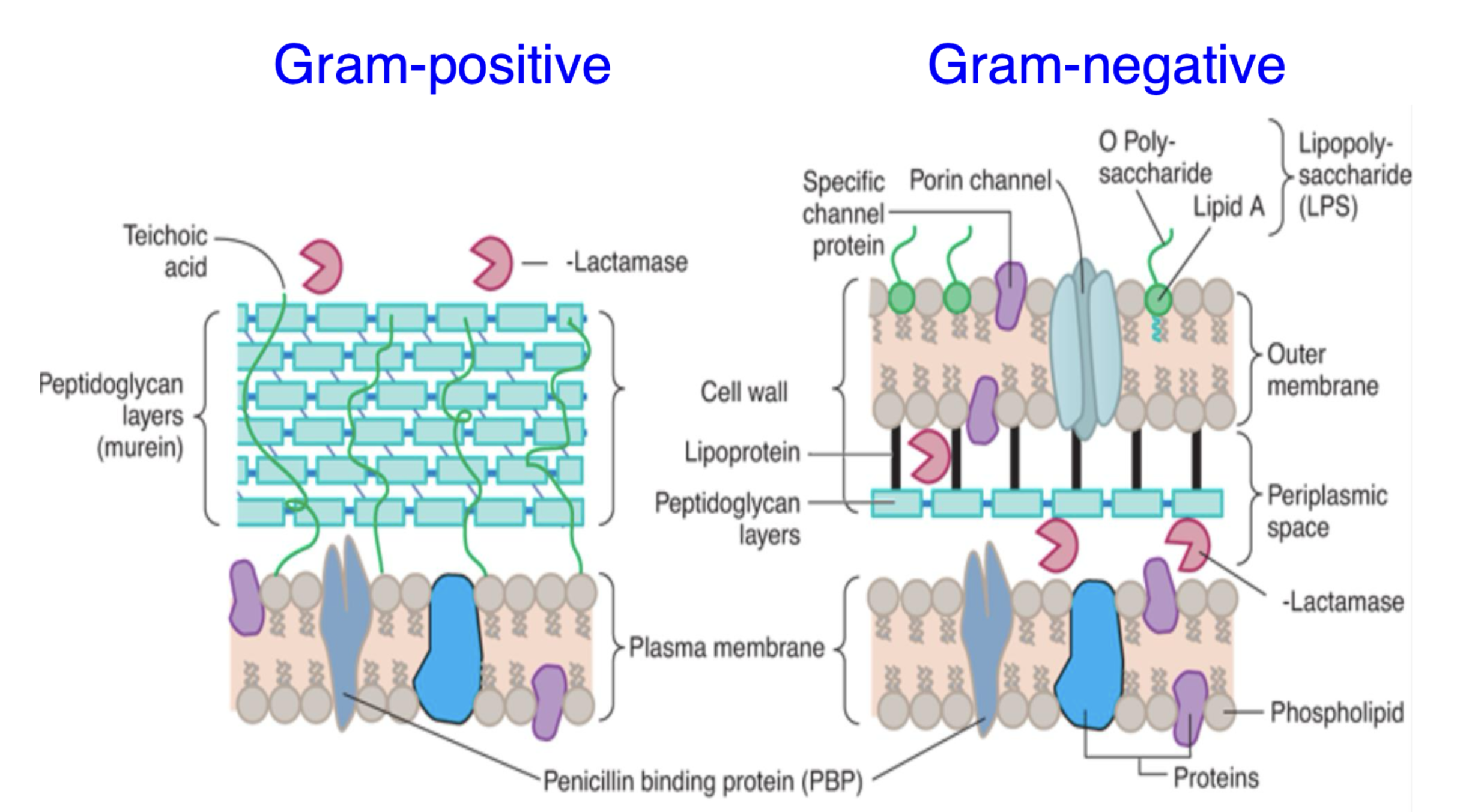
What is a unique feature of Gram-positive cell walls?
They have a thick peptidoglycan layer with teichoic acid embedded in the wall.

21
New cards
What is a defining feature of Gram-negative cell walls?
They have an outer membrane containing lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and a thin peptidoglycan layer.
22
New cards
Where is β-lactamase located in Gram-negative bacteria?
β-lactamase is located in the periplasmic space between the outer membrane and the plasma membrane.
23
New cards
What is the role of porin channels in Gram-negative bacteria?
Porin channels allow the passage of small molecules through the outer membrane.
24
New cards
Peptidoglycan contains D-amino acids to protect it from _______ by host peptidases.
hydrolysis
25
New cards
What causes penicillin allergy?
Penicillin covalently binds to plasma proteins, forming antigenic conjugates that trigger an immune response.