Geography Bootcamp
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

43 Terms
Geography
The study of our physical surroundings and how humans interact with them.
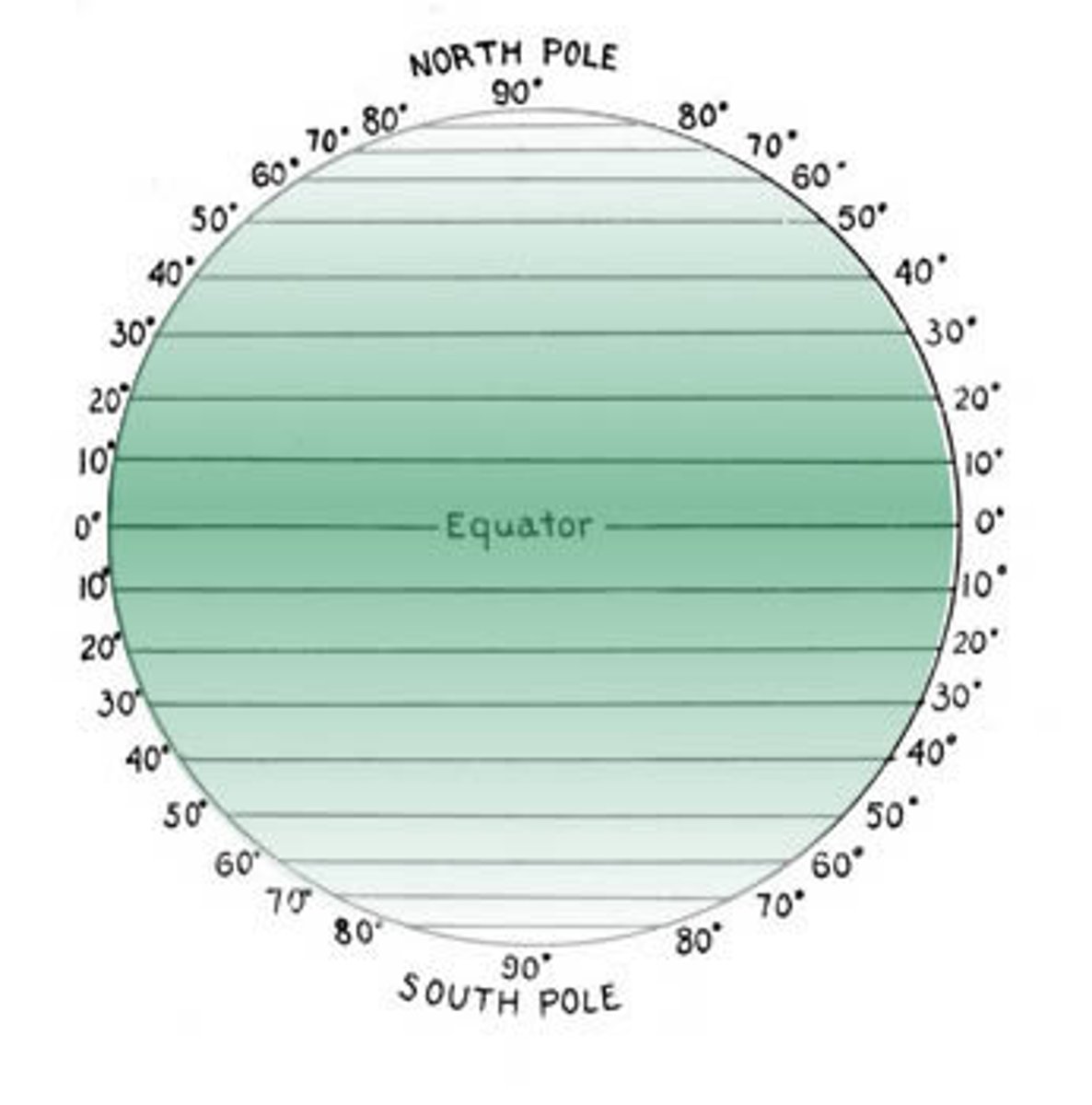
Latitude
How far a place on Earth is from the equator, measured in degrees. It is measured with imaginary lines around the Earth that run East to West.
LAT IS FLAT!
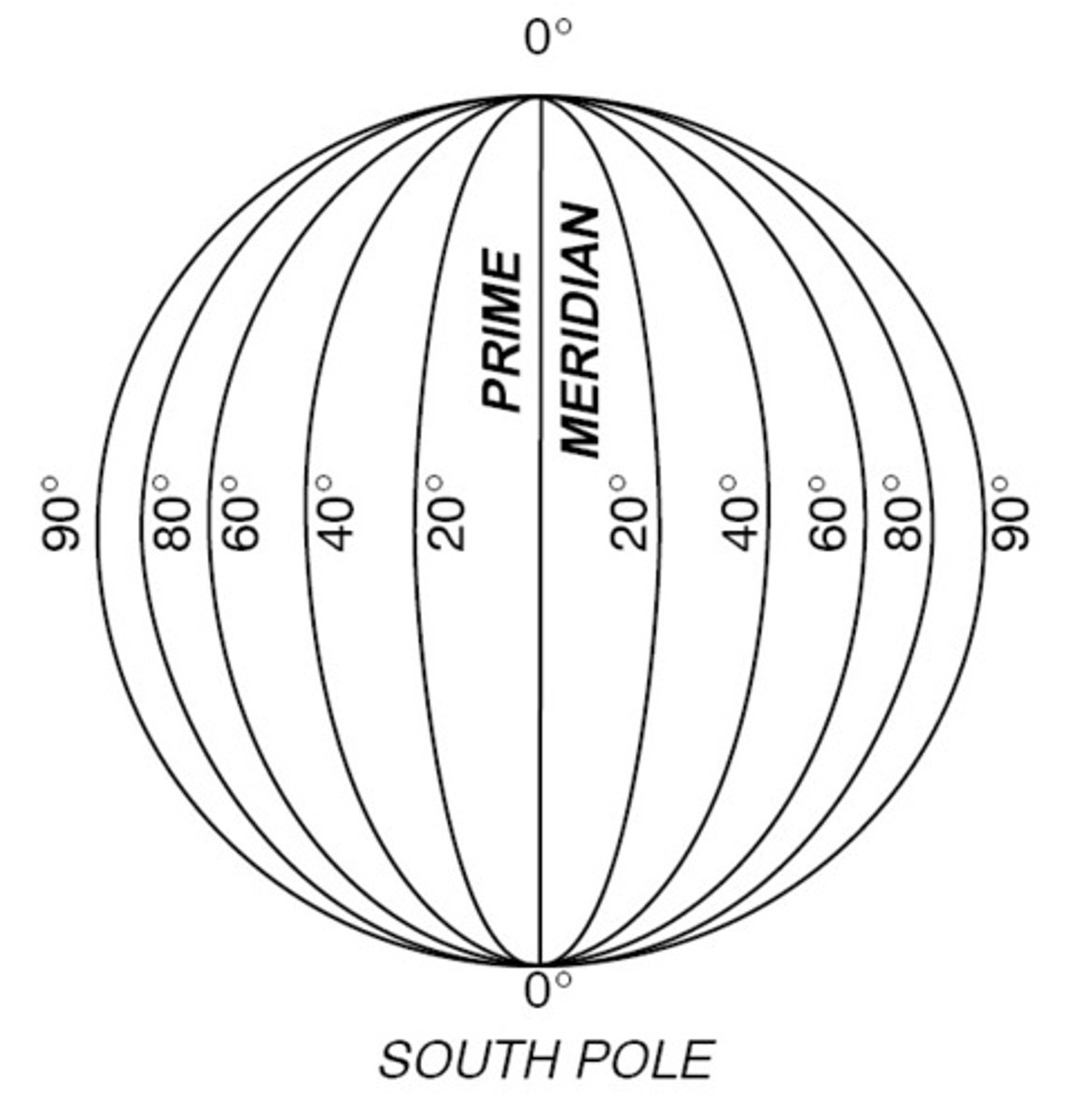
Longitude
How far a place is on Earth from the Prime Meridian, measured in degrees. It is measured with the help of imaginary lines that run North to South.
Absolute Location
Using Latitude and Longitude to show the location of a place on Earth. 22 degrees N, 100 degrees W
Cardinal Directions
North
South
East
West
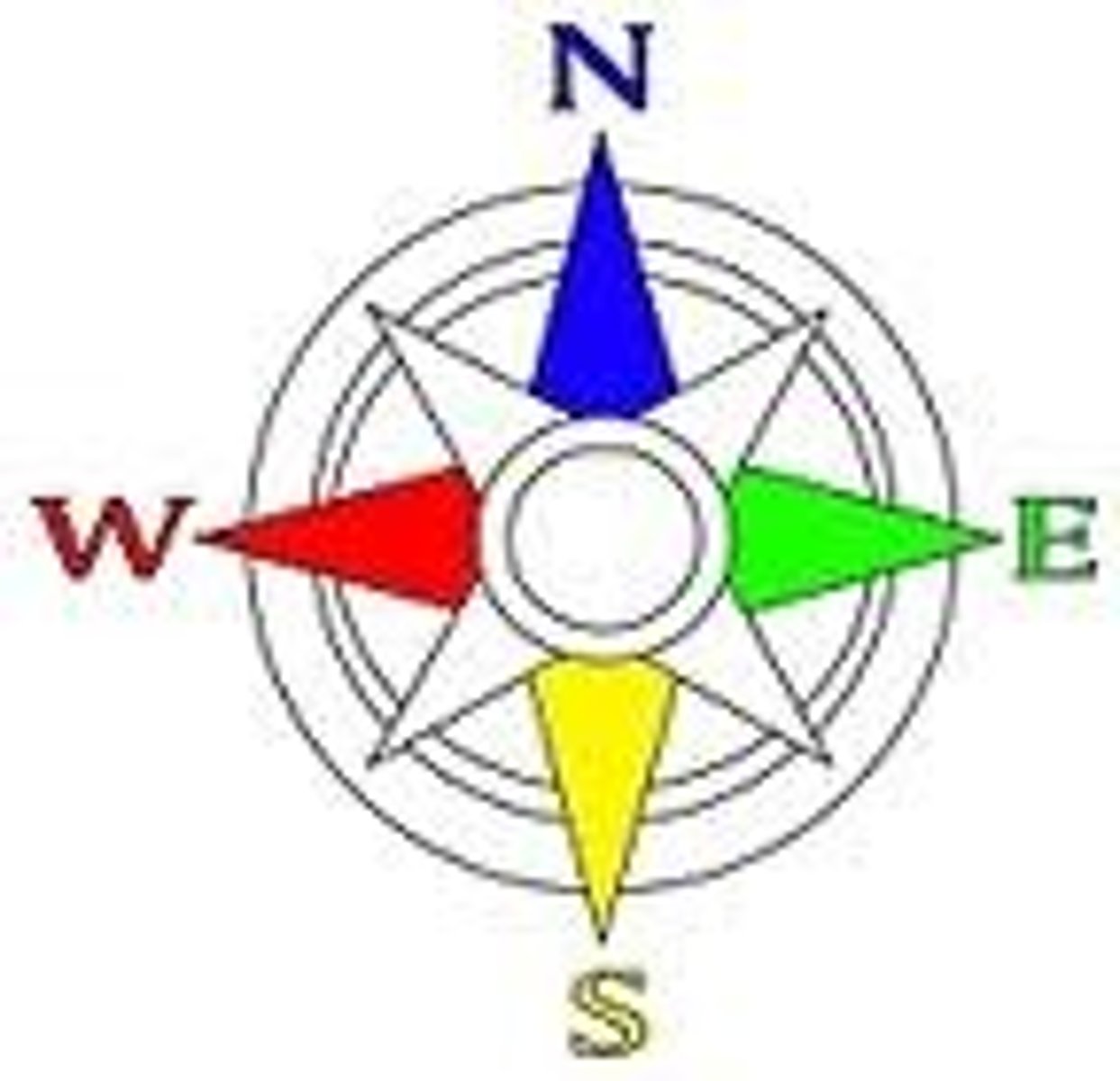
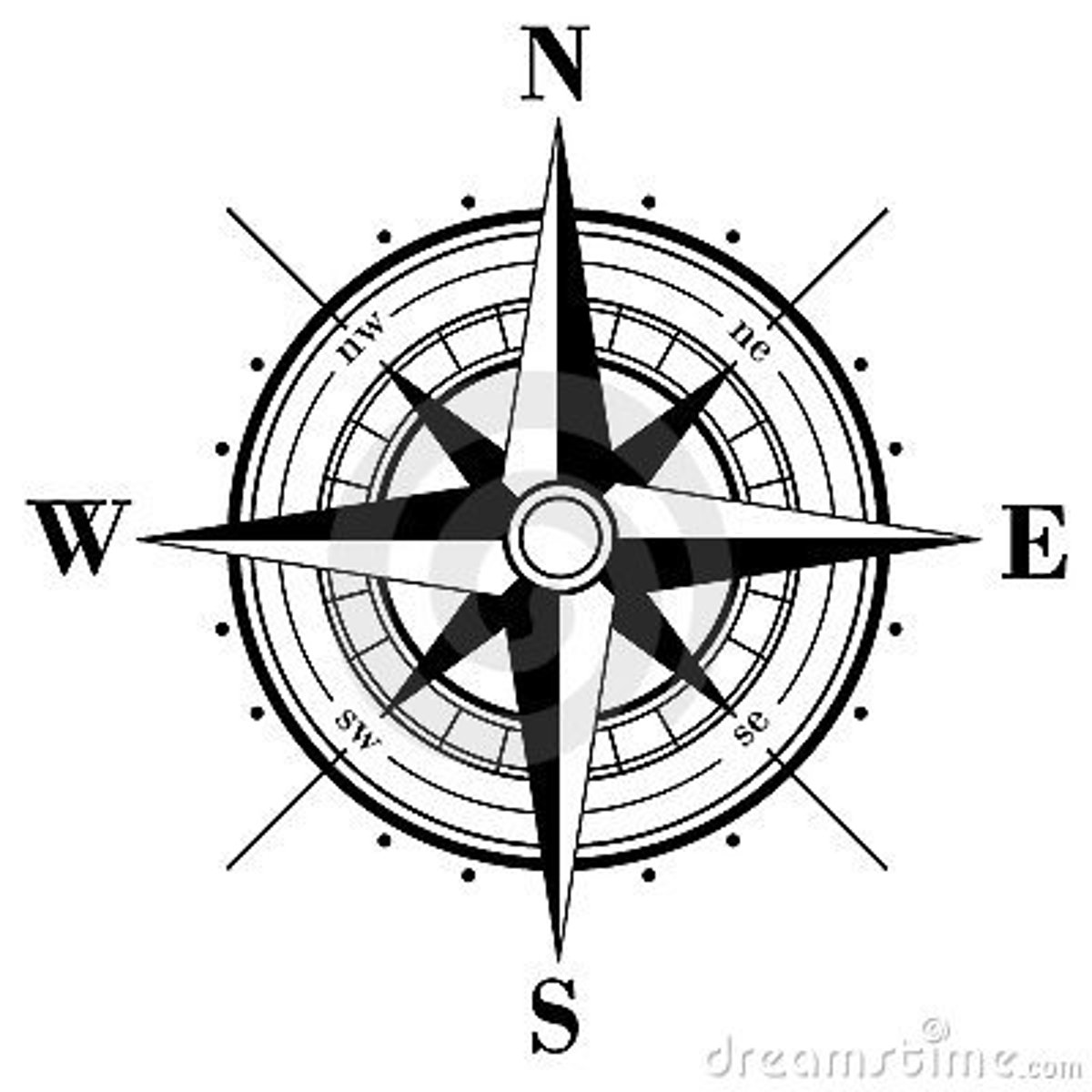
Compass Rose
Symbol on the map that shows direction (North, South, East, and West)
Continents
Large pieces of land that cover parts of the Earth: Asia, Europe, Africa, North America, South America, Australia, and Antarctica.
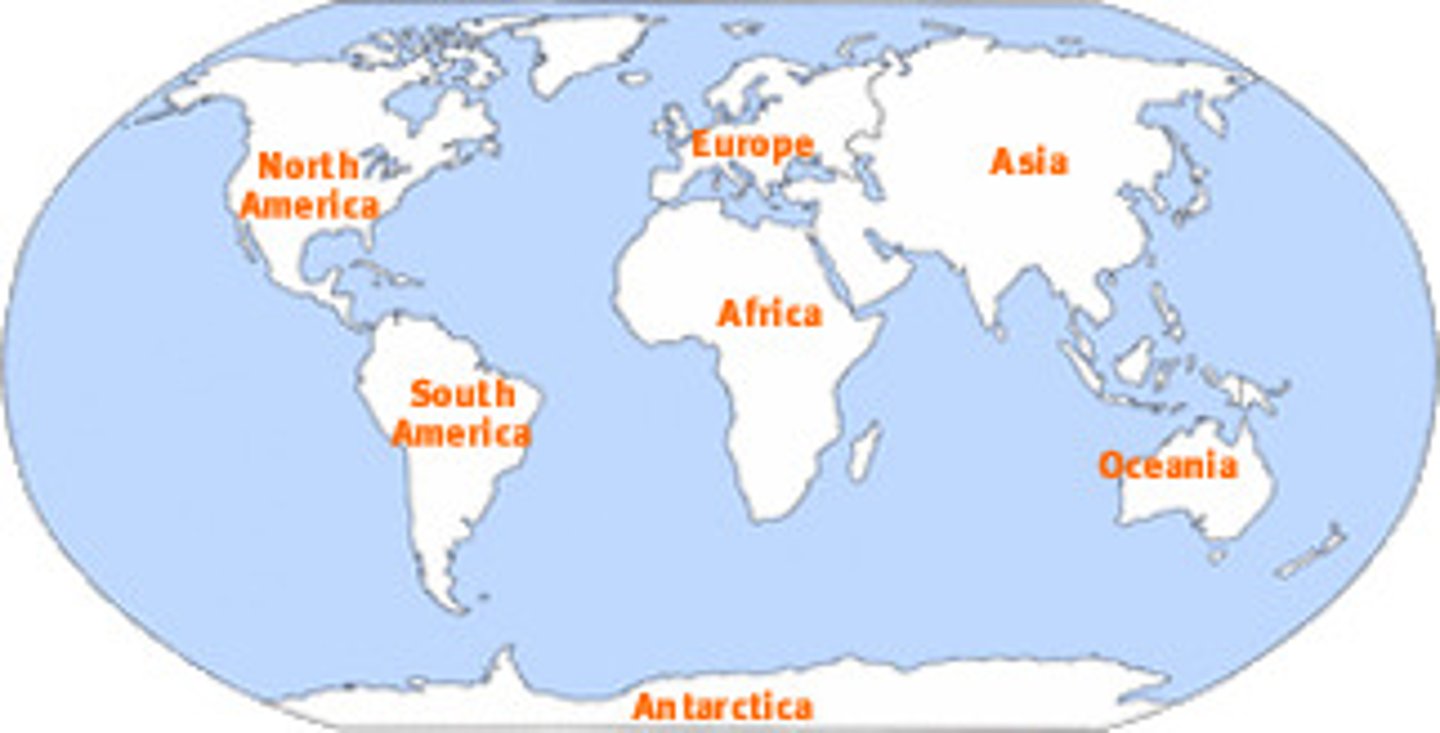
Equator
Imaginary line that divides the world into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. 0 degrees Latitude.
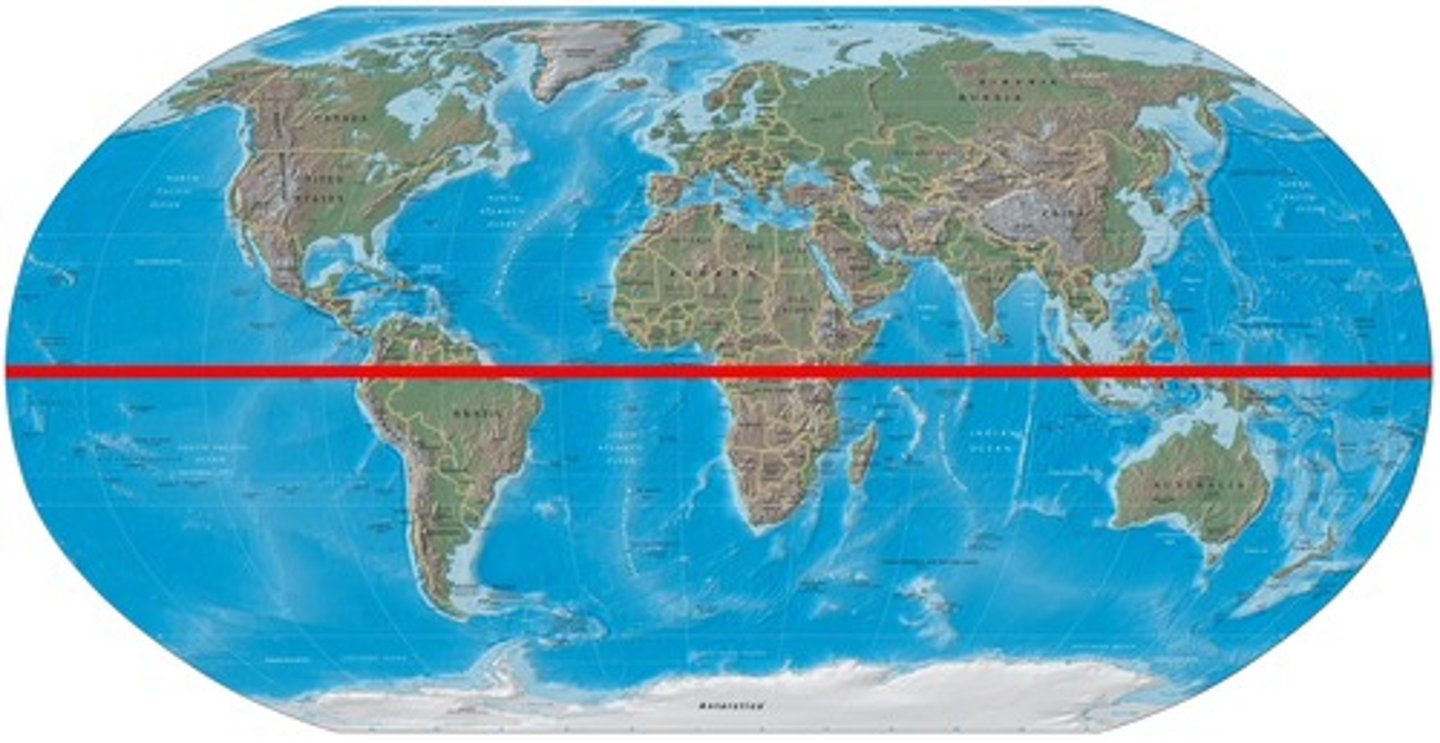
Hemisphere
Equal halves of a sphere.
Human-Environment Interaction
How people impact or are impacted by their natural environment.
Landforms
The different shapes and types of land on Earth.
Legend/Key
A table that shows what symbols mean on a map.
Location
Tells where thing are; can be absolute or relative.
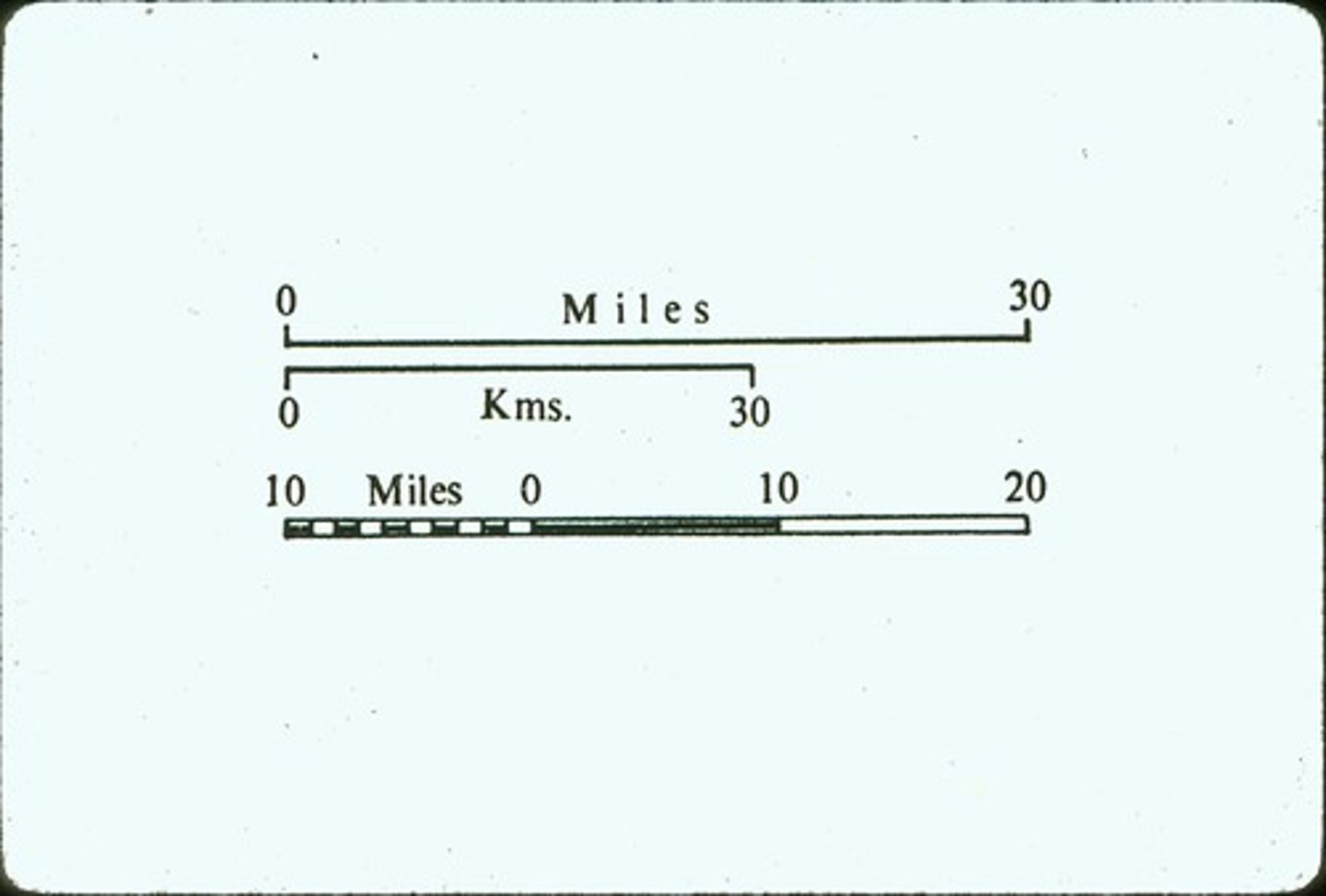
Map Scale
A scale to help to measure distance on a map that represents distance on the Earth.
Movement
Studies how people, products, and information moves.
Natural Resource
Everything humans get from the Earth to meet their needs for food, clothing, and shelter.
Physical Map
Shows landforms like deserts, mountains, plains and other landforms in a given area.
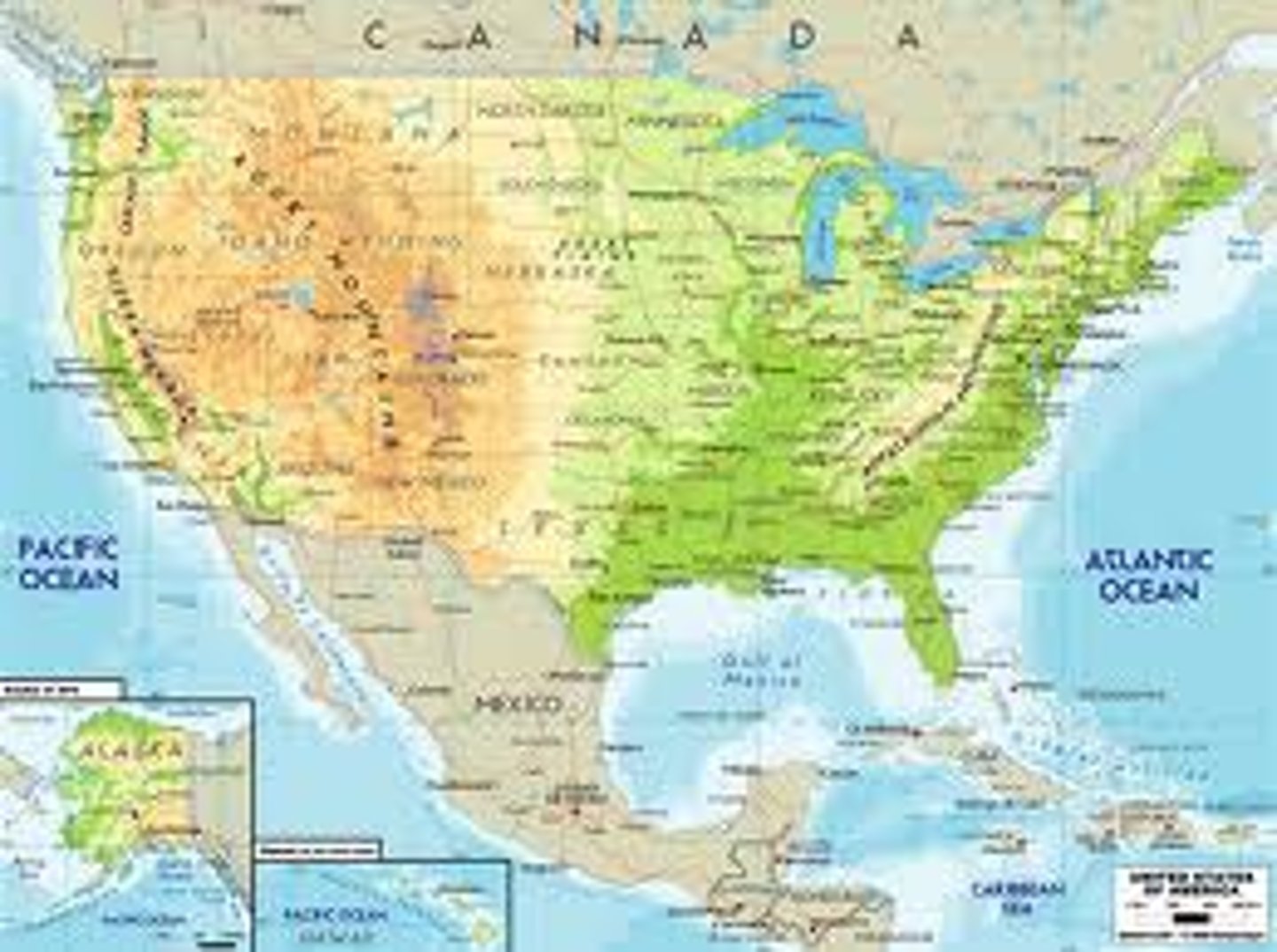
Political Map
Shows governmental boundaries of countries, states, and counties, the location of major cities, and they usually include significant bodies of water.
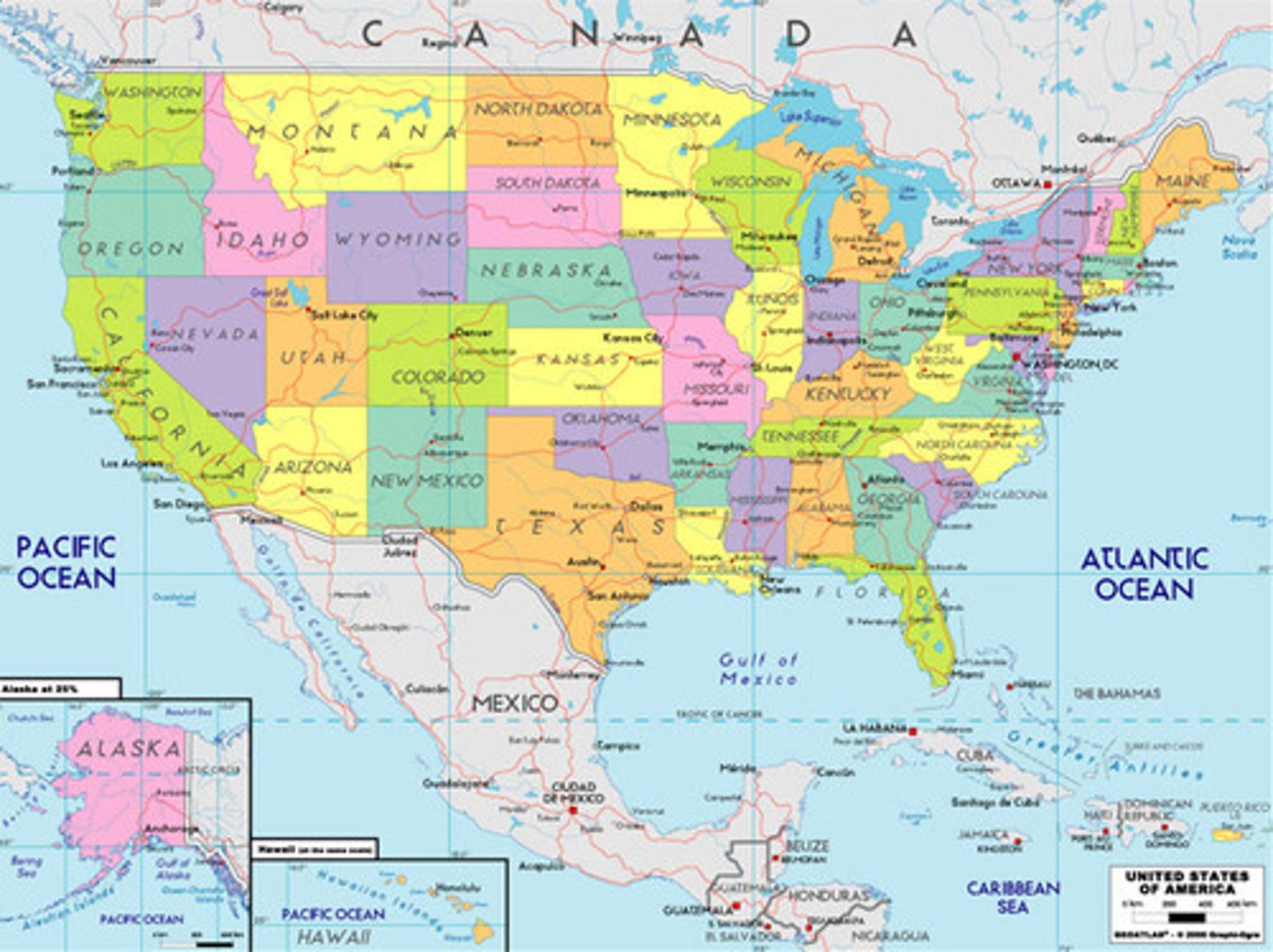
Thematic Map
A map that emphasizes a particular theme or special topic. They are different because they do not just show natural features like rivers, cities, political subdivisions and highways.
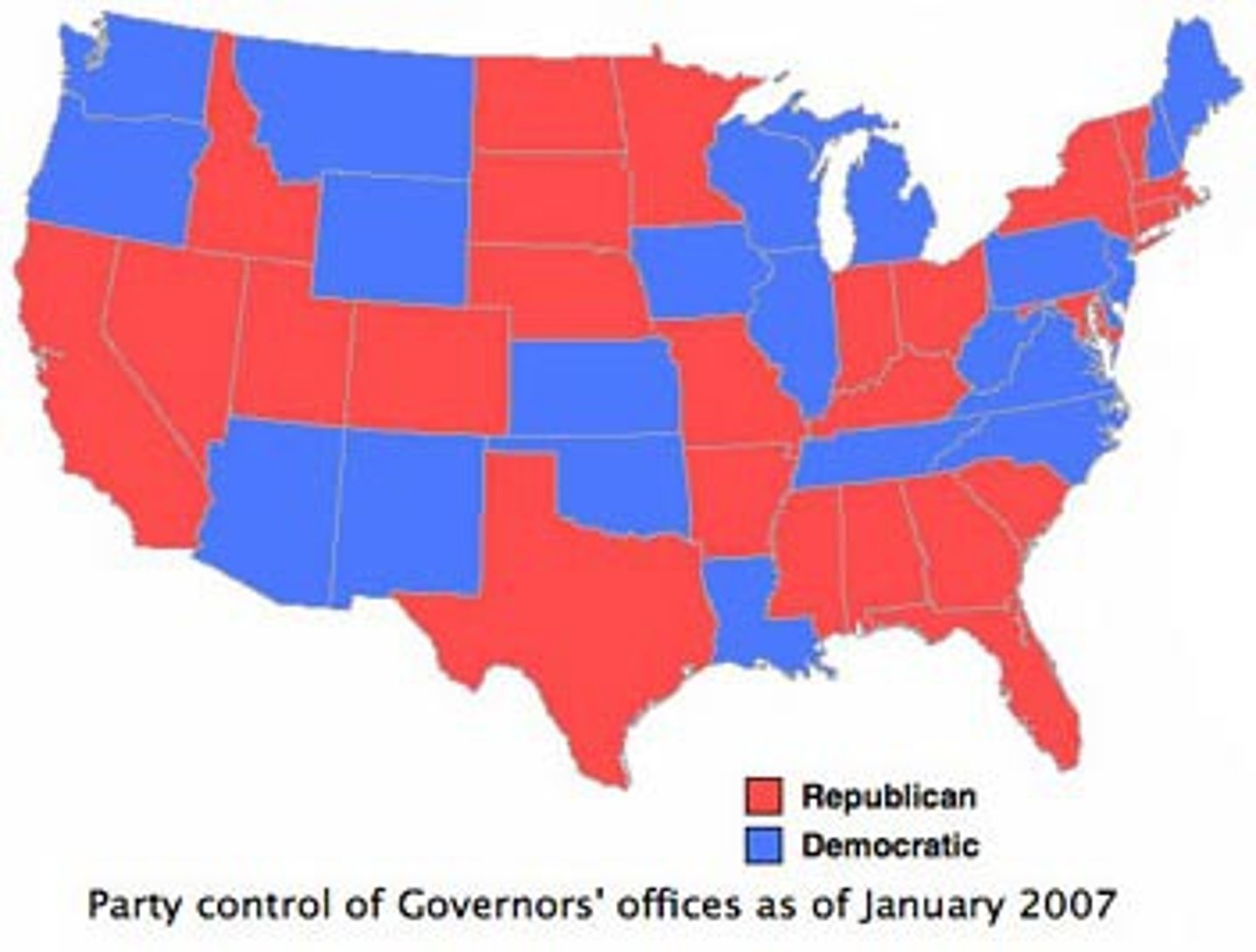
Place
Studies how one place is different from another. Differences can be physical, human, or traditional.
Prime Meridian
Imaginary line that runs North and South on the globe that divides the Earth into the Western and Eastern Hemispheres. 0 Degrees Longitude.
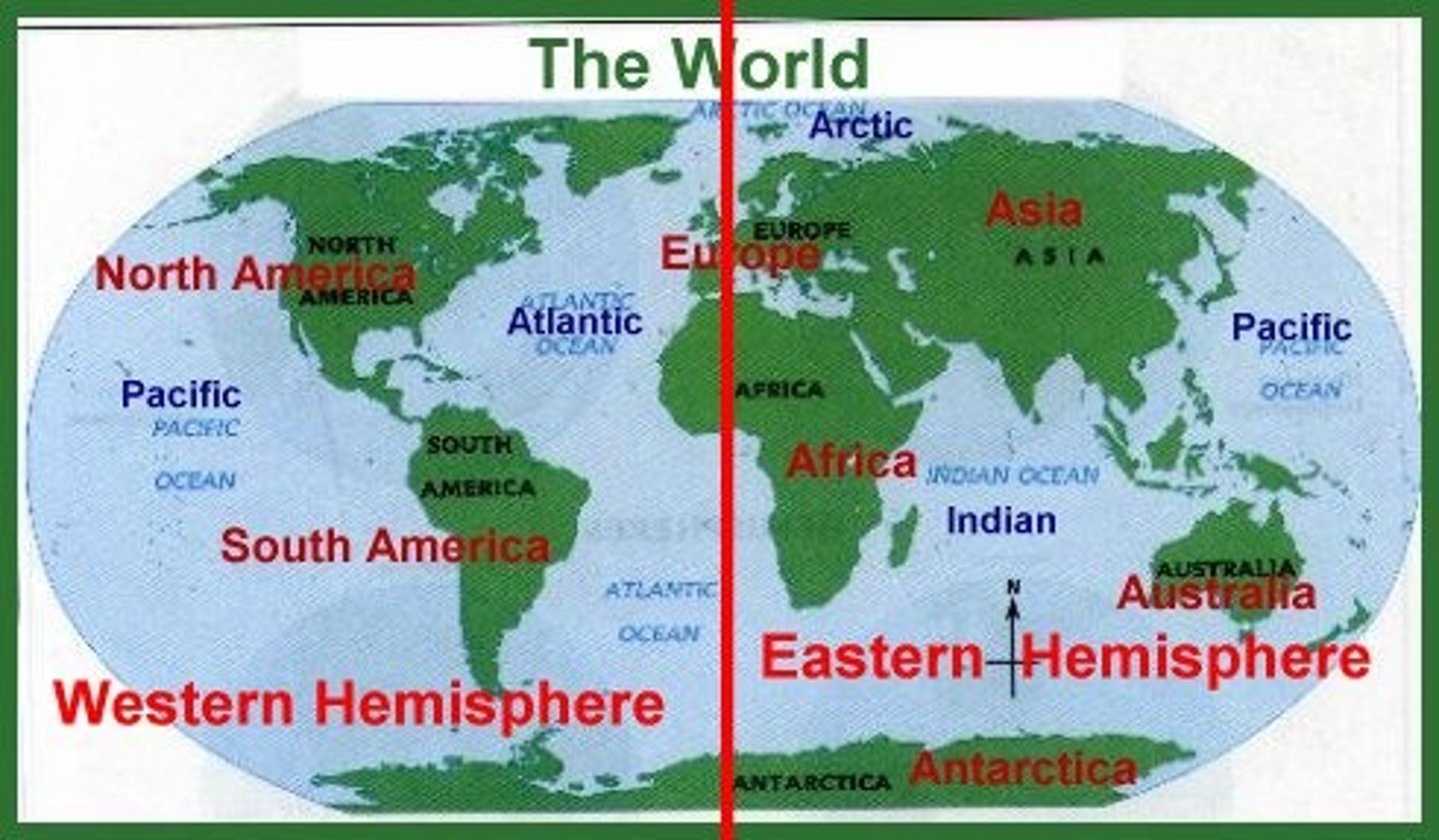
Region
Grouping places by their similar characteristic such as language, area, politics, religion, etc.
Relative Location
The use of cardinal directions to find the general location of a place.
Physical Features
Important parts of the Earth's surface, such as mountains, rivers, plains, and oceans.
Human Features
Parts of the Earth's surface that have been made by humans, such as roads, monuments, buildings, etc.
River
A large, flowing body of water that usually empties into a sea or ocean.

Mountain
A landform with high elevation.

Plateau
an area of high, flat land

Plains
a large area of flat land with few trees
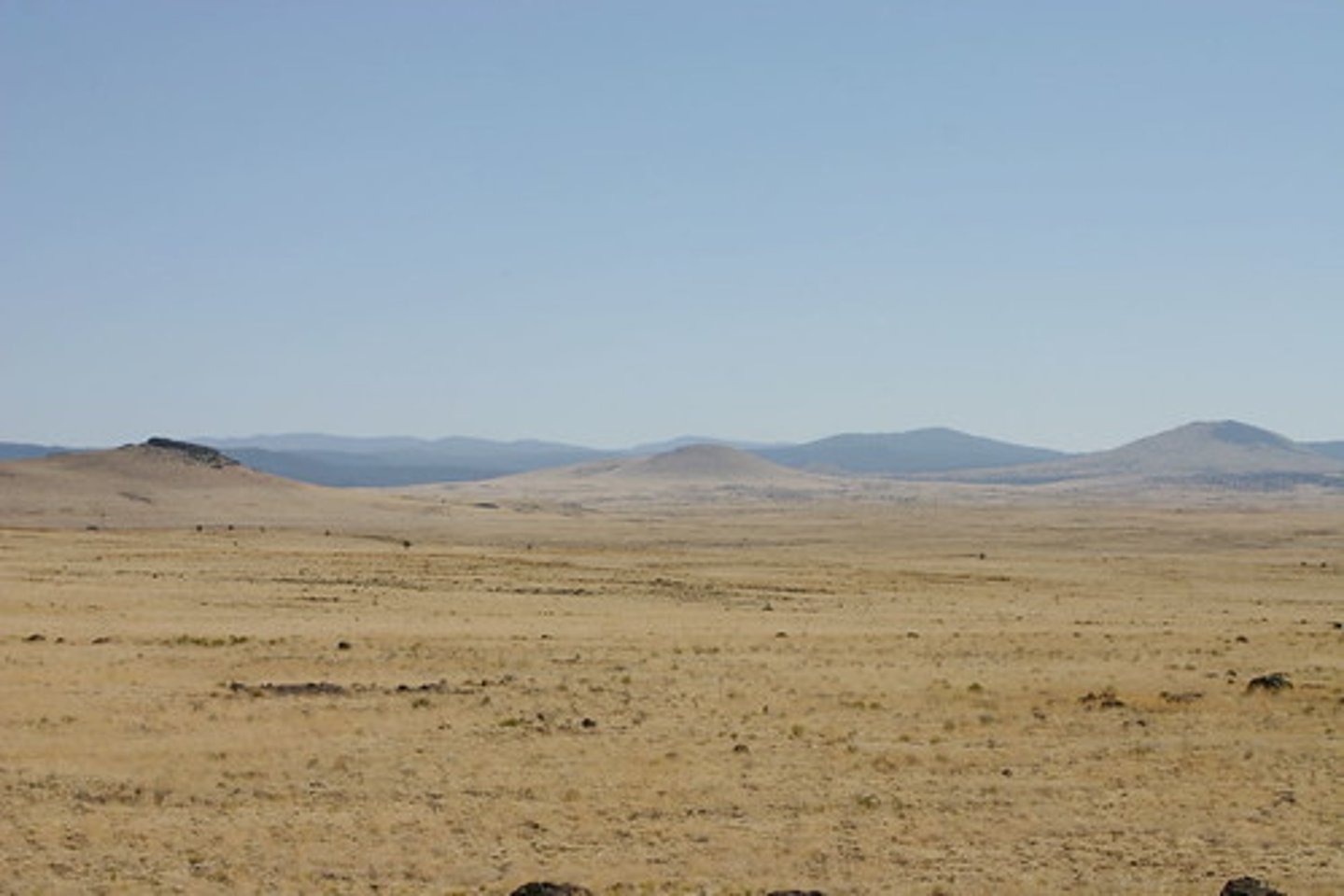

desert
An extremely dry area with little water and few plants
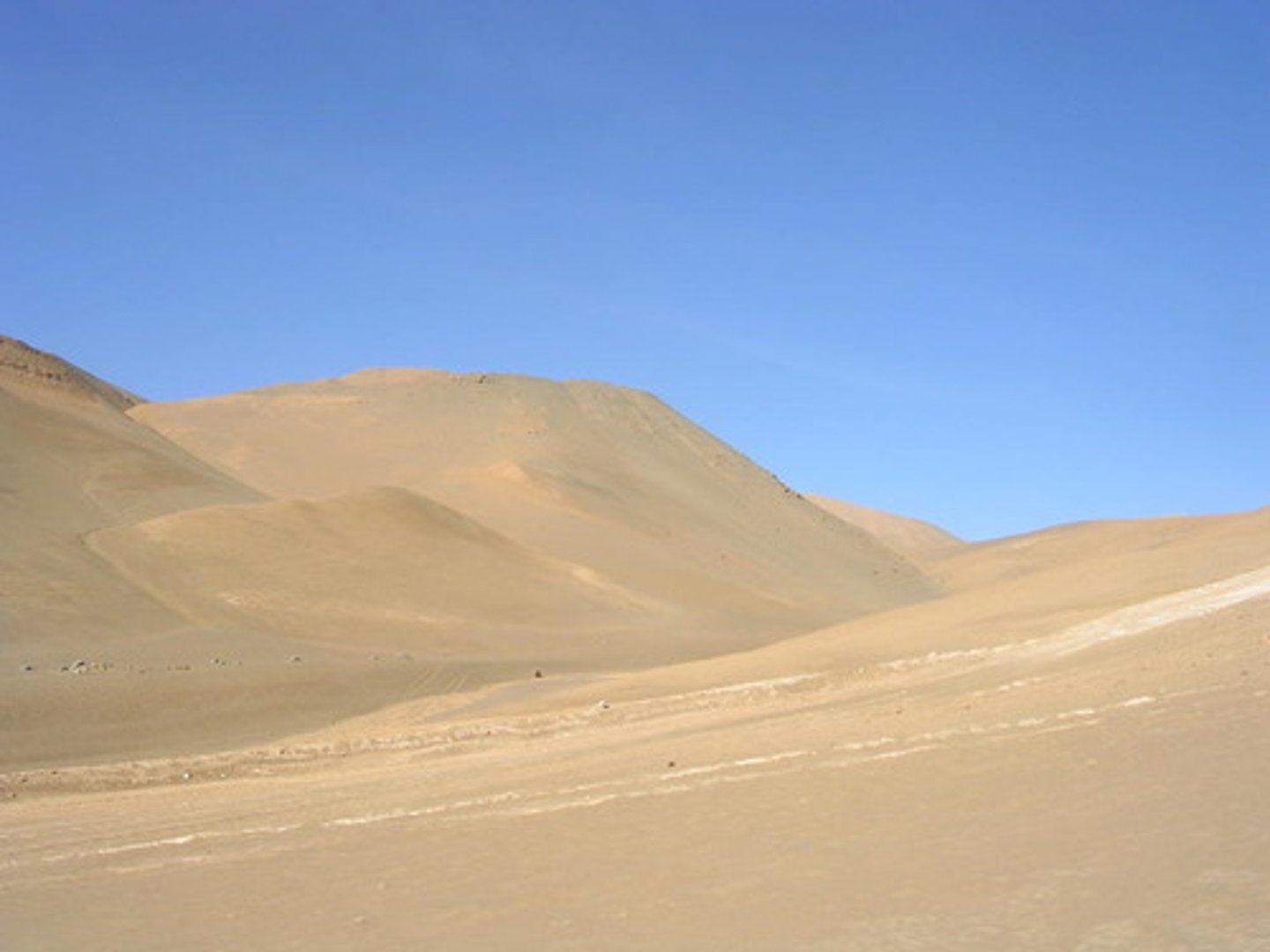

peninsula
A piece of land that is surrounded by water on three sides.
sea
large body of water completely or partly surrounded by land
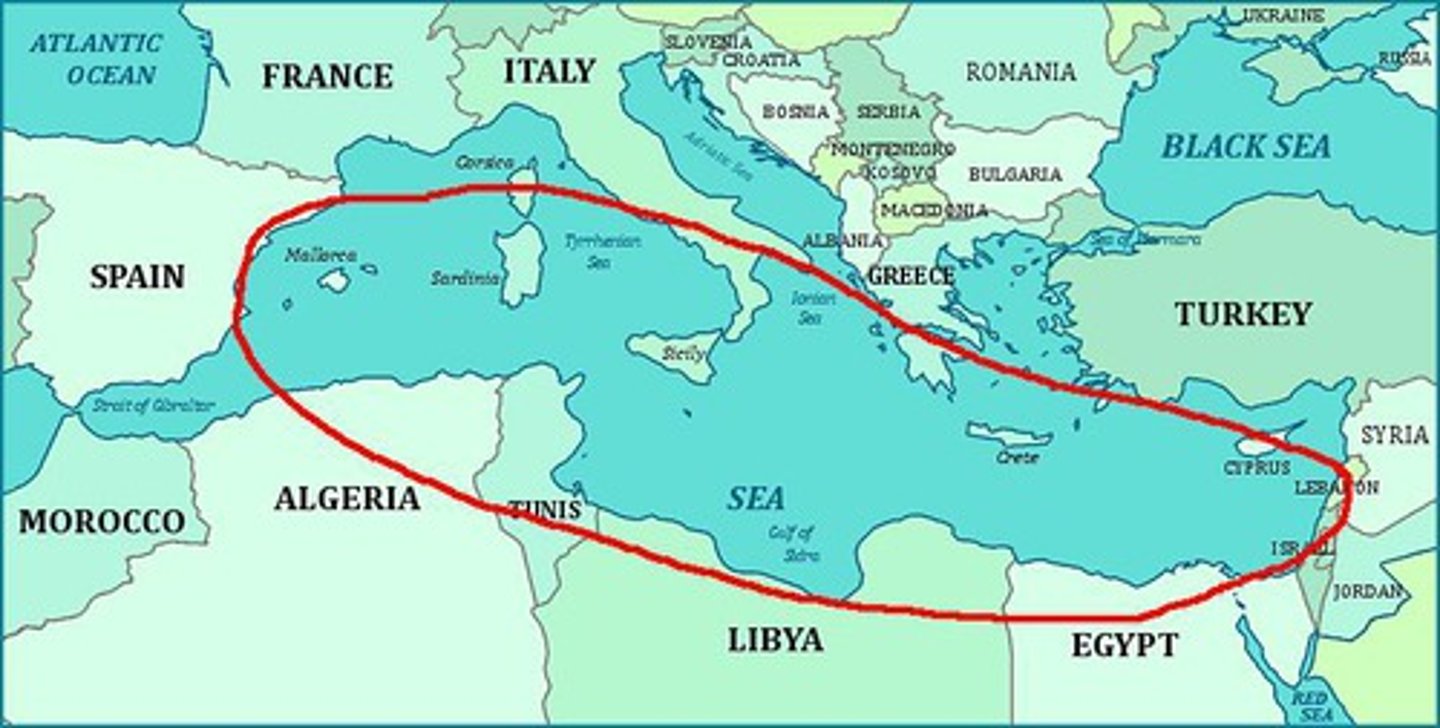
coast
the shore of a sea or ocean

valley
an area of low land between hills or mountains

lake
a large body of fresh water surrounded by land
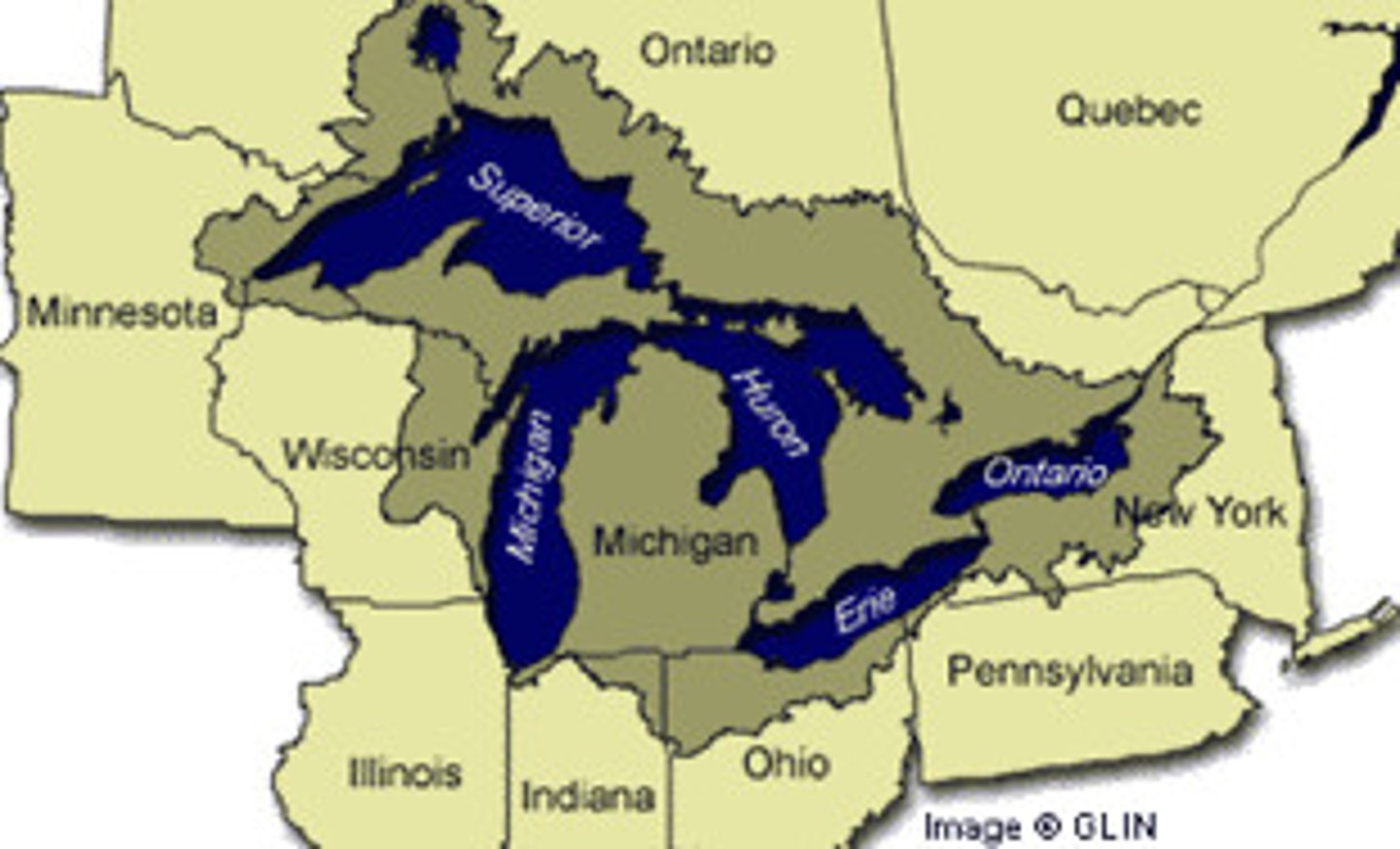
island
a piece of land surrounded completely by water
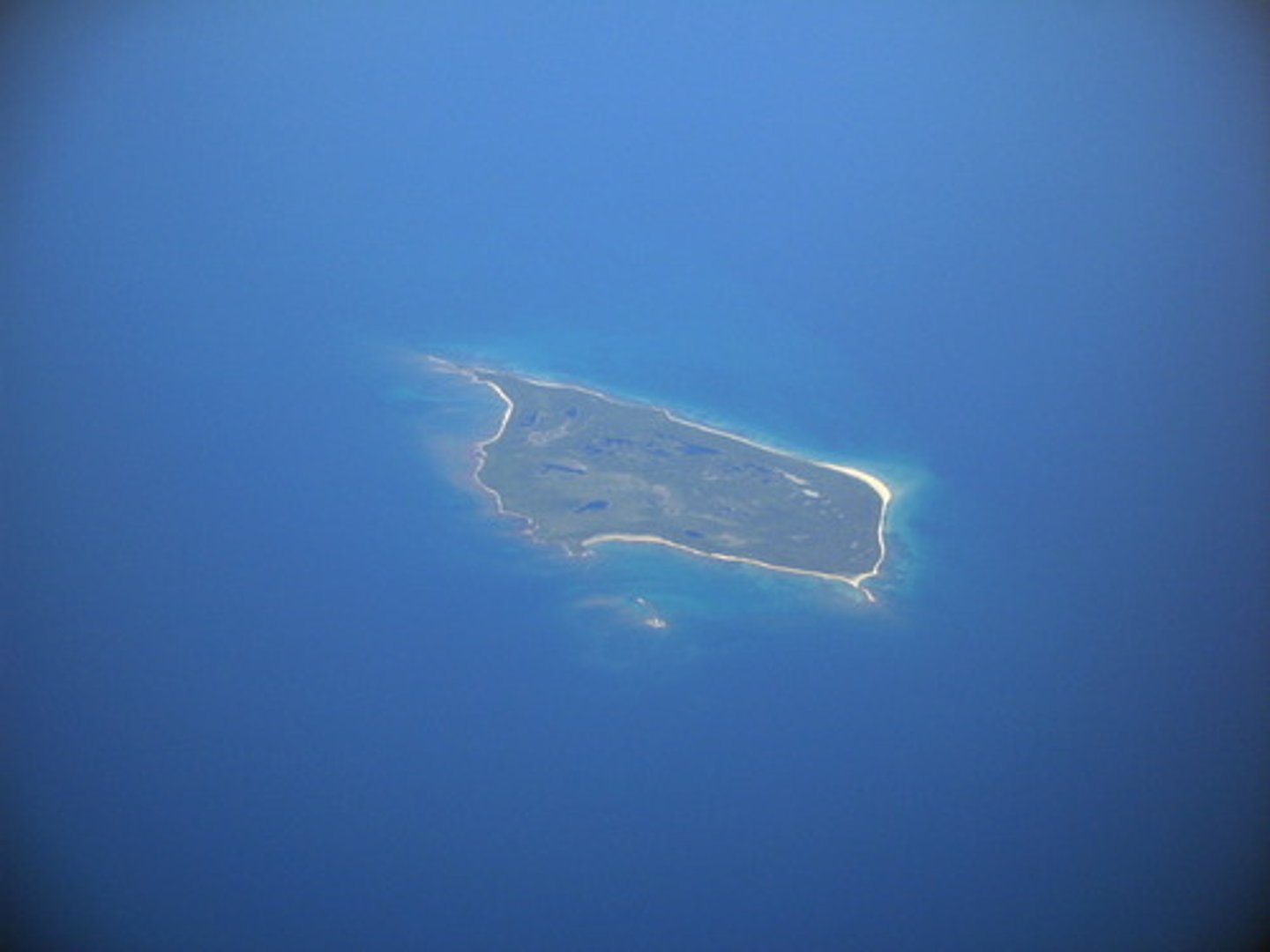

delta
a low triangular area where a river divides before entering a larger body of water
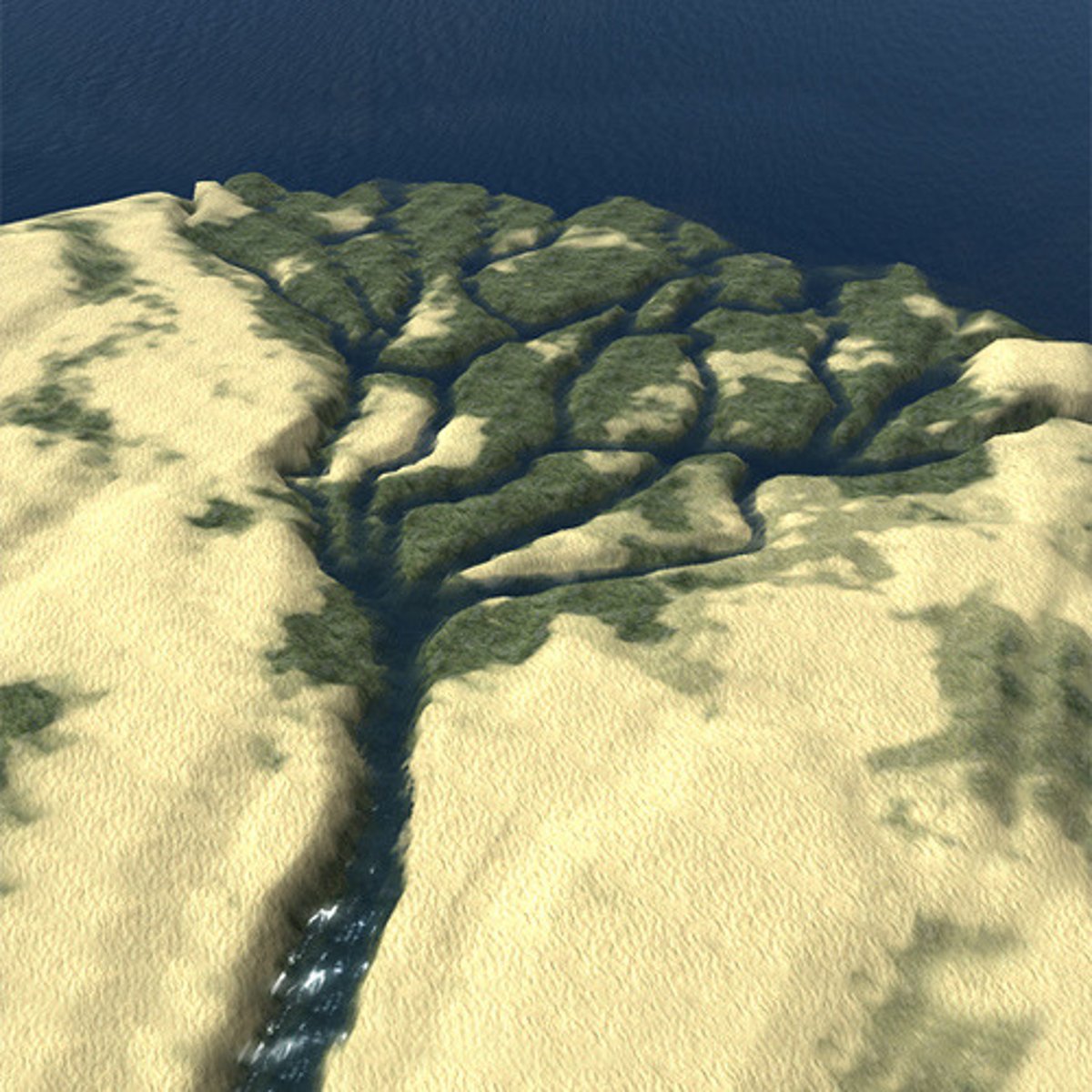

tributary
A stream or river that flows into a larger river
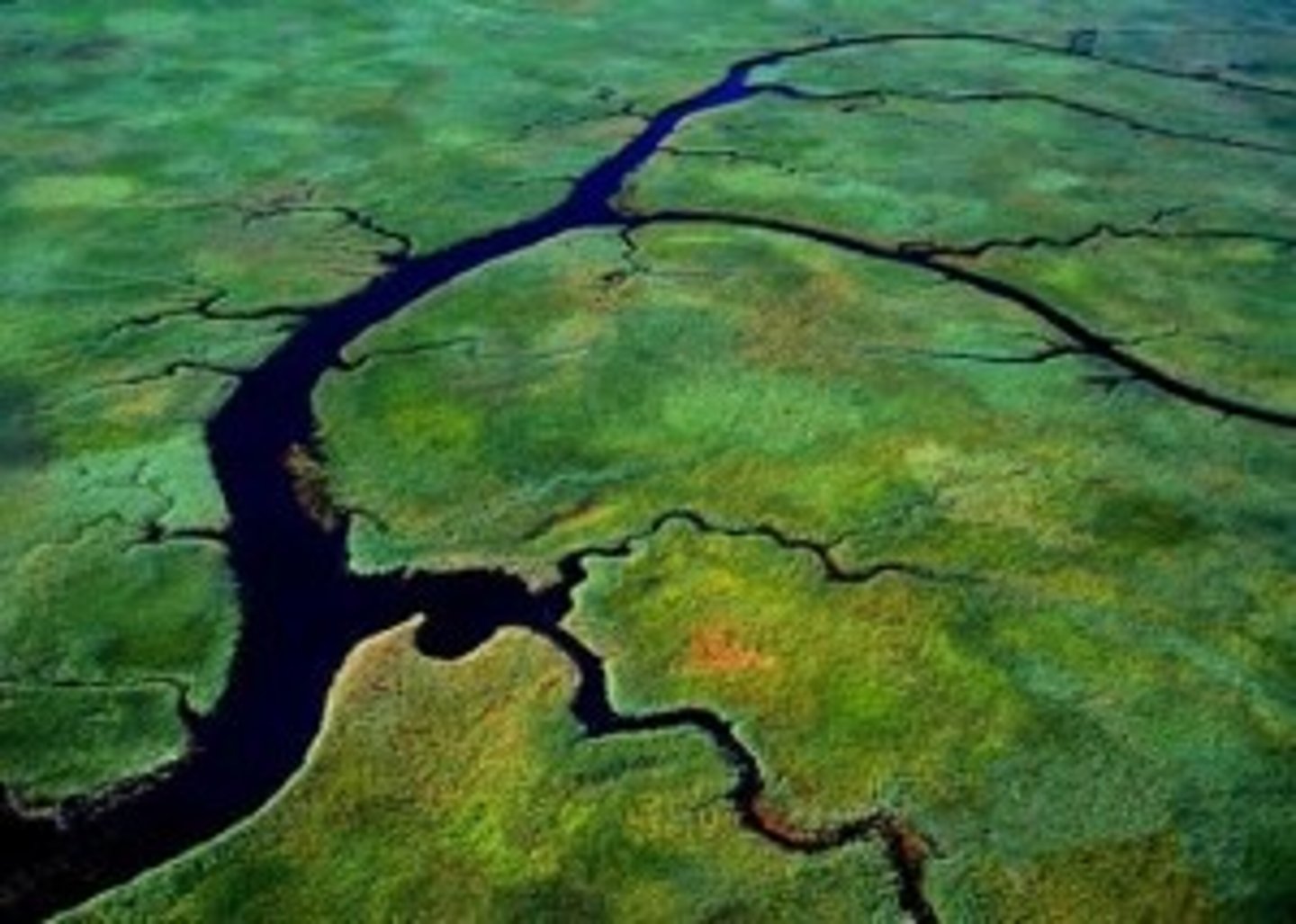

cliff
steep, high wall of rock, earth, or ice

gulf
a deep inlet of the sea almost surrounded by land, with a narrow mouth.
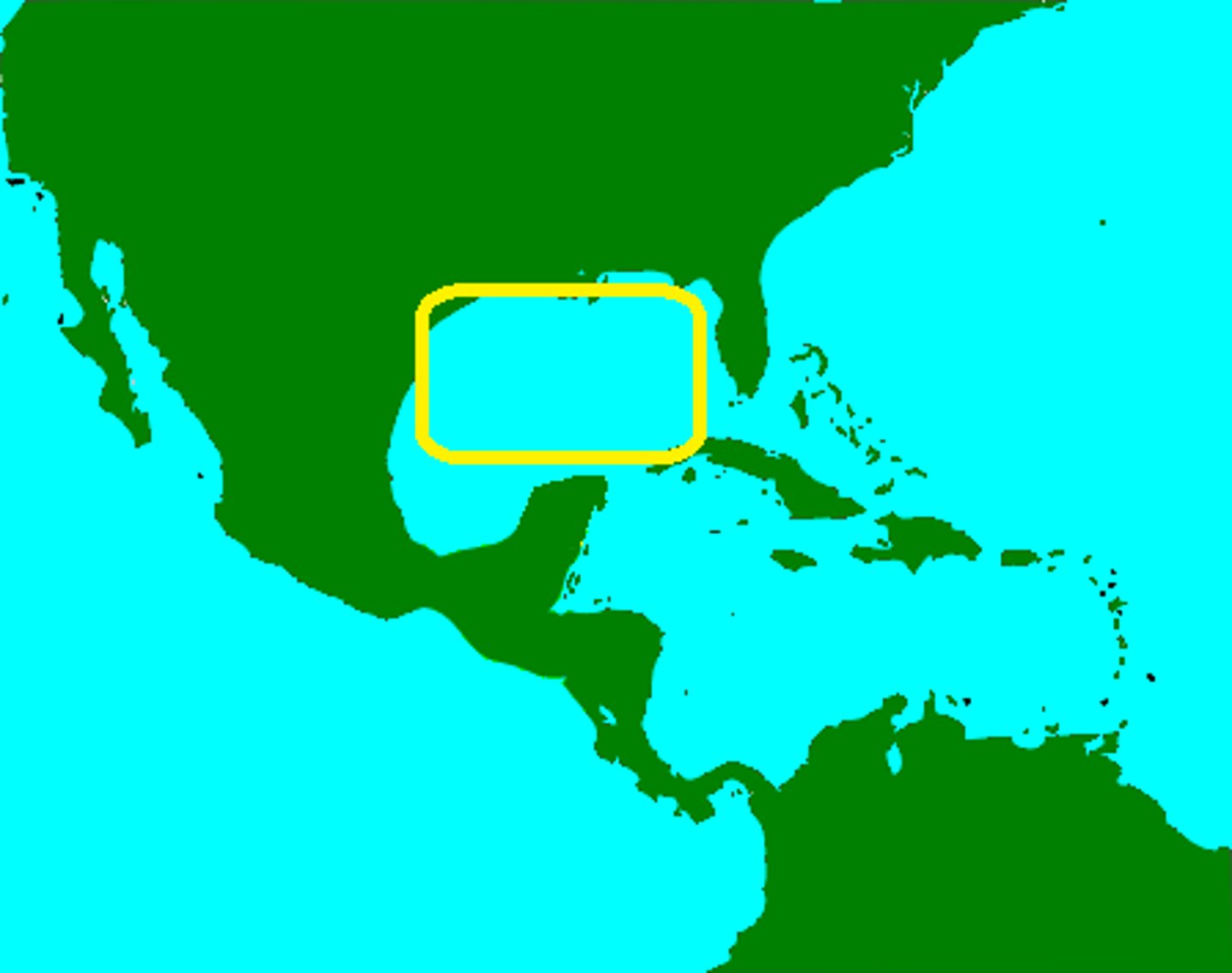
cataract
a large waterfall

bay
part of a large body of water that is smaller than a gulf
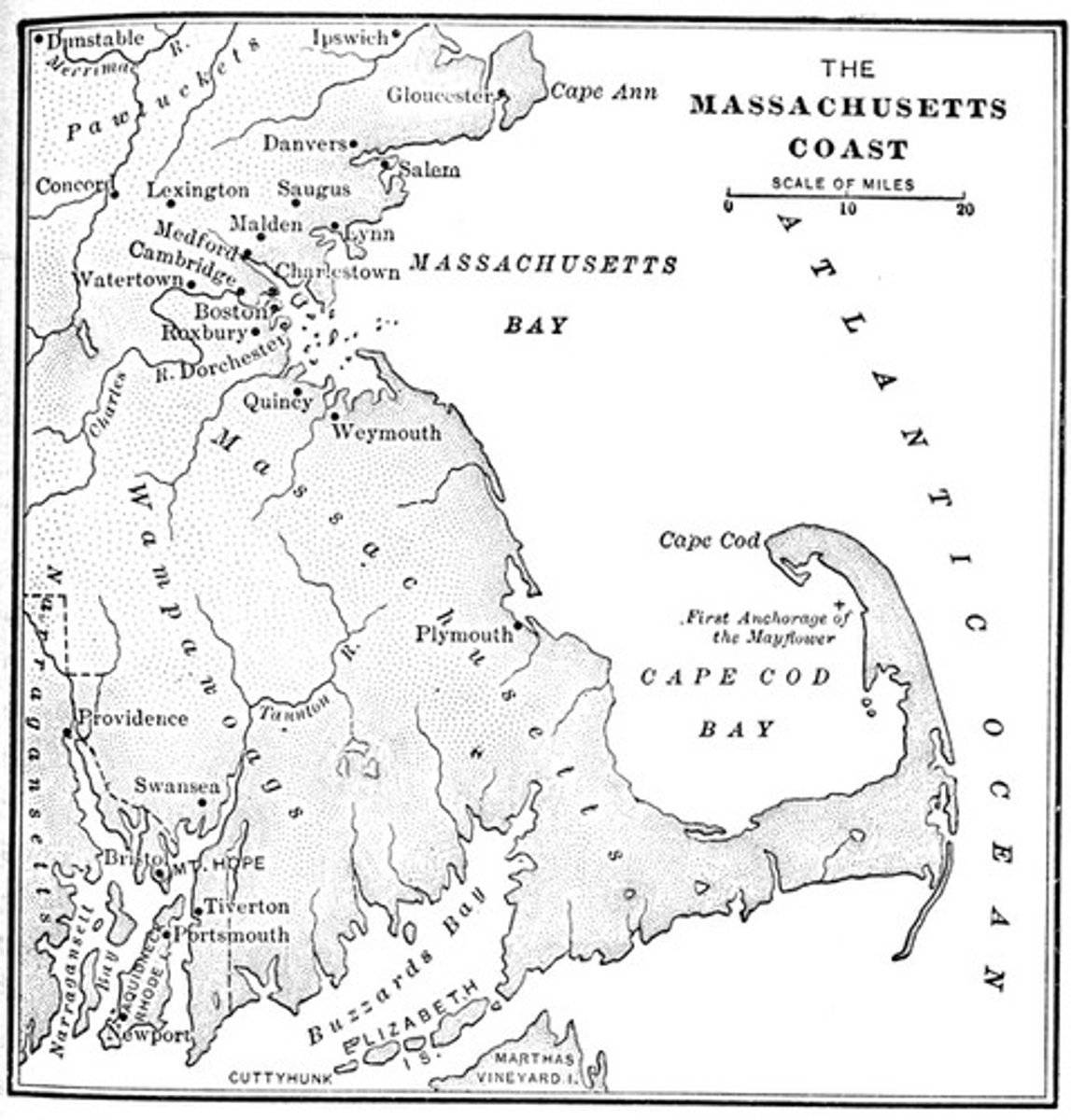
hill
a small area of land that is higher than the land around it
