3 Adrenocoticoids and adrenocortical antagonists
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Synthesized under the control of ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic hormone)
Natural adrenocortical steroids
– the predominant glucocorticoid in humans
Cortisol (hydrocortisone)
– the major mineralocorticoid of the adrenal cortex
Aldosterone
an aldosterone precursor, has both mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid activity
11-Deoxycorticosterone,
Control water and electrolytes
Mineralocorticoid
Homeostasis
Glucorticoid
A wide array of steroid compounds with various ratios of mineralocorticoid to glucocorticoid properties
Synthetic adrenocortical steroids
effects are mediated by two separate and specific intracellular receptors, the MR (mineralocorticoid receptor) and GR (glucocorticoid receptor)
Synthetic adrenocortical steroids MOA
Both the [] interact with these receptors resulting to complexes that modulate the transcription rate of specific genes and lead to an increase or decrease in the levels of specific proteins.
natural and synthetic steroids
Oral Adrenocortical Steroids
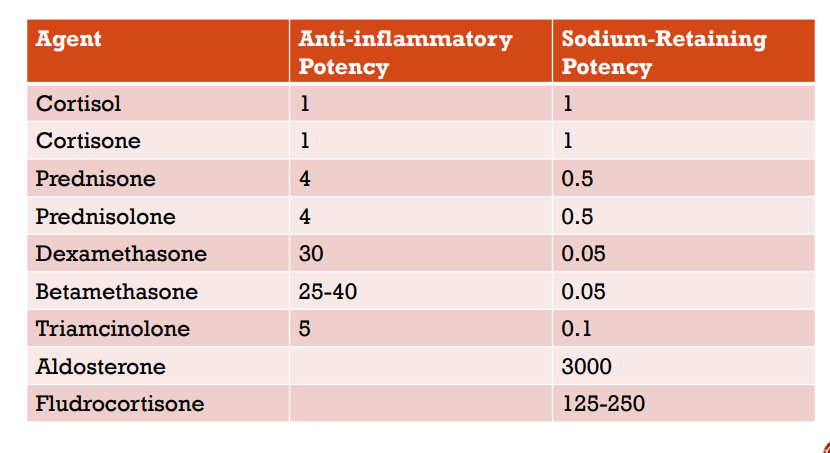
Anti inflamm and Sodium Retainin
Agent Table
Topical Adrenocortical Steroids
Potency
Potency Agent
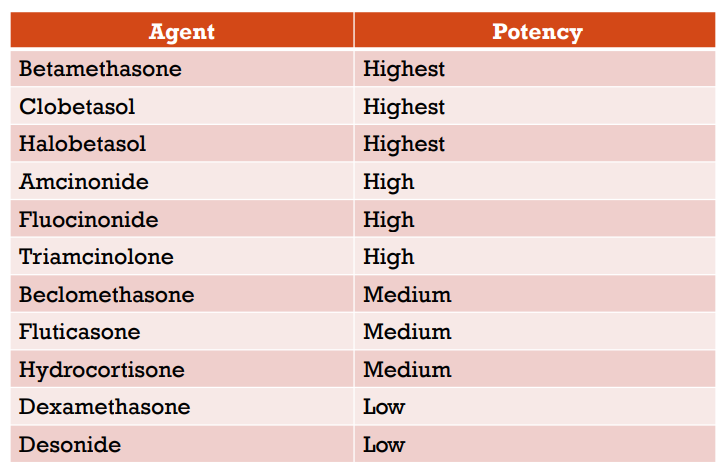
Agents with the longest half-life tend to be the most potent
Corticosteroids
Short-acting: Corticosteroids
: Cortisol (8-12 hours)
Intermediate-acting Corticosteroids
Prednisolone (12-36 hours)
Long-acting Corticosteroids
Dexamethasone (39-54 hours)
Corticosteroids Routes
PO, IV, IM, SQ, Inhalation, otic, rectal, topical
Corticosteroids
may relieve the clinical manifestations of the disease state while causing less severe suppression of the adrenal-hypothalamic-pituitary axis
Alternate-day therapy
Corticosteroids
Patients must be weaned off the drug over several days before discontinuation by using
progressively lower doses
used in replacement therapy for primary or secondary insufficiency (Addison’s Disease)
Glucocorticoids
also called adrenal insufficiency, is an uncommon disorder that occurs when your body doesn't produce enough of certain hormones. The adrenal glands, produce too little cortisol and, often, too little aldosterone
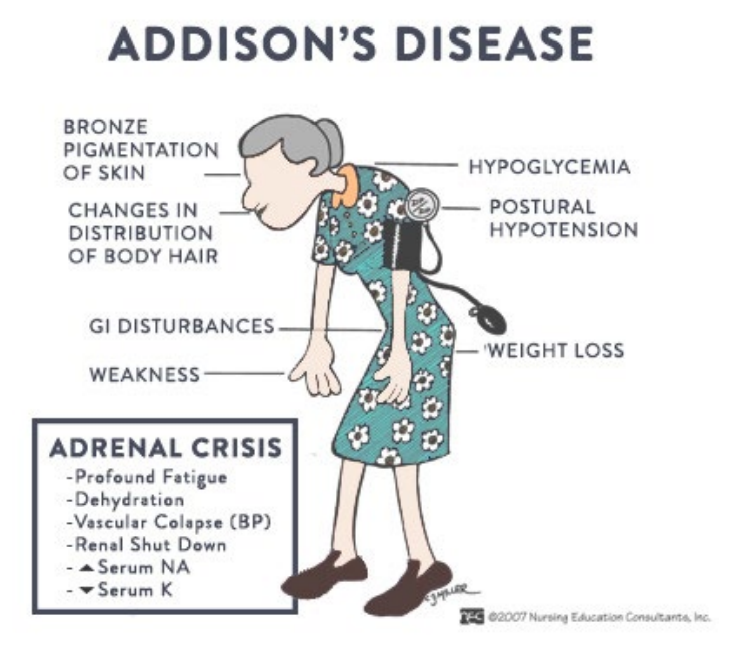
Addison's disease
Addison’s Disease This replacement therapy requires the use of both
mineralocorticoid and a glucocorticoid.
Addison’s Disease Symptoms
● The unique manifestation of Addison’s Disease is the skin discoloration. There is bronze pigmentation of the skin
● Hypoglycemia and Low Blood Pressure
● Profound/Chronic Fatigue
● Weight Loss
● Dehydration
● Craving for Salty Food
Inflammation and Immunosuppression
Glucocorticoids
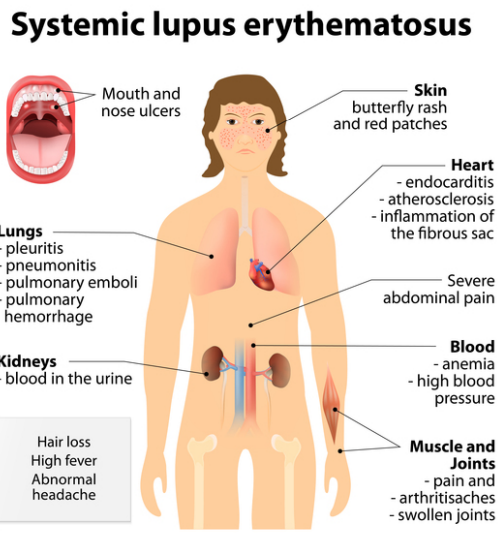
Used to treat RA, SLE, and other autoimmune diseases
Also used in hypersensitivity and allergic reactions
Can reduce organ or graft rejection
Glucocorticoids
This test measures the suppression of plasma cortisol following the administration of dexamethasone.
3. Diagnosis of Cushing syndrome (Dexamethasone Suppression Test)
Failure to suppress cortisol may indicate
primary Cushing syndrome.
Other Indicaitons:
Sarcoidosis, dermatologic disorders, idiopathic nephrosis of children, neuromuscular disorders such as Bell’s Palsy, shock, adrenocortical hyperplasia, stimulation of surfactant production and acceleration of lung maturation in a preterm fetus, and neoplastic diseases including adult and childhood leukemia
Glucocorticoids
is a disorder that occurs when your body makes too much of the hormone cortisol over a long period of time.
Cushing syndrome.
is sometimes called the “stress hormone” because it helps your body respond to stress.
also helps maintain blood pressure. regulate blood glucose, also called blood sugar
Cortisol
Cushing syndrome symptoms
● The opposite of Addison’s Disease
● When our body is always in a state, it triggers the body to produce and release too much cortisol
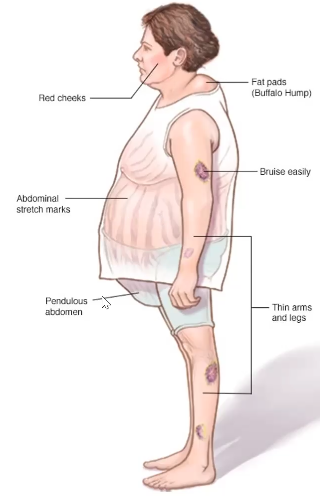
● The unique manifestation of cushing syndrome is Buffalo Hump wherein there is a fatty pads in the neck
● Striae or Abdominal Stretch Marks
● Pendulus Abdomen
● Bruise Easily
● Proportion of the body. In the middle part of the body, fat is concentrated compared to the arms and legs
primarily affect the kidney, regulating salt and water balance and increasing sodium retention and potassium loss.
Mineralocorticoids
agent of choice for long term mineralocorticoid replacement
Mineralocorticoids
Fludrocortisone
used in replacement therapy to maintain electrolyte and fluid balance in hypoadrenalism
Mineralocorticoids
Fludrocortisone
Mineralocorticoids
Fludrocortisone AEs
Sodium retention, hypokalemia, edema, hypertension
An adrenolytic agent
Suppresses the adrenal cortex and causes selective atrophy of the zona fasciculata and zona reticularis
Can reduce plasma cortisol levels in Cushing syndrome produced by adrenal carcinoma
Mitotane
adrenocortical carcinoma
Mitotane
Mitotane AEs
GI distress, confusion, lethargy, rash
blocks the activity of 11-hydroxylase, reducing cortisol production
Used diagnostically to assess adrenal and pituitary function
Metyrapone
An antifungal agent
At high doses, a potent inhibitor of several P450 enzymes involved in steroidogenesis in the adrenals and gonads
Can be used for Cushing syndrome
Ketoconazole