PBS Semester 1 Study Guide
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
define biomedical sciences
Application of principles of natural science to clinical medicine
what are the 3 parts of the hair shaft?
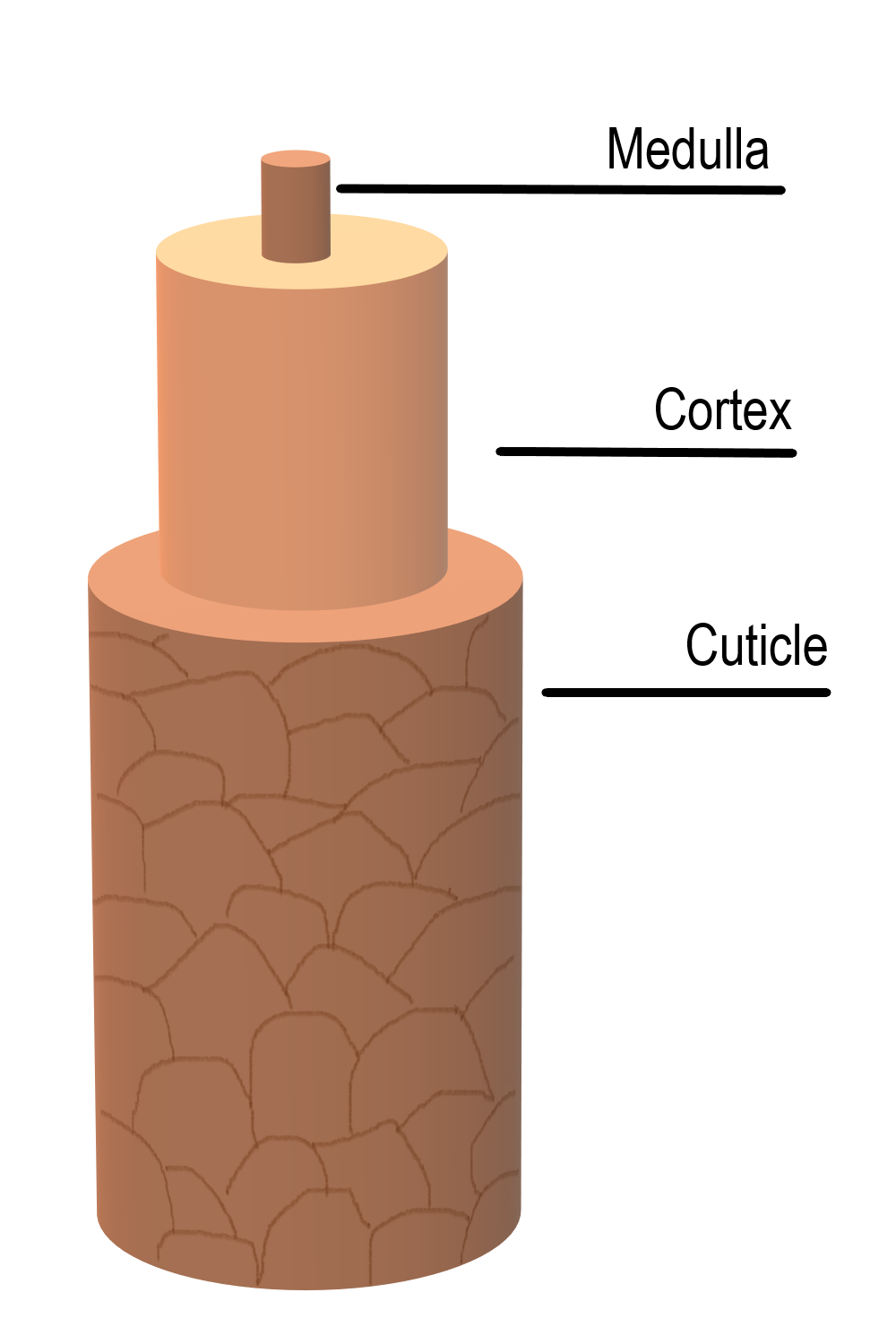
medulla (intermost)
cortex (middle
cuticle (outermost)
what are the 4 objective lenses of a microscope?
scanning: 40
low: 100
high: 400
oil: 1000
How to focus a microscope?
start w/ the lowest power
use the coarse adjustment knob
use the fine focus nob
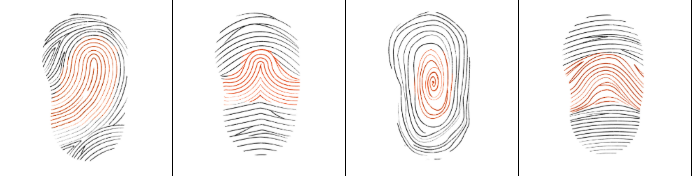
loop
tented arch
whorl
arch
What is fingerprint minutiae?
Tiny characteristics within the fingerprint
How would you read a polygraph test?
Look at the graph for changes compared to the subject’s baseline control data
Define independent variable
variable that is changed or manipulated
Define dependent variable
Outcome, measurable effect
Define control variable
variables that remain constant
Define control group
A group in an experiment where the IV is not applied, serves as a standard for comparison
Difference between accuracy and precision
accuracy: how close a measurement is to it's true value
precision: the ability to reproduce the measurement
What are red blood cells?
(erythrocytes): transports oxygen from the lungs to the body tissues, and carry carbon dioxide back to the lungs
What are white blood cells?
(leukocytes): destroy bacteria and foreign invaders; fight disease
How does the angle affect the blood stain pattern in blood spatter?
the longer the blood droplet, the smaller the angle
bigger the angle the more elongated
a 90 degree straight above angle the circular
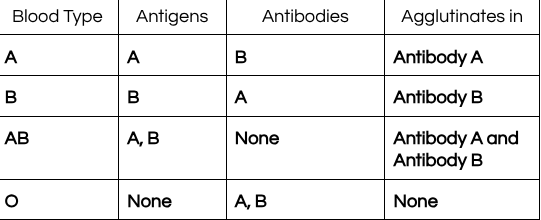
remember blood agglutinates with what type of blood it is
What is the universal donor and universal recipient?
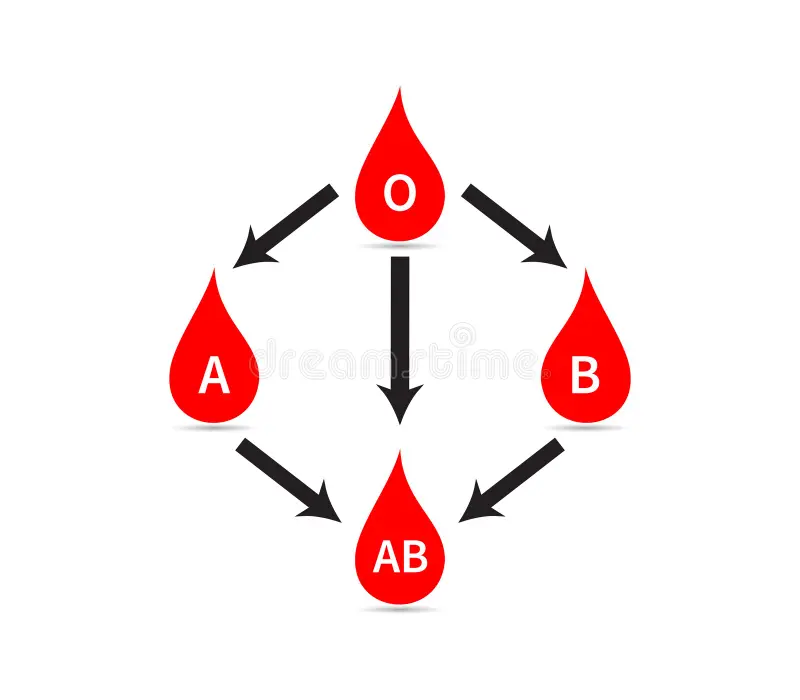
universal donor: O
universal recipient: AB
What is DNA?
A molecule that carries genetic info and found in the cells of all living things
Define antigen and antibody
antigen: proteins found on the surface of the cell membrane (RBCs)
antibody:opposite of antigens (found in the plasma)
What are the DNA instructions for?
Instructions to build proteins
What are the building blocks of DNA?
Nucleotides (phosphate, sugar, nitrogenous bases)
What are the 3 parts of a nucleotide?
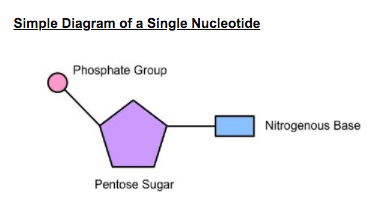
nitrogenous bases: adenine and thymine, guanine and cytosine
What is the backbone of DNA?
Phosphates and sugarsW
What type of bond holds the 2 DNA strands together
Nitrogenous bases, hydrogen bond
Chargaff’s Rule gives us the base pairing rules. What are they?
adenine = thymine
guanine = cytosine
Difference between a purine and pyrimidine?
purines: double ring structure (A + G)
Pure As Gold
pyrimidines: single ring structure (T and C)
Cut The Pie
Define genes and chromosomes
gene: segments of DNA that provide the instructions for a specific protein
chromosomes: tightly coiled packages of DNA - the nucleus
What makes DNA different from each other?
Different sequences of the bases
What are the 3 steps to perform DNA fingerprinting and analysis?
Break open the cell and the nucleus
Purify the DNA
Precipitate the DNA
Clean the DNA
What kind of charge does DNA have? Which direction will DNA travel through a gel?
Negative
Negative to the positive end
How many mL are in a uL? How many uL are in a mL?
mL to uL
mL x 1000 = uL
uL to mL
uL / 1000 = mL
What are the general steps to an autopsy?
external examination
internal examination
examination of organs
Who can perform an autopsy?
Medical examiner and coroner
Define manner, mechanism, and cause of death
manner: the circumstances that resulted in death (natural, unnatural, homicide, suicide, accident or unknown)
mechanism: what happens physiologically to result in death aka how the body reacts (cardiac arrest)
cause: what directly caused the victim’s death (gunshot)
What is rigor mortis, algor mortis and livor mortis (lividity)?
rigor mortis: after the body stops function, muscles contract and stiffen
algor mortis: after death, the body begins cooling or heating to match the temperature of the body’s surroundings (postmortem change in body temperature)
livor mortis: blood at the mercy of gravity, blood settles and collects on the body facing the ground. bluish color seen on skin where blood pools
Equation to convert equation between Celsius to Fahrenheit
F = (C x 1.8) +32
Equation to convert between Fahrenheit to Celsius
C = (F-32) / 1.8
Define ambient temperature
The temperature of the surroundings
(has to between 68-73)
Glaister equastion
98.4-rectal temperature / 1.5 = apx hours since death
difference between physiological, estimated and legal time of death
physiological: the time when the decedent’s vital functions actually ceased
estimated: the time the medical examiner estimates the death occurred
legal: time of death recorded on the death certificate when the body was found
What does a toxicologist do?
analyzes these sample for the presence of any substances that may have contributed to the decedent’s death
What are the 5 main components of the digestive system and what do they do?
oral cavity: food enters
esophagus: transports food from mouth to stomach
stomach: breaks down food
small intestine: continues to break down food and absorbs nutrients
large intestine: reabsorbs water and forms waste
What are confirmatory test?
Specific tests that can determine the exact identity and composition
What are platelets?
(thrombocytes): small cell fragments involved in blood clotting
What is plasma?
plasma: liquid that holds all cell fragments (antibodies found here)