EEG Recording and Methodology
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
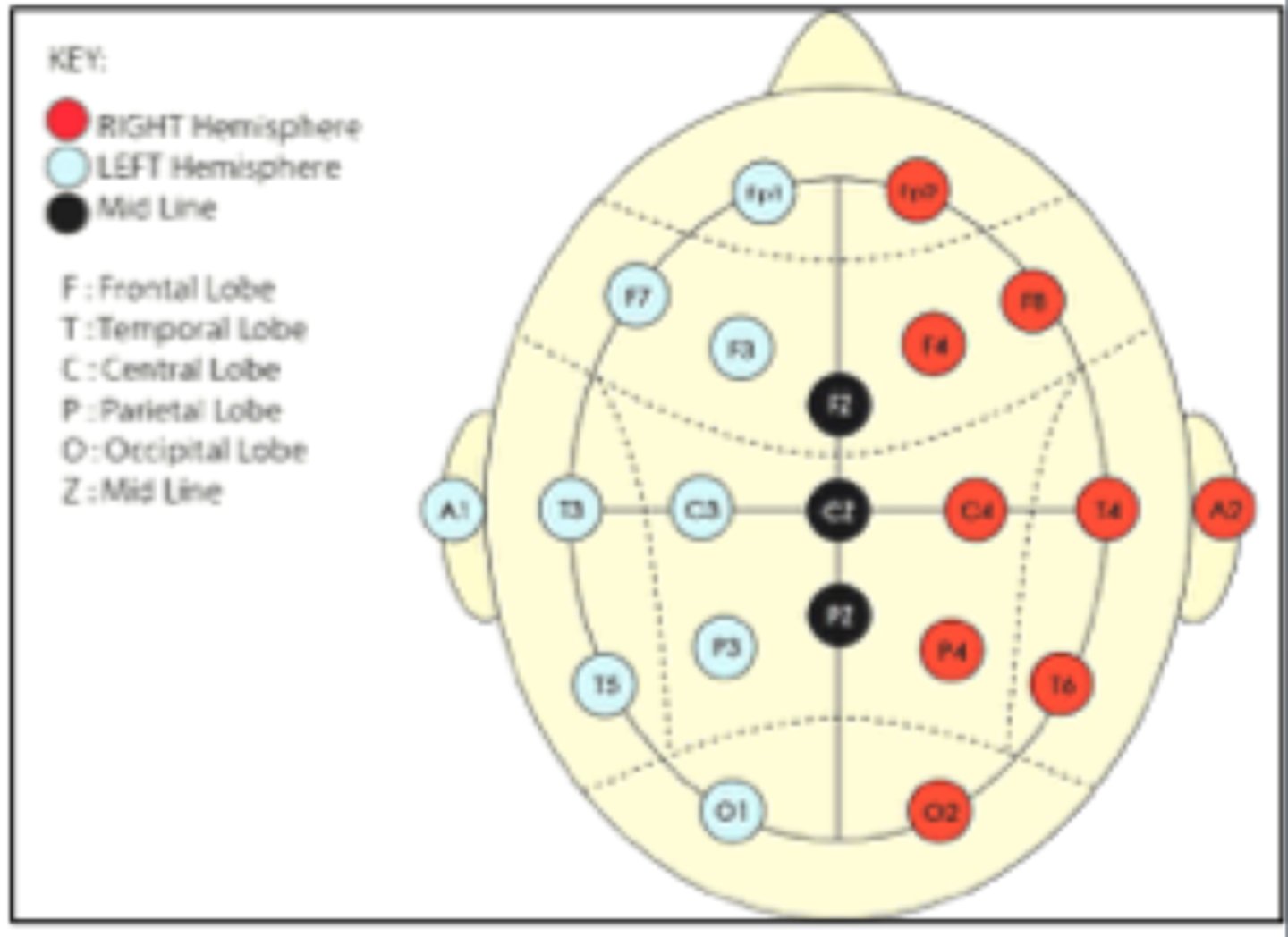
10-20 electrode placement system
measurement system designed to accommodate different head sizes
-even numbers on the left, odd on the right
-labels for brain region
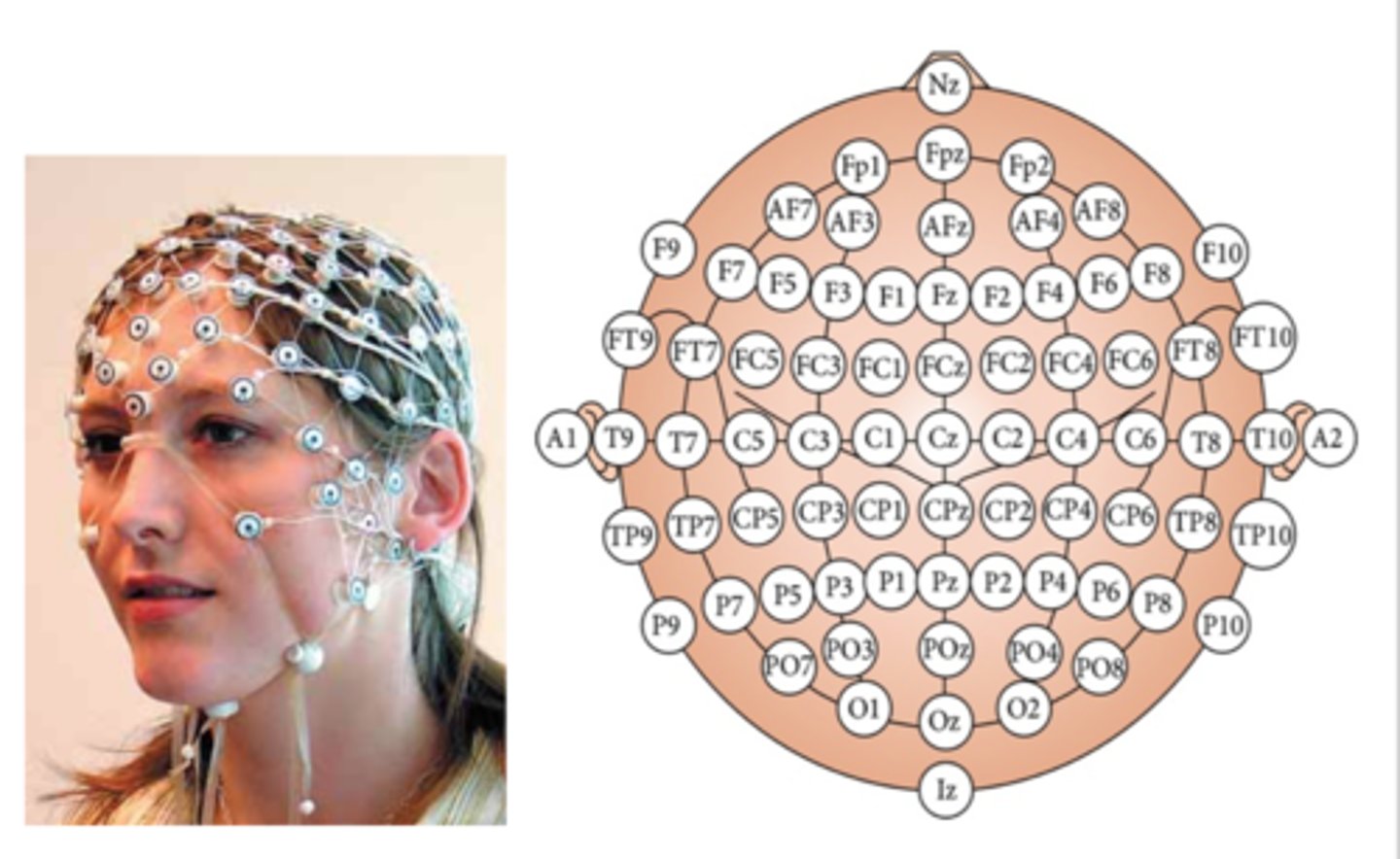
10-10 electrode placement system
electrode placement system where electrodes along straight lines are placed 10% of the nasion to inion distance from one another
How are numbers organized on an electrode cap?
low numbers are located closer to the midline, and they go up on either side from the midline (1-9 on left, 2-10 on right)
What impedances are involved in EEG and do we want them low or high?
electrode and amplifier input, electrode should be low, amplifier input should be high
electrical double layer
a build up of charges at metal interfaces - filters out low frequencies from the EEG signal (high pass filter), occurs with many kinds of metals
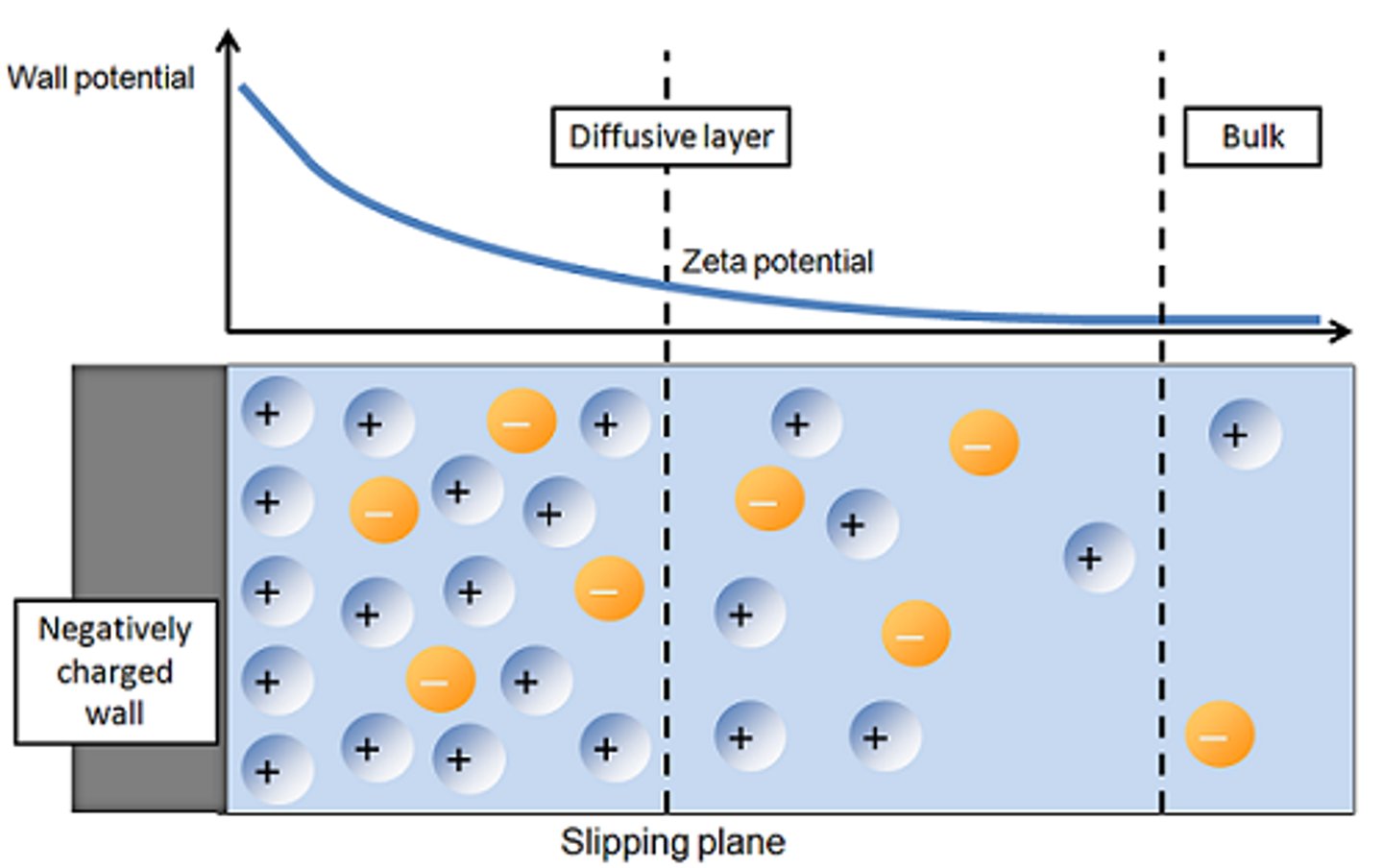
How can an electrical double layer be eliminated?
by using a reversible electrode, like Ag/AgCl (ideally with them mixed together to avoid damage to the metals with cleaning)
What happens if electrode impedance is too high?
current from other sources will be induced in the electrode circuits
What value should electrode impedance be at?
less than 10kOhms, but modern systems with high amplifier input impedance can have as high as 30-50kOhms
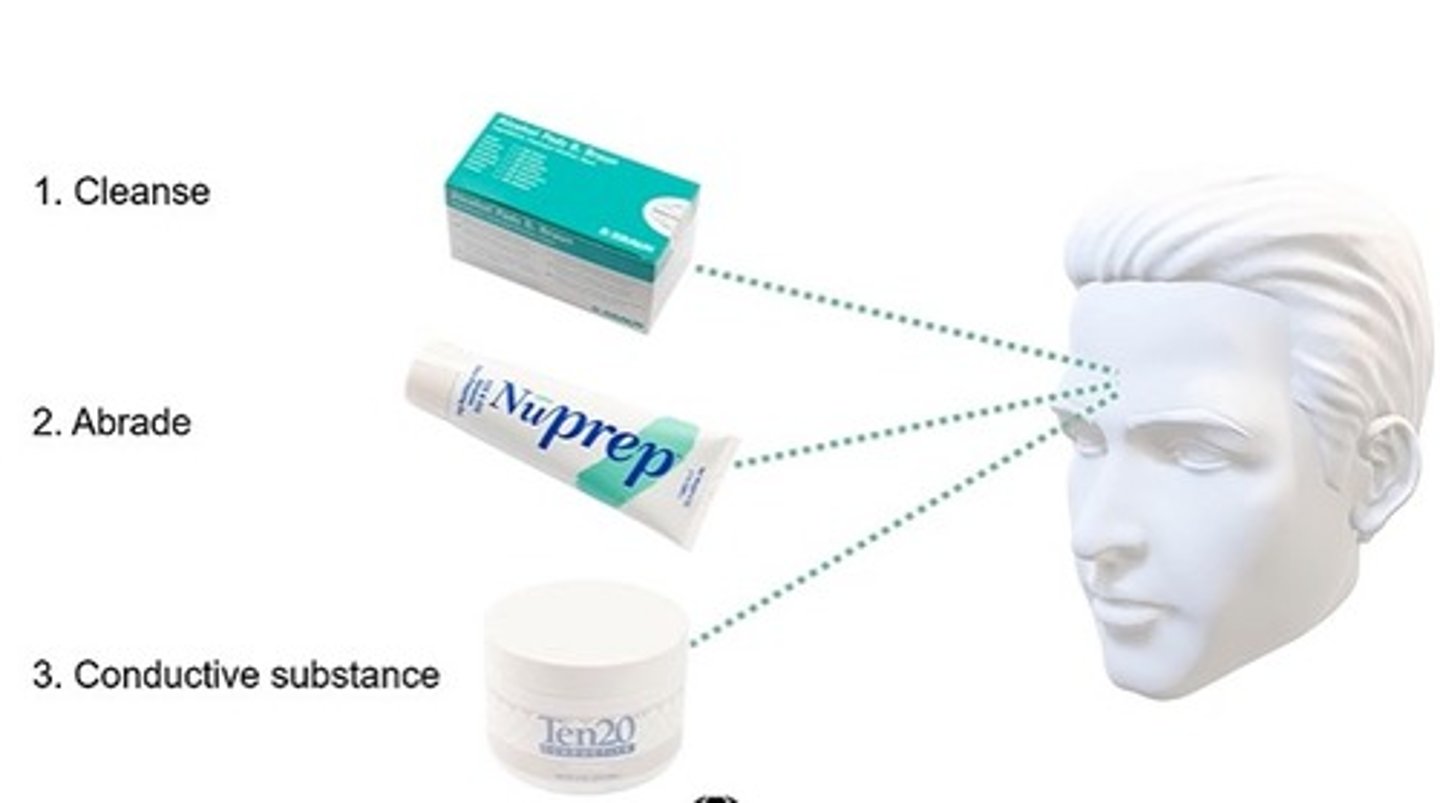
Electrode Impedance
Measure of the opposition of electrical current flow across the electrode; test performed at the start of each programming session
Amplifier Input Impedance
ability of amplifier to counteract electrode impedance and avoid voltage loss
How does electrode size impact EEG recording?
bigger is better, until electrodes encroach on each other's space, creating a larger field with less specificity
How does metal choice for electrodes impact recording?
Certain metals act as high pass filters, making the signal 2 peaks instead of a box, especially metals like Pt, Au, even Sn and Ag. This matters much less with a high amplifier input impedance though
What minimum of electrodes are needed to record EEG?
an electrode pair consisting of an active and reference electrode, and a ground electrode
Is it possible to have an entirely passive reference electrode?
No, anywhere you place an electrode will record some level of activity
What are common choices for referential montages (common reference) electrodes?
mastoids, nose, non-cephalic sources, linked mastoids, average
bipolar montage
A channel setup based on recordings from two exploring electrodes. Used for EOG generally (hEOG for us), could also be banana reference
What is the gain on our amplifiers?
20 000
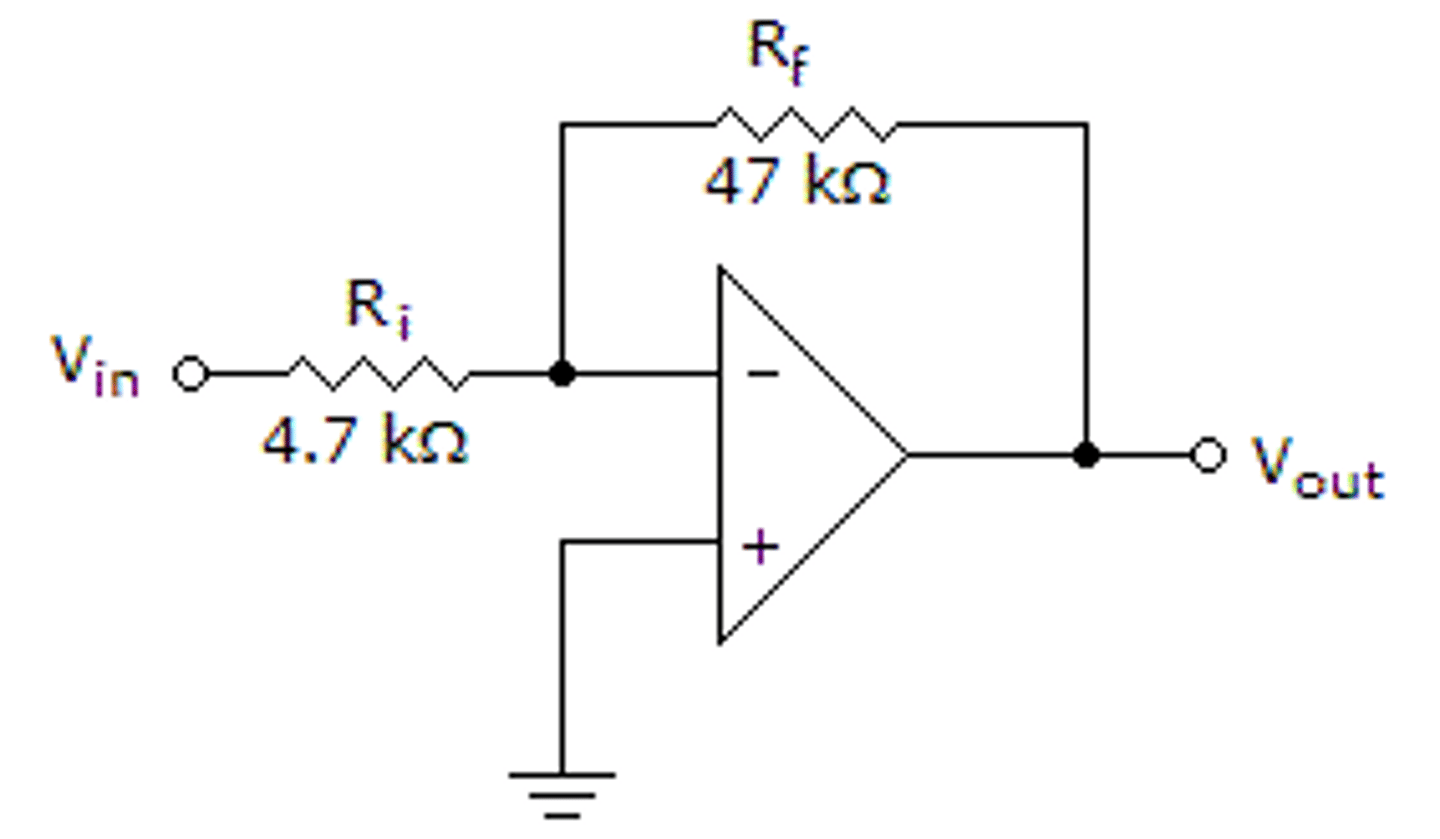
Differential amplifier
electronic amplifier that contains two single-ended amplifiers that are 180 degrees out of phase that amplifies the difference between two input voltages. The kind of amplifier used on our EEG lab
How do we know that differences in voltage recorded by different electrodes are due to something being recorded by that electrode and not just noise?
All electrodes have a common reference, so most noise should be removed from their individual signals
Where is the ground electrode generally located?
in the middle of the electrode array
ground electrode
This electrode does not impact measurements with modern computerized equipment. It is usually placed in the middle of the forehead, but can be placed anywhere on the body. A way to shunt DC voltages off the participant, arbitrarily assigned "0V"
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
A rating of the ability of a differential amplifier to eliminate identical inputs. Should be very high (-80 to -100 dB, meaning that "noise" is cut in half every 6 dB so many many times)
analog filtering
filtering performed on continuous-time signals and yields continuous time signals; filters out highest frequencies (low-pass filter) and often some low frequencies (high-pass filter). Done to prevent aliasing
What does our lab typically use for high and low pass filters during analog filtering?
30Hz low pass filter (to eliminate 60Hz room noise) and 0.01Hz high pass
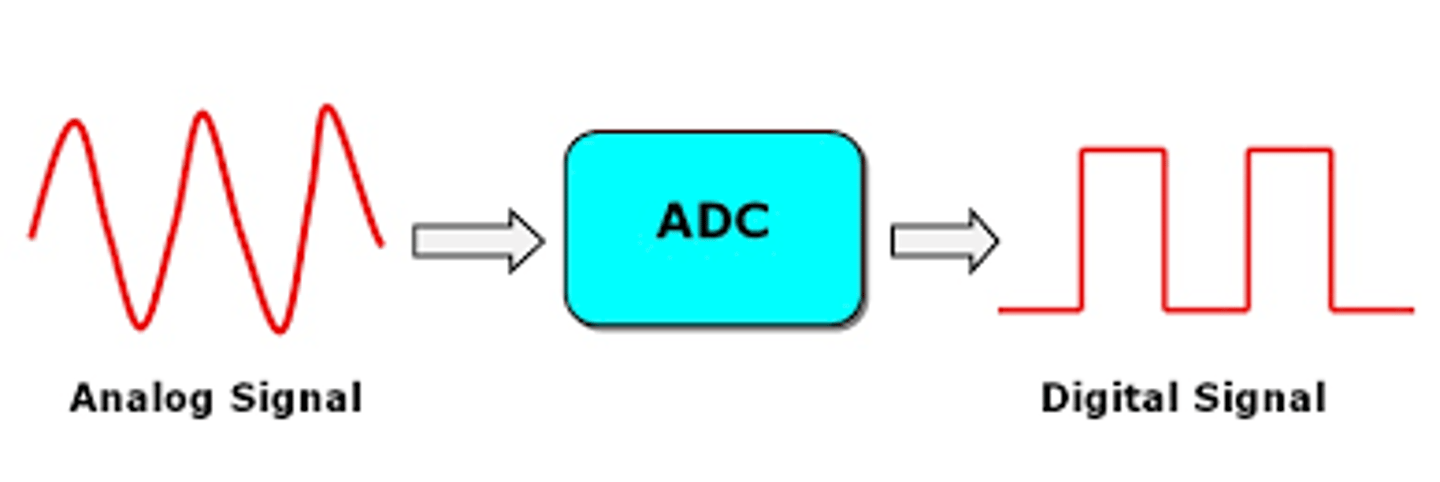
analog to digital converter
Device for sampling analog data and producing a digital sample of it.
sampling interval
the time between each data point written in A-D conversion
What is the typical range of sampling intervals used in the lab?
1, 2 or 4ms
sampling rate
The number of times per second a signal is measured and converted to a digital value. Measured as a frequency, depends on the sampling interval. Is equal to 1000ms/sampling interval
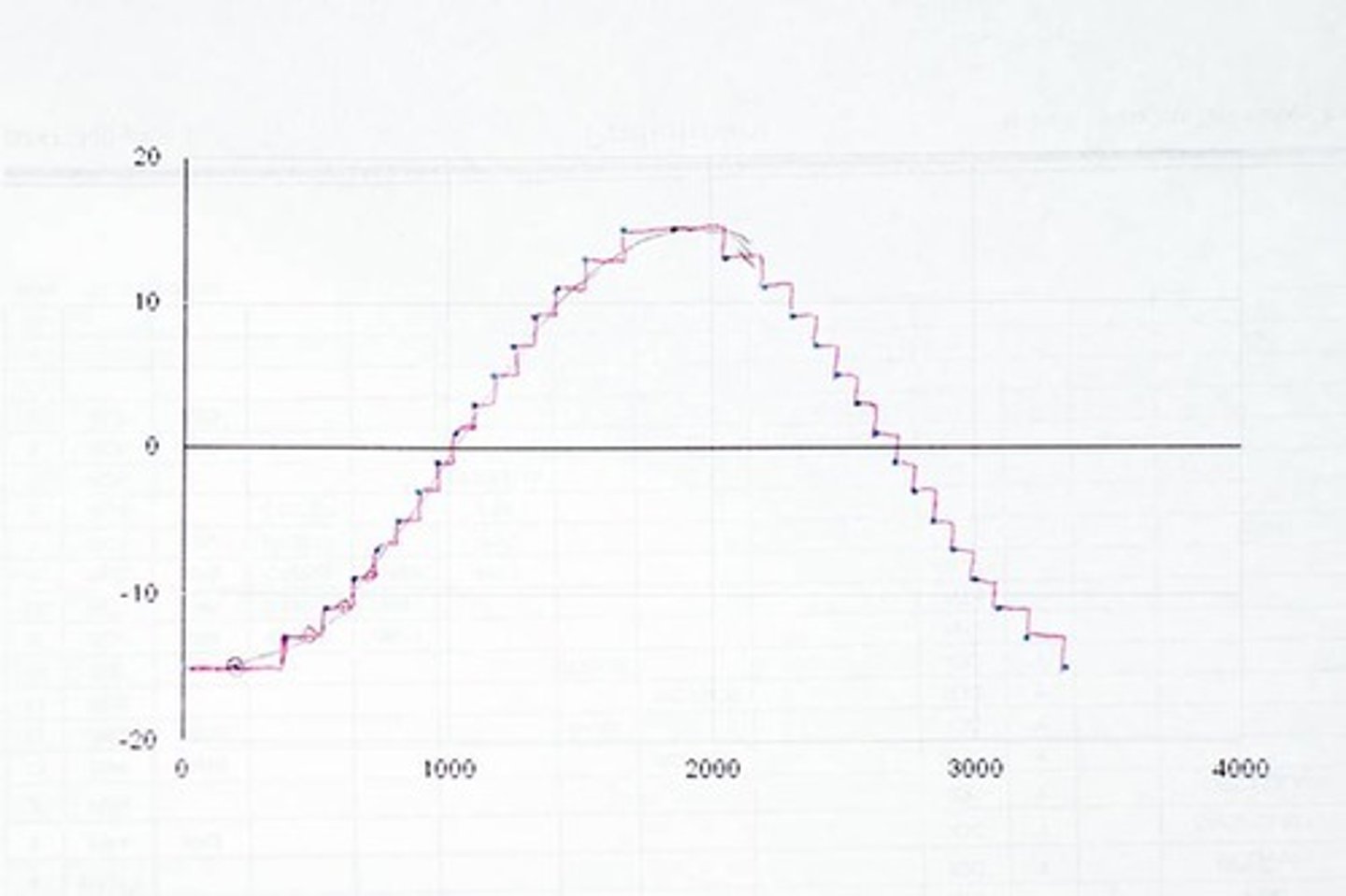
What considerations go into determining an appropriate sampling rate?
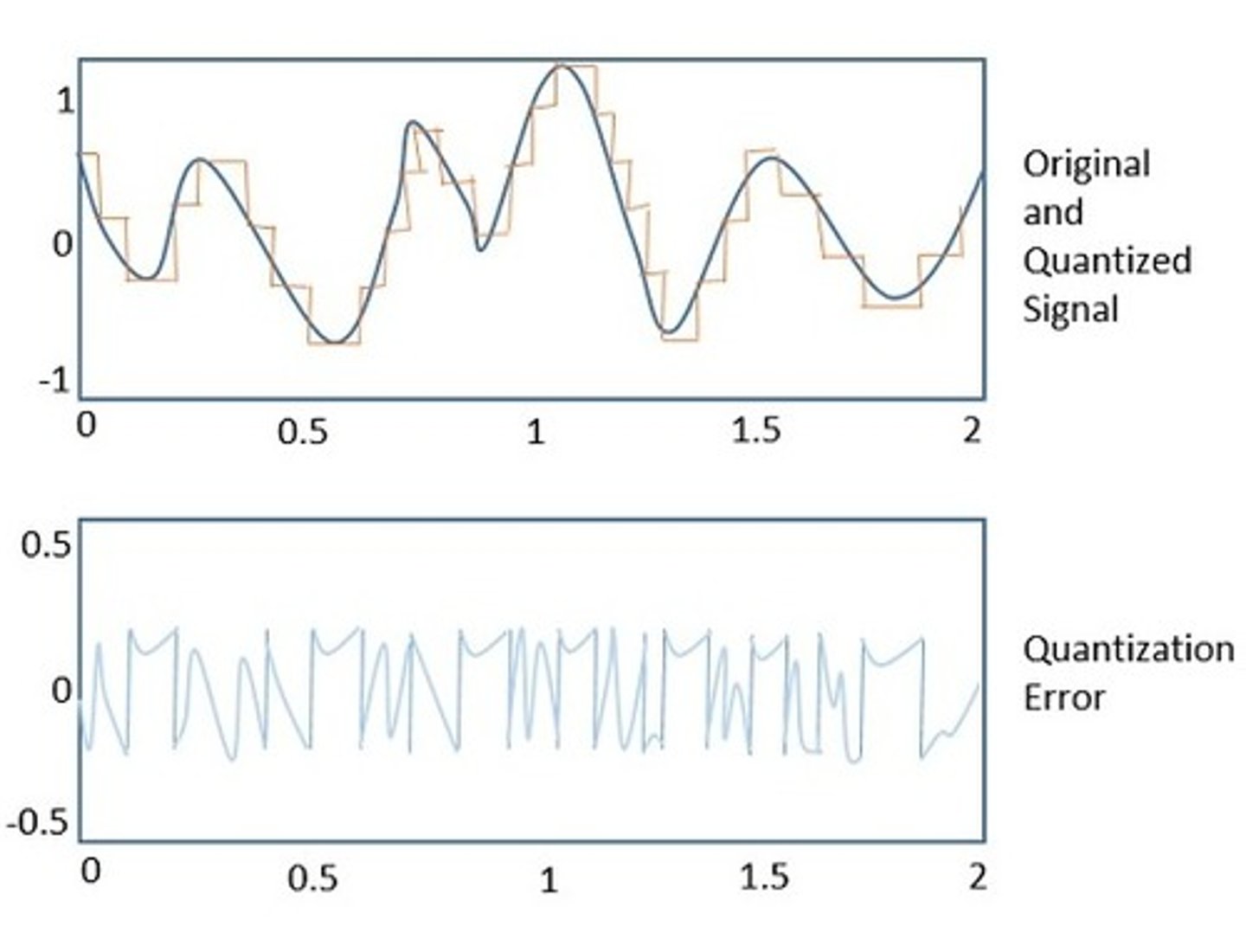
Generally, a cost-benefit analysis. Faster is generally better and reduces quantization error, but it also increases file size and thus storage cost
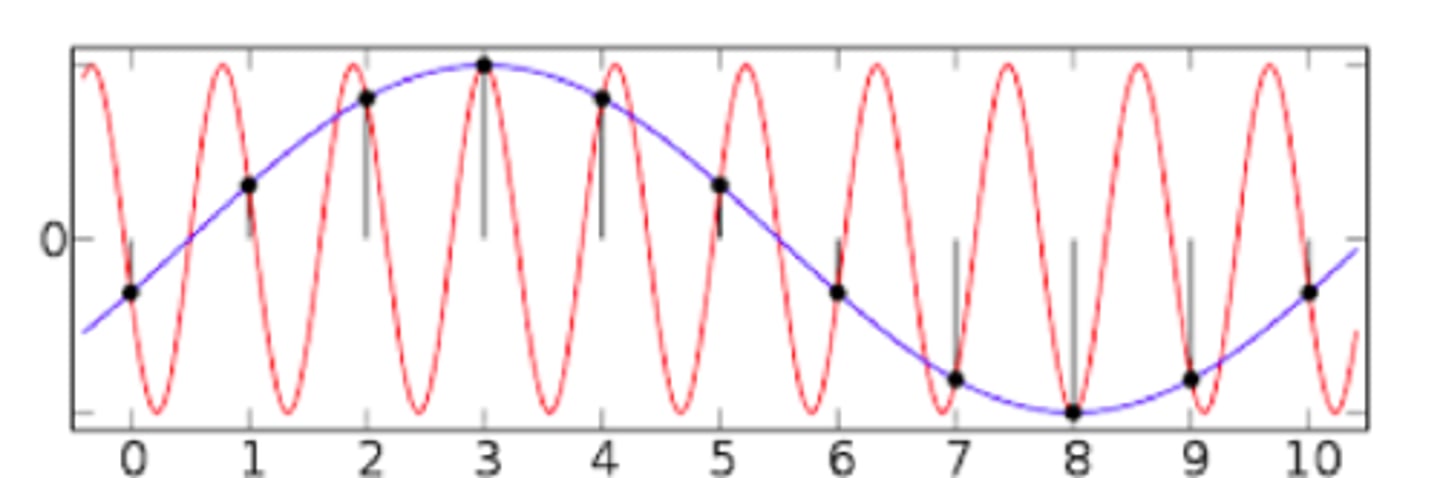
Nyquist limit
The highest frequency waveform that can be measured without the appearance of aliasing, half of the sampling rate
aliasing error
occurs when you use too low of a sampling frequency, causes frequencies above the Nyquist limit to appear as low frequencies
resolution
how many chunks of data exist, usually measured in "bits" or steps of information. Not indicative of the size of the chunk
bit
A contraction of "Binary Digit"; the single unit of information in a computer, typically represented as a 0 or 1
step
another measure of resolution, 2 to the power of the number of bits
What does the resolution of an EEG system depend on?
amplification gain, the A-D range, A-D converter resolution (in bits/steps). Calculation: resolution = A-D range/ res in steps , divide again by the gain to get in pre-amplification units
What is the typical A-D range of an EEG system?
10V (5V up and down)
What should the resolution of an EEG system be?
Ideally as good as possible, but as long as the resolution steps are smaller than the EEG swings expected, it is sufficient. Larger resolutions may also be slower
What size are ERPs typically?
in the range of 1 microvolt
Quantization Error
The difference between the actual signal level and the integer value chosen to represent it, mostly a shape issue in A-D conversion. Improves with higher resolution and sampling frequency