Unit 5 - Chemical reactions and balancing equations
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Physical Properties
Can be observed or measured without changing the composition of the matter
Chemical Properties
a substance’s ability to undergo changes that transform it into a different substance
Chemical reactions
The process by which substances interact to form new substances with different compositions
Chemical change
A change in matter on a molecular level that produces one or more new substances
Unexpected color change
New molecules created in a chemical reaction radiate light differently, producing new colors
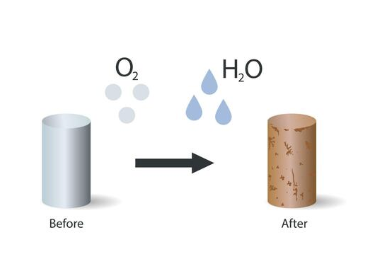
Rusting
A chemical reaction that causes rust called oxidation
Combustion reaction
A chemical reaction between substances, usually a hydrocarbon with oxygen, to produce CO2, water (H2O), light, and heat
Precipitate forms
A chemical reaction that causes a solid suddenly appears in a solution and settles to the bottom, collects on another object, or makes the solution cloudy
Bubbles form
When gases produced in a chemical reaction are released
Temperature change
When the temp. increases, energy was released during a chemical reaction.
When the temp. decreases, energy was absorbed during a chemical reaction
Change in Odor
when two or more compounds or elements are mixed and a scent or odor is present, a chemical reaction has taken place
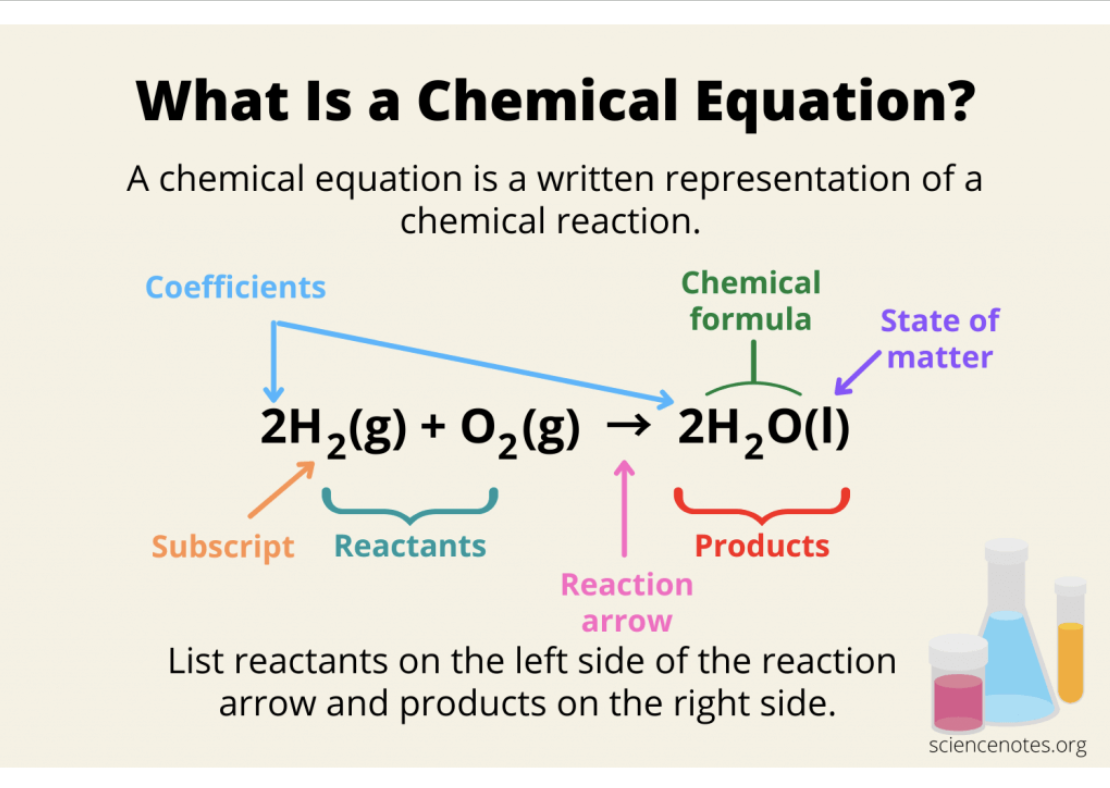
chemical equation
A representation of a chemical reaction using symbols and chemical formulas
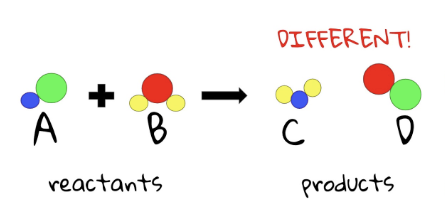
reactants
The starting substances that are combined to make products
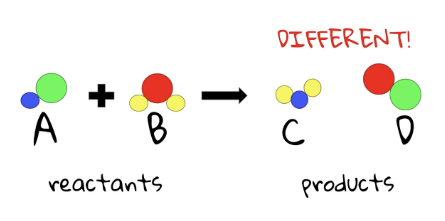
products
the new substances which result from the chemical reaction
Chemical Formula
represents the composition of a molecule or compound.
It lets you know how many of each atom there are.

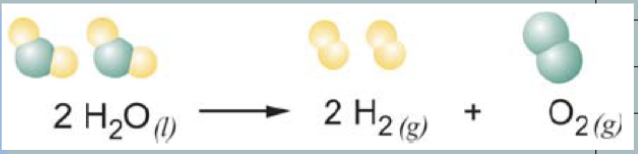
Reaction Symbols
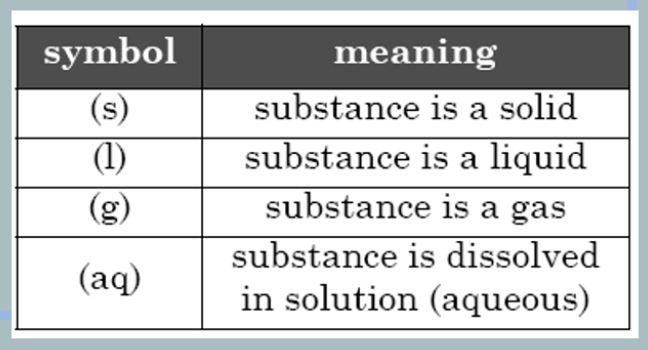
The small symbols in the parentheses (s, l , g, aq) next to each chemical formula indicate the state of matter of each substance in the reaction
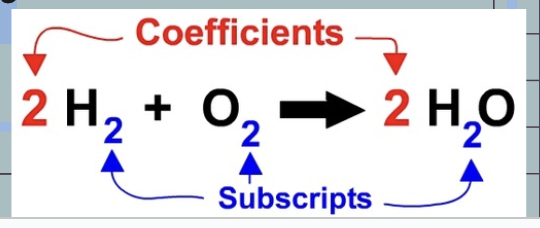
Subscripts
Tells you the amount of atoms of an element in each molecule
H2O ~ There are two hydrogen atoms in a water molecule
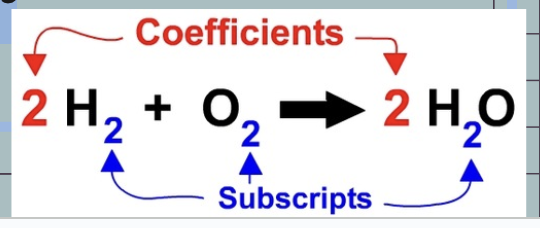
Coefficients
tells you how many molecules of a substance there are
3H2O ~ There are three water molecules, this means there are 6 total hydrogen atoms and 3 total oxygen atoms
The Law of Conservation of Mass
Mass is neither created nor destroyed during chemical or physical reactions
Balancing Equations
The Law of Conservation of Mass is applied by balancing the number & type of atoms on either side of the equation
A balanced chemical equation has the same number of each type of atom on the product side and the reactant side
We change the coefficients of the molecules.
Synthesis reactions
Two or more substances combine to form a new compound
A + B → AB
Forming bonds releases energy (Exothermic)
Decomposition reaction
A chemical reaction in which a single compound is broken down into 2+ smaller compounds
AB —energy→ A + B
Breaking bonds requires energy
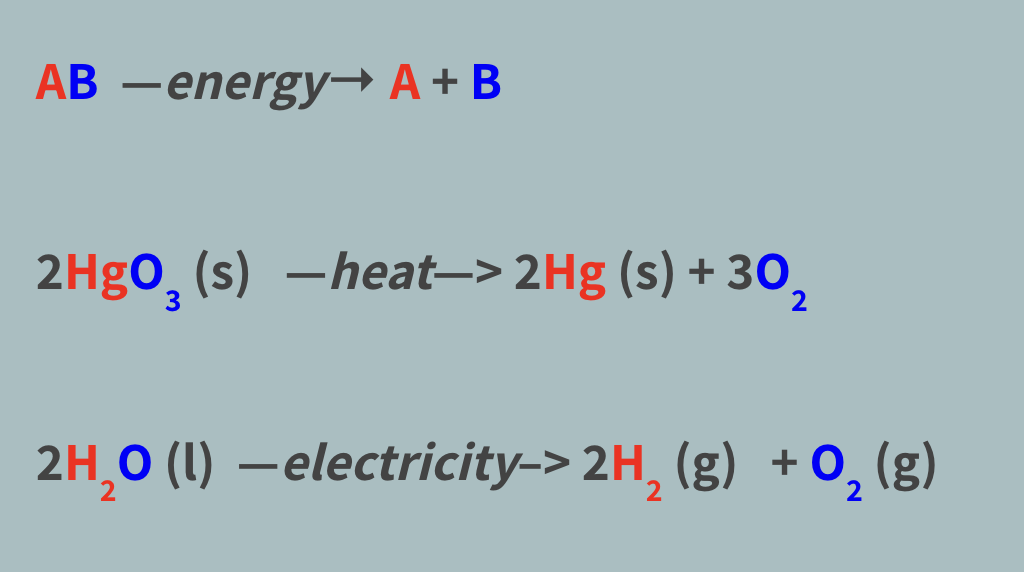
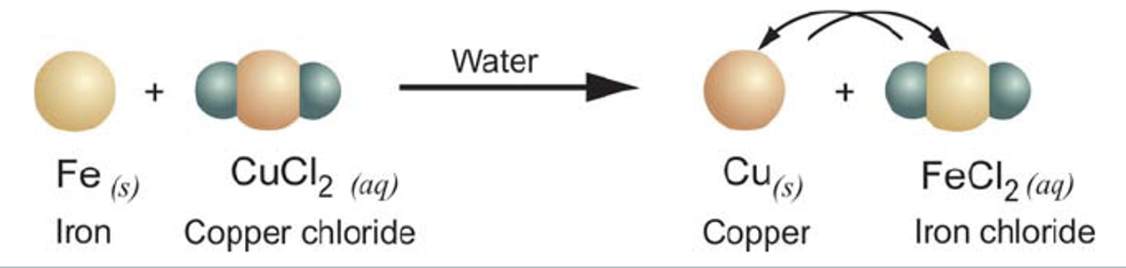
Single replacement/Single displacement reaction
When one element replaces a similar element in a compound
AX + B → BX + A
Double Displacement Reaction
Ions from two compounds in a solution exchange places to produce two new compounds
AB + CD → AD + CB
Signs of a Double Displacement Reaction
a precipitate that settles out of the solution,
a gas that bubbles out of the solution,
or a molecular compound (like water)
Chemical energy
energy stored in the chemical bonds of a substance
Chemical reactions always involve energy changes
Making and breaking bonds involve energy changes
Activation Energy
The energy required to break the bonds in the reactants for a chemical reaction to occur.
Must supply energy to break bonds!
Endothermic
more thermal energy is ABSORBED than released.
Endo = into
Surroundings feel COLD
REACTANTS + ENERGY → PRODUCTS
REACTANTS + HEAT → PRODUCTS
Exothermic
more thermal energy is RELEASED than absorbed
Exo = exit
Surroundings feel HOT
REACTANTS → PRODUCTS + ENERGY
REACTANTS → PRODUCTS + HEAT