Anemia and Iron
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Anemia
Inability of the blood to supply tissue with adequate oxygen
Anemia causes
- ineffective hematopoiesis
- insuffisient erythropoiesis
- blood loss or hemolysis
Severity depends on
- Rate of onset
- Severity of blood loss
- Ability of body to adapt
Diagnosis
- patient history
- physical exam
- labs
Retic count categories
- Hypoproliferative
- Hyperproliferative
Anemia categories
- Normocytic, Normochromic
- Macrocytic, normochromic
- Microcytic, hypochromic
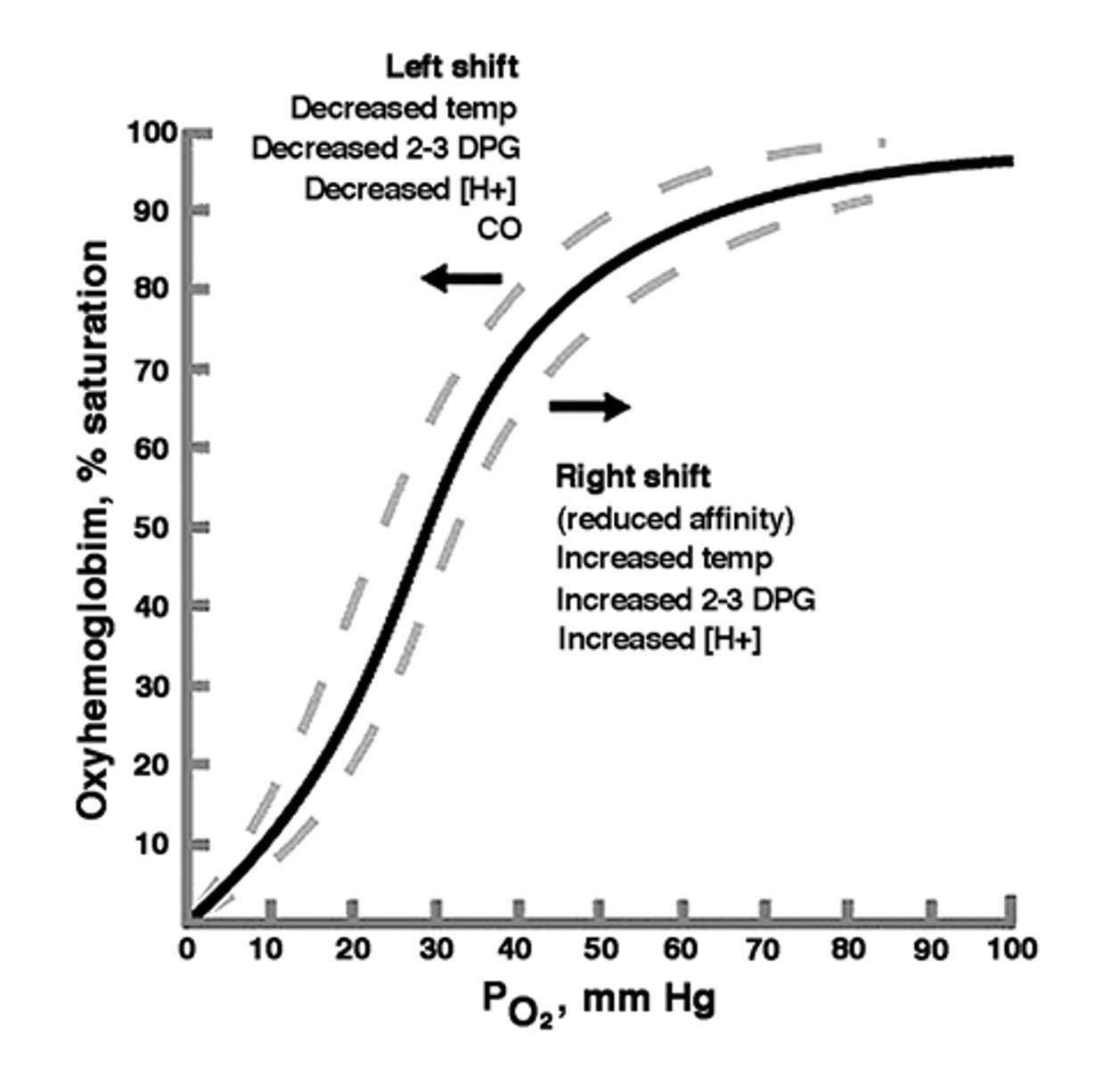
Response to anemia
- Right shift= Increase oxygenated blood flow
- Erythropoietin (EPO) production
EPO
- Glycoprotein/Hormone
- Growth Factor
- in kidneys due to tissue hypoxia
- Constant small amount for RBC level
EPO function
- primarily on CFU-E
- Releases marrow retics early= reduced marrow transit time
- Decreases apoptosis
EPO increases
reticulocyte count
Recombinant EPO
treatment for certain types of anemia, end stage renal disease, HIV associated anemia
Functional Iron
- 70%
- Hgb iron in the blood
- myoglobin in muscles
Stored iron
- 20%
- Ferritin and hemosiderin
- Macrophages and hepatocytes
Stored iron inclusion stains
- Wright stain: Pappenheimer bodies
- Prussian blue stain: Siderotic granules
Transported iron
- 10%
- transferrin in plasma
Factors that increase iron requirements
- menstruation
- pregnancy
- infancy/children
Heme iron molecules
- myoglobin
- hemoglobin
Heme iron
- Fe 2+ (Ferrous)
- red meat
- absorbed in intestines
Non-heme iron molecules
- Transferrin
- Ferritin
- Hemosiderin
Non-heme iron
- Fe 3+ (ferric)
- vegetables and grains
- needs to be reduced to be absorbed

Iron excretion
- not effective
- Exfoliated skin
- Hair
- Sloughed intestinal epithelial
Absorption is influenced by:
- Amount & type of iron from food
- State of the GI mucosa and pancreas
- iron stores
- Erythropoietic needs
Erythropoietic needs is
Inversely related to the amount of iron stores and the rate of erythropoiesis
Transporting Ferric iron (Fe 3+)
- reduced to ferrous by ferrireductase
- transported through luminal membrane of enterocyte
- stored as ferritin or oxidaized by ferroportin
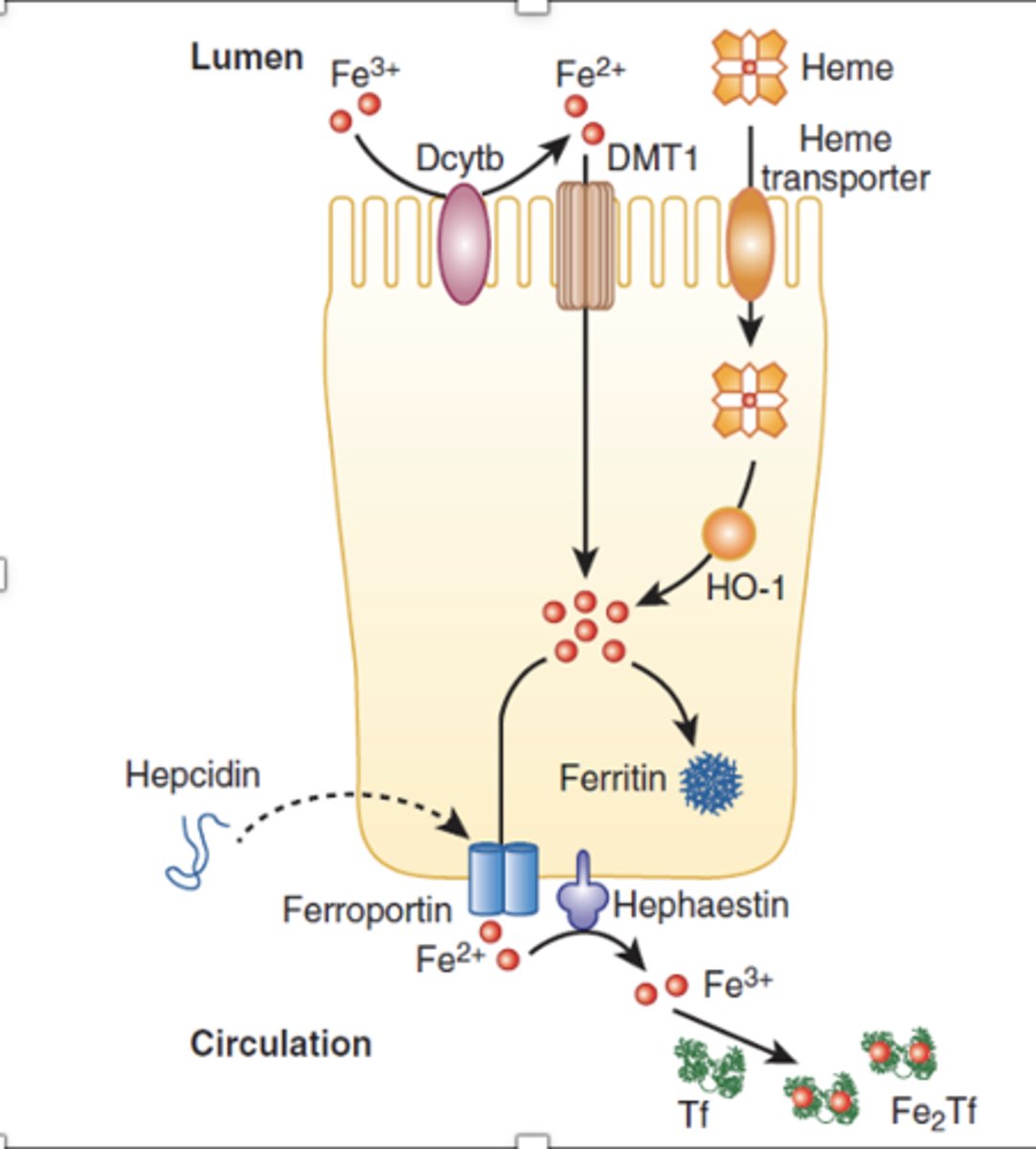
Transporting Ferrous iron (Fe 2+)
- Absorbed by luminal enterocyte membrane heme transporter
- Iron is removed by HO-1
- stored as ferritin or oxidized by ferroportin
Iron Transport in blood
exported from enterocyte is ferrous (2+)
- converted to ferric (3+) to be carried by apotransferrin
Transferrin structure
2 iron + apotrasnferrin
(diferric)
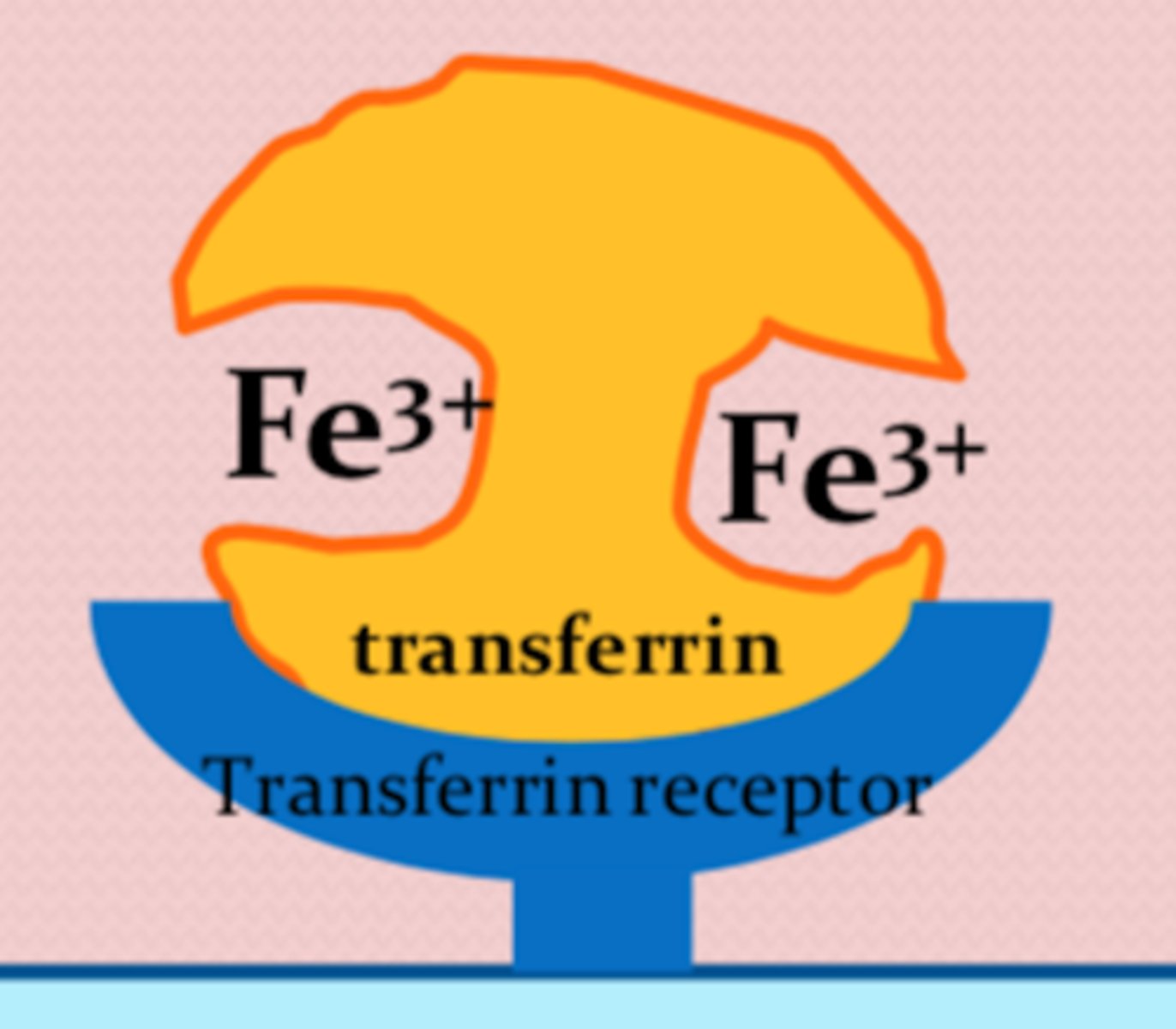
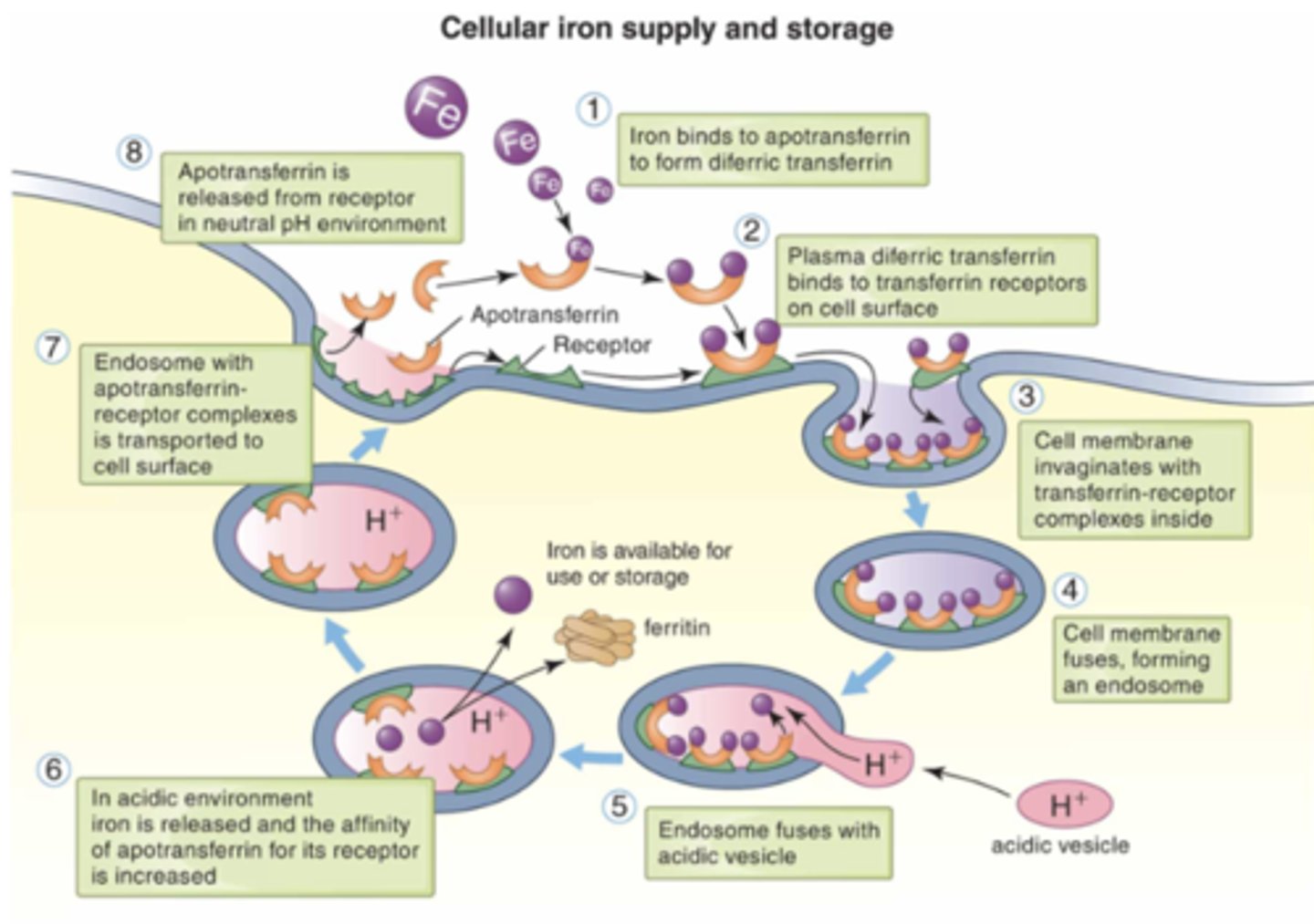
Transferrin function
- transports iron from plasma to erythroblasts in bone marrow
- binds transferrin receptors (TfR) on the erythroblast membrane
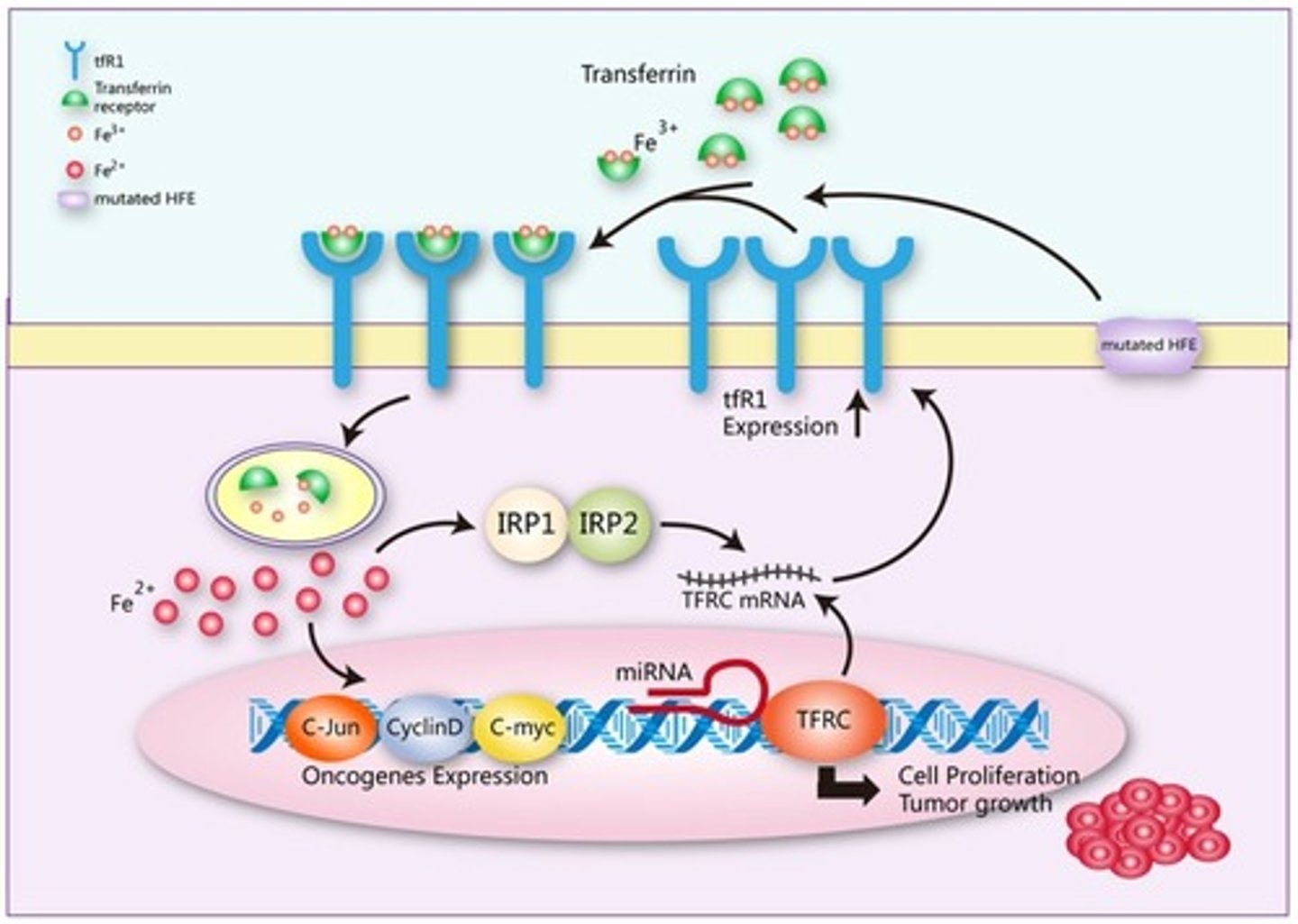
Release of iron
- Transferrin binds to TfR on RBCs
- releases iron, and transferrin returns to circulation
Excess iron stored as
ferritin and hemosiderin
- Macrophages (RES) in liver, bone marrow, and spleen
Ferritin
- primary storage form
- Ferric iron + apoferritin = ferritin
Hemosiderin
Secondary storage form
- Partially degraded, slow release
Removed from storage by
transferrin
Iron state for oxygen binding
ferrous (2+)
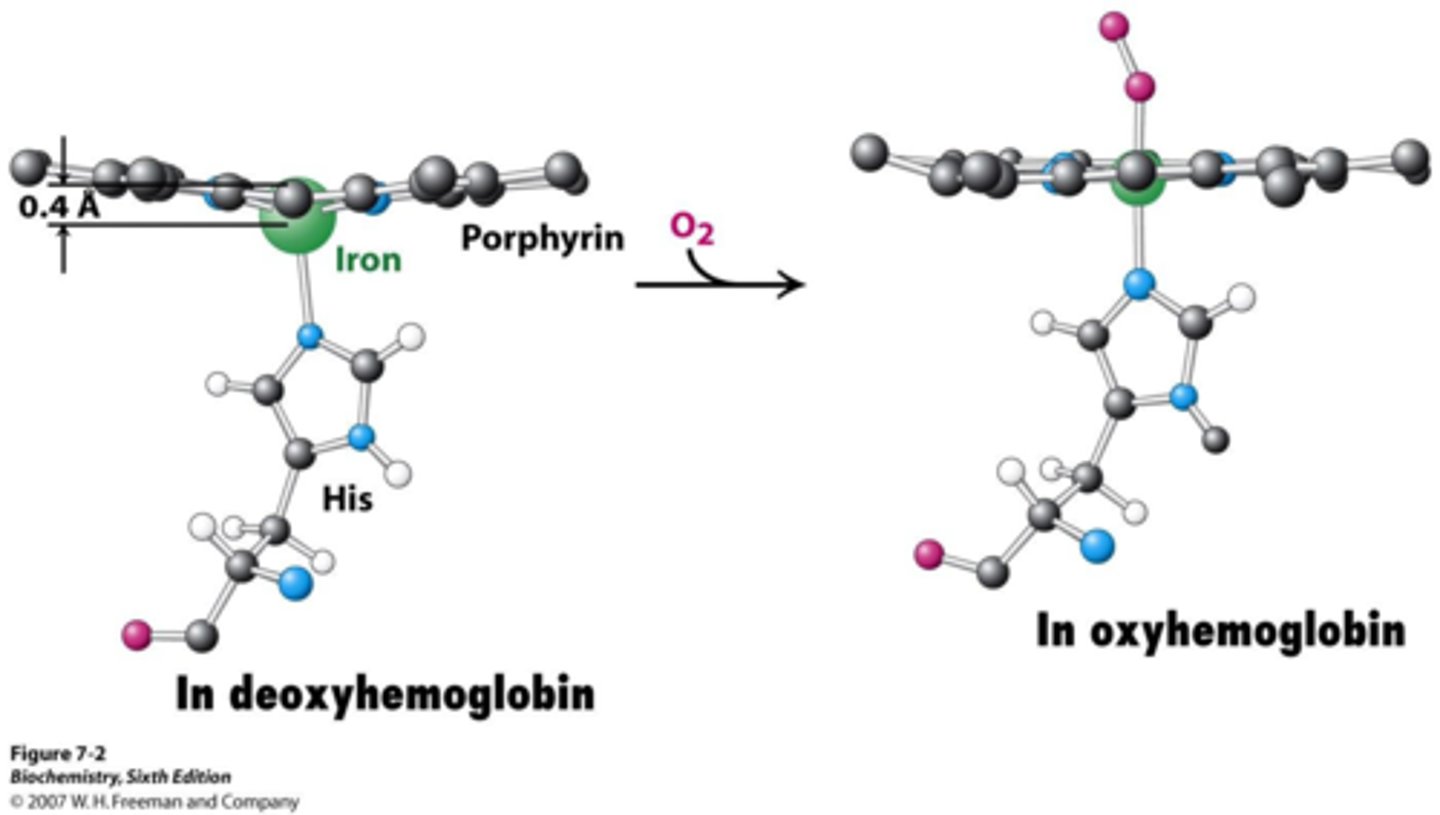
Methemoglobin Reductase Pathway
ferric (3+) reduced to ferrous (2+)
Hepatocytes
- regulate iron levels by release hepcidin
- increase iron level= increase hepcidin
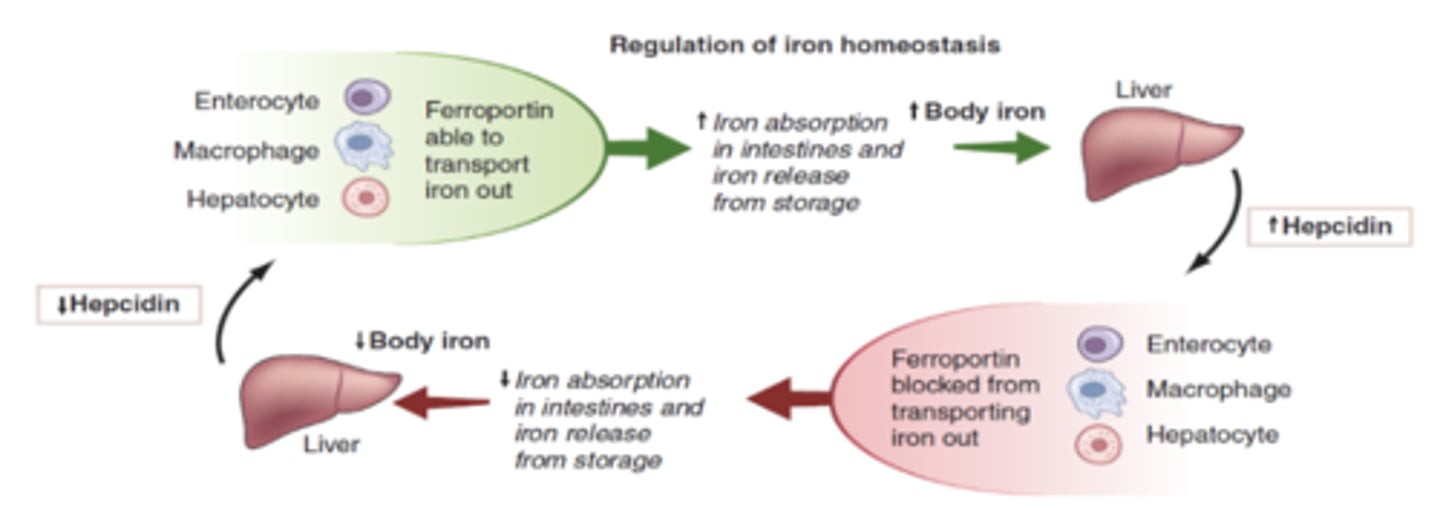
Hepcidin
binds to ferroportin and blocks iron from entering circulation