maceo lecture 04 (keynesian model & the multiplier)
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Keynesian Model Assumptions
Prices don’t adjust in the short run
a. If there is an increase in demand for goods and services in an
economy, firms would respond by changing the output rather than
prices
2. Y* (potential output) doesn’t change in the short run
a. Given by the natural use of resources in an economy at a point in time
3. Expenditure plans realised, except for firms’ investment expenditure
Contributions to Keynesian
1. Aggregate expenditure or demand may determine output (doesn’t account
for supply or inflation!!)
2. Importance of expectations
• And a key implication
1. Government policy can help stabilise the economy
a. Can smooth out any booms or busts in the business cycle
Theories of Business Cycle

Keynesian Model of Aggregate Expenditure

Keynesian Consumption Function
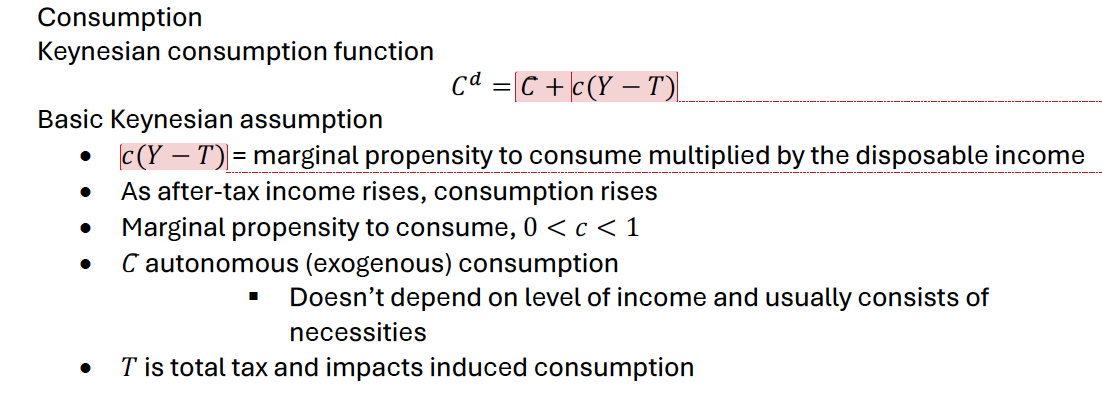
Keynesian- Government Spending, Tax, Exports
last sentence: Exports do contribute to GDP, but it depends on foreign or overseas household/economy income

Keynesian- Investment

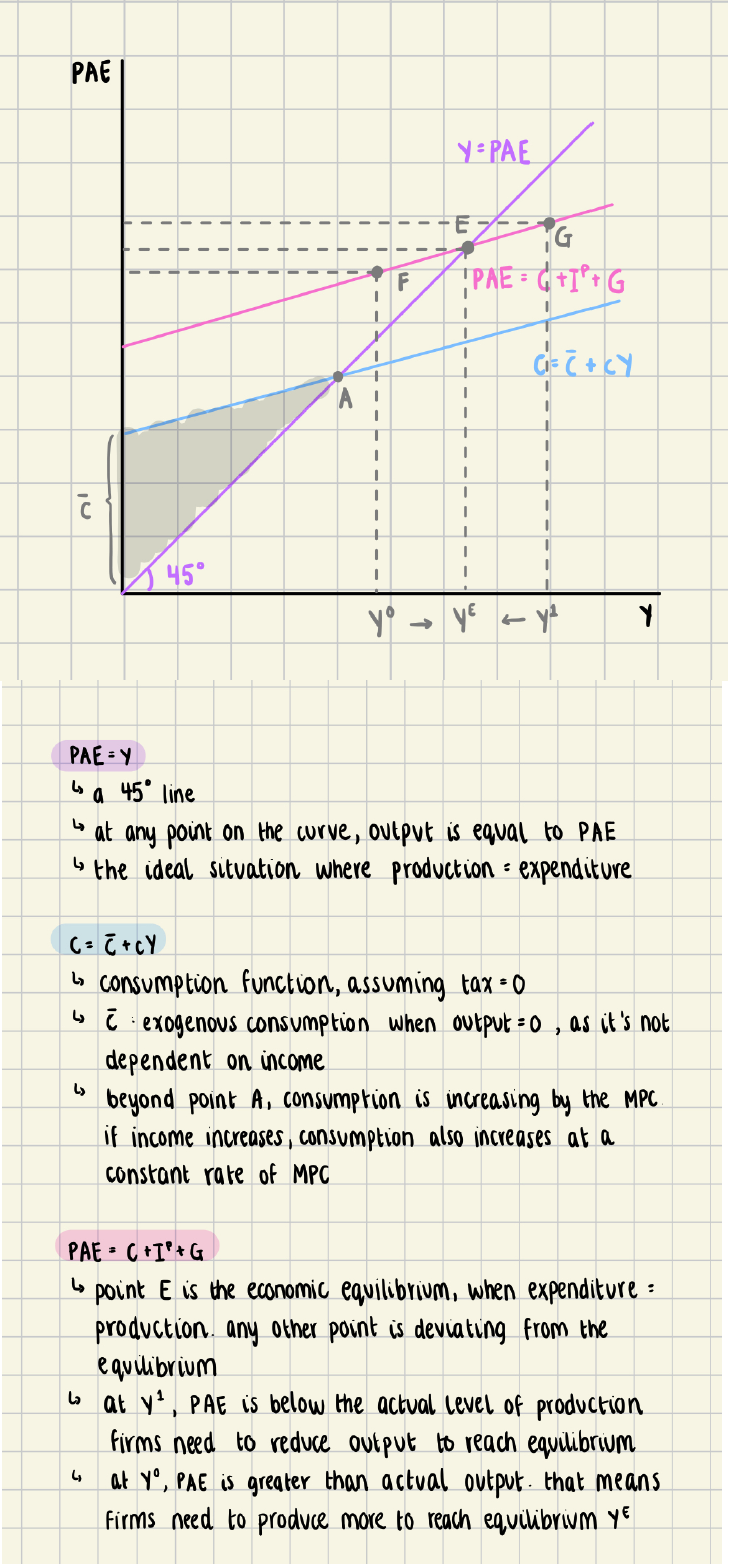
Keynesian Equilibrium

Keynesian Cross Diagram
Economies have the tendency to move towards equilibrium from any
disequilibrium
• Graph illustrates how firms respond to contractionary output gap or
expansionary output gap because neither are good
• Expansionary gap is not sustainable because firms are producing too much
• Contractionary gaps are undesirable because firms are producing too little
Algebraic Representation of Keynesian Equilibrium
Highlighted part: Commented [jk17]: Exogenous component of PAE
![<p><mark data-color="#ff9e9e" style="background-color: #ff9e9e; color: inherit">Highlighted part:</mark> <em>Commented [jk17]: Exogenous component of PAE</em></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/addcd796-9ff3-4dbd-abab-56ae882c685f.png)
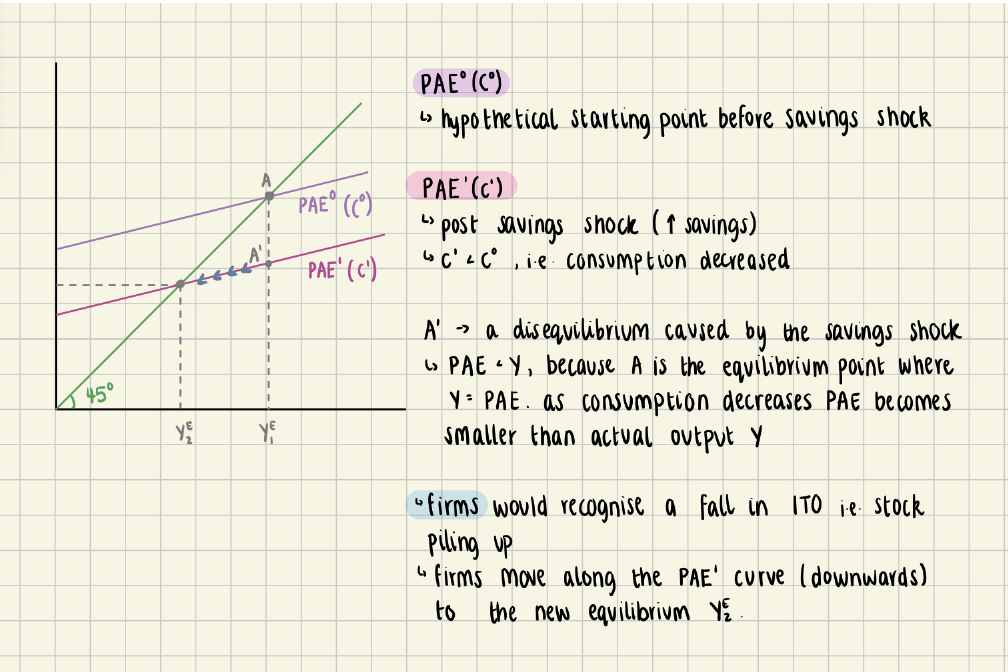
Keynesian Cross Diagram when Consumption Falls
Can look at a comparative static exercise that if a community wants to increase
saving
• When an economy tries to save more the economy (according to Keynesian’s
theory) fails
• Three things can be done with income, consume, save or tax
o Saving more means less money in the circular flow
o More people save, more demand decreases for goods and services
o As a result, firms will reduce their investment, decrease employment
o Everything goes back to Okun’s law about how as output decreases,
unemployment will increase
Paradox Thrift

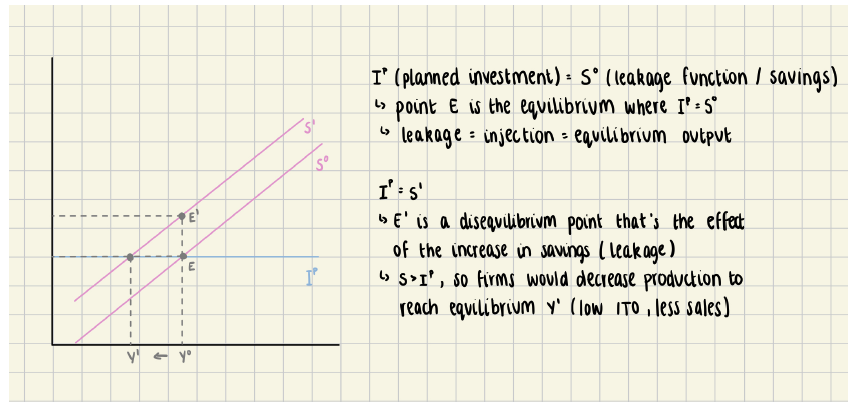
Keynesian Model of the Economy using Savings

Keynesian Model of the Economy: with savings DIAGRAM
Firms would recognise that inventory stock is increasing so they would move
along the post savings shock curve (𝑃𝐴𝐸#) and reduce production until the new
equilibrium Y2E
• Savings decreases output
The Multiplier Intro

Multiplier Equation (two sector)


Multiplier Numerical Example (two sector)

Multiplier Diagram (two sector)
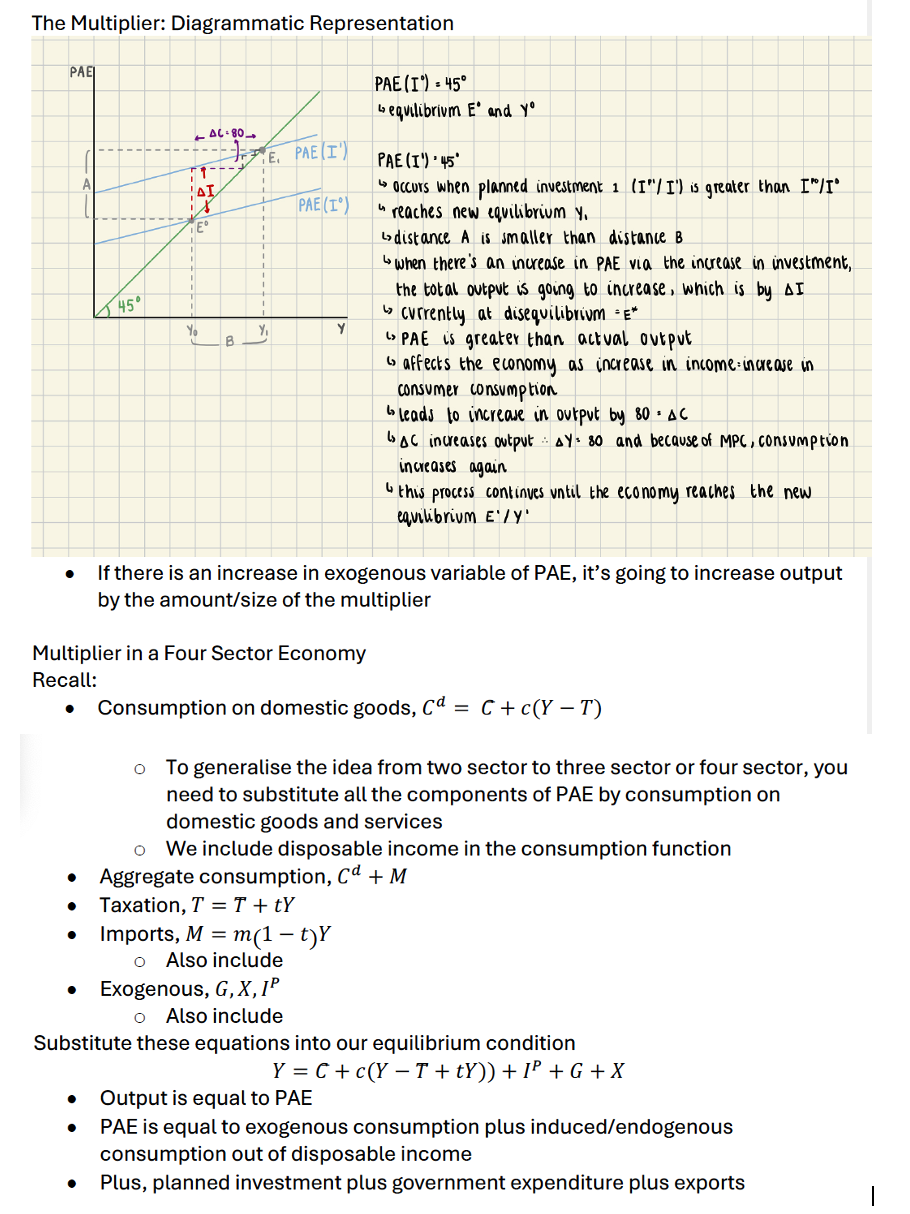
Multiplier in (three/four sector)

Balanced-Budget Multiplier
