Keplers laws
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Ellipse
the shape of the pathway that planets orbit in
Eccentricity
the measurement of how elongated a closed circle is
0
the eccentricity of a perfect circle
e = d / L
the correct formula for determining the eccentricity of an ellipse
Earth Years
the orbital period of revolution measured in
Astronomical Units
What is distance in our solar system measured in
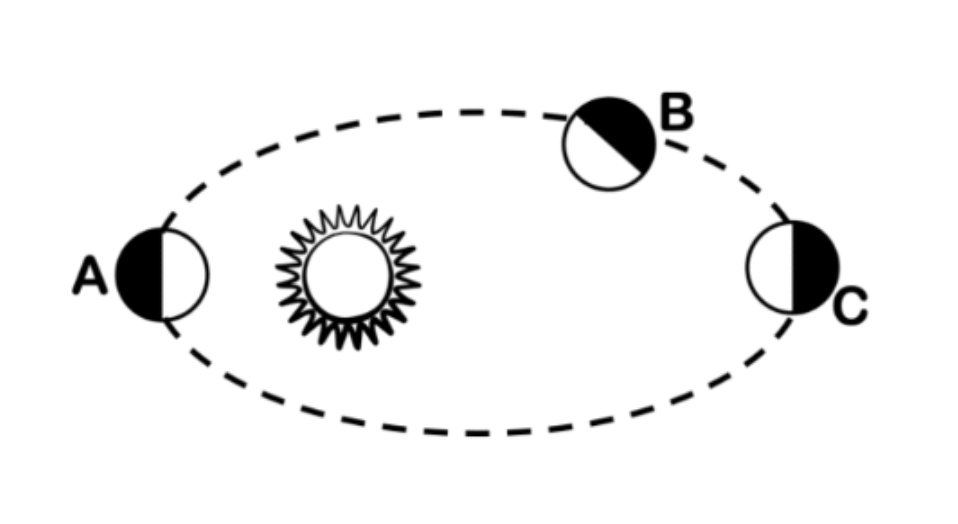
A
Where on the diagram is the planet at perihelion?
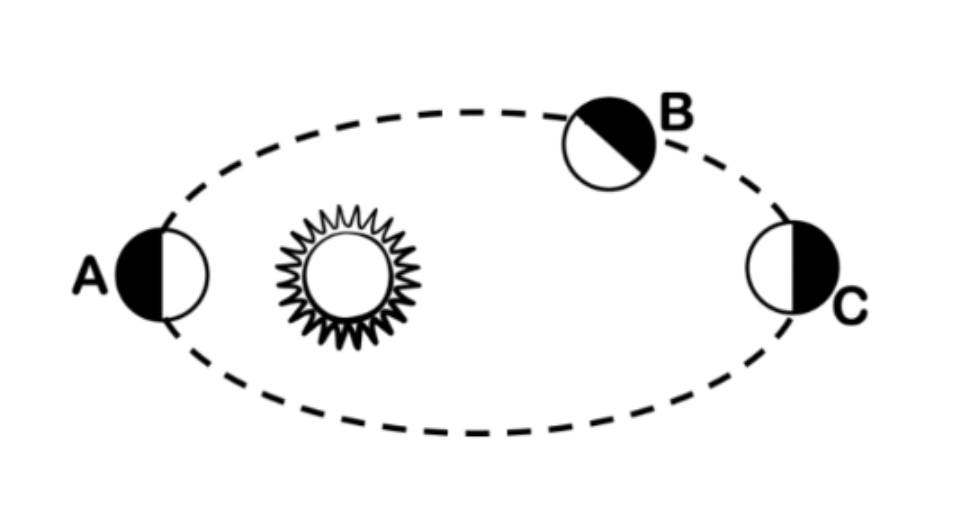
C
Where on the diagram is the planet at aphelion?
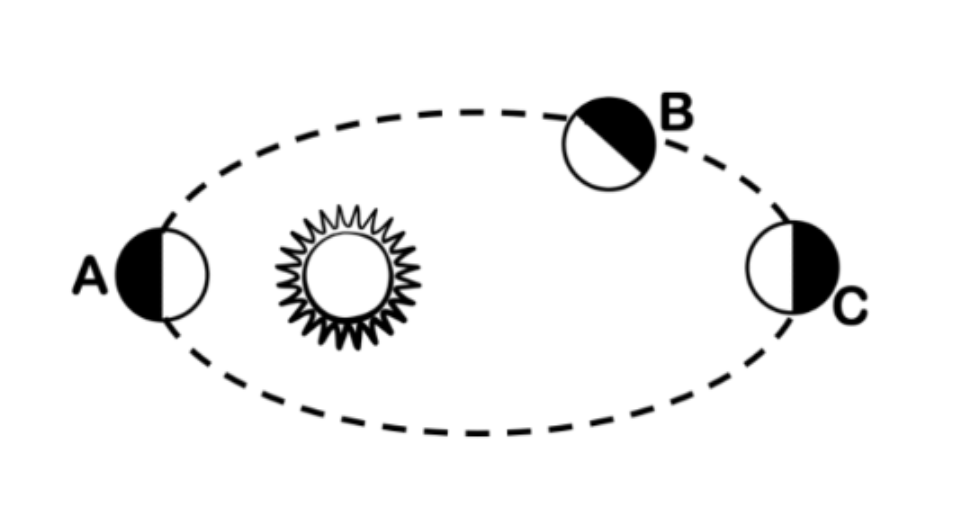
A
Where on the diagram would the planet be orbiting the fastest?
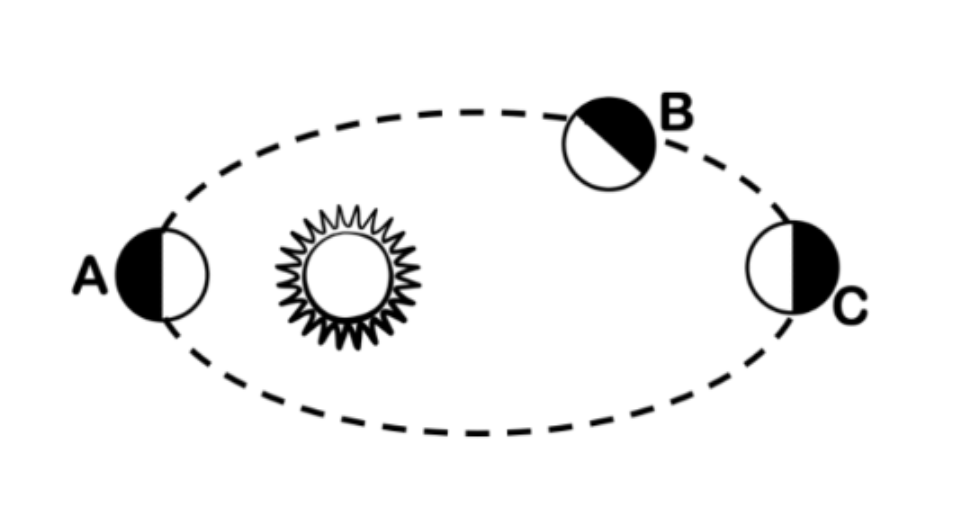
C
At what location is the planet orbiting the slowest?
150 million kilometers
What is the Earth's average distance from the sun?
Venus
Which of the following has an orbital period most similar to Earth's?
3rd law
Which of Kepler's Laws explains:
Mercury has a shorter orbital period than Neptune
2nd Law
Which of Kepler's Laws explains:
Each planet revolves around the sun with equal area in equal time.
1st law
Which of Kepler's Laws explains:
The greater the eccentricity, the more elongated an ellipse is.
3rd law
Which of Kepler's Laws explains:
Earth is 1 AU from the sun and has an orbital period of 1 Earth year.
2nd law
Which of Kepler's Laws explains:
The closer a planet’s orbit is to the sun, the faster it completes a revolution.
3rd law
Which of Kepler's Laws explains:
Orbital periods are proportionate to the distance from the sun.
1st law
Which of Kepler's Laws explains:
e = d ÷ l
1st law
Which of Kepler's Laws explains:
Planets orbit in an ellipse with the sun at one focus.
2nd law
Which of Kepler's Laws explains:
Planets orbit faster at perihelion and slower at aphelion.
Electrostatics
charge accumulates on objects. Objects interact based on their charge.
Charges
What do the interactions of object based on?
Electrical current
charge flows through a circuit.
On what objects are in the circuit and how the objects are connected
What are charge flows based on?
the atomic level
Where does charge come from?
Protons charge
+
Electrons charge
-
in the nucleus of an atom
Where do protons and neutrons exist in
tightly bound
How do protons and neutrons fit in the nucleus
an electron cloud around the nucleus
Where are electrons found
not tightly bound
Can electrons move in the electron cloud?
none
Neutrons charge
having the same number of protons and electrons
When are atoms neutral
It makes it negative
What happens when you add electrons to an object
makes it positive
What happens when you remove electrons to an object
size and sign
What does the force of objects depend on?
repel
pos + pos charge
repel
neg + neg charge
attracts
pos + neg charge
they need to be charged
What do both objects need to have for there to be an electrostatic force between them
Columb’s law
the force experienced by two charged particles (q1 and q2) is directly proportional to the product of their electric charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
mass
What are gravitational forces directly proportional to
inverse square of the distance.
What are gravitational forces proportional to
there does not need to be contact between the two objects
Gravitational forces act at a distance. What does this mean?
a place where a force is felt.
Gravitational forces are field forces. What is meant by a field?
arrows pointing the way the field would push/pull an object.
How can a field be represented?
mass
What creates a gravitational field?
between any 2 masses in a straight line
Where do gravitational forces act?
Towards each other
Which direction do gravitational forces act?
Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation
Every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is
Fg = m g
when you are calculating the gravitational force from Earth (or a planet) where g is known.
calculating gravitational forces between other objects.
Fg = G m1 m2 / r2
always along a line connecting the centers of mass.
what direction does the gravitational force go