Unit 1 - Levels of Organization
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Anatomy
The study of internal and external body structures and relationship between structures
Word description: cutting up
Ana - up
Tome - cutting
Anatomy subdivisions
Microanatomy
Gross Anatomy
Micro anatomy
The Study of tiny structures of the body - Microscope is required
Ex. Cytology, Histology
word description:
Micro - small
Anatomy - study of structures
Cytology
The study of internal structures of individual cells
Word definition:
Cyto - cell
Logy - study of
Histology
The study of tissues ( Group of cells )
Word definition:
Histo - tissue
Logy - study of
Gross Anatomy
The study of large structures of the body - visible to eye
Body Cavities
Ex. Bones, heart, stomach
Word description:
Gross - big, large
Anatomy - study of structure
Body Cavities
Spaces ( compartments in the body that hold and protect organs
Ex.
Dorsal body cavity
Abdominal body cavity
Pelvic body cavity
Cranial body cavity
Vertebral body cavity
Ventral body cavity
Lateral view
Side view
Anterior View
Front view
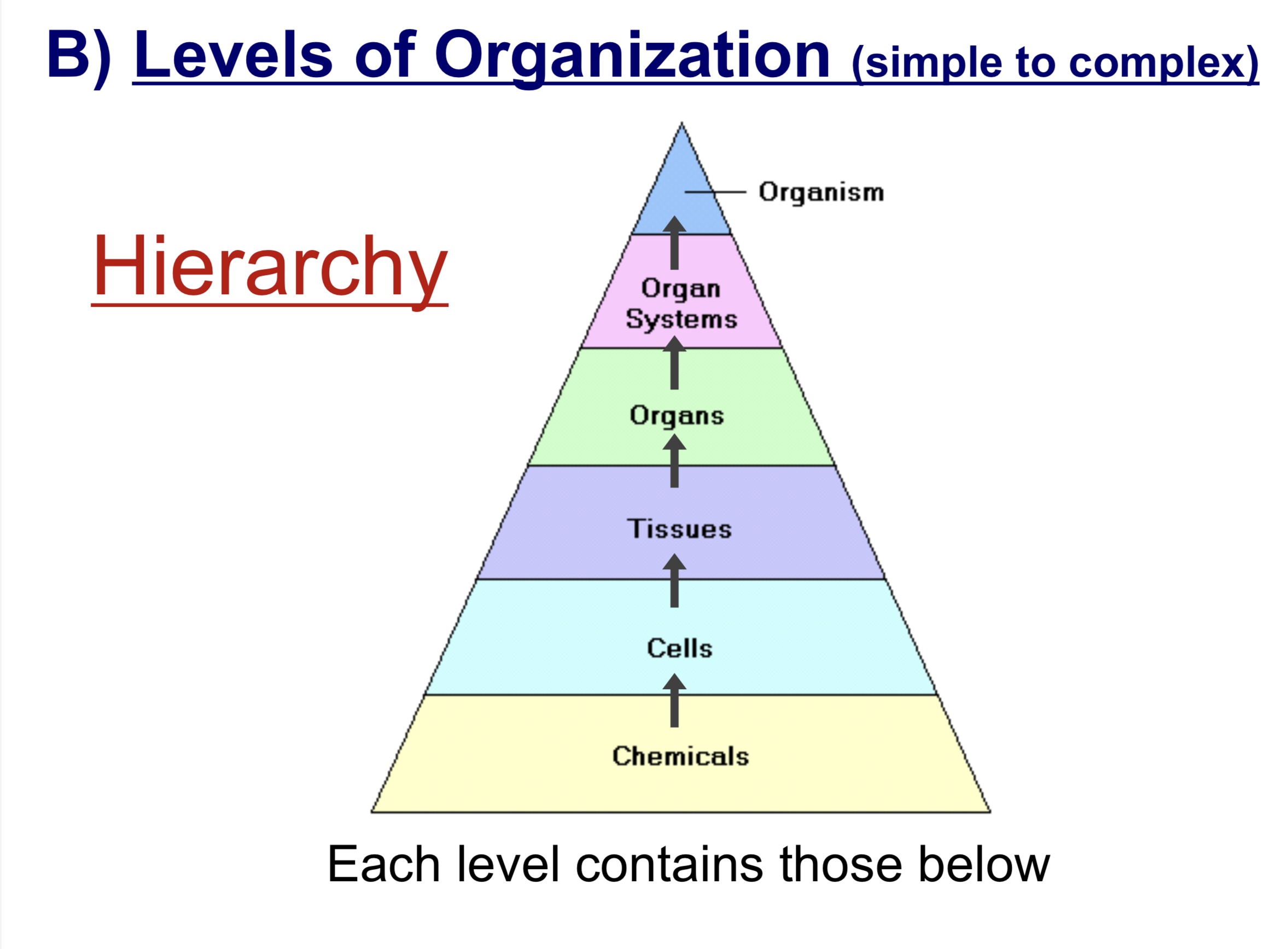
Levels of Organization
How life is structured from simplest to most complex form
Chemical Level ( basic level )
Cellular Level
Tissue Level
Organ Level
Organ system Level
Organism Level
Chemical Level
Includes atoms and molecules
Ex. Hydrogen ( H )
18 grams of water contains ( 6.02 × 10E23 ) molecules
Cellular Level
Molecules form organelles which form cells
Cells
Basic unit of structure and function
Cell facts
All cells contain chemicals
Different types of cells have different functions
Ex. Erythrocytes - neurons - muscle cells
Tissue Level
A group of structurally similar cells with a common function
4 major types:
Epithelial
Connective Tissue
Muscle
Nervous
Epithelial Tissue
Covering and Lining Tissue
Functions:
Covers body surfaces
Protects body from injury, germs, fluid loss
Can absorb ( intestine ) filter ( kidneys ) and secrete ( glands )
Connective Tissue
Holds everything together
Function:
Provide structure, strength, cushioning, transport
Types of connective Tissue
Bone - support and protect
Cartilage - flexible support ( nose, ears )
Blood - transport oxygen, nutrients, waste
Fat - store energy, insulate, cushioning organs
Tendons & Ligaments - Connect muscle to bone and bone to bone
Muscle Tissue
Produce movements by contracting and relaxing
Made of cells called muscle fibers
Contain protein - slide to allow movement
Need energy ATP to work
Types of Muscle Tissue
Skeletal Muscles - attached to bones - voluntary movement
Cardiac Muscle - only in the heart - involuntary movement
Smooth Muscle - Walls of organs - involuntary movement
Nervous Tissue
Control and communicate using signals
Made of 1. Neurons that transmit signals and 2. Supporting cells (Glial Cells )
Function:
Receive: information ( sight, sound, temp )
Process: Brain
Respond: by sending signals to muscles/ glands
Organ Level
Two or more tissues working together for a common function
Ex. Stomach - made of all 4 major tissues - function is digestion
Organ Systems
Several related organs working together towards a common purpose
Ex. Respiratory system ( Trachea, lungs, etc )
Organisms
All systems function together to maintain life
Ex. Humans
Heirarchy