Thermochemistry and Thermodynamics
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
enthalpy (H)
the amount of heat energy contained within a system

endothermic reactions
heat transfer from the surroundings to the system
ΔH>0
exothermic reactions
heat transfer from system to surroundings
ΔH<0
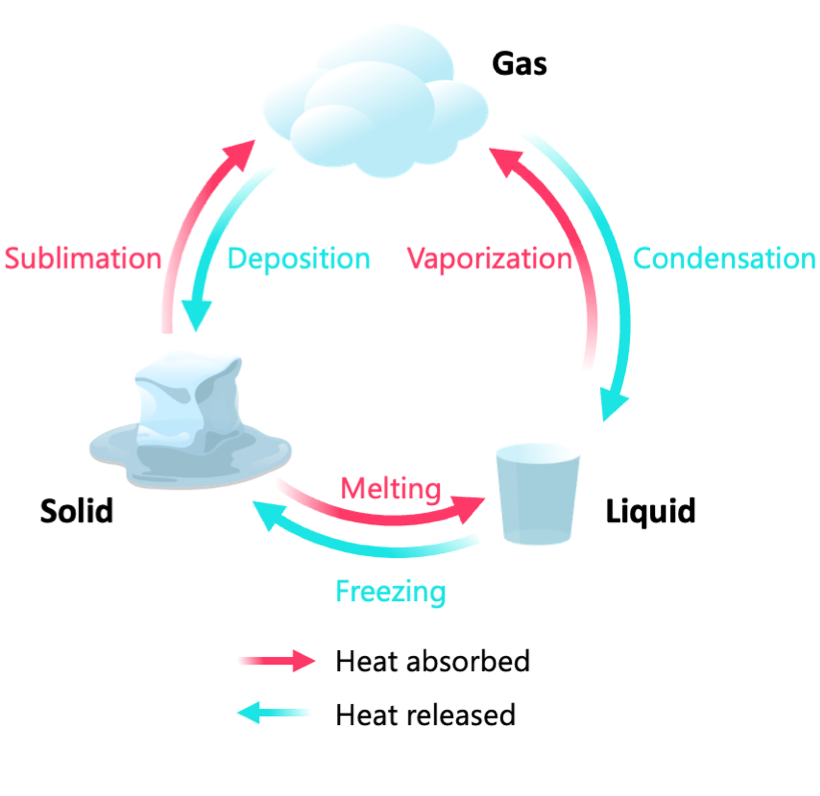
what are the different phase changes?
endothermic
sublimation: solid → gas
vaporization: gas → liquid
melting: solid → liquid
exothermic
deposition: gas → solid
condensation: gas → liquid
freezing: liquid → solid
specific heat capacity (non phase change)
amount of energy reqired to raise the temperature of 1 gram of substance by 1 degree celsius
units: J/gC
NOTE: specific heat of a molecule changes between its phase
q=mCΔT → only applies when there is no phase change occuring
specific heat capacity (yes phase change)
q=mCΔHfus/vap
ΔHfusion= heat to go from solid → liquid
ΔHvaporization= heat to go from liquid → gas
why does temperature stay constant during phase changes?
all the heat energy goes into altering the substance’s phase and not to raising the temperature
bomb calorimetry
amount of heat produced by a chemical reaction
qrxn=-qcal
qcal=CΔT
C= heat capacity of calorimeter (kJ/C)
standard enthalpy change
the enthaply change that occurs in a chemical reaction under standard conditions
bond breakage/formation: ΔHo=ΣΔHo bonds broken-ΣΔHo bonds formed
enthalpies of formation: ΔHorxn=Σ(n x ΔHof products)- Σ(m x ΔHof reactants)
Hess’s law: use enthalpy of intermediates get final value
entropy (S)
amount of disorder and randomness of a system (larger molecules have HIGHER entropy)
higher s = lower energy = more stable
3rd law of thermodynamics
entropy of a pure susbatnce at absolute 0 temperature is zero → no motion or kinetic energy
how to calculate entropy change
ΔSrxn > 0: entropically favorible → products favored/more disordered
ΔSrxn < 0: entropically unfavorible → reactants favored/more disordered
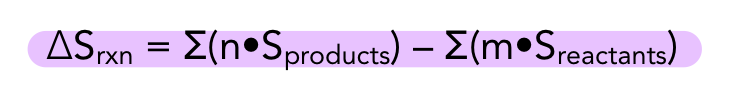
which state of matter has the highest entropy?
gases (more disordered)
how does dissolution affect entropy?
more dissolution INCREASES entropy
how does temperature increase affect entropy?
entropy INCREASES with temperature INCREASE
how does an increase in molecules affect entropy?
INCREASE in entropy
how do spontaneous reactions affect entropy?
increase entropy
gibbs free energy (ΔG)
criteria for spontaneity
ΔG= ΔH-TΔS
units: (kJ/mol)
gibbs free energy in relation to spontaneity
ΔG > 0 = not spontaneous
ΔG < 0 = spontaneous
ΔG = 0 : equilibrium
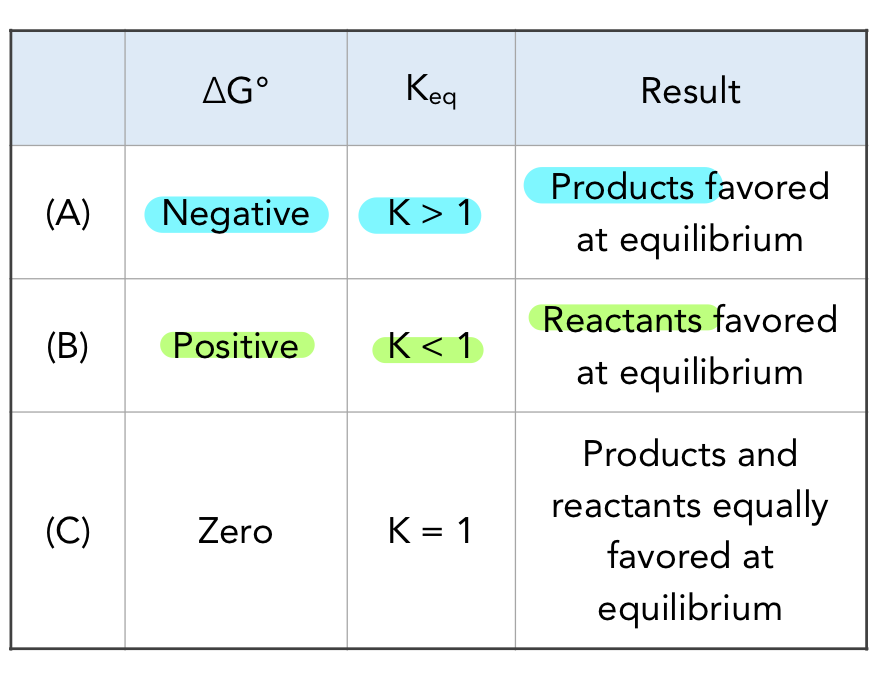
how is Keq related to ΔG