L6: Opaque eye pt II
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Describe the anatomy of the lens
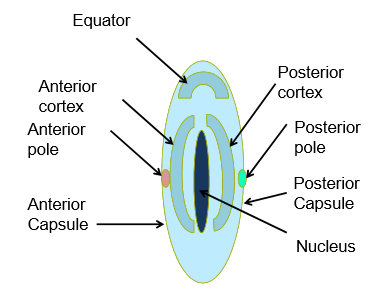
What are the clinical signs of lens instability
Decreased transparency
Phacodonesis
Iridodonesis
Aphakic crescent
Define phacodonesis
Wobbly lens
Define Iridodonesis
Wobbly iris
Define aphakic crescent
Clear crescent shape in the pupil where the lens has moved out of the way
(seeing directly though pupil into vitreous)
How do you diagnose lens instability
clinical appearance
Tonometry
Intraocular pressure may be high
What are the causes of primary lens luxation
Genetic mutation
esp in terrier breeds
What are the causes of secondary lens luxation
Chronic uveitis (zonular degradation)
Glaucoma (stretches zonules)
Cataract (secondary uveitis)
Trauma (mechanical rupture, uveitis)
Intraocular neoplasm
How do you treat lens luxation
Surgical emergency
Describe aqueous humour flow in the anterior chamber
Ciliary body→ pupil → iridocorneal angle (drainage angle)
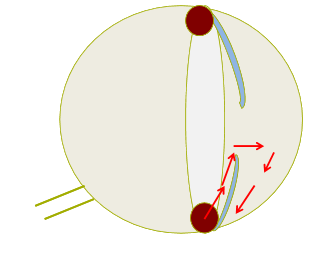
Describe blood aqueous barrier in the anterior chamber
Epithelial barrier located in the ciliary body and iris which separates the eye from the systemic circulation
Becomes leaky when inflamed
Uveitis, trauma, neoplasia
What are the clinical signs of uveitis
Aqueous humour flare
Hyphaema
Hypopyon
How do you diagnose uveitis
clinical signs
Tonometry
What are some diseases that cause vitreal opacities
Liquefaction
persistent hyaloid artery
PHTVL/PHPV
Vitreal degeneration
Haemorrhage
Vitritis
Asteroid hyalosis
Synchysis scintillans

What does this show
persistent hyaloid artery
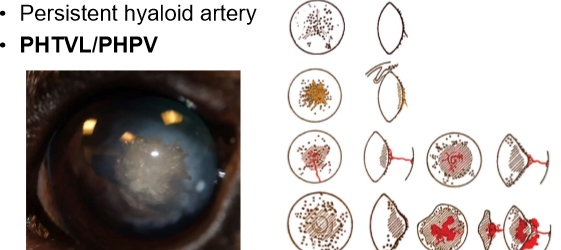
What does this show
PHTVL/PHPV
What does this show
vitreal degeneration
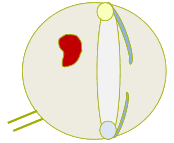
What does this show
haemorrhage
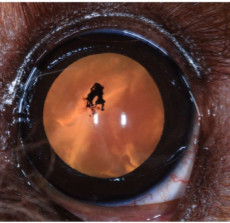
What does this show
vitritis
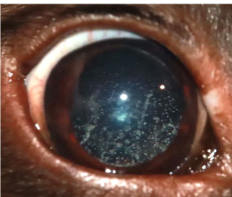
What does this show
Asteroid hyalosis
What is the anatomy and physiology of glaucoma
What is the anatomy and physiology of glaucoma
Anatomy and Physiology of Glaucoma: Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve, often due to increased pressure in the eye. This can lead to vision loss and blindness if not treated. The main structures involved are the optic nerve, the trabecular meshwork, and the drainage angle in the eye.
What are the acute clinical signs of glaucoma
Corneal oedema
Episcleral congestion
Conjunctival hyperaemia
Epiphora
Mydriasis
Aqueous flare
Absent menace
What are the chronic clinical signs of glaucoma
Signs of acute glaucoma
Optic nerve head cupping
Haab’s stria
Buphthalmia
Lens subluxation/luxation
What are the diagnostic tests for glaucoma
Tonometry
interpret alongside clinical signs
Gonioscopy
What are the types of glaucoma
Congenital
primary
secondary
What are the types of primary glaucoma
Open angle
Closed angle
How do you manage glaucoma
Medical
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
Prostaglandin analogues
Adrenergic agents
B blockers and alpha agonists
Cholinergic agonists
Osmotic agents
surgical
Referral level
Select patients
If there is corneal oedema can you see into the eye?
no, so remember other diagnostic tests like tonometry
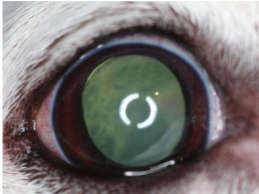
If you see something wobbling inside the eye what should you think
Lens luxation
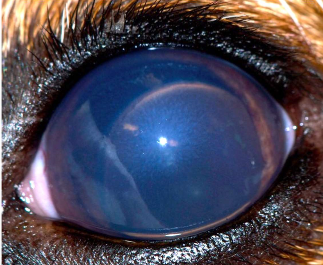
What does this show
Lens luxation ± glaucoma