Dibenzalacetone by Aldol Condensation
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What is the limiting reagent (LR) in the dibenzalacetone synthesis?
Acetone is the limiting reagent.
How do you determine the theoretical yield?
Use the moles of acetone (limiting reagent) and stoichiometry to calculate the maximum amount of dibenzalacetone possible.
What is the role of NaOH in this reaction?
NaOH deprotonates the alpha carbon of acetone to form an enolate ion, enabling nucleophilic attack on benzaldehyde. It also catalyzes dehydration to form the final product.
What is the role of ethanol in this reaction?
Ethanol acts as a co-solvent:
Dissolves benzaldehyde and acetone in aqueous NaOH.
Keeps intermediates (like benzalacetone) soluble.
Helps precipitate the final product (dibenzalacetone) by limiting its solubility.
How do the relative quantities of reactants affect the main product?
Excess benzaldehyde (2.2:1 ratio) favors dibenzalacetone formation.
Excess acetone (or 1:1 ratio) favors monobenzalacetone as the major product.
What are the main side products in this reaction?
Monobenzalacetone (benzalacetone) is the major side product.
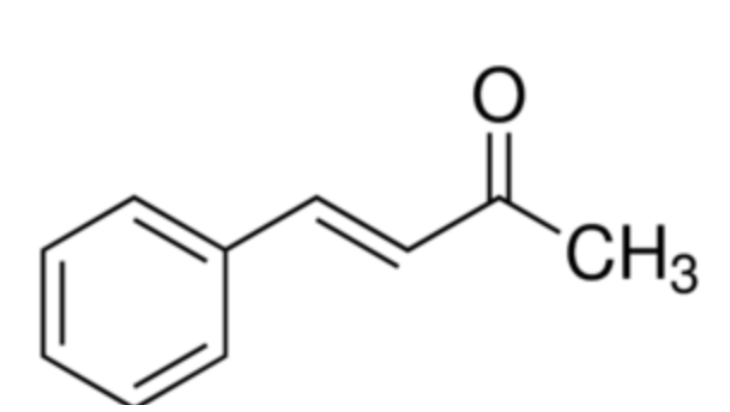
How can the dibenzalacetone product be purified?
Recrystallization from hot ethanol.
Dissolve crude in boiling ethanol.
Filter by vacuum filtration.
Rinse crystals with ice-cold ethyl ether.
Melting point
the crude product had a melting range from 85°C to 110°C, The literature melting point for pure dibenzalacetone is 110-112°C
Why might the % yield be low?
Product lost during transfer or filtration.
Incomplete reaction (remaining monobenzalacetone).
Solubility losses during recrystallization.
Side reactions or retro-aldol reaction.
Impurities in starting materials.
Why is the IR C=O bond absorption shifted lower (1649 cm⁻¹)?
Due to conjugation between the C=O group and adjacent C=C bonds, which weakens the C=O bond, lowering the stretching frequency.
What are uses of dibenzalacetone?
Dibenzalacetone is used in sunscreens due to its strong UV light absorption properties.
Why must the solvent dissolve reactants but not the product?
To allow the product (dibenzalacetone) to precipitate out easily, pushing the reaction toward completion (Le Chatelier's Principle).
What would happen if NaOH was left out?
No enolate formation.
Reaction would proceed extremely slowly or not at all.
Why is it important that dibenzalacetone precipitates during the reaction?
Precipitation removes the product from solution, shifting the reaction equilibrium forward and increasing yield.