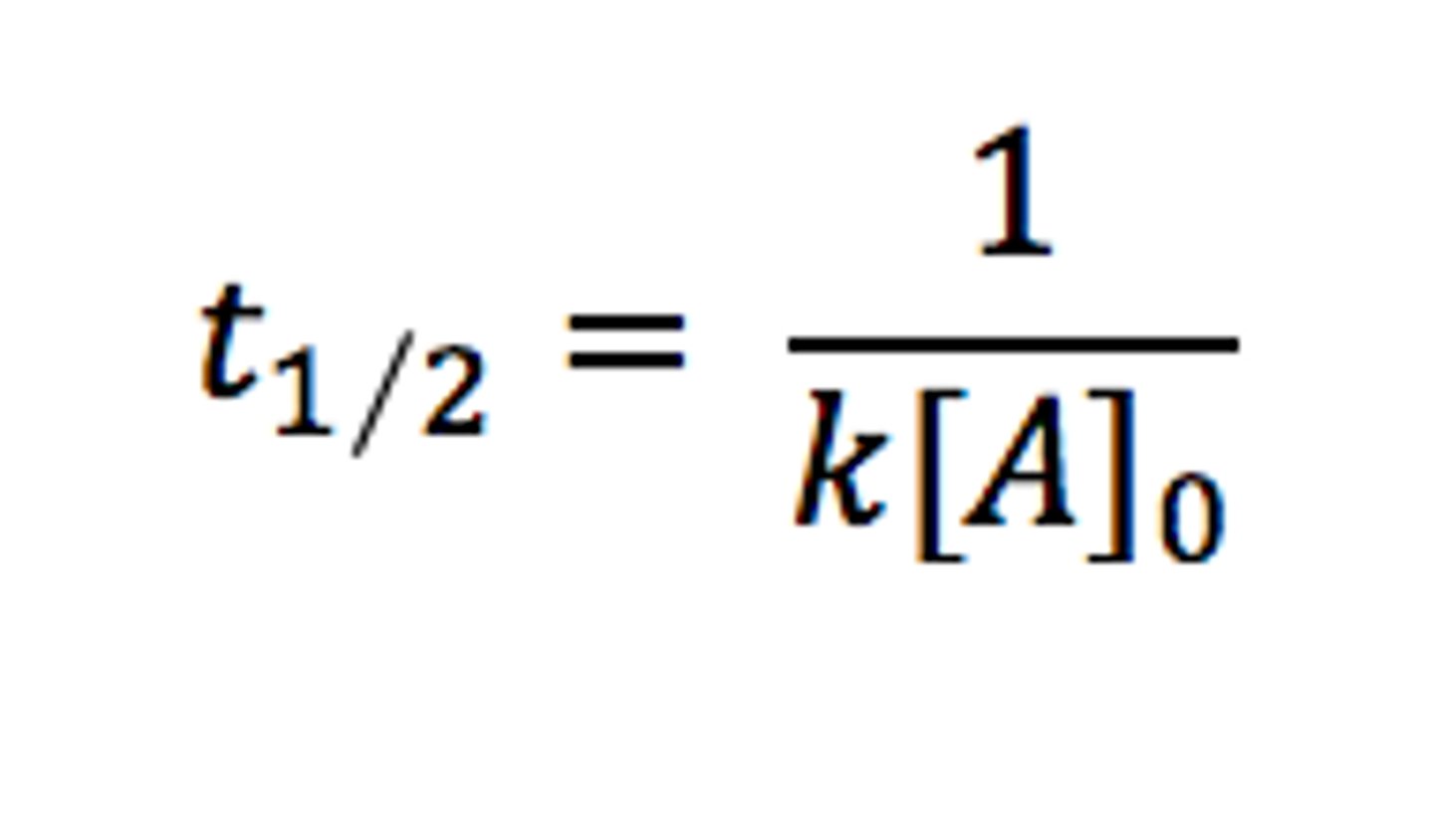Openstax- Chemistry Chapter 12: Kinetics- vocab and equations
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Activated Complex
Also transition state, unstable combination of reactant species representing the highest energy state pf a reaction system
Activation energy
energy necessary in order for a reaction to take place
Average Rate
rate of a chemical reaction computed as the ratio of a measured change in amount or concentration of substance to the time interval over which the change occured
Biomolecular reaction
elementary reaction involving the collision and combination of two reactant species
Catalyst
substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself being consumed by the reaction
Collision theory
model that emphasizes the energy and orientation of molecular collisions to explain and predict reaction kinetics
Elementary Reaction
reaction that takes place precisely as depicted in its chemical equation
Half-life of a reaction
time required for half of a given amount of reactant to be consumed
Heterogeneous Catalyst
catalyst present in a different phase from the reactants, furnishing a surface at which a reaction can occur
Homogeneous catalyst
catalyst present in the same phase as the reactants
Initial rate
instantaneous rate of a chemical reaction at t=0 s (immediately after the reaction has begun)
Instantaneous rate
rate of a chemical reaction at any time, determined by the slope of the line tangential to a graph of a concentration as a function of time
Integrated rate law
equation that relates the concentration of a reactant to elapsed time of reaction
Intermediate
molecule or ion produced in one step of a reaction mechanism and consumed in another
Method of initial rates
use of a more explicit algebraic method to determine the orders in a rate law
Molecularity
number of reactant species (atoms, molecules, or ions) involved in an elementary reaction
Overall reaction order
Sum of the reaction orders for each substance represented in the rate law
Rate Constant (k)
proportionality constant in the relationship between reaction rate and concentrations of reactants
Rate expression
mathematical representation relating reaction rate changes to amount, concentration, or pressure of reactant or product species per unit of time
Rate law
Also rate equation, mathematical equation showing the dependence of reaction rate on the rate constant and the concentration of one or more reactants
Rate of reaction
measure of the speed at which a chemical reaction takes place
Rate-determining step
Also, rate-limiting step, slowest reaction in a reaction mechanism; determines the rate of the overall reaction
Reaction mechanism
stepwise sequence of elementary reactions by which a chemical change takes place
Reaction Order
value of an exponent in a rate law, expressed as an ordinal number
Termolecular reaction
elementary reaction involving the simultaneous collision and combination of three reactant species
Unimolecular reaction
elementary reaction involving the rearrangement of a single species to produce one or more molecules of product
Relative reaction rate equation
aA----> bB= -1/a(Δ[A]/Δt)= 1/b(Δ[B]/Δt)
Zero- Order Integrated Rate Law
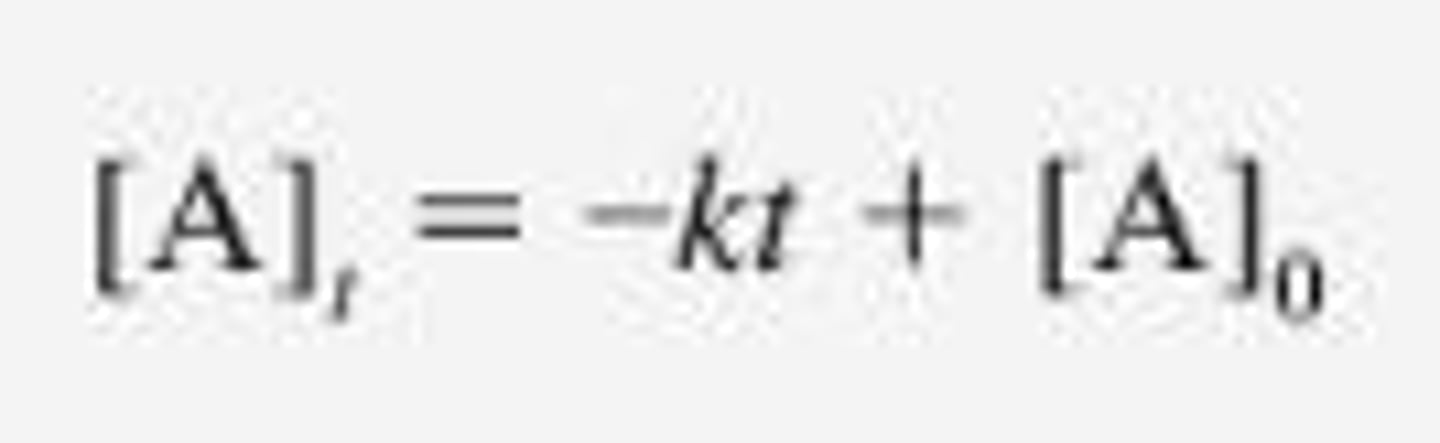
First- Order Integrated Rate Law
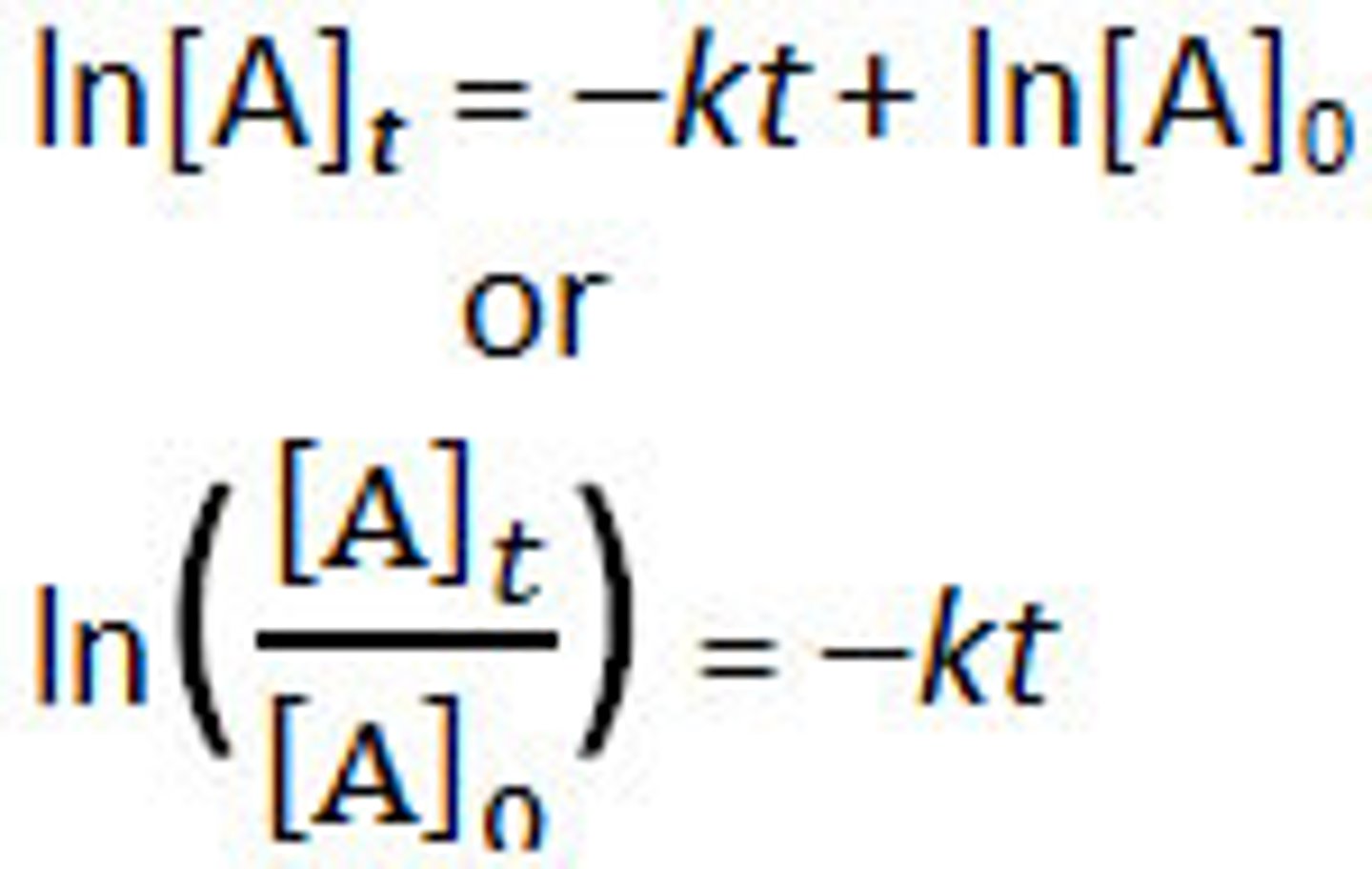
Second- Order Integrated Rate Law
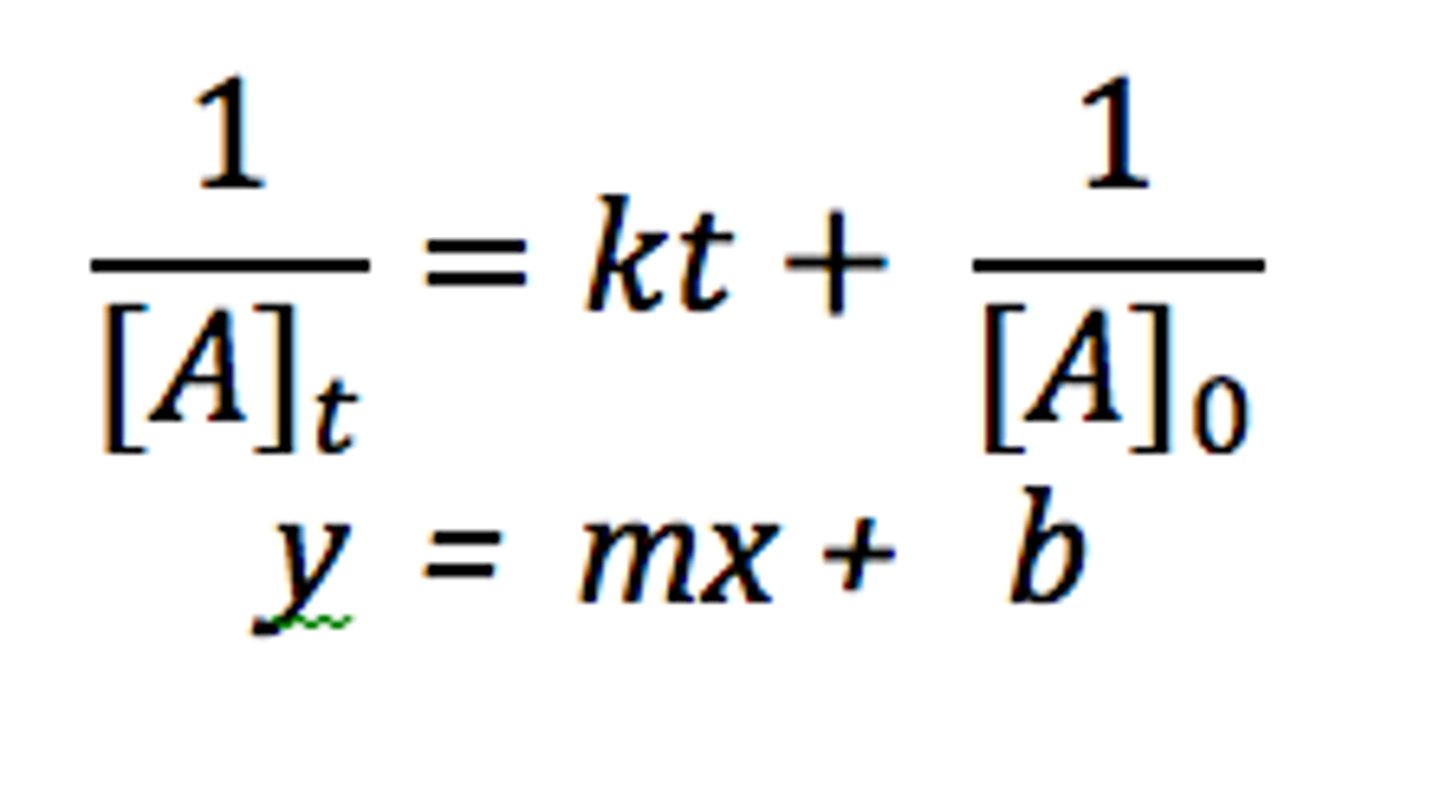
Zero- Order Half Life
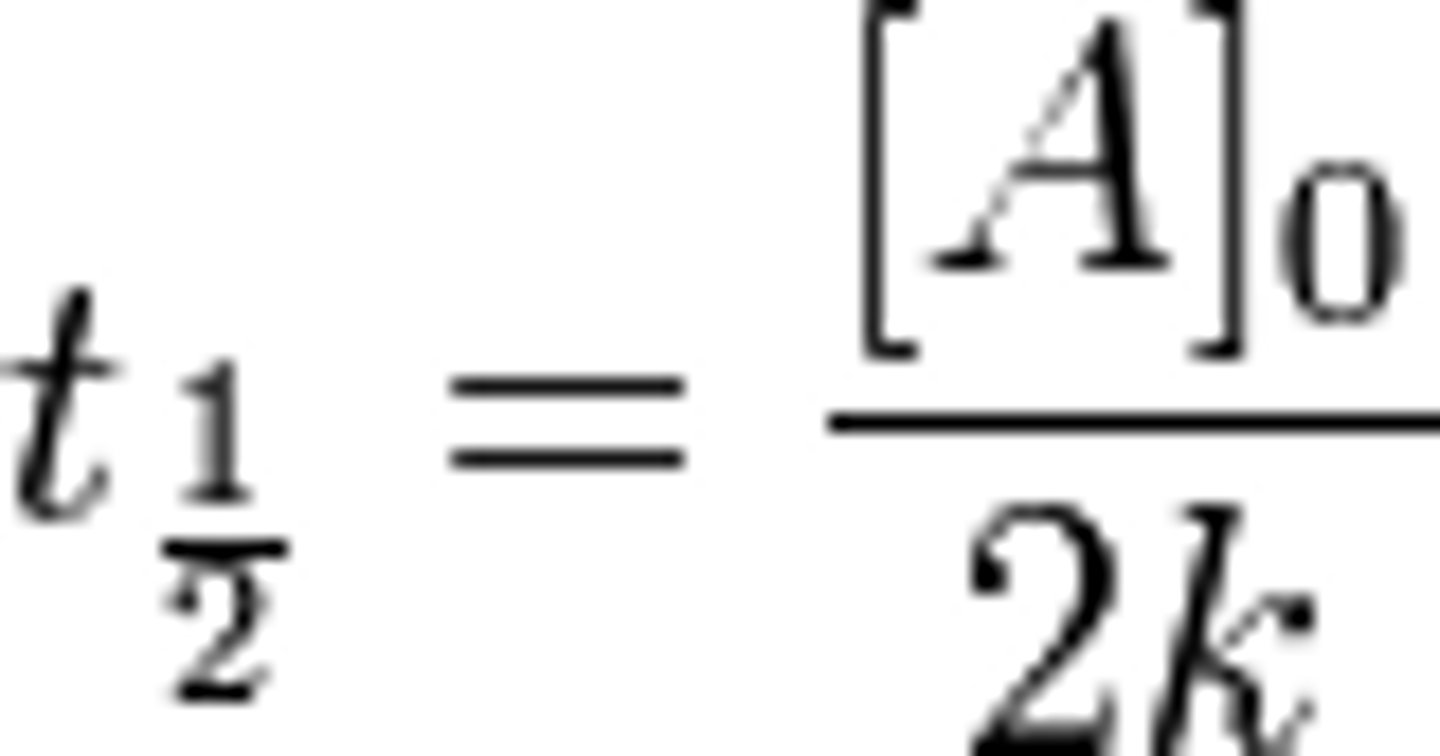
First Order- Half Life
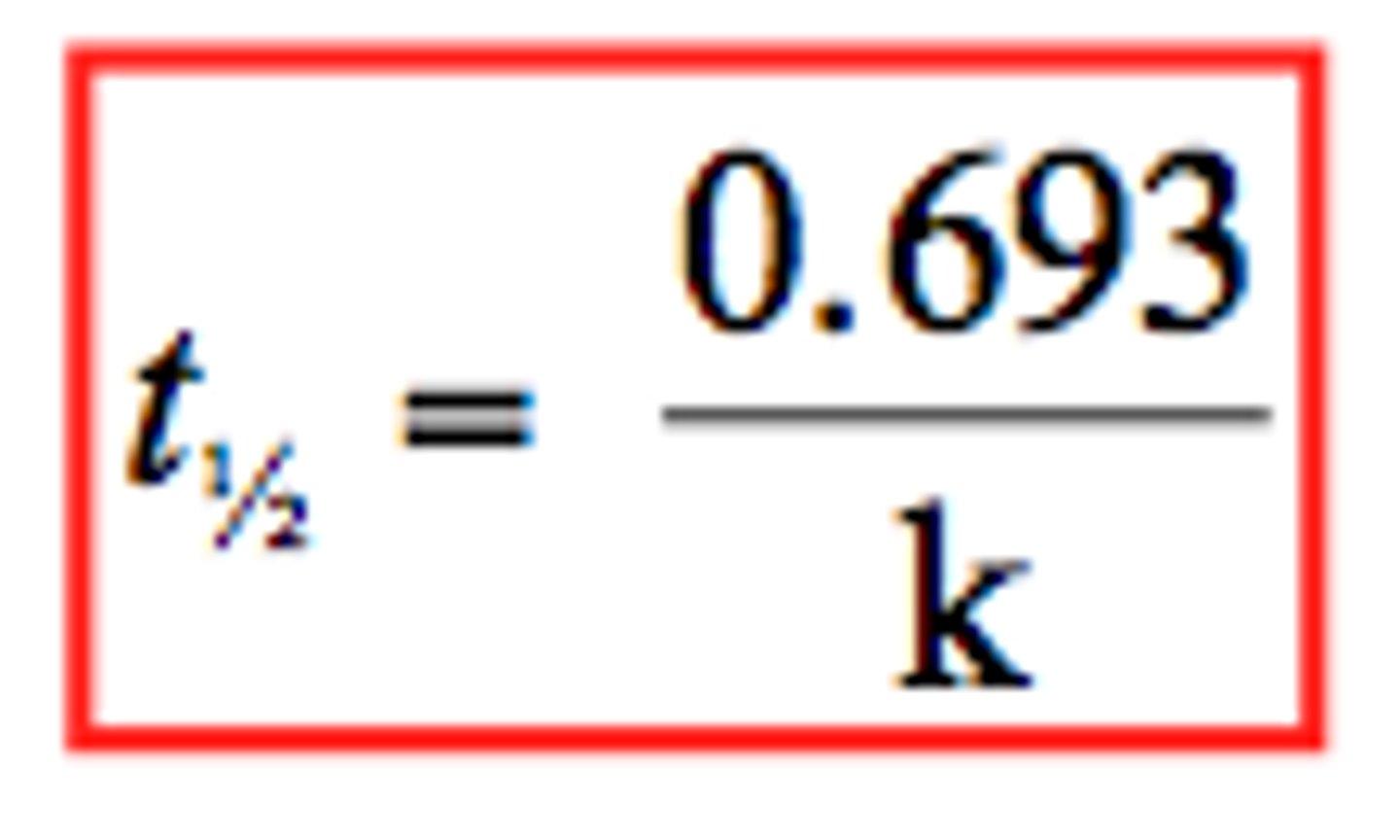
Second Order Half Life