The Child with Integumentary Dysfunction: Burns
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Objectives
1.Interpret normal and abnormal assessment findings in the child with burn injuries.
2.Predict potential complications in children with burn injuries.
3.Formulate a plan of care for children with burn injuries.
4.Explain the rehabilitation process for children with burn injuries.
Don’t have to know any formulas – rule of nines
Common Patterns and Developmental Levels
●Hot water scalds common in toddlers- turn handles pots and pans
●Electrical burns – put mouth common in young children
●Flame-related burns common in older children
●Chemical burns- severity depend how long theu were exposed on skin
●Child abuse
●Child with matches or lighters:
○1 in 10 house fires
Most burns are thermal- ex. Fired
What are the characteristics of a burn injury
1) Extent of injury described in terms of total body surface area: age-related charts- how much of body was burned
2) Depth of injury
○First-degree: superficial
○Second-degree: partial thickness
○Third-degree: full thickness
○Fourth-degree: full thickness and underlying tissue
3) Severity of injury

•Don’t have to memorize.
•Pg 1548

1- red
2-blister
3- tissue w no bone
4- bone
What are the types of severity in a burn injury
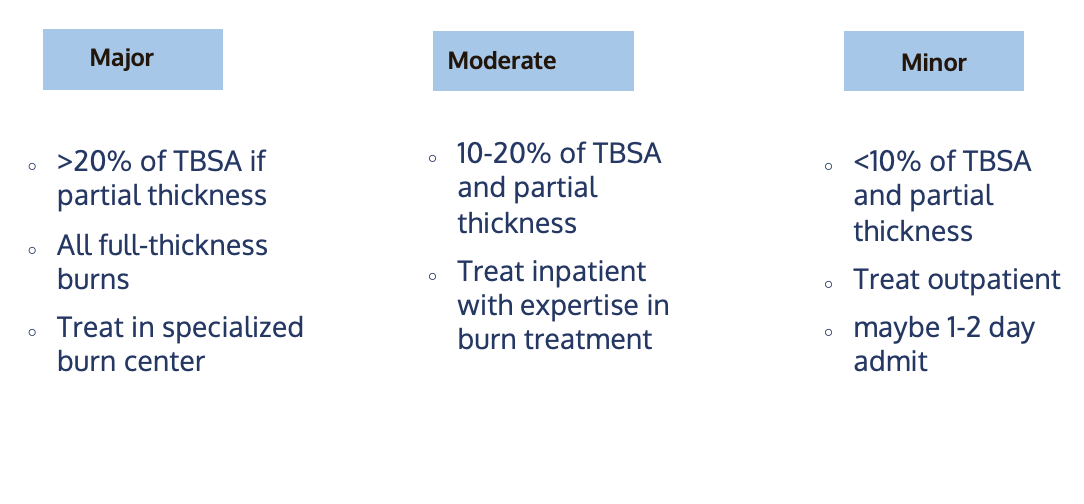
How do you manage minor burns
●Usually managed outpatient
●Wound cleaned with water and soap
●Débridement- clean out or dead tissue.
●Dressings per orders-
●Infection prevention
●Updated Tetanus vaccine
●Families can care for them at homd
How do you manage major burns
●Airway maintenance first priority
●Fluid replacement therapy
○Critical in first 24 hours- crystaloids, LR and NS , D5 . To keep kidneys functioning and prevent system damages
●Nutrition
○Enhanced metabolic demands- high protein high calorie diet , can have oral or tube feedings . Vit A, C, zinc can promote wound healing
●Medication
○Antibiotics, pain- morphine , fentanyl, propofol, sedatives. Meds given IV
●Wound Management
○Prevent infection and close wound as fast as can. Get meds before debridement. Can use human skin, sheets, different grafts.
Swelling or trauma to face or neck- put on 100% oxygen or can see trauma on them . If loc changes and severe burns- can be intubated
Repsiratory distress- watch closelt
Priority
1.Airway
2.s/s shock
3.Prevent infection
What are the complications of burns
•Airway compromise
•Maintain body temperature
•Infection
•Profound shock
•Pneumonia, pulmonary edema, pulmonary embolus, aspiration
•Renal Failure
•Loss of function of burned area
Explain rehab process for a kid with burn injury
•Begins once wound coverage is achieved
•Prevention & management of contractures
•Physical & Occupational Therapy
•Multi-disciplinary team
•Facilitate adaptation of child and family
oScar tissue doesn’t grow as child does- Scar tissue will not expand as they grow- have to have surgeries
o
•Prevent future injuries
What a burn injuries associated with child abuse
•History doesn’t match injury
•Document thoroughly
•Report any and all suspected abuse to CPS
Social services consult
Objectives for The child with Musculoskeletal
Dysfunction
1.Describe common conditions affecting the musculoskeletal system that require hospitalization in children.
2.Interpret normal and abnormal assessment findings in the child with musculoskeletal illness.
3.Formulate a care plan for a child hospitalized with a musculoskeletal illness.
4.Implement appropriate nursing interventions for a child with musculoskeletal illness.
5.Predict potential complications of musculoskeletal illness in children.
6.Outline preoperative and postoperative care of the child with surgical treatment for musculoskeletal illness.
7.Teach families about care of the child with musculoskeletal illness.
8.Explain techniques to care for a child immobilized with an injury or a debilitating condition.
9.Explain the functions of the various types of traction and appropriate nursing care of the child in traction.
What is traction
●Traction
○Forward force produced by attaching weight to distal bone fragment
○
●Countertraction
○Backward force provided by body weight
○
●Frictional force
○Provided by patient’s contact with the bed
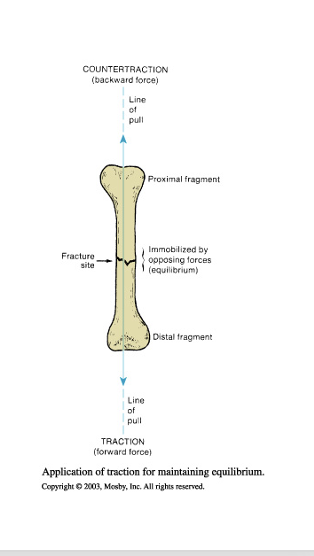
What are the types of traction
Traction depends on:
oChild’s age
oCondition of soft tissues
oType and degree of fracture
oManual- use hands to align leg and bone and position skin.on affected side. Ex. Putting on cast but someone else is holding fracture leg still.
oSkin- Apply directly to skin but indirect to any bone. adhesive bandages, splints, temporary
oSkeletal- halo, direct to bone itself, pins wires or tongs are directly inserted to help realign it. If they have a halo never pull on rods
oImmediately know where screwdriver is if need to do CPR
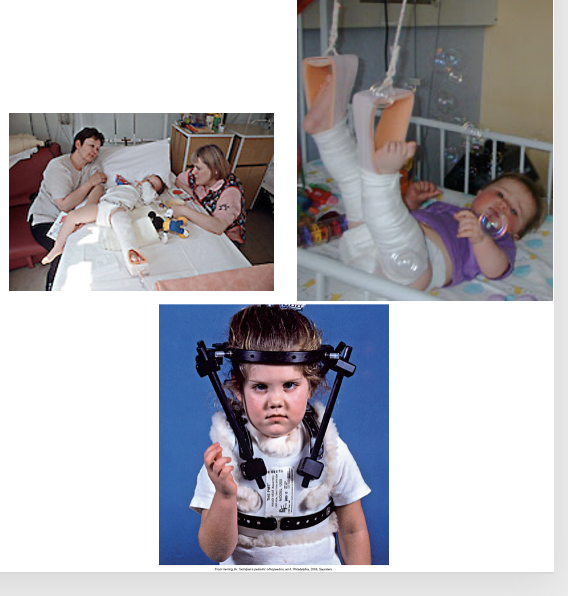
How do you care for a kid in traction
●Purpose- relief and realign bone and prevent future injury- prevent deformities in extremity
●General considerations
●Skin traction
●Skeletal traction
●Skin integrity
●Prevent complications
You can change the weights to pull on bone to prevent further injury
Make sure don’t release traction- ONLY BY provider
Don’t ever let weights fall on the ground- have someone help you
Under 3 less than 25 lb- flat on bed but legs up at 90- flyant traction- femur or hips
Look at bandages, splint is its too tight or loose
Halos- worried about infection- orders on how to keep clean
Cover pins so kid doesn’t scratch themselves.
Only replace straps or bandages when necessary
Watch pressure points- turn but also keep in mind how align them properly. Massage under straps to promote circulation.
Good diet/ nutrition.
Cast or splint- neuro assessment- 6ps- pulse, pallor, pain, paresthesia, , report if it changes
Do rom w other extremeties, deep breathing- areate the lungs
Give pain management- shouldn’t hurt but unconfortable
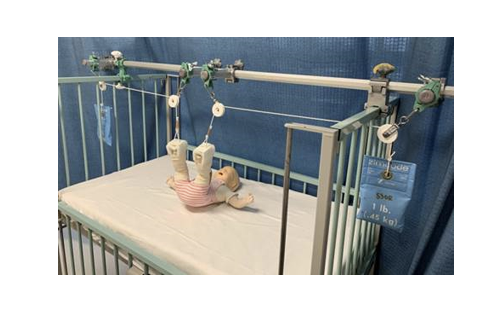
What is Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH)
●Femoral head slips in and out of socket
○Shortened limb, restricted abduction- away, asymmetry of gluteal & thigh fat folds- when prone fast creases are asymmetrical, telescoping of thigh
○Ortolani test- when hip clicks with abduction, Barlow test- when it dislocates from abduction, Allis sign-when you put their knee up and one knee is lower than the other - will be done by provider
●Nursing Management
○Cast care
○Skin integrity
○Education
Swaddling incorrectly can cause risk for DDH
Don’t force their hips into swaddling- want them to be in relaxed frog position.
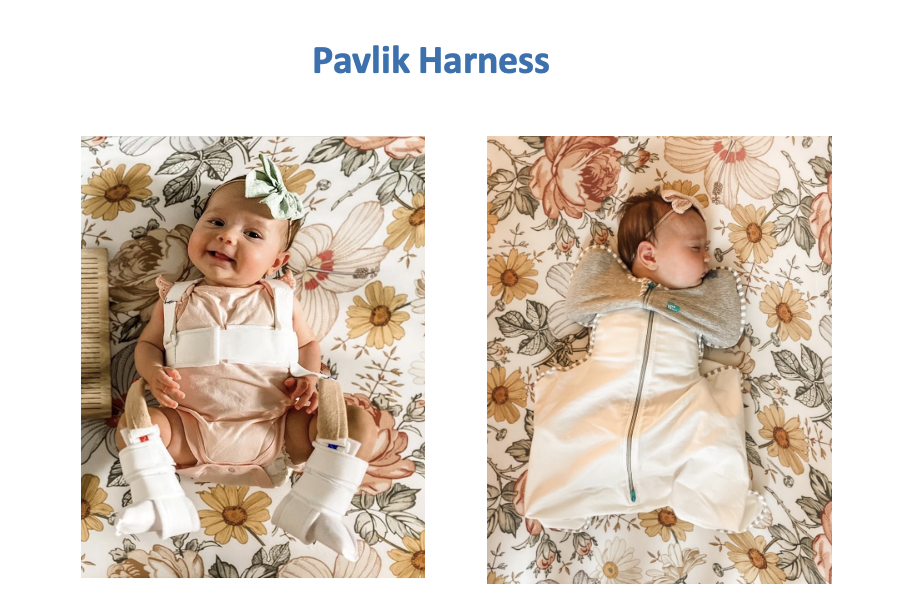
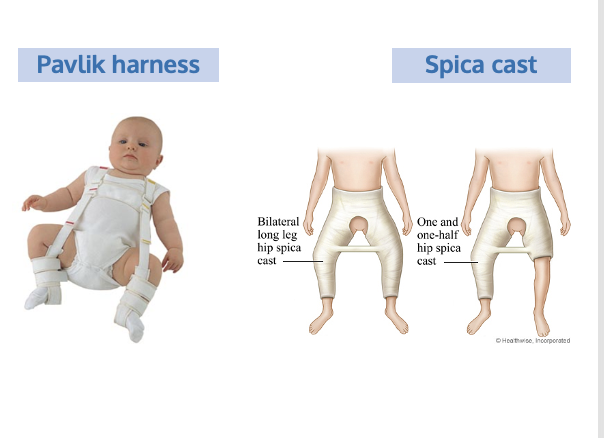
What is the medical management for Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH)
•Medical Management
oPavlik Harness- newborn to 6 months. Wear 22-24 hrs a day. Can wear stuff underneath
oRevaluated 6-12 months
oSurgery
oClosed reduction + spica cast if older than 6 months. Don’t use bar as a handle
Bryant’s traction
No toys they can put down their cast
Skin integrity- keep clean and dry
Special car seats

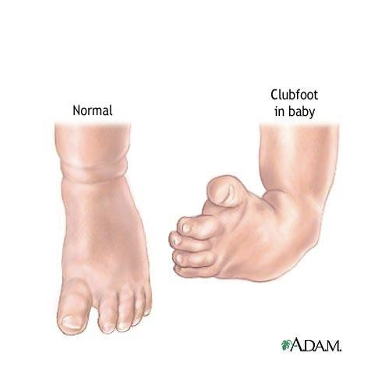
What is Clubfoot (talipes equinovarus)
●Congenital abnormality, foot is twisted out of normal position
○Cause unknown
○Unilateral or bilateral
●Medical management
○Casting, shoes, surgery
●Nursing management
○Education
Cast and skin care
Complete assessment to see how to tx it
1st stage- correct deformity
2nd stage- maintain correction until normal balance is regained and prevent deformity from occurring again
Serial casting- get casted for wks at a time over and over again bc they grow fast. Do for up to 10-12wks.
Will have corrective shoes after serial casting to maintain that and prevent deformity from happening again, if it doesn’t work w casting and shoes can do surgery.
Do neuro checks- keep cast clean and dry
Compartment syndrome – don’t want
What is Osteogenesis Imperfecta
●Brittle-bone disease
○Frequent fractures, blue sclera, thin soft skin, short stature, hearing loss, delay in walking- loss of collagen
●Medical Management
○No cure- meds can slow release of calcium
○Physical therapy promote strength
○Casting, bracing, splinting, wheelchairs
●Nursing Management
○Positioning
○Education- don’t pull ankles up, move them on blankets
○Cast care
Some types can cause infant mortality and some are minor
Bones break easily- handle w care
Freq er visits- may be accused of being abusive
What is Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE)
●Femoral head slips off femur neck
oLimp, pain, stiffness, loss of motion,
can’t bear weight
●Medical Management
○X-Ray
○Non-weight bearing
○Surgery- pain management, cast care
●Nursing Management
○Education
○Post-op care
Think ice cream slips off cone
Emergency bc worried about blood supply dying to the femur
See more in teenage phase in boys- acute trauma or genetic, large BMI can cause it
Limp on effected side, stiff, loss of motion on side, continual or intermittient pain radiates down leg

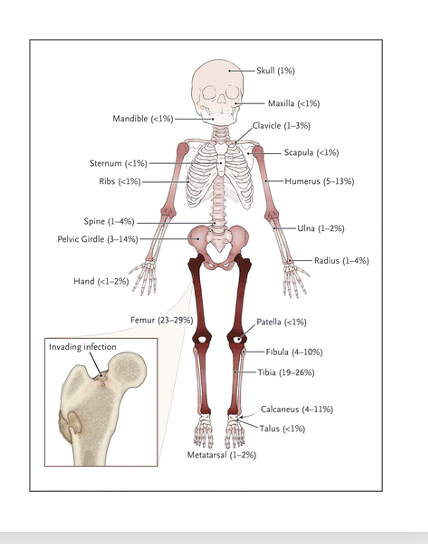
What is Osteomyelitis
●Bone infection dt staph. More fre kids under 10
○History of trauma can put them at risk
○Appear ill, irritable, fever, rapid pulse, dehydration, tachycardia. Very sick
○Localized at site: tenderness, warmth, swelling, pain, resistant to passive movement, very guarded
●Medical Management
○Antibiotics- start abx culture and adjust. Will have PICC linesHigh dose abx , possible surgery
●Nursing Management
○Pain management
○Comfort care- pain meds
Don’t have them bear weight on extremity
If they have a penetrating injury or absess they will go in and do surgery or if they dont respond to abx
Elevated ESR- erythrocyte sedimentation rate, CRP- reactive protein these labs monitor inflammation these 2 would be elevated.