1.4 cell walls and envelopes
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
why is it impossible for microbes to survive and grow using just glycolysis and hexose sugars?
A. its not impossible
B. too few ATP are generated
C. the NAD+ needed will run out
D. pyruvate will build up and back up
E. C and D
E
loosely, gram + bacteria have _____ while gram - have ______
walls; envelopes
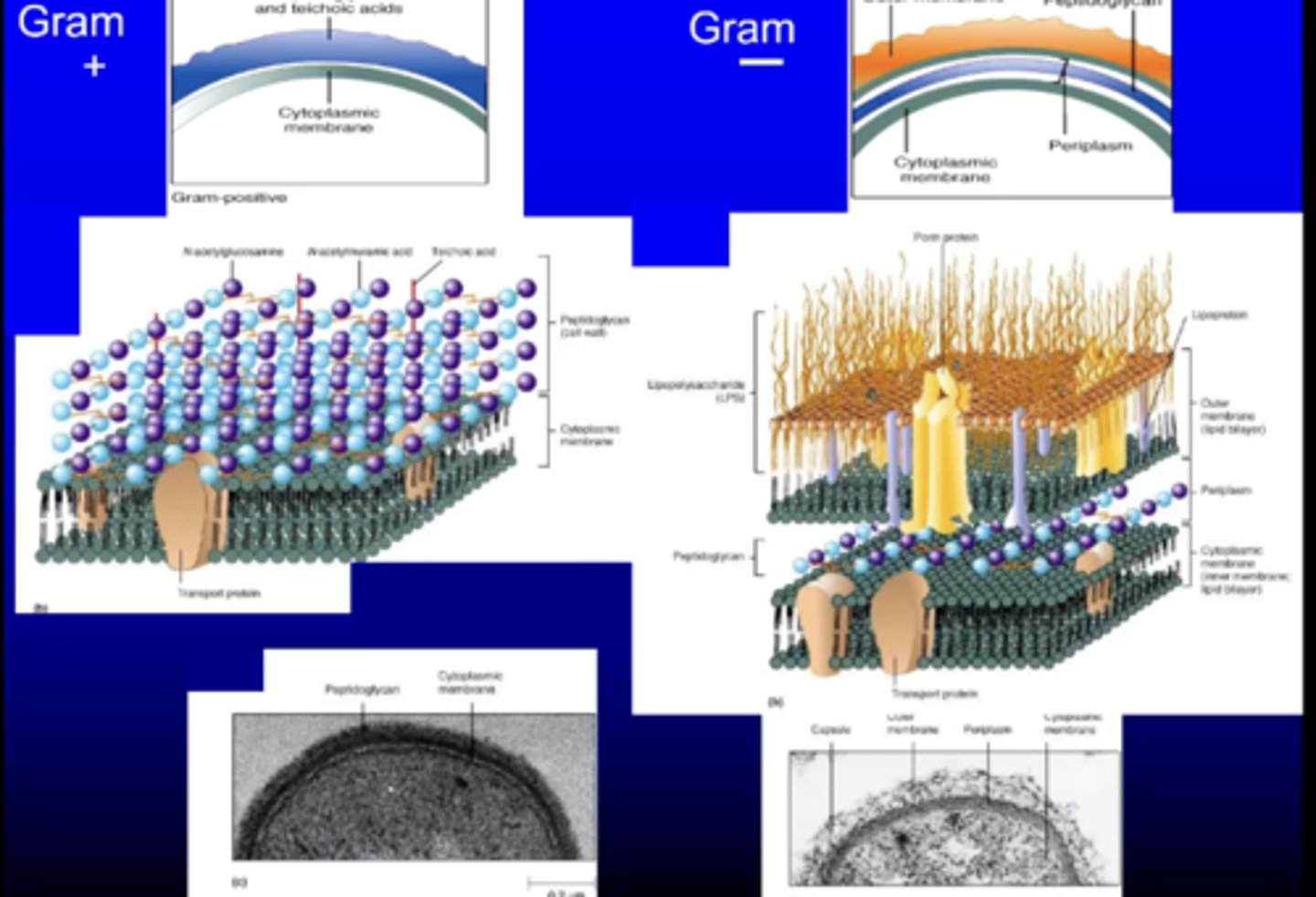
teichoic acids are often beneficial in ______ or ______. why?
probiotics; yogurts; it interacts with the immune system to reduce inflammation and protect against harmful bacteria
mycolic acid is only found in?
mycobacteria
what is the unique feature of bacteria compared to other microbes? (and is often a target for abx)
peptidoglycan
what aspect of bacteria is the only aspect that is more complex than euk?
envelope, wall, or membranes
peptidoglycan is a ______ ______ polymer
sugar; peptide
bacteria cell walls help to maintain _______ and _____ provide them with ________ and is important in resisting changes in ________
size; shape; strength; osmolarity
the lipid bilayer contains what three things
-transport machinery
-secretion apparatus
-environmental sensors
what transport machinery is anchored to the cytoplasmic membrane in bacteria?
flagella and pili
peptidoglycan is created via what repeating structures?
disaccharide and cross-linking peptides
before the cross-linkage is made, what makes up the disaccharide chain?
double D-alanine
what aspect of peptidoglycan is often a target for abx
peptide cross links
gram + have _____ ______ and do not have _______
teichoic acids; LPS
teichoic acids are + or - charged?
- (anionic)
the very outer surface of gram + or - bacteria is surrounded by?
+/- polysaccharide capsules
mycobacteria are gram -/+?
+
mycobacteria are different in their outer layers how?
they are surrounded by mycolic acid (lipids) that allow them to be acid fast
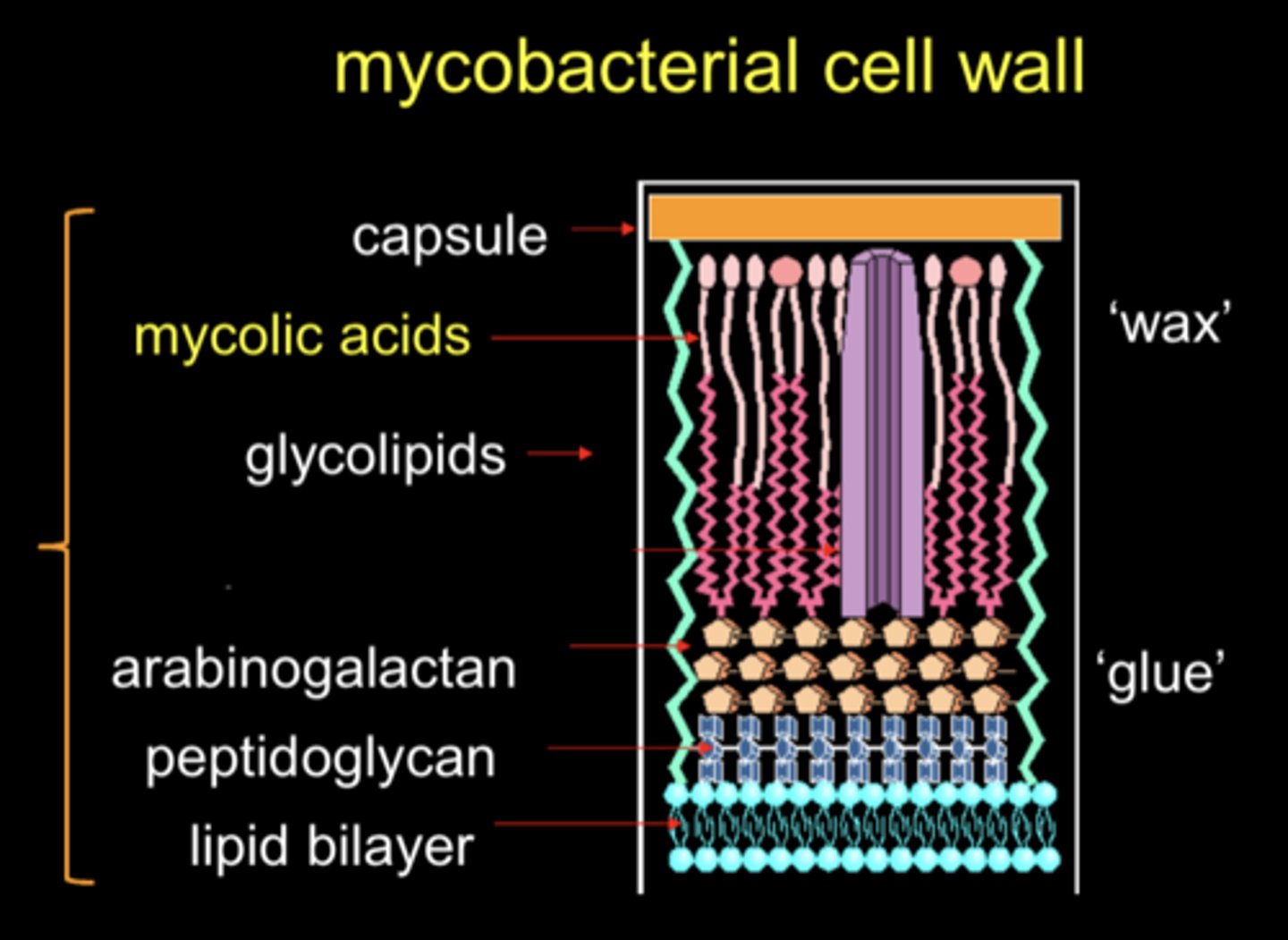
mycolic acids are thought to be compared to ______ as it is very resistant to _____ ______
wax; drying out
what does acid fast mean?
Resistant to decolorization so acid is used to decolorize
the outer half of the outer membrane of Gr - bacteria is composed of?
LPS (lipopolysaccharide)
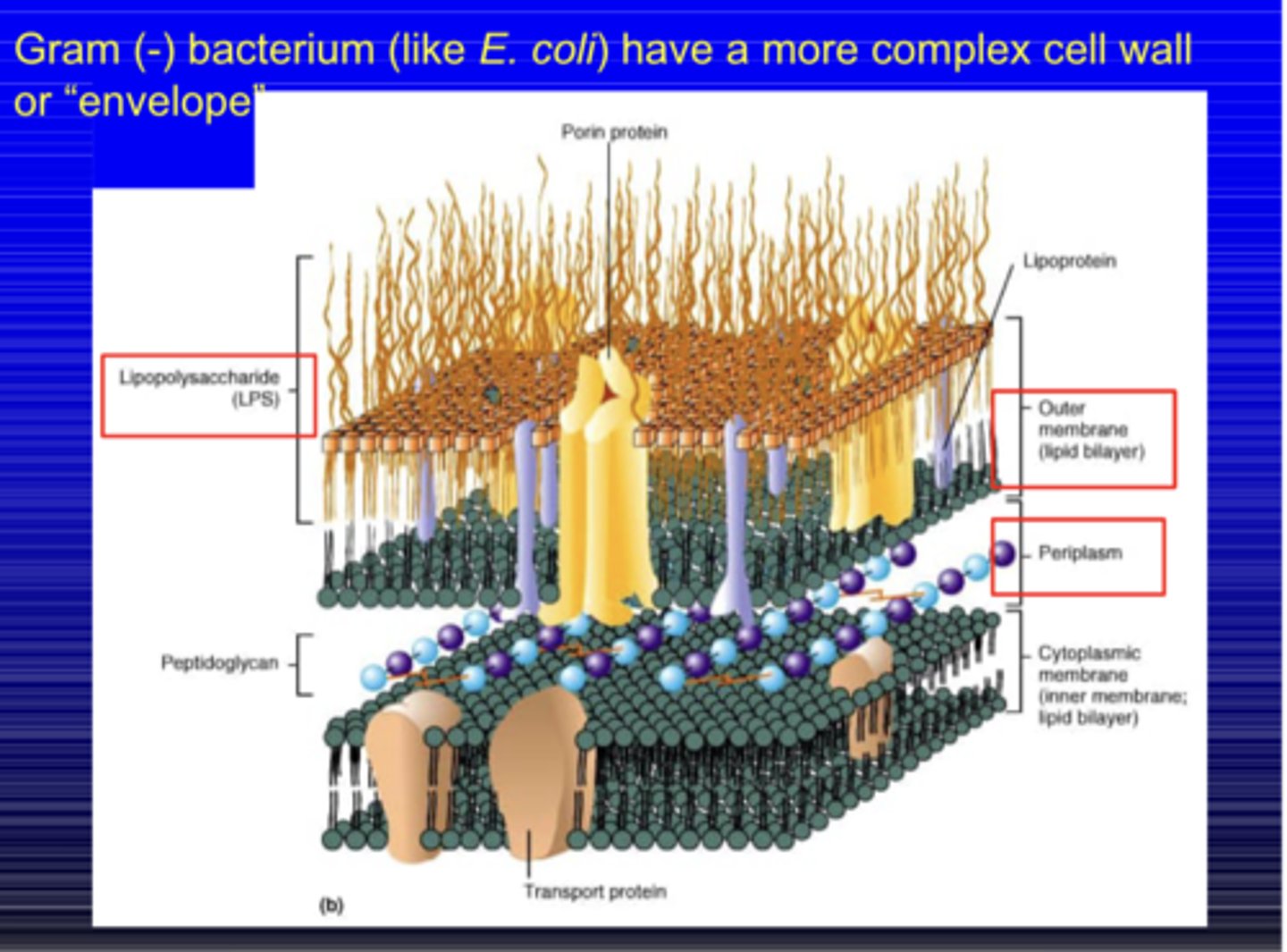
is LPS found in Gr + bacteria?
no
what are the two parts of LPS
O-antigen and Lipid A
the O-antigen is helpful sometimes in ?
strain typing
what is Lipid A?
component that is an "endotoxin" and bioactive leading to inflammatory responses
what is the generalized structure of Lipid A
carbohydrate chain
what is the space between the outer and inner cytoplasmic membrane in gr - bacteria? what does it contain
periplasm; protein, lipoprotein
beyond the cell wall, what structure may gr-/+ have?
carbohydrate capsule
what is the use of carbohydrate capsule?
adhesion, contrib to forming biofilm, evasion of immune system, reduce phagocytosis
carbohydrate capsules allow bacteria to grow in the _____ ______
blood stream (which is hard to do without)
if the carbohydrate capsule is loosely attached it is known as?
slime
how are carbohydrate capsules overcome or utilized in medicines?
polysaccharide vaccines and strain typing
what type of serology does a Gram - bacteria with a carbohydrate capsule give off?
HOK
(H-type of flagella, O-LPS part, K-capsule)
what is used to "stain" polysaccharide capsules
use India ink to stain the background (not the actual capsule)
flagella are composed of a polymerized protein called ______ which is recognized by the ______ ______
flagellin; immune system
what about the flagella of spirochetes (gr -) is unique
it is anchored in the periplasmic space (instead of wall)
pili/fimbriae are mainly present in gram - or +? flagella?
gram negative; both
major function of pili/fimbriae
attachment to surfaces and cells
the pili/fimbriae are the main virulance factor for which bacteria
escherichias (ie E. coli)
how are fungi cell walls different?
lack peptidoglycan and contains chitin