Biology 311C Buskirk Exam 1 UT Austin (copy)
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
is hydroxyl polar or non polar?
polar
Is a carboxyl polar or non polar?
MEGA POLAR
Is an amino polar or non polar?
polar
Is a phosphate polar or non polar?
polar
Is a Methyl polar or non polar?
non-polar
What is Hydroxyls charge?
none
What is Carboxyls charge?
negative
What is Aminos charge?
positive
What is Phosphates charge?
negative
What is Methyls charge?
none
Hydroxyl
-OH (alcohol)
Carboxyl
COOH (acid)
Amino
NH2
Phosphate
PO4 3-
Methyl
CH3
One glycerol (an alcohol with 3 carbon atoms each bonded to an OH group) and 3 fatty acid molecules react to form a triglyceride fat or oil by condensation. How many water molecules are formed/released in this reaction?
3
Which statement about unsaturated fats is true?
They have double bonds in their fatty acid chains.
Unsaturated fats would be expected to...
contain double bond carbons and be liquid at room temperature
Amylose starch is a polysaccharide that is readily digested using hydrolytic enzymes that are found in many types of organisms, including animals and plants. Cellulose is a polysaccharide with different bond angles between glucose monomers. Cellulose is digested only by cellulase enzymes, found only in specialized bacteria and fungi. Which of the following would we find in nature?
Cellulose is a structural polysaccharide used in building plant cell walls and tree trunks.
Triglycerides X and Y are about the same size. However, molecule X, an oil, is a liquid at room temperature while molecule Y, a fat, is solid at room temperature. Which of these explains the difference?
Molecule X has double bonds between C atoms in its hydrocarbon chains, unlike Y.
Glucose and fructose are 6-carbon monosaccharides that have the same chemical formula but different positions of atom attachments on the carbon chain. These two compounds are called what?
structural isomers
A polypeptide (protein) is made by condensation reactions joining 100 amino acids together in a single, unbranched chain. This condensation synthesis reaction would produce (release) how many water molecules?
99
Which of the following large biological molecules will self-assemble into a bilayer when mixed with water?
phospholipids
In the lab you have isolated an unidentified liquid from a plant sample. You add the liquid to a beaker of water and shake vigorously. After a few minutes, the water and the other liquid separate into two layers. To which group of bio molecules does the unknown liquid most likely belong?
lipids
Which of the following statements regarding an unsaturated fatty acid is true?
Molecules of this type are usually liquid at room temperature.
One end of the main chain of any polypeptide ends in the amino group of that last amino acid. What functional group must be on the amino acid at the other end of that polypeptide chain?
carboxyl
A particular protein is held in its folded shape by weak interactions between different pairs of amino acid R groups. Each answer A-D gives the properties of two different R groups. Decide how each pair could possibly form a weak bond, or not. To answer, indicate which one of these pairs would NOT form any type of weak bond between them, i.e., would NOT be attracted.
positively charged R group : nonpolar uncharged R group
The tertiary structure of a folded protein is determined by
the bonds between R groups on different parts of the chain
The tip of the R group in this amino acid (valine) has ______ properties and could possibly form which type of bond with another amino acid to hold a protein's three-dimensional shape? CH-CH3-H3C
properties - nonpolar and uncharged: bond - hydrophobic interaction
You would like to synthesize a drug that has basic properties (acts like a base) when present inside cells and body fluids. Which one or more of the following functional groups should you add to the carbon chain of the drug to make it function as a base?
amino
Individual amino acid molecules are acids because they always possess which functional group?
carboxyl
In order to determine whether two atoms will share electrons in polar vs non-polar covalent bonds, you need to know which property of the two atoms?
electronegativity
Which of the following is the explanation as to why water molecules are considered polar?
Oxygen is more electronegative than Hydrogen
Rank these four examples of a covalent bond between two atoms from (1) most polar to (4) least polar: N-H, O-O, C-H, O-H
1 O-H, 2 N-H, 3 C-H, 4 O-O
Which one of the following characteristics does NOT apply to water?
The water molecule readily joins hydrophobic interactions.
Which kind of bond is broken when water evaporates? [from liquid to gaseous phase]
hydrogen bond
Solutes that easily dissolve in water are said to be
hydrophilic and polar molecules
If a frog clings to surfaces through hydrogen bonds, it would have the most difficulty clinging to which of the following surfaces?
a surface coated with a thin film of vegetable oil
Which of the following chemical equations describes a condensation reaction?
monosaccharide + monosaccharide --> disaccharide + H2O
The monomers of this group of biomolecules are polar but never electrically charged.
carbohydrates
The monomers of this group of biomolecules are polar but not electrically charged
carbohydrates
Which of the following functional groups (look at the chart) when covalently bonded to a carbon atom on molecules in cells often dissociates to donate a H+ ion and become negatively charged?
carboxyl
Three 5-carbon monosaccharide molecules (simple sugars, like ribose) react by condensation to form a short chain (a "tri-saccharide"). How many oxygen atoms will be in the resulting tri-saccharide?
13
Which of the following is considered a non-polar covalent bond in biological molecules?
C-H
Hydrogen bonds between water molecules are examples of
dipole-dipole interaction
How many hydrogen bonds are in this diagram?
0
Why is this an unlikely arrangement of two water molecules? O-HH-O
water molecules are polar and a partially positive region of one will repel the partially positive region of another
When a pure crystal of table salt (Na+Cl-) dissolves in water, _____ bonds are being broken in the salt crystal, and the salt is forming ____ bonds with water
ionic/ ion-dipole
A soap molecule has one end that is polar (hydrophilic) and one end a short hydrocarbon chain that is non-polar (hydrophobic). How does soap help clean up oil and grease, which are large molecules with mainly C-C and C-H covalent bonds? Choose the correct mechanism from A-E and then explain why that cleans up the dishes!
The polar end of the soap forms hydrogen bonds with water and the nonpolar end of the soap forms hydrophobic interactions with oil and grease.
A functional group that is non-polar is __. Molecules consisting of many of these groups are likely to form ___ with each other.
methyl; hydrophobic association
Which of these best describes a fatty acid?
a long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group at one end
Two types of bio-molecules that contain phosphate functional groups are:
nucleotides and phospholipids
Which of these, A-E, is the most polar covalent bond?
A. C-C
B. N-H
C. O-H
D. O-O
E. C-H
O-H
Which of these, A-D, is the least polar covalent bond?
A. C-C
B. N-H
C. O-H
D. C-H
C-C
Which of these three-carbon molecules, glycerol or propane, has more polar groups and fewer non-polar bonds?
glycerol
Which of these three-carbon molecules, glycerol or propane, is more hydrophobic?
propane
If there were LESS hydrogen bonding among water molecules, there would be
less surface tension
If there were LESS hydrogen bonding among water molecules, would it take_____to raise the temperature of water?
less heat
One region on the surface of a large protein consists entirely of C-C and C-H covalent bonds, In a water medium, this region could potentially form which type of weak attraction with the surface of another non-polar molecule?
nonpolar covalent bond
(If less polar medium) Heavier insects than water striders would be able to walk on the surface of a pond. True/False
False
(in less polar medium) More salts (ionic substances) would go into solution in blood and body fluids.True/False
False
(in less polar medium) Sweating would be a less effective means of keeping cool.True/False
True
(in less polar medium) More salts (ionic substances) would go into solution in blood and body fluids.True/False
False
A long chain polymer is synthesized in chemical reactions from 25 monomers. How many water molecules are produced/released?
24
Which of these is a case of hydrolysis?
Digesting starch chains into sugars
How many H atoms in a 4C chain with 1 double bond?
8
Two molecules, A and B, consist of only C and H atoms and have the same number of C atoms, but Molecule A has a double bond between two C atoms. Which molecule has more H atoms?
Molecule B
When sugars dissolve in water, which process is occurring for sugars?
forming hydrogen bonds
Which of the following are characteristics of the hydroxyl functional group, OH group abundant in monosaccharides?
it readily forms hydrogen bonds with water
If a molecule is made by joining two glucose molecules together by a condensation reaction, the resulting molecule has ____ carbon atoms and ____oxygen atoms
10 and 11
Which type of isomers are (1) fructose and (2) glucose to each other?
structural
All molecules in which one of the following groups have the general formula n(CH2O)?
all polysaccharides
All molecules in which one of the following groups have the general formula n(CH2O)?
all monosaccharides
Sucrose (table sugar) is a disaccharide. How does sucrose dissolve in water?
By forming its components, glucose and fructose and by forming dipole-dipole bonds with water
Which of these is the definition of a "saturated" hydrocarbon chain in a lipid?
a hydrocarbon chain with no double bonds between adjacent carbon atoms
A fatty acid with two double bonds between carbon atoms in its long hydrocarbon chain is likely to have which properties?
Solid at room temperature and insoluble in water
If a glycerol molecule (a 3-carbon alcohol) reacts by condensation with three fatty acid molecules to form a triglyceride, how many water molecules form?
one
What type of bonds/interactions occur between fatty acid tails of adjacent phospholipids within a membrane?
hydrophobic interactions
What are the building block molecules that react to form one triglyceride (="triacylglycerol") molecule ?
3 glycerol molecules and 3 fatty acids
A fatty acid with two double bonds between carbon atoms in its long hydrocarbon chain is likely to have which properties?
Liquid at room temperature and water soluble
What type of bonds/interactions occur between fatty acid tails of adjacent phospholipids in membranes?
hydrophobic interactions
What type of bonds/interactions form between phospholipid polar heads and water?
polar covalent bonds
Why does cholesterol belong in the Lipids?
It contains mostly non-polar covalent
Which of the following functional groups, can you add to a carbon chain, to make the molecule more basic/less acidic?
amino
Which bonds are created during the formation of the primary structure of a protein?
peptide bonds
The structural level of a protein LEAST affected by a disruption in hydrogen bonding is the
primary level
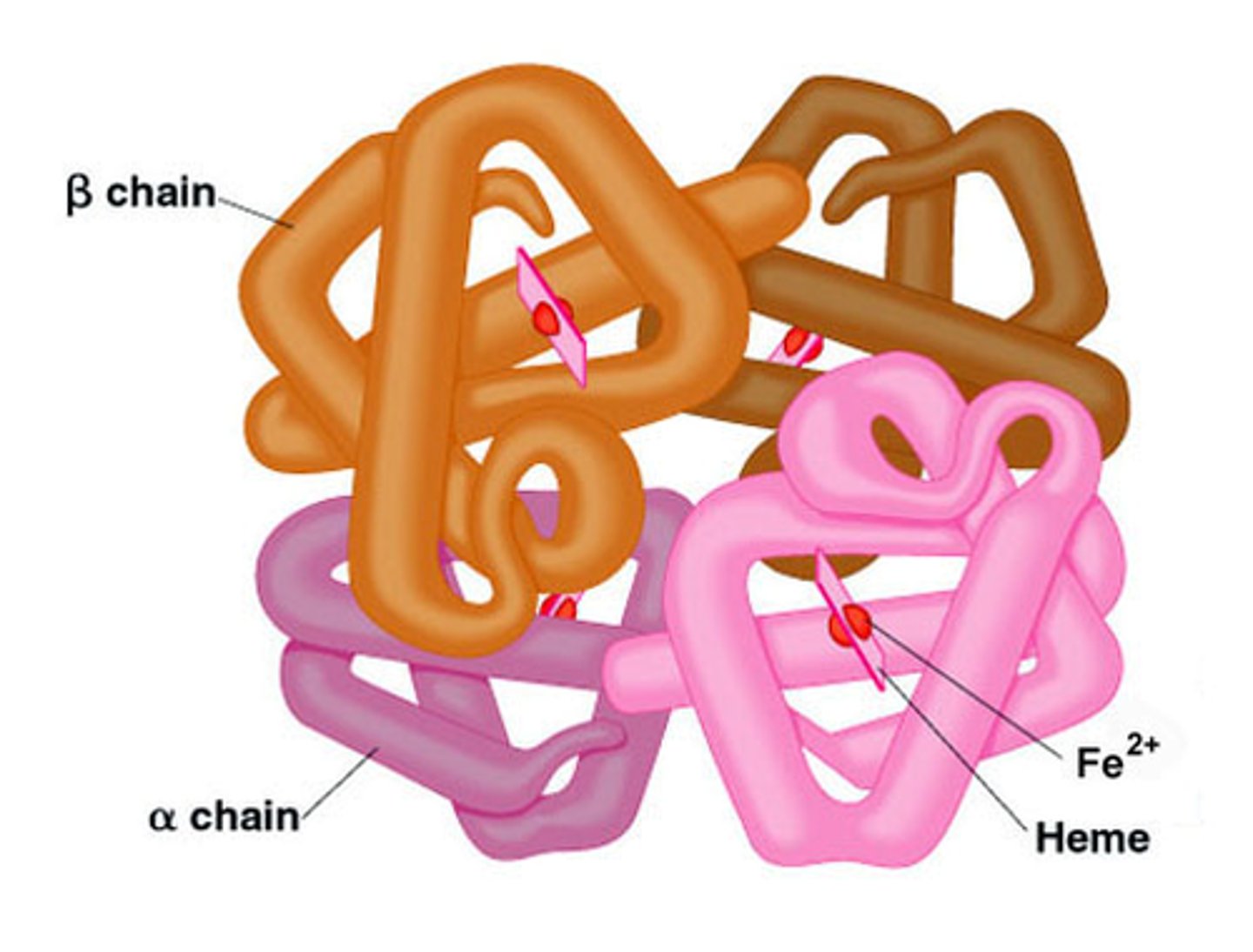
What is the highest level of protein structure shown by an antibody? [see figure on AE3 handout.]
Quaternary
In order to function, a particular enzyme must bind snugly to a spherical, positively charged particle. The enzyme's active site should have a pocket of what shape and lined with R groups of what property?
concave; negatively charged
A certain small, compact protein functions entirely within the non-polar middle of a phospholipid bilayer. The R groups sticking out on the small protein's surface are expected to have what properties?
non-polar
Which part of each amino acid is participating in forming a peptide bond?
amino + carboxyl
Is the R group involved in forming a peptide bond?
Yes
The -SH at the tip of the R group at far right could form what kind of bond?
disulfide bridge
Which is the best statement of the hypothesis tested by the Miller-Urey experiment?
Life originated from interactions between simple chemicals in the early earth
Which type of reaction links 2 organic monomers together to produce a chain?
oxidation
Which of these happens when phospholipids aggregate in water in the absence of enzymes?
Phospholipids cluster to form a double layer that resembles a membrane
Which of these is a correct distinction between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
Eukaryotic cells have whip-like flagella while prokaryotic flagella are rigid hooks.
Which is a true distinction between the domains Archaea and Bacteria?
Bacteria are prokaryotic cells while Archaea are not
Animal cells do not have chloroplasts. Do plant cells have mitochondria?
No
Which of these best describes a ribosome?
A membrane vesicle containing rRNA
Where in a cell is the primary structure of a protein formed?
Inside the smooth ER